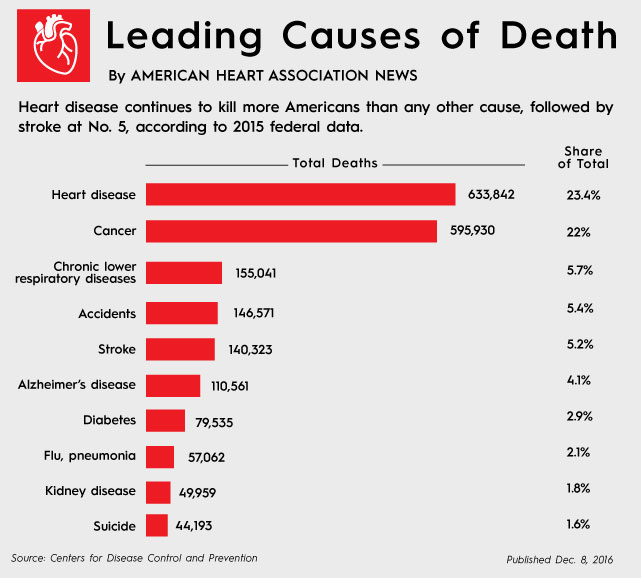
Health Cost In America
- From 2016 to 2017, the direct and indirect costs associated with cardiovascular disease were $363.4 billion. That includes $216 billion in direct costs and $147.4 billion in lost productivity and mortality.
- Cardiovascular disease and stroke accounted for 13% of all healthcare expenditures from 2014 to 2015, more than any other diagnostic group.
- Heart attacks and coronary heart disease were two of the 10 most costly conditions that were treated in U.S. hospitals in 2013, tallying a respective $12.1 billion and $9 billion.
- The National Institutes of Health is projected to spend $1.6 billion on heart disease research in 2022, with an additional $430 million focused specifically on coronary heart disease.
- Nearly one in six U.S. healthcare dollars is spent on cardiovascular care.
The Mortality Rate For Diseases Of The Nervous System Is Higher In The Us Than In Comparably Wealthy Countries
In recent years, mortality rates for diseases of the nervous system have been both increasing and consistently higher in the U.S. than in comparable countries. In the U.S., the age-adjusted mortality rate for Alzheimers disease has increased from just under 12 deaths per 100,000 population in 1980 to over 33 in 2015. The sharp increase in mortality in 1999 for the United States coincides with a change in ICD coding.
You May Like: What Ejection Fraction Is Heart Failure
Types Of Cardiovascular Disease
There are a wide range of cardiovascular diseases. The most common type is coronary artery disease. This refers to problems with the blood vessels of the heart, including blockages. These blockages can cause a lowered blood flow to the heart, increasing the risk for a heart attack.
Stroke is another type of cardiovascular disease. A stroke happens when blood flow to the brain is fully or partially blocked. In the United States, heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular diseases cause one in three deaths.
Other types of cardiovascular diseases include:
- Aortic disease: A problem with the blood vessel that carries blood from the heart to the brain and the body
- Arrhythmia: Abnormal heart rates or rhythms
- Cerebrovascular disease: Blockages or narrowing within the blood vessels that carry blood to the brain
- Congenital heart disease: A heart problem that you are born with
- Deep vein thrombosis: A blockage or blockages in the vessels that carry blood from the brain or body to the heart
- Heart failure: Difficulty with heart pumping that can cause a buildup of fluid
- Pericardial disease: A problem with the lining of the heart
- Peripheral artery disease: A blockage or narrowing in the blood vessels of the abdominal organs, arms, or legs
- Valve disease: A problem with the valves of the heart
Read Also: Heart Rate Variability Monitor
Cdc: Us Heart Disease Deaths Spiked At Pandemic’s Start Reversing Long Decline
Oct. 31 — U.S. death rates from heart disease spiked in 2020 at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic after a steady decline from 2010 to 2019 and reversing a decades-long drop since at least the 1990s.
Death rates increased among adults of all ages, and across sex, race and ethnicity groups, particularly among younger adults and non-Hispanic Black adults.
That’s according to preliminary research to be presented at the American Heart Association’s Scientific Sessions 2022 conference running Saturday to Monday in Chicago. The heart group released the abstract Monday.
“Prior to 2020, death rates from heart disease had been declining among adults for decades, which has been recognized by the CDC as one of the ten greatest public health achievements of the last century,” Rebecca C. Woodruff, an epidemiologist at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention — the study’s lead author — said in a news release.
She added: “The increases in death rates from heart disease in 2020 represented about five years of lost progress among adults nationwide and about 10 years of lost progress among younger adults and non-Hispanic Black adults.”
That translated to the national heart disease death rate increasing by 4.1% in 2020, while the rate dropped by 9.8% from 2010 to 2019, the researchers said.
The Cost Of Heart Disease
- Between 2014 and 2015, cardiovascular disease and stroke cost the United States $351.2 billion in healthcare services, medicines, and lost productivity due to death.
- Researchers expect that CVD costs will rise to $749 billion by 2035.
- The National Institutes of Health spent more than $1.5 billion on heart disease research in 2021.
- 1 in every 6 healthcare dollars is spent on cardiovascular disease.
- Hospitalization for a heart attack costs a median $53,384, and bypass surgery can cost $85,891 to $177,546.
- Individuals with hypertension spend approximately $2,000 per year more than their non-hypertensive peers on health care.
Read Also: How To Check Your Resting Heart Rate
Aha: Heart Disease Death Rates In Us Spiked In 2020
FRIDAY, Nov. 4, 2022 — Deaths from heart disease increased in 2020 in the United States, following a steady decline from 2010 to 2019, according to a study presented at the American Heart Association Scientific Sessions 2022, held from Nov. 5 to 7 in Chicago.
Rebecca C. Woodruff, Ph.D., M.P.H., from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, and colleagues examined the percentage change between 2010, 2019, and 2020 heart disease death rates overall and by heart disease subtypes and demographic subgroups.
The researchers found that across age, sex, and race and ethnicity groups, there was a decrease in heart disease death rates during 2010 to 2019, followed by an increase in 2020. The national heart disease death rate decreased by 9.8 percent from 2010 to 2019 and increased by 4.1 percent in 2020, to approximately the same rate as in 2015. In 2020, 55 percent of total heart disease deaths were due to coronary heart disease. For non-Hispanic Black adults, there was a 10.4 percent decrease in the heart disease death rate from 2010 to 2019, followed by an increase of 11.2 percent in 2020, resulting in similar rates for 2020 and 2010. Heart disease death rates decreased from 2010 to 2019 among adults aged 35 to 54 and 55 to 74 years and increased in 2020 , resulting in higher heart disease death rates in 2020 than 2010.
Heart Disease Statistics And Maps
Find facts, statistics, maps, and other data related to heart disease.
Heart disease, a leading cause of death in the United States, creates an enormous burden for people, communities, and healthcare providers and systems.
The reports, products, and resources in this section can help public health officials and other health professionals find up-to-date information about heart disease:
To receive email updates about this page, enter your email address:
Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website’s privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance on other federal or private website.
CDC.gov Privacy Settings
We take your privacy seriously. You can review and change the way we collect information below.
Cookies used to make website functionality more relevant to you. These cookies perform functions like remembering presentation options or choices and, in some cases, delivery of web content that based on self-identified area of interests.
Also Check: What Is Ideal Heart Rate
Hospital Discharge Rates For In
- Greece: not available.
- Denmark, Luxembourg and Turkey: 2016.
- Germany, Malta and Finland: 2018.
This article presents an overview of European Union statistics related to cardiovascular diseases and focuses on cardiovascular health and mortality, as well as cardiovascular healthcare.
Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death in the EU. They cover a broad group of medical problems that affect the circulatory system , often resulting from atherosclerosis, the abnormal build-up of plaque that is made of, among constituents, cholesterol or fatty substances that is deposited on the inside walls of a persons arteries. Some of the most common diseases that affect the circulatory system include ischaemic heart disease and cerebrovascular diseases .
This article is one of a set of statistical articles concerning health status in the EU which forms part of an online publication on health statistics.
While most data in this article relate to 2019, there are some for 2020: for the first time, this article includes data that may have been impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic and its related restrictions. For this reason, particular attention should be paid when comparing the 2020 data with data from earlier years.
Heart Attack And Stroke Statistics
- Approximately 1.5 million heart attacks and strokes occur in the United States each year.
- Someone in the U.S. has a stroke every 40 seconds, accounting for one out of every 19 deaths.
- Cerebrovascular disease accounted for 7 million deaths worldwide in 2020.
- Each year, approximately 605,000 new heart attacks and 200,000 recurrent heart attacks occur in the U.S.
- In 2016, heart attacks, strokes, and heart failure caused 2.2 million hospitalizations.
- Acute myocardial infarctions accounted for 260,000 emergency room visits in 2017, and cerebrovascular disease accounted for another 492,000.
Also Check: What Age Can You Have A Heart Attack
Where Are Trends Likely To Reverse Or Are Already Rising
Comparison of trends in CHD mortality decline at the international level is complex because challenges in definitions of metrics used, differences in data quality and methods of acquisition, and consistency in cause of death recording and certification. Additionally, information from countries undergoing social and political change can show results due to process rather than cause of death. Nevertheless, data from countries that exhibit unusual changes can be informative in understanding the dynamics of mortality changes.
Using data from vital statistics and from risk factor survey data, Critchley et al.39 described trends in CVD mortality for Syria, Tunisia, occupied Palestinian territories , and Turkey. In the periods from the late 1990âs to the late 2000âs, age standardized rates of CHD rose by 20% in Tunisia and 62% in Syria, but declined by 17% in oPt and 29% in Turkey. BMI and diabetes increased in all of these areas over this time period, though cholesterol and blood pressure increased only in Tunisia and Syria, the countries where the CHD mortality rates increased.39 Cigarette smoking declined substantially in Turkey and oPt, the countries where the CHD mortality rates decreased. Thus, these findings are suggestive but somewhat inconsistent regarding risk factor explanations for the CHD mortality rate changes.
COVID vaccination rates have also been substantially lower in rural areas than in urban areas, he added.
Heart Disease #1 Cause Of Death Rank Likely To Be Impacted By Covid
Report Highlights:
- Heart disease remains the #1 cause of death worldwide in the latest annual Statistical Update from the American Heart Association
- Experts say the effects of COVID-19 are likely to influence cardiovascular health and mortality rates for many years, directly and as a result of increased lifestyle-related risks during and after the pandemic.
- The 2021 Statistical Update also offers new insight into the importance of maternal health complications and how those affect cardiovascular health of mothers and their babies.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Wednesday, Jan. 27, 2021
DALLAS, Jan. 27, 2021 Heart disease remains the leading cause of death worldwide, according to the American Heart Associations Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics 2021 Update, published today in the Associations flagship journal Circulation, and experts warn that the broad influence of the COVID-19 pandemic will likely continue to extend that ranking for years to come.
Globally, nearly 18.6 million people died of cardiovascular disease in 2019, the latest year for which worldwide statistics are calculated. That reflects a 17.1% increase over the past decade. There were more than 523.2 million cases of cardiovascular disease in 2019, an increase of 26.6% compared with 2010.
Experts predict the global burden of cardiovascular disease will grow exponentially over the next few years as the long-term effects of the current COVID-19 pandemic evolve.
Additional Resources:
Recommended Reading: Heart Shaped Lips Surgery
What Are The Risk Factors For Cardiovascular Disease
The most important behavioural risk factors of heart disease and stroke are unhealthy diet, physical inactivity, tobacco use and harmful use of alcohol. The effects of behavioural risk factors may show up in individuals as raised blood pressure, raisedblood glucose, raised blood lipids, and overweight and obesity. These intermediate risks factors can be measured in primary care facilities and indicate an increased risk of heart attack, stroke, heart failure and other complications.
Cessation of tobacco use, reduction of salt in the diet, eating more fruit and vegetables, regular physical activity and avoiding harmful use of alcohol have been shown to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Health policies that create conduciveenvironments for making healthy choices affordable and available are essential for motivating people to adopt and sustain healthy behaviours.
There are also a number of underlying determinants of CVDs. These are a reflection of the major forces driving social, economic and cultural change globalization, urbanization and population ageing. Other determinants of CVDs include poverty,stress and hereditary factors.
In addition, drug treatment of hypertension, diabetes and high blood lipids are necessary to reduce cardiovascular risk and prevent heart attacks and strokes among people with these conditions.
The United States Has A Much Higher Rate Of Maternal Mortality Than Comparable Countries
Women in the United States are more than four times as likely to die due to complications from childbirth than women in comparable countries. Additionally, the maternal mortality rate in the United States has risen 113% since 1990. For context, Canada was the only other country during this period to experience an increase in maternal mortality over the same time period, growing just over 60% . Researchers point to multiple factors that contribute to the alarming maternal mortality rate in the United States, including: Racial disparities a lack of continuity between, or access to, primary care and maternal care services a need for standardized and evidence-based protocols for child birth and clinical care and poor data collection on maternal death and patterns of risk.
You May Like: What Blood Vessel Carries Blood Back To The Heart
Recommended Reading: What Can Cause Heart Attacks
Good Genes Are Nice But Joy Is Better
The best way to treat acute myocardial infarctions, commonly known as heart attacks, has been long established by international consensus. The types of treatments and recommended procedures are well-defined, widely known, and readily available in modern hospitals.
Yet, a newly published analysis of heart attack care and outcomes across six high-income nations has found baffling variations in the kind of treatment patients receive and in how well patients fare.
The study, published online in BMJ on May 5, was led by researchers at Harvard Medical School and The University of Texas Medical Branch as part of the International Health System Research Collaborative, an effort dedicated to understanding the tradeoffs inherent in different nations approaches to delivering health care.
It turns out there is a lot that different health care systems can learn from one another about how to deliver the best possible care, even for common, well-understood medical conditions like heart attack, said Bruce Landon, professor of health care policy at HMS, a professor of medicine at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, and co-principal investigator of the collaborative. This approach also allows us to better understand differences in outcomes that stem directly from health systems as opposed to other country-specific factors that might influence health outcomes.
Why Are Cardiovascular Diseases A Development Issue In Low
At least three-quarters of the world’s deaths from CVDs occur in low- and middle-income countries. People living in low- and middle-income countries often do not have the benefit of primary health care programmes for early detection and treatment of peoplewith risk factors for CVDs. People in low- and middle-income countries who suffer from CVDs and other noncommunicable diseases have less access to effective and equitable health care services which respond to their needs. As a result, for many peoplein these countries detection is often late in the course of the disease and people die at a younger age from CVDs and other noncommunicable diseases, often in their most productive years.
The poorest people in low- and middle-income countries are most affected. At the household level, evidence is emerging that CVDs and other noncommunicable diseases contribute to poverty due to catastrophic health spending and high out-of-pocket expenditure.At the macro-economic level, CVDs place a heavy burden on the economies of low- and middle-income countries.
Also Check: Copd And Congestive Heart Failure
How Can The Burden Of Cardiovascular Diseases Be Reduced
The key to cardiovascular disease reduction lies in the inclusion of cardiovascular disease management interventions in universal health coverage packages, although in a high number of countries health systems require significant investment and reorientationto effectively manage CVDs.
Evidence from 18 countries has shown that hypertension programmes can be implemented efficiently and cost-effectively at the primary care level which will ultimately result in reduced coronary heart disease and stroke. Patients with cardiovascular diseaseshould have access to appropriate technology and medication. Basic medicines that should be available include:
Heart Disease In The United States
- Heart disease is the leading cause of death for men, women, and people of most racial and ethnic groups in the United States.1
- One person dies every 34 seconds in the United States from cardiovascular disease.1
- About 697,000 people in the United States died from heart disease in 2020thats 1 in every 5 deaths.1,2
- Heart disease cost the United States about $229 billion each year from 2017 to 2018.3 This includes the cost of health care services, medicines, and lost productivity due to death.
Coronary Artery Disease
- Coronary heart disease is the most common type of heart disease, killing 382,820 people in 2020.2
- About 20.1 million adults age 20 and older have CAD .2
- In 2020, about 2 in 10 deaths from CAD happen in adults less than 65 years old.2
Early Action Is Important for Heart Attack
- In the United States, someone has a heart attack every 40 seconds.2
- Every year, about 805,000 people in the United States have a heart attack.2 Of these,
- 605,000 are a first heart attack2
- 200,000 happen to people who have already had a heart attack2
- About 1 in 5 heart attacks are silentthe damage is done, but the person is not aware of it.2
Don’t Miss: What Is A Normal Heart Rate For A Pregnant Woman
