An Inability To Do What You Were Able To Do Before
Defining this symptom can be somewhat difficult because its less a universal heart attack sign and more dependent on your individual experiences and baseline energy levels.
Its a significant change in your functional status, is how I would put it, says Dr. Cho. You were able to be on the treadmill 20 minutes, but now you can barely do 10 because you just feel so tired.
Why Your Sleep Pattern Is Vital To Your Heart And Brain Health
“Many women are concerned about their breast cancer risk, and they perceive that as their greatest health threat,” said Dr. Deirdre Mattina, a cardiologist at the Cleveland Clinic. But “we know that one in three women are going to die of heart disease” every year.
For both women and men, signs of heart problems rarely occur in isolation.
“Symptoms often occur in clusters,” Jurgens said. “Very rarely does someone come in with just one symptom.”
And though sudden cardiac events heart attack or stroke, for example certainly appear without warning, many symptoms worsen over time.
Mattina said that patients with heart failure, for example, may report no longer being able to walk as far as they used to, or a gradual decline in the ability to take in full breaths.
“We’re looking for a pattern,” Mattina said.
Here are the most common ways for six different cardiovascular conditions that present in patients.
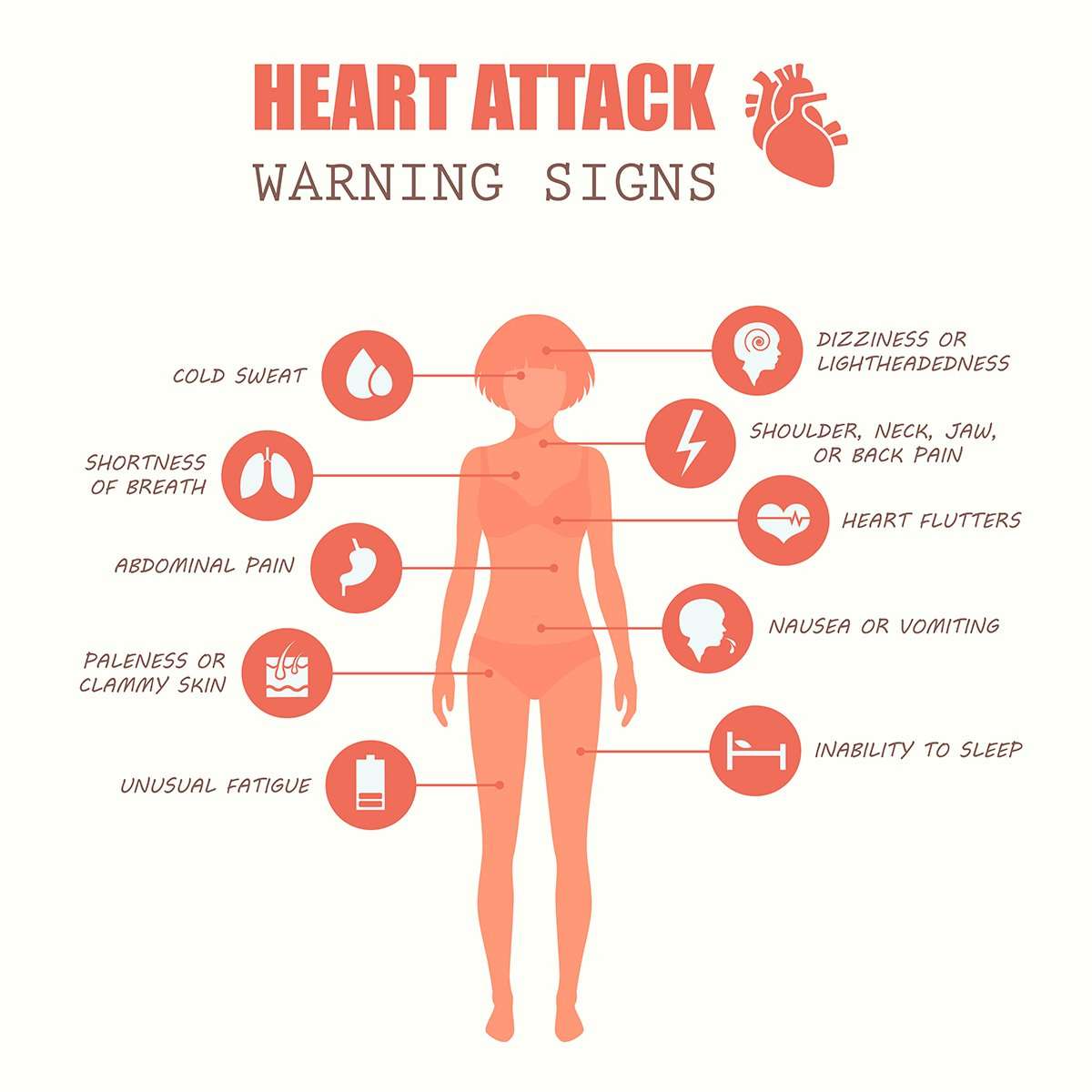
Symptoms Of A Heart Attack In Women
In recent decades, scientists have realized that heart attack symptoms can be quite different for women than for men.
While pain and squeezing sensations in the chest are still the most common symptoms in women, many frequently self-reported symptoms differ greatly from those common in men. Lack of knowledge about the differences in symptoms across genders may be one of the reasons why women generally wait longer than men do to seek out care if they suspect they are having a heart attack.
Symptoms of heart attack in women include:
- unusual fatigue lasting for several days or sudden severe fatigue
- sleep disturbances
- upper back, shoulder, or throat pain
- jaw pain or pain that spreads up to your jaw
- pressure or pain in the center of your chest, which may spread to your arm
Base your decision to seek care on what feels normal and abnormal for you. If you are experiencing symptoms that feel new to you, and dont agree with your doctors conclusion, get a second opinion.
Read Also: Heart Rate Jumps From 80 To 120
Angina In Women Can Be Different Than Men
Angina is a warning sign of heart disease, and recognizing it and getting treated early may prevent a heart attack.
Coronary artery disease occurs when fatty build-up in your coronary arteries, called plaque, prevents adequate blood flow thats needed to provide oxygen to your heart muscle.
As coronary artery disease progresses, you may have tightness, pressure or discomfort in your chest during physical activity or when stressed. It may go away shortly after you stop the activity or get rid of the stress. If the blockages worsen, it may take longer for the pain to go away, or you might experience pain at rest.
Angina symptoms in women can also include nausea, vomiting, pain in the neck, jaw, throat, abdomen or back and feeling out of breath. Once the extra demand for blood and oxygen stops, so do the symptoms. These symptoms are not always recognized as a symptom of a heart condition in women. As a result, treatment for women can be delayed.
Heart Attack Treatment For Women

The treatment for heart attack in women is the same as it is for men.
A recent study in the United Kingdom showed that women having a heart attack were 50% more likely than men to be misdiagnosed, leading to a delay in treatment and poorer outcomes. However there is no evidence to show that the same is true for New Zealand women.
Also Check: What Is Bpm Heart Rate
Heart Attack In Women Over 50
After menopause, which generally occurs around age 50, your risk of heart attack increases. During this period of life, your levels of the hormone estrogen drop. Estrogen is believed to help protect the health of your heart, which could explain why the average age of first heart attack is roughly 5 years older in women than in men.
There are additional symptoms of a heart attack that women over the age of 50 may experience. These symptoms include:
- severe chest pain
A silent heart attack is like any other heart attack, except it occurs without the usual symptoms. In other words, you may not even realize youve experienced a heart attack.
The American Heart Association estimates that as many as 170,000 Americans experience heart attacks each year without even knowing it. Though less symptomatic than a full heart attack, these events cause heart damage and increase the risk of future attacks.
Silent heart attacks are more common among people with diabetes and in those whove had previous heart attacks.
Symptoms that may indicate a silent heart attack include:
- mild discomfort in your chest, arms, or jaw that goes away after resting
- shortness of breath and tiring easily
- sleep disturbances and increased fatigue
- abdominal pain or heartburn
- skin clamminess
Women And Heart Disease
The term heart disease refers to several types of heart conditions, including coronary artery disease and heart attack.
Although heart disease is sometimes thought of as a mans disease, almost as many women as men die each year of heart disease in the United States.
This map shows death rates from heart disease in women in the United States. The darker red indicates a higher death rate.
Don’t Miss: Which Shoulder Hurts Heart Attack
When Should You See Your Doctor
Its always better to err on the side of caution if something doesnt feel right. If you have noticed that you are shorter of breath with regular activity, you should go to your general doctor or your cardiologist, says Dr. Cho. It depends on the severity and the acuteness if it has started recently or not.
When you do visit, be sure to:
- Bring a list of your symptoms and when they are occurring.
- Let them know about any related family history of heart disease.
- Talk about stress or anything going on in your life that might contribute to a problem.
Your doctor likely will listen to your symptoms and check your pulse and blood pressure. They may order blood work, which will show whether your heart is damaged. They also may use an electrocardiogram to tell whether the electrical activity of your heart is normal, or an echocardiogram to view images of the heart to see if damage has occurred. Some patients may get stress tests, a coronary computed tomography angiogram or a cardiac catheterization.All of this is important in identifying any problems and taking steps to intervene before a possible heart attack.
How Is A Heart Attack Diagnosed
To diagnose a heart attack, a doctor will ask you about your symptoms, your health, and your family health history. The doctor will also order tests.
Doctors often use these types of tests to diagnose a heart attack and choose the best treatment.
- Blood tests. During a heart attack, heart muscle cells die and burst open. This process releases proteins into your blood. Heart attack blood tests measure the amount of these protein “markers” of heart damage. Common heart attack blood tests include:
- Cardiac troponin . This is the most common blood test. This marker is released from the injured heart muscle. It is not found in the blood of healthy people. Troponin levels go up three to six hours after your heart attack starts, so the test may not find a heart attack right away.
- Creatine Kinase-MB . The CKMB test measures the amount of damage to the heart because of blocked blood flow. The test can tell whether treatments to restore blood flow to the heart are working. CKMB levels rise about four to six hours after a heart attack starts and peak 24 hours later.
- Myoglobin. This test helps diagnose a heart attack in the very early stages. After a heart attack, myoglobin levels rise within one to four hours but peak after 12 hours.
Recommended Reading: What Heart Rate Burns Fat
Other Warnings It May Be A Heart Attack
If suffering with either diabetes, obesity, high cholesterol it may be a major cause for concern that your pain is more serious.
If you are also a smoker or have a family history of heart issues these warnings should definitely not be ignored.
Age is another factor and if over the age of 45 and suffering with chest pains or unusual heartburn, quick action is strongly recommended.
What Are The Risk Factors For Heart Disease
High blood pressure, high LDL cholesterol, and smoking are key risk factors for heart disease. About half of all people in the United States have at least one of these three risk factors.6
Several other medical conditions and lifestyle choices can also put people at a higher risk for heart disease, including
Read Also: Under Resting Conditions, Heart Rate Is Primarily Under The Control Of What Control System
How Can I Prevent A Heart Attack
All women can make changes to help prevent a heart attack. These changes include making healthier food choices, being more physically active, and not smoking. Once you know your heart attack risk factors, you and your doctor can work together to lower your risk.
Even if you had a heart attack before, you can make changes to help prevent another heart attack. Learn more steps to prevent heart attack and heart disease.
Angina And Heart Attacks
Angina is a syndrome caused by the supply of oxygen-rich blood to the heart becoming restricted.
People with angina can experience similar symptoms to a heart attack, but they usually happen during exercise and pass within a few minutes.
However, occasionally, people with angina can have a heart attack. It’s important to recognise the difference between the symptoms of angina and those of a heart attack. The best way to do this is to remember that the symptoms of angina can be controlled with medicine, but symptoms of a heart attack cannot.
If you have angina, you may have been prescribed medicine that improves your symptoms within 5 minutes. If the first dose does not work, a second dose can be taken after 5 minutes, and a third dose after a further 5 minutes.
If the pain persists, despite taking 3 doses of glyceryl trinitrate over 15 minutes, call 999 and ask for an ambulance.
Page last reviewed: 28 November 2019 Next review due: 28 November 2022
You May Like: How To Reduce Your Heart Rate
Heart Attack Symptoms In Women
If you have any of these signs, call 911 and get to a hospital right away.
What You Can Do Now To Prevent An Early Heart Attack
Although some risk factors are beyond your control, there are many thingsyou can do to protect your heart health. It’s estimated that 80% of heartdisease, including heart attacks and strokes, can be prevented throughlifestyle changes, such as:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese increases your heart disease risk. Get tips on how to watch your weight.
- Eating a heart-healthy diet: Avoid processed foods and excess sugar. Eat a diet rich in whole, nutritious foods .
- Exercising regularly: A consistent workout routine can boost your heart health. Aim for at least 150 minutes per week. Learn the kinds of exercise that can boost heart health.
Recommended Reading: When Should I Worry About Heart Palpitations
Can Women Reduce Their Risk Of Having A Heart Attack
As a woman, your hormones might give you some protection from CHD in your pre-menopause years. Post menopause, your risk rises and continues to rise as you get older. As you get older it is increasingly important to be aware of the risk factors that can affect your risk of developing CHD. The more risk factors you have, the higher your risk. Risk factors include:
- being overweight
- not doing enough physical activity.
Identifying and managing risk factors early on could help lower your risk of a heart attack in the future.
- Get tips and advice on healthy living.
We recommend that all women over the age of 40 visit their local GP or nurse for a health check to check their cardiovascular risk. If you’re aged 4074 and living in England, you can ask for an NHS health check. Similar schemes are also available in other parts of the UK.Your doctor should invite you to review your risk every five years, but you can also just make an appointment yourself to check your blood pressure and cholesterol. This check might help to highlight anything that could put you at increased risk of having a heart attack.
If you have a family history of heart or circulatory disease make sure you tell your doctor or nurse. You’re considered to have a family history of heart or circulatory disease if:
What Are The Symptoms Of Heart Disease
Although some women have no symptoms, others may have5
- Pain in the neck, jaw, or throat
- Pain in the upper abdomen or back
These symptoms may happen when you are resting or when you are doing regular daily activities. Women also may have other symptoms, including5
Sometimes heart disease may be silent and not diagnosed until you have other symptoms or emergencies, including5
- Heart attack: Chest pain or discomfort, upper back or neck pain, indigestion, heartburn, nausea or vomiting, extreme fatigue, upper body discomfort, dizziness, and shortness of breath
- Arrhythmia: Fluttering feelings in the chest
- Heart failure: Shortness of breath, fatigue, or swelling of the feet, ankles, legs, abdomen, or neck veins
If you have any of these symptoms,
Recommended Reading: Can You Die From Congestive Heart Failure
Urgent Advice: Phone 999 Or Go To A& E Immediately If You Are Pregnant And:
- you have central chest pain or discomfort in your chest that doesnt go away it may feel like pressure, tightness or squeezing
- the pain radiates down your left arm, or both arms, or to your neck, jaw, back or stomach
- you feel sick, sweaty, lightheaded or short of breath
- you have severe sudden chest pain or chest pain that you feel through to your back
- experience chest pain or tightness while exercising which eases at rest
- you experience unconsciousness
- you experience seizures or fitting
- you have difficulty breathing
- you are breathless at rest or with minimal effort
- you have a low or undetectable heart beat
- you have blue or pale tingling of knees, hands and lips
- you have chest pain and breathlessness, nausea, sweating or are coughing up blood
- are experiencing dizziness that is persistent or associated with blurred vision, headache, or palpitation
- are experiencing palpitations that last more than 10 minutes
Read further information about:
Its not known exactly what causes takotsubo cardiomyopathy. But, its often brought on by emotional or physical distress.
Read further information about takotsubo cardiomyopathy
Heart Attacks Striking Younger Women
Younger women are having more heart attacks, says a recent study.Researchers were surprised to find that while the heart attack rate hasdecreased among older adults, it’s risen among those ages 35-54, especiallywomen. TheAtherosclerosis Risk in Communities studyreviewed more than 28,000 hospitalizations for heart attacks in fourcities.
“This observational study found a trend in young women,” saysVirginia Colliver, M.D., cardiologist withJohns Hopkins Community Physicians-Heart Carein Bethesda, Maryland. “But the research doesn’t provide insight into whythe uptick in heart attacks is happening to younger people. I suspect ithas to do with more people having risk factors for heart disease at anearlier age.”
You May Like: Heart Bypass Surgery Recovery
What You Can Do To Reduce Your Risk Of Heart Disease
You may already know many of the risk factors for heart disease, such as family history, weight gain around the middle, smoking and high blood pressure. But there are other lesser-known risk factors that are also important. Heres what to do about them:
A note about declining estrogen in menopause. After the age of 55, your risk of heart attack increases greatly, especially if youve gone through menopause. This may be because of estrogen’s protective effects on the inner lining of the blood vessels when estrogen declines, so does the health of the blood vessel walls. But, hormone replacement therapy carries risks too. The Womens Health Initiative showed that both equine-based and synthetic hormone replacement therapies increase heart disease risk in postmenopausal women.
You may also notice that other risk factors increase around menopause. This is more likely if youve had less than healthy diet and lifestyle habits in the past and thats most of us! But remember, you can still do so much to reduce your risk going forward.
