Managing Heart Attack Risk Factors
Here are ways to manage your risks for a heart attack:
- Look at which risk factors apply to you, then take steps to eliminate or reduce them.
- Learn about high blood pressure and high cholesterol levels. These may be “silent killers.”
- Change risk factors that aren’t inherited by making lifestyle changes. Talk with your healthcare provider to find out how to do so.
- Talk with your healthcare provider to find out if you have risk factors that can’t be changed. These can be managed with medicine and lifestyle changes.
Surgical Treatment For Heart Attack
Surgery or procedure to unblock a clogged artery may be performed if youve suffered a heart attack. The following surgeries and processes are used to treat a heart attack:
Angioplasty and stenting of the heart
The goal of this surgery is to clear blocked cardiac arteries. Another name for it is percutaneous coronary intervention . This technique is frequently carried out as part of a procedure to locate blockages .
A heart specialist directs a thin, flexible tube to the constricted area of the heart artery during angioplasty. Then, a small balloon is inflated to help expand the narrowed artery and enhance blood flow.
During angioplasty, a tiny wire-mesh tube may be inserted into the artery. The artery is kept open by the stent. It lessens the possibility of the artery narrowing once more. In addition, some stents have a drug coating that keeps the arteries open.
Surgery to bypass the coronary arteries
CABG is commonly known as Open-heart surgery. A surgeon pulls a healthy blood artery from another section of the body to construct a new pathway for blood in the heart. The blood then bypasses the blocked or constricted coronary artery. When a person is having a heart attack, CABG may be performed as an urgent procedure.
Are There Other Causes Of Heart Attack Besides Blockage
Sometimes a coronary artery temporarily contracts or goes into spasm. When this happens the artery narrows, and blood flow to part of the heart muscle decreases or stops.
The causes of spasms are unclear. A spasm can occur in normal-appearing blood vessels as well as in vessels partly blocked by atherosclerosis. A severe spasm can cause a heart attack.
Another rare cause of heart attack is spontaneous coronary artery dissection, which is a spontaneous tearing of the coronary artery wall.
Recommended Reading: Is 116 Heart Rate High
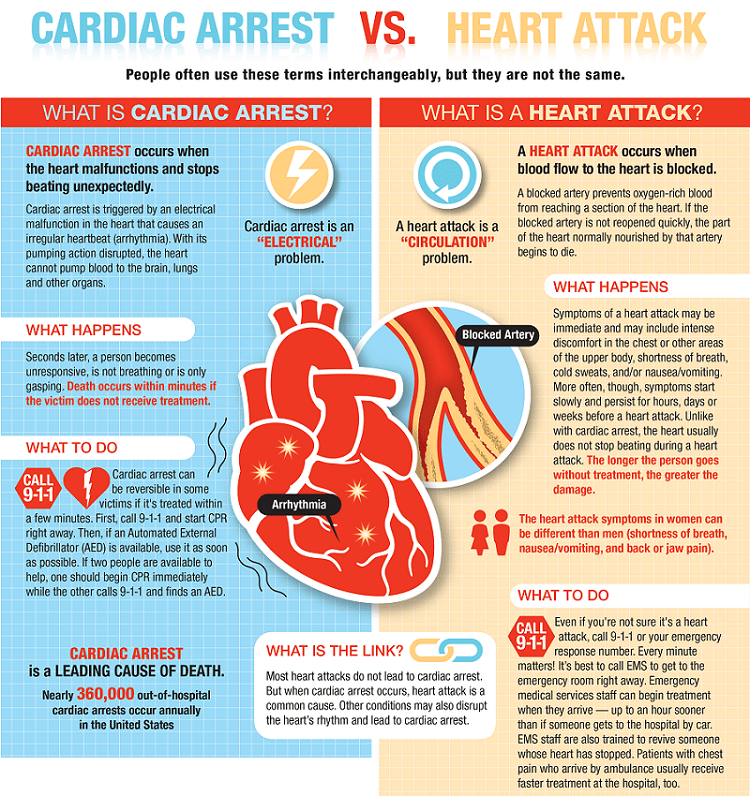
Types Of Heart Attacks
A heart attack occurs when one of the coronary arteries become blocked or restricted, reducing the flow of blood and oxygen to the heart.
There are two main types of heart attack:
- ST-elevation myocardial infarction : A coronary artery is completely blocked, preventing parts of the heart muscle from receiving blood and oxygen.
- NonST-elevation myocardial infarction : A coronary artery is only partially blocked, which may cause less damage to the heart muscle.
The heartbeat display pattern that appears on an electrocardiogram test is known as the ST segment. Only STEMI heart attacks show elevated activity on an EKG. However, both STEMI and NSTEMI heart attacks may be considered major heart attacks.
Medications For Heart Attacks
Less severe heart attacks may be treated with medication. Your doctor will prescribe you medications based on your condition, risk factors, and overall health. These drugs may include:
- clot busters to dissolve clots that are blocking arteries
- blood pressure medications to help reduce the hearts workload and control blood pressure
- blood thinners to prevent blood clots
- statins to help lower LDL cholesterol
Also Check: What Arm Hurts With Heart Attack
Diagnosing Heart Attack Today
Although many people think of a heart attack as an event that causes disabling chest pain, it is not always so straightforward. Because everyone’s symptoms can be different, diagnosing a heart attack requires the combination of a doctor’s judgment, signs and symptoms, and test results. “No one method is ideal on its own, but when they are used together, we can reach a conclusion that is highly accurate,” says Dr. Januzzi.
To understand the significance of the possible causes of chest pain, it is important to determine what is actually going on inside the body.
In a heart attack, the amount of blood reaching heart muscle cells is inadequate to keep them alive. Usually, something has stopped blood flow through an artery that nourishes the heart . Most often, this occurs when a plaque of atherosclerosis ruptures, spilling its cholesterol-rich contents into the center of the artery and triggering a blood clot. Sometimes, it is caused by a spasm of the artery that narrows the interior of the artery temporarily, preventing blood flow. As a result, cells in the area of the heart muscle fed by the artery are injured. If blood flow is restored within an hour or two, some of the injured cells may recover. If not, they begin to die from lack of oxygen. If the damage is permanent and extensive, the heart may no longer be able to contract and pump well. When this happens, the person may develop heart failure, or even die.
Prevention Of A Heart Attack
You can help prevent a heart attack by managing certain risk factors and making healthy lifestyle choices.
Your doctor may also prescribe certain medications to reduce your heart attack risk. These may work by reducing your bloods ability to clot, lowering your blood pressure, or improving your cholesterol levels.
Also Check: What Causes High Heart Rate After Surgery
How Can I Reduce My Risk Of Having A Heart Attack
Although there are several risk factors that you cant control, there are many ways you can help yourself and reduce your risk of a heart attack. These include:
- Schedule a checkup: Find a primary care provider and see them at least once a year for a checkup or wellness visit. An annual checkup can catch many of the early warning signs of heart disease, including signs that you can’t feel. These include your blood pressure, blood sugar levels, cholesterol levels and more.
- Quit tobacco products: This includes smokeless tobacco and all vaping products.
- Exercise regularly: Aim for 20 to 30 minutes of moderately intense physical activity a week.
- Eat a healthy diet: Examples include the Mediterranean or Dash diets. A plant-based diet approach is an excellent alternative.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Your primary care provider can advise you on a healthy goal weight and provide you resources and guidance to help you reach that goal.
- Manage your existing health conditions: This includes high cholesterol levels, high blood pressure and diabetes.
- Reduce your stress: Consider techniques such as yoga, deep breathing and meditation.
- Take your medications: Dont just take medications when you remember to or when you have a doctors appointment coming up.
- Keep all your medical appointments: Seeing your healthcare providers regularly can help uncover heart-related issues or other medical problems you didn’t know you had. This can also help treat problems sooner rather than later.
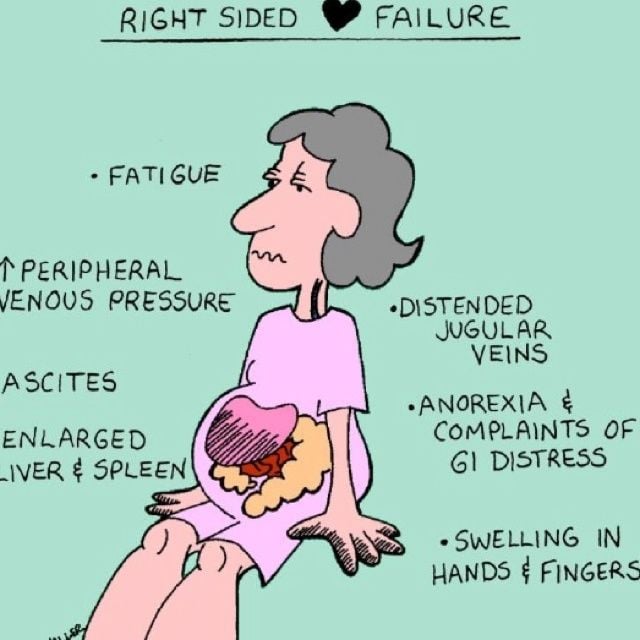
What Are The Different Types Of Heart Failure
Heart failure may affect different patients very differently the affected parts of the heart, the resulting symptoms and the time course of heart failure onset can vary widely. For this reason, different medical terms are used to exactly describe the different types of heart failure. Its very important to define the type and cause of heart failure because it determines treatment. Exact diagnosis may be difficult since symptoms may be very similar, for example, all types of heart failure cause shortness of breath, fatigue and some degree of congestion, usually in the lungs but also in other parts of the body such as the liver, intestines, kidneys and lower limbs.
Acute heart failure develops suddenly and symptoms are initially severe. Acute heart failure may follow a heart attack, which has caused damage to an area of your heart. It may also be caused by a sudden lack of ability by the body to compensate for chronic heart failure. If you develop acute heart failure, it may be severe initially, but may only last for a short period of time and improve rapidly. It usually requires treatment and medication to be administered by injection .
Chronic heart failure is very common. Symptoms appear slowly over time and gradually get worse.
Left-sided heart failure means that the power of the left heart chamber, which pumps blood throughout the body, is reduced thus, the left chamber must work harder to pump the same amount of blood.
You May Like: How Long Should You Exercise At Your Target Heart Rate
Treatment For A Heart Attack
Understandably, treatment for those diagnosed with heart attack can be complex. But this section on heart attack treatments will help you talk with your doctors and healthcare providers.
As you learn about your treatment plan, dont be afraid to ask questions. Be sure to voice any concerns you may have.
What Are The Complications Of A Heart Attack
Complications associated with heart attacks include:
- Arrhythmias : Management options include medication, pacemaker placement, implantable cardioverter defibrillator placement and other options.
- Heart failure: If enough heart tissue has died, your heart is now weakened and cant pump blood effectively, which can lead to heart failure.
- Heart valve problems: Depending on the area of heart damage, your heart valves may be affected. Catheter-based procedures or surgery are treatment options for heart valve problems.
- Sudden cardiac arrest: This sudden stoppage of your heart can be caused by arrhythmia.
- Depression and anxiety: Talk to your healthcare provider. Management includes medication and counseling. Joining a support group can help.
Don’t Miss: Heart Attacks In Teens
The Warning Signs Of Heart Attacks
- Painful pressure, squeezing, fullness in chest
- Excessive sweating followed by flimsiness and dizziness.
- Back, neck, or jaw discomfort or pain.
- Discomfort in one or both shoulders and arms.
- Difficulty in breathing along with shortness of breath after or during chest pain.
- Extreme or unexpected fatigue, nausea, or vomiting.
It is important to remember that atherosclerosis, which blocks arteries due to fat or cholesterol build-up, has no symptoms. There may not be any symptoms because when a coronary artery narrows and restricts blood flow, neighboring blood arteries that supply the heart occasionally enlarge to make up for it.
Do Women Fare Better Or Worse Than Men After A Heart Attack
Younger women under age 45 have a better outcome than men of a similar age. Scientists believe this is because of estrogen’s heart-protective effects. However, after menopause ends the protective benefits of estrogen, women fare worse than men. More specifically:
- Women between the ages of 45 and 65 who’ve had a heart attack are more likely to die within a year of the event compared with men of this same age.
- Women over age 65 are more likely to die within weeks of their heart attack than men over age 65.
Don’t Miss: Can Drinking Too Much Alcohol Cause Heart Attack
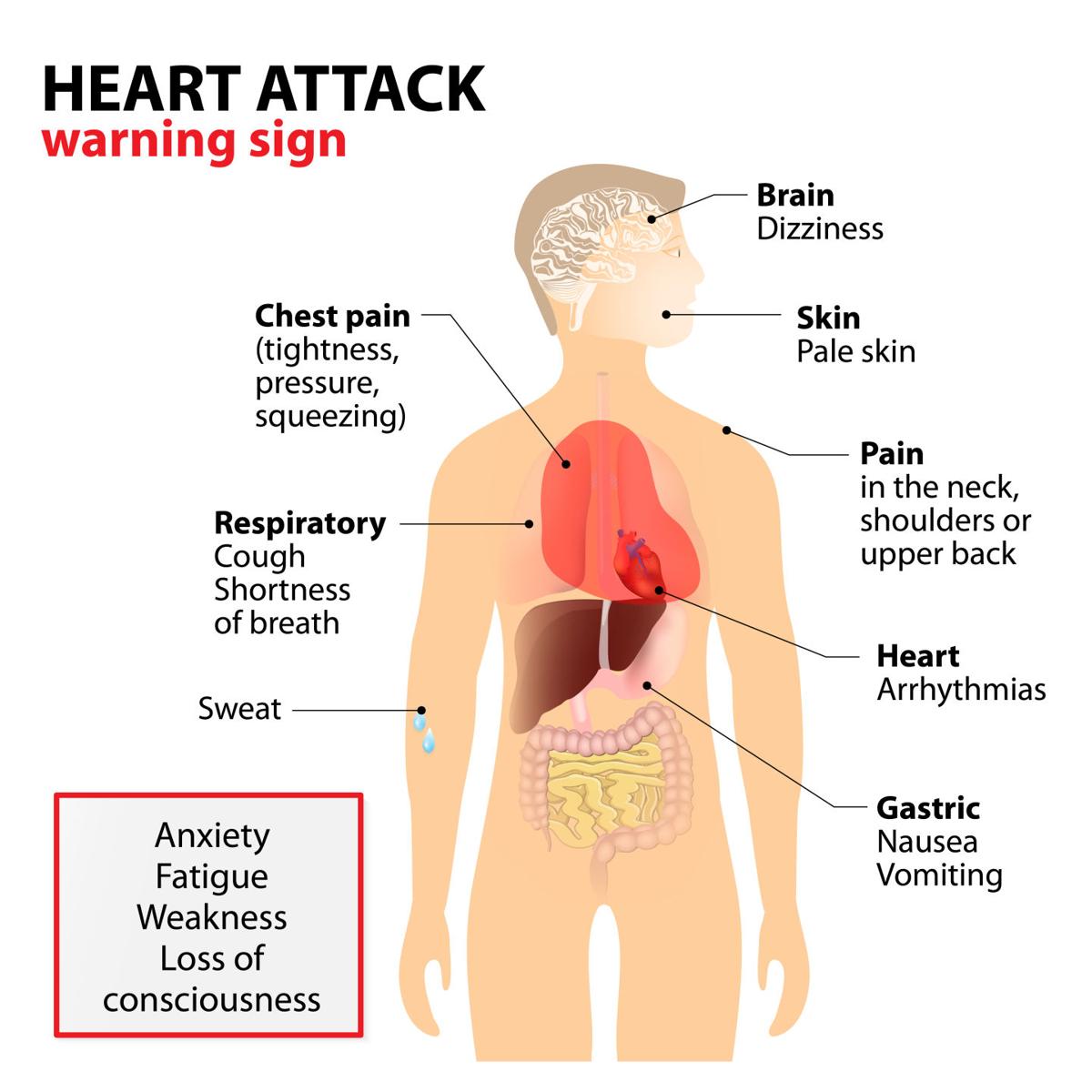
What Are The Symptoms Of A Heart Attack
Heart attacks can have a number of symptoms, some of which are more common than others. The symptoms you have are also influenced by your sex, as with men and women being more likely to have different heart attack symptoms.
Common heart attack symptoms
Symptoms most often described by people having a heart attack:
- Chest pain . This symptom can be mild and feel like discomfort or heaviness, or it can be severe and feel like crushing pain. It may start in your chest and spread to other areas like your left arm , shoulder, neck, jaw, back or down toward your waist.
- Shortness of breath or trouble breathing.
- Nausea or stomach discomfort. Heart attacks can often be mistaken for indigestion.
- Heart palpitations.
- Feeling lightheaded, dizzy or passing out.
Heart attack symptoms in women
Medical research in recent years has shown that women may have the above symptoms, but also have a higher chance of experiencing symptoms different from those listed above.Women are less likely to describe the following:
- Chest pain, especially in the center of the chest.
- Discomfort that feels like indigestion.
Women are more likely to describe the following:
- Shortness of breath, fatigue and insomnia that started before the heart attack.
- Pain in the back, shoulders, neck, arms or abdomen.
- Nausea and vomiting.
Who Is More Likely To Develop Heart Diseases
There are many different factors that can make you more likely to develop heart disease. Some of these factors you can change, but others you cannot.
- Age. Your risk of heart disease goes up as you get older.
- Sex. Some factors may affect heart disease risk differently in women than in men.
- Family history and genetics. A family history of early heart disease raises your risk of heart disease. And research has shown that some genes are linked to a higher risk of certain heart diseases.
- Race/ethnicity. Certain groups have higher risks than others.
- Lifestyle habits. Over time, unhealthy lifestyle habits can raise your risk heart disease:
- Eating a diet high in saturated fats, refined carbohydrates, and salt.
Read Also: How Many Times Can You Have Open-heart Surgery
Treatment And Medication Options For A Heart Attack
Once you arrive at a hospital after experiencing heart attack symptoms, doctors will confirm a heart attack through a combination of heart monitoring, blood tests, and imaging tests.
You may be started right away on an intravenous clot-busting drug, which will help dissolve the blood clot that caused your heart attack.
More commonly, you will undergo a procedure to open up your blocked artery and keep it open, known as coronary angioplasty and stenting.
The Different Kinds Of Heart Attack
Not all heart attacks are the same. The task force that redefined the diagnosis of heart attack also identified six different types, as follows.
-
Type 1, the most common situation: A heart attack occurring from a blood clot or other blockage in blood flow through an artery in the heart. The person usually has coronary artery disease. This is an oxygen supply problem, due to reduced blood flow.
-
Type 2: A heart attack occurring when the heart needs more oxygen than it can get. This type of heart attack is an oxygen demand problem, resulting from higher need for blood flow.
-
Type 3: A fatal heart attack that causes death before the diagnosis can be confirmed with blood tests.
-
Type 4a: A heart attack that occurs during angioplasty, a procedure in which a blocked blood vessel is opened with a balloon on the end of a flexible tube inserted in the artery.
-
Type 4b: A heart attack that occurs when a clot blocks blood flow through a stentâa small metal mesh tube that has been inserted in the artery during angioplasty to keep the artery open.
-
Type 5: A heart attack that occurs during coronary artery bypass surgery.
Read Also: What Is Good Heart Rate Recovery
Why Didnt I Have Any Warning
The process of atherosclerosis has no symptoms. When a coronary artery narrows and constricts blood flow, other nearby blood vessels that serve the heart sometimes expand to compensate, which may explain why there are no warning signs.
Such a network of expanded nearby blood vessels is called collateral circulation, and it helps protect some people from heart attacks by delivering needed blood to the heart. Collateral circulation can also develop after a heart attack to help the heart muscle recover.
Consume A Balanced Healthful Diet
- Eating a low-fat, high-fiber diet rich in whole grains, five pieces a day of fresh fruit and vegetables, and other nutrients are advised.
- The maximum weight of salt you should consume daily is 6g , as eating more than that will raise your blood pressure.
- Saturated and unsaturated fats are two different types. Avoid saturated fats as they will raise the amount of harmful cholesterol in your blood.
Also Check: How To Know Your Heart Rate
When Can I Resume My Usual Activities
Recovery from a heart attack after youre released from the hospital depends on the severity of the heart attack, how soon treatment began, methods used and the health conditions you had if any before your heart attack. Your healthcare provider can explain the next steps for your recovery and what you can expect. In general, most people can return to work or resume their usual activities anywhere between two weeks to three months after their heart attack.
Common Heart Attack Types And Treatments
The type of heart attack you experienced determines the treatments that your medical team will recommend. A heart attack occurs when a blockage in one or more coronary arteries reduces or stops blood flow to the heart, which starves part of the heart muscle of oxygen.
The blockage might be complete or partial:
- A complete blockage of a coronary artery means you suffered a STEMI heart attack or ST-elevation myocardial infarction.
- A partial blockage is an NSTEMI heart attack or a non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction
Treatments differ for a STEMI versus NSTEMI heart attack, although there can be some overlap.
Hospitals commonly use techniques to restore blood flow to part of the heart muscle damaged during a heart attack:
- You might receive clot-dissolving drugs , balloon angioplasty , surgery or a combination of treatments.
- About 36 percent of hospitals in the U.S. are equipped to use a procedure called percutaneous coronary intervention , a mechanical means of treating heart attack.
At a hospital equipped to administer PCI, you would likely be sent to a department that specializes in cardiac catheterization, sometimes called a cath lab. There, a diagnostic angiogram can examine blood flow to your heart and reveal how well your heart is pumping. Depending on the results of that procedure, you may be routed to one of three treatments: medical therapy only, PCI or coronary artery bypass grafting .
Also Check: Congestive Heart Failure Mayo Clinic
