When A Coronary Angioplasty Is Used
Like all organs in the body, the heart needs a constant supply of blood. This is supplied by the coronary arteries.
In older people, these arteries can become narrowed and hardened , which can cause coronary heart disease.
If the flow of blood to the heart becomes restricted, it can lead to chest pain known as angina, which is usually triggered by physical activity or stress.
While angina can often be treated with medication, a coronary angioplasty may be required to restore the blood supply to the heart in severe cases where medication is ineffective.
Coronary angioplasties are also often used as an emergency treatment after a heart attack.
Donât Miss: What Is The Best Heart Rate To Burn Fat
What To Expect When Getting A Stent
Having a stent placed is a minimally invasive procedure, meaning it is not a major surgery. Stents for coronary arteries and carotid arteries are placed in similar ways. A stent graft is placed to treat an aneurysm in a procedure called aortic aneurysm repair. Airway stents are placed in a procedure that helps open airways in the lung. For most stents, you will be given medicine to make you sleep during the procedure. The stent procedure may be planned ahead of time or it may be performed in an emergency situation.
Donât Miss: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
Opening Arteries Without Open
Atherosclerosis causes the blood vessels throughout the body to become narrow and sometimes completely blocked. When narrowing occurs in the arteries that carry blood to and from the heart, it can cause serious conditions such as coronary artery disease and carotid artery disease.
Balloon angioplasty is a minimally invasive cardiac catheterization procedure used to open narrow and blocked arteries. Heart stents are tiny lattice-shaped metal tubes that serve as scaffolding to keep the artery open.
Because UT Southwestern cardiologists are active in heart research and national-level work, we are at the vanguard of the newest technologies and most innovative approaches to angioplasty and cardiac stenting. Our offerings include:
- Transradial angioplasty: Minimally invasive procedure performed through the wrist instead of the groin
- Laser-assisted angioplasty: Similar to a balloon angioplasty but uses a laser-tipped catheter instead of a balloon to open the artery
- Drug-eluting stent: Releases medication at intervals to reduce the risk of the vessels becoming narrow again
- Bare-metal stents
Our team works closely with each patient to choose the personalized, science- based treatments most likely to result in the best outcomes.
Don’t Miss: Can Zinc Cause Heart Palpitations
Balloon Angioplasty And Heart Stents
UT Southwestern Medical Centers skilled heart experts perform balloon angioplasty and heart stenting to open clogged and blocked heart arteries.
These minimally invasive procedures help restore blood flow to and from the heart and allow patients to avoid open-heart surgery.
Leaders in Heart and Vascular Care
Combining attentive, compassionate care with our extensive clinical and research resources, UT Southwestern’s cardiology experts and vascular specialists deliver individualized care within pre-eminent health care facilities.
Your Cardiac Catheterization At The University Of Michigan
If you have reduced blood flow to the heart due to a narrowed coronary artery, you may be a good candidate for angioplasty and stenting, minimally invasive procedures that can restore blood flow and let you get back to your daily life. At Michigan Medicine, our Advanced Interventional Cardiology Program offers comprehensive and individualized care, using the latest technologies currently available for angioplasty and stenting, performed by our skilled team of interventional cardiologists.
Don’t Miss: Average Exercise Heart Rate
How Long Does A Heart Stent Last
There is no fixed life of a stent. A lot depends on how your body responds to its presence, your medical dosage, diet, medical history and your lifestyle. They have been known to last for up to 15 years after which one may require a heart stent replacement. Stents for heart operation come with their share of risks. So, post surgery, regular monitoring of heart condition by a physician is advisable.
Though there are associated risks, stent technology has helped millions reclaim their lives. Care for your heart through regular exercise and a healthy diet. That may go a long way in preventing such extreme measures like heart surgeries to be required in the first place. However, the incidence of heart ailment is even found in regularly exercising men and women. The best we can do is keep our body in shape and eat right.
Disclaimer: This article is meant for reference purposes only. It is not intended to supplant the advice of a certified medical practitioner.
Diagnostic Tests And Procedures
To diagnose narrowed arteries or an aortic aneurysm, your doctor may have you undergo some of the following tests and procedures:
- Chest magnetic resonance imaging to look for aneurysms in the aorta. This test works well for detecting aneurysms and pinpointing their size and exact location.
- Computer tomography angiography and magnetic resonance angiography to take pictures of your blood vessels. These tests may give your doctor more information about the flow of blood and whether arteries are narrowed or have aneurysms.
- Coronary angiography to see how blood flows through your coronary arteries. This type of test involves injecting dye into your blood so that your blood vessels can be seen by X-ray.
- Fractional flow reserve can help determine how narrow the artery is. This is an added test done during CTA or coronary angiography to check the blood pressure in a specific artery.
- Ultrasound to see whether plaque has narrowed or blocked your carotid or peripheral arteries or to see if you have an aneurysm and where it may be located. This painless test uses high-energy sound waves to create pictures of the insides of your blood vessels.
- Echocardiography to evaluate the structure and function of your heart. Echocardiography uses sound waves to create moving pictures of your heart.
- Nuclear imaging to see whether the blood is flowing normally to the heart. Your doctor will inject a tracer substance that will show whether the heart is receiving enough blood flow.
Also Check: Heart Attacks Young People
Medication After Stent Surgery
As part of the heart stent recovery time and process, the majority of patients take blood-thinning medicines for a year or less following their angioplasty. This medication typically combines clopidogrel and low-dose aspirin. You should always stick to the medication schedule provided by your doctor as stopping your medicines too soon will dramatically increase the chances of a sudden blockage, which can lead to a heart attack.
After around a year, the clopidogrel will be decreased until you are off the medication, but most patients continue to take low-dose aspirin for life. This is completely normal for those recovering from stents.
Heart Blockage Moderate Coronary Artery Disease
A moderate amount of heart blockage is typically that in the 40-70% range, as seen in the diagram above where there is a 50% blockage at the beginning of the right coronary artery. Usually, heart blockage in the moderate range does not cause significant limitation to blood flow and so does not cause symptoms. Moderate coronary artery disease is treated much in the same way as mild disease, basically attention to risk factors, medications, and healthy lifestyle modification. Occasionally, heart blockage at the higher end of the moderate range may require additional testing to see if it is significant or not and may be responsible for symptoms.
Read Also: Causes Of Left Sided Heart Failure
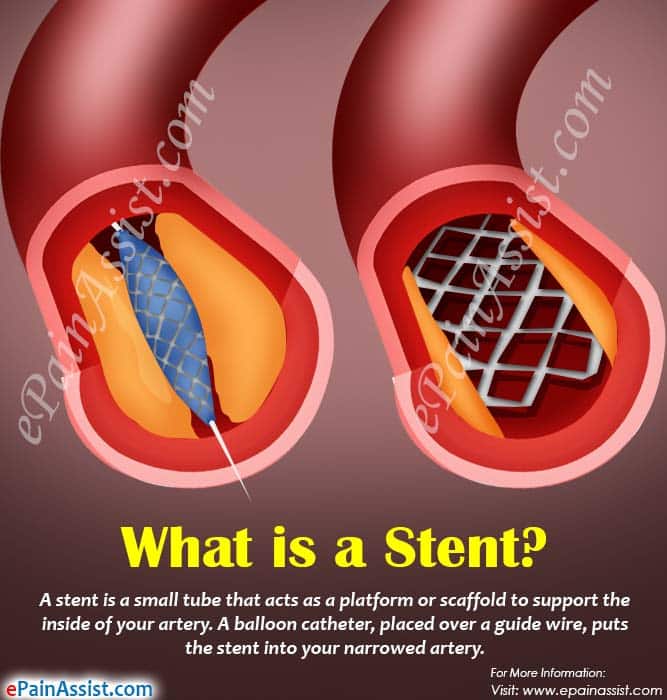
What Is A Stent And What Is Its Function
A stent is a small mesh tube made of either stainless steel or cobalt chromium alloys that is placed by a catheter into a narrowed coronary artery. The stent helps enlarge a segment of the artery to improve blood flow, which should reduce or eliminate symptoms of chest pain. Stent technology is continually developing so we now use stents coated with medication which helps prevent the stent from clogging and narrowing .
What Is A Heart Stent Operation
Heart surgery using stents is an indispensable and lifesaving surgical procedure mostly used when the patient has severe heart blockage, risk of a heart attack or arterial blockage. This article is an eye-opener on heart stent surgery. It discusses in detail, the risks from heart stents and their side effects. Read on to know in detail about heart stent surgery.
Heart surgery using stents is an indispensable and lifesaving surgical procedure mostly used when the patient has severe heart blockage, risk of a heart attack or arterial blockage. This article is an eye-opener on heart stent surgery. It discusses in detail, the risks from heart stents and their side effects. Read on to know in detail about heart stent surgery.
Heart blockage is local blocking or narrowing in the arterial network of the body by accumulated deposits of plaque, which is mostly bad cholesterol. Every artery in the body is a blood pipeline. These pipelines get blocked with accumulation of bad cholesterol, assimilated through food. At such times, a heart surgery using stents is carried out by doctors to open up the clogged pipelines and make blood flow possible again.
Also Check: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
Read Also: Guideline Directed Medical Therapy Heart Failure
Minimally Invasive Heart Surgery
and Minimally Invasive Coronary Artery Bypass Graft
What the Procedure Does
An alternative to standard bypass surgery . Small incisions are made in the chest. Chest arteries or veins from your leg are attached to the heart to bypass the clogged coronary artery or arteries. The instruments are passed through the ports to perform the bypasses. The surgeon views these operations on video monitors rather than directly. In PACAB, the heart is stopped and blood is pumped through an oxygenator or heart-lung machine. MIDCAB is used to avoid the heart-lung machine. Its done while the heart is still beating. Requires several days in the hospital.
Reason for the Procedure
- Manages blockage of blood flow to the heart and improves the supply of blood and oxygen to the heart.
- Reduces risk of heart attack.
- Improves ability for physical activity.
Recommended Reading: Does Benadryl Lower Heart Rate
One Of The Central Questions
This has been one of the central questions of cardiovascular medicine for a long time: Is medical therapy alone or medical therapy combined with routine invasive procedures the best treatment for this group of stable heart patients? said study co-investigator Robert Harrington, MD, professor and chair of medicine at Stanford and the Arthur L. Bloomfield Professor of Medicine. I do see this as reducing the number of invasive procedures.
Robert Harrington
The study was designed to reflect current clinical practice, in which patients with severe blockages in their arteries often undergo an angiogram and revascularization with a stent implant or bypass surgery. Until now, there has been little scientific evidence to support whether these procedures are more effective in preventing adverse heart events than simply treating patients with medications such as aspirin and statins.
If you think about it, theres an intuitiveness that if there is blockage in an artery and evidence that that blockage is causing a problem, opening that blockage is going to make people feel better and live longer, said Harrington, who regularly sees patients with cardiovascular disease at Stanford Health Care. But there has been no evidence that this is necessarily true. Thats why we did this study.
Ischemia, which is reduced blood flow, often causes symptoms of chest pain known as angina. About two-thirds of those heart patients enrolled in the study suffered symptoms of chest pain.
Read Also: Open Heart Surgery Success Rate
Who Needs A Stent
Stents are used to reduce symptoms in patients with obstructive artery disease who suffer chest pain/tightness or shortness of breath that might be experienced with exercise or during periods of strong emotions. Stents may be used instead of bypass surgery in some selected patients. Diabetic patients with multiple coronary blockages may do better with bypass surgery.
Coronary And Carotid Artery Stenting
Procedures to place a stent to treat coronary and carotid arteries are similar. In both, your doctor will use cardiac catheterization to thread a thin tube with an empty balloon on the end through a blood vessel to the narrowed or blocked artery. Once in place, the balloon is filled with air and the stent is opened and placed in the artery.
- The procedure to place a coronary stent is called percutaneous coronary intervention , commonly known as coronary angioplasty. Sometimes the procedure is done in an emergency, such as during a heart attack. The stent provides support to the artery after the artery is re-opened.
- The procedure to place a stent in the carotid artery is called carotid artery stenting. This is a minimally invasive treatment for severe carotid artery disease.
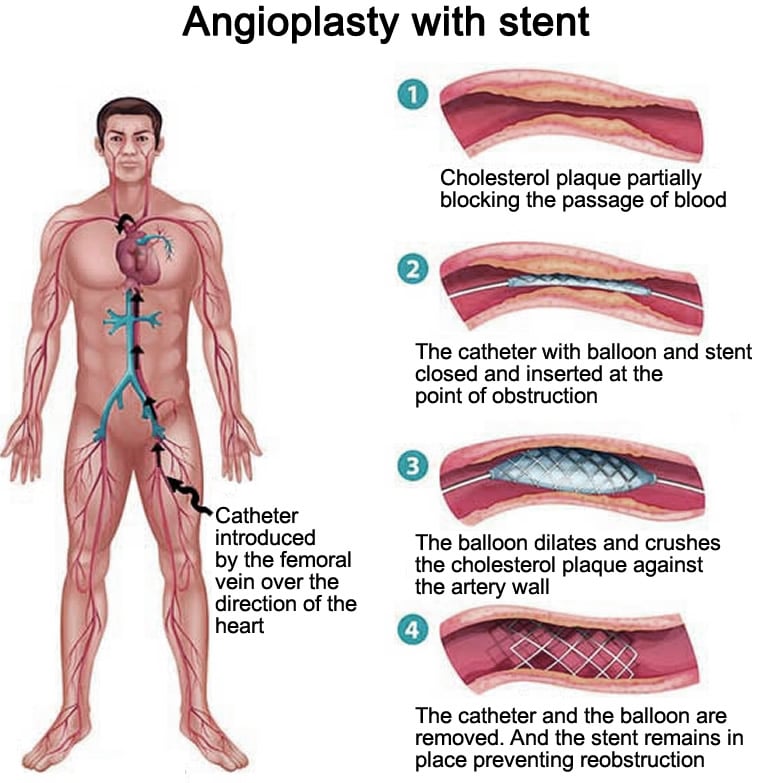
Placing a stent in a coronary artery. From left to right, first, an image of the coronary arteries surrounding the heart. Then, close-up images of the artery with plaque and a catheter inserted with balloon and stent attached. The third image shows the balloon inflated to push the artery open and open the stent. Finally, the artery and stent in the final image are shown after the catheter and balloon are removed. Placing a stent in a carotid artery.
Don’t Miss: Heart Valve Repair Surgery
Heart Surgery Using Stents: The Procedure In A Nutshell
Lets try and understand how this advanced surgical procedure is carried out in detail. When a cardiologist suspects blockage in blood circulation network or narrowing of arteries, he carries out an angiography procedure. This procedure is an X-ray imaging technique which provides a clear image of all the arteries. By observing the angiogram, the doctor can exactly ascertain and locate the presence of any heart blockage or narrowing of arteries. Intravascular ultrasound may also be used to assess the size and exact position of the blockage.
The angiography procedure is carried out by first inserting a very narrow guidance line through the femoral artery in the thigh, from where it is progressively inserted to the desired location. By desired location, we mean the part of the network that has to be imaged. Consequently, a catheter is inserted along the guidance line to that point and an x-ray opaque dye is inserted. The dye spreads with the blood flow in that local region. Then a detailed x-ray image is created and blockage if any, is spotted and marked. The catheter is removed, but the guidance line stays in the location. Then the catheter is reinserted inside, with a balloon attached to its tip to predilate the blockage site and restore the normal size of the artery.
Read Also: Can Congestive Heart Failure Be Cured
What Is A Stent
A stent is a very small tube your healthcare provider can put inside your artery to keep it open after they move plaque out of the way. This helps your blood get through your artery more easily.
Types of stents
Stents are tube-shaped devices that stay inside your artery permanently. They look like tiny fishing nets made of metal instead of organic or man-made fiber.
- A bare metal stent keeps your artery open after angioplasty has pushed a buildup of plaque to the artery walls.
- A drug-eluting stent does the same thing as a bare-metal stent, but it has medicine on it to help prevent your artery from getting narrow again.
- Researchers are experimenting with biodegradable stents, although these arent currently available in clinical practice.
Don’t Miss: How To Make Heart Palpitations Go Away
What Happens During Angioplasty
Angioplasty may be done as part of your stay in a hospital. Procedures may vary depending on your condition and your doctorâs practices. Most people who have angioplasty and stent placement are monitored overnight in the hospital.
Generally, angioplasty follows this process:
You will be asked to remove any jewelry or other objects that may interfere with the procedure. You may wear your dentures or hearing aid if you use either of these.
You will be asked to remove your clothing and will be given a gown to wear.
You will be asked to empty your bladder before the procedure.
If there is a lot of hair at the area of the catheter insertion , the hair may be shaved off.
An IV line will be started in your hand or arm before the procedure. It will be used for injection of medicine and to give IV fluids, if needed.
You will be placed on your back on the procedure table.
You will be connected to an electrocardiogram monitor that records the electrical activity of your heart and monitors your heart rate using electrodes that stick to your skin. Your vital signs will be monitored during the procedure.
There will be several monitor screens in the room, showing your vital signs, the images of the catheter being moved through your body into your heart, and the structures of your heart as the dye is injected.
You will get a sedative in your IV to help you relax. However, you will likely stay awake during the procedure.
What Are The Risks Associated With Heart Stents
There are two kinds of stents. One type is a bare stent which is made up of 316 L type stainless steel. Heart stents being foreign objects for the body, they have certain associated side effects. They trigger an immune response from the body causing platelet accumulation at the stent site. This is taken care of, by lifelong intake of aspirin and intake of drugs likeClopidogrel for 6 months after the procedure. Still the scarring left by the stents does cause problems and in time, there may be renarrowing of the arteries at the operated site.
To prevent this, drug-coated or drug-eluting stents were developed that prevent the accumulation of arterial tissue over the stent and suppress immune response against it. Heart stent surgery using these drug-eluting stents is preferred now. However, this type has been known to cause blood clots in some case studies. About 1% to 2% people undergoing a drug-eluted stent surgery suffer from the growth of blood clots at the stent site. Hence the patient has to use blood thinning, anti-blood clotting drugs like Plavix for a prolonged period of time, which causes additional side effects. These effects include gastrointestinal bleeding and strokes in some cases. So stents are lifesavers but they also come with their share of risks.
You May Like: What Happens With Congestive Heart Failure
