What Conditions And Disorders Affect The Blood Vessels
A wide range of problems can affect your blood vessels, including:
- Aneurysm, a bulge in a weak or damaged portion of an artery. Aneurysms can occur anywhere in your body. If they rupture , they may cause life-threatening internal bleeding.
- Arterial diseases, including coronary artery disease, carotid artery disease and peripheral artery disease . These diseases cause arteries to narrow, usually due to atherosclerosis.
- Atherosclerosis, which is the buildup of plaque inside your arteries. It can lead to a heart attack or stroke.
- Blood clots, or clumps of blood that form inside veins or arteries. Clots block blood flow and can lead to deep vein thrombosis , pulmonary embolism, stroke or occlusion of an artery.
- High blood pressure, or hypertension, occurs when theres too much force against the walls of your arteries.
- Raynauds disease, which causes arteries that supply blood to your skin to get very narrow in response to cold temperatures.
- Varicose veins, or twisted and enlarged veins that usually form in the legs or feet.
- Vascular malformations, which are abnormal clusters or connections between blood vessels. Conditions such as arteriovenous malformations are often congenital .
- Vasculitis, which is blood vessel inflammation. Blood vessel walls can thicken and narrow, which prevents blood from flowing freely.
What Do The Heart And Blood Vessels Do
The heart’s main function is to pump blood around the body. Blood carries nutrients and waste products and is vital to life. One of the essential nutrients found in blood is oxygen.
The right side of the heart receives blood lacking oxygen from the body. After passing through the right atrium and right ventricle this blood is pumped to the lungs. Here blood picks up oxygen and loses another gas called carbon dioxide. Once through the lungs, the blood flows back to the left atrium. It then passes into the left ventricle and is pumped into the main artery supplying the body. Oxygenated blood is then carried though blood vessels to all the body’s tissues. Here oxygen and other nutrients pass into the cells where they are used to perform the body’s essential functions.
A blood vessel’s main function is to transport blood around the body. Blood vessels also play a role in controlling your blood pressure.
Blood vessels are found throughout the body. There are five main types of blood vessels: arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules and veins.
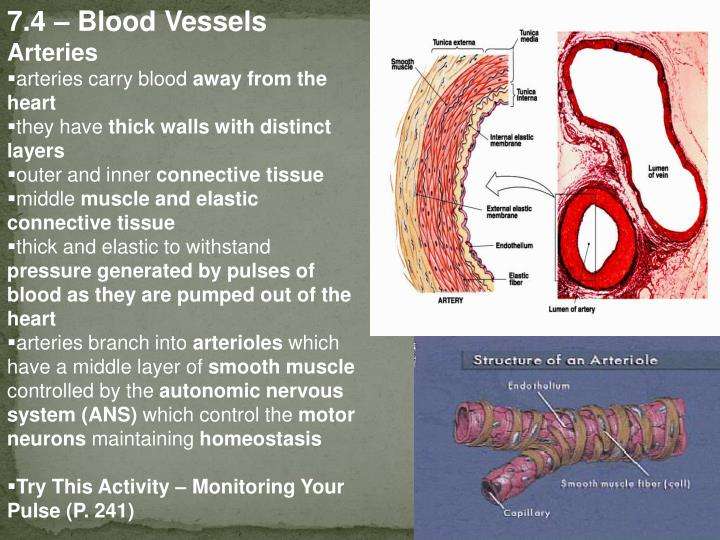
Arteries carry blood away from the heart to other organs. They can vary in size. The largest arteries have special elastic fibres in their walls. This helps to complement the work of the heart, by squeezing blood along when heart muscle relaxes. Arteries also respond to signals from our nervous system, either tightening or relaxing .
What Are The Blood Vessels Made Of
Blood vessels have three layers of tissue:
- Tunica intima: The inner layer surrounds the blood as it flows through your body. It regulates blood pressure, prevents blood clots and keeps toxins out of your blood. It keeps your blood flowing smoothly.
- Media: The middle layer contains elastic fibers that keep your blood flowing in one direction. The media also helps vessels expand and contract.
- Adventitia: The outer layer contains nerves and tiny vessels. It delivers oxygen and nutrients from your blood to your cells and helps remove waste. It also gives blood vessels their structure and support.
Recommended Reading: Why Is Resting Heart Rate Important
What Are The Parts Of The Heart
The heart has four chambers two on top and two on bottom:
- The two bottom chambers are the right ventricle and the left ventricle. These pump blood out of the heart. A wall called the interventricular septum is between the two ventricles.
- The two top chambers are the right atrium and the left atrium. They receive the blood entering the heart. A wall called the interatrial septum is between the atria.
The atria are separated from the ventricles by the atrioventricular valves:
- The tricuspid valve separates the right atrium from the right ventricle.
- The mitral valve separates the left atrium from the left ventricle.
Two valves also separate the ventricles from the large blood vessels that carry blood leaving the heart:
- The pulmonic valve is between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery, which carries blood to the lungs.
- The aortic valve is between the left ventricle and the aorta, which carries blood to the body.
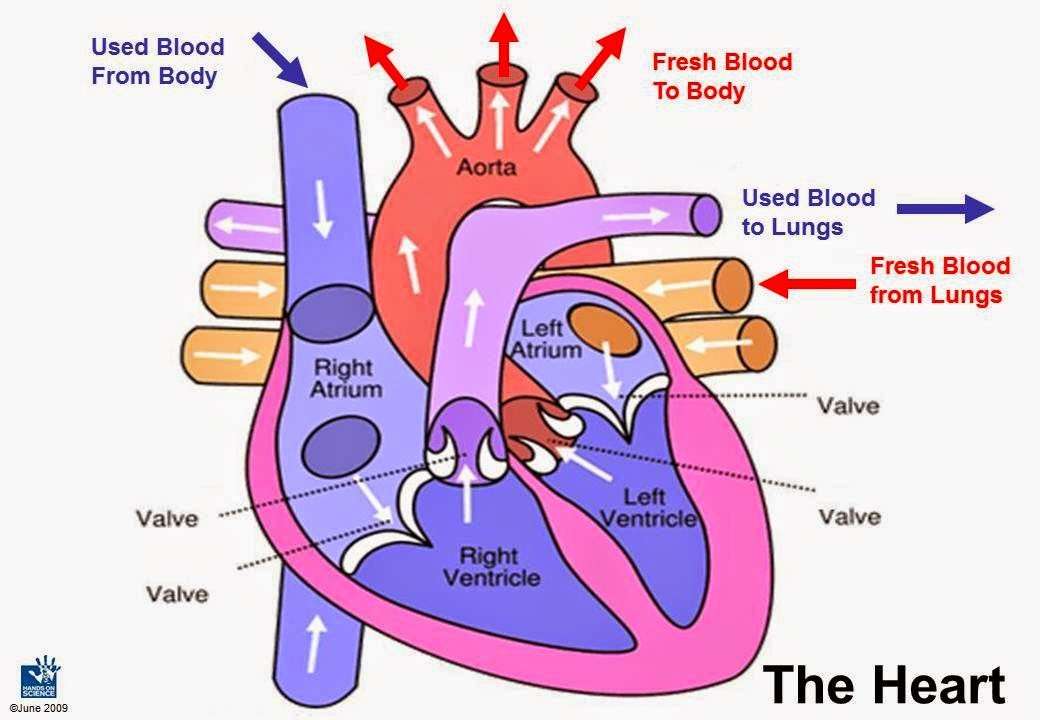
How Does Blood Flow Through The Heart
The right and left sides of the heart work together. The pattern described below is repeated over and over, causing blood to flow continuously to the heart, lungs, and body.
Right side of the heart
- Blood enters the heart through two large veins, the inferior and superior vena cava, emptying oxygen-poor blood from the body into the right atrium.
- As the atrium contracts, blood flows from your right atrium into your right ventricle through the open tricuspid valve.
- When the ventricle is full, the tricuspid valve shuts. This prevents blood from flowing backward into the right atrium while the ventricle contracts.
- As the ventricle contracts, blood leaves the heart through the pulmonic valve, into the pulmonary artery and to the lungs, where it is oxygenated. The oxygenated blood then returns to the heart through the pulmonary veins.
Left side of the heart
- The pulmonary veins empty oxygen-rich blood from the lungs into the left atrium.
- As the atrium contracts, blood flows from your left atrium into your left ventricle through the open mitral valve.
- When the ventricle is full, the mitral valve shuts. This prevents blood from flowing backward into the atrium while the ventricle contracts.
- As the ventricle contracts, blood leaves the heart through the aortic valve, into the aorta and to the body.
Read Also: What Are The Signs Of Heart Failure
The Three Major Types Of Blood Vessels: Arteries Veins And Capillaries
Blood vessels flow blood throughout the body. Arteries transport blood away from the heart. Veins return blood back toward the heart. Capillaries surround body cells and tissues to deliver and absorb oxygen, nutrients, and other substances. The capillaries also connect the branches of arteries and to the branches of veins. The walls of most blood vessels have three distinct layers: the tunica externa, the tunica media, and the tunica intima. These layers surround the lumen, the hollow interior through which blood flows.
How Do The Heart And Blood Vessels Work
The heart works by following a sequence of electrical signals that cause the muscles in the chambers of the heart to contract in a certain order. If these electrical signals change, the heart may not pump as well as it should.
The sequence of each heartbeat is as follows:
- The sinoatrial node in the right atrium is like a tiny in-built ‘timer’. It fires off an electrical impulse at regular intervals. This controls your heart rate. Each impulse spreads across both atria, which causes them to contract. This pumps blood through one-way valves into the ventricles.
- The electrical impulse gets to the atrioventricular node at the lower right atrium. This acts like a ‘junction box’ and the impulse is delayed slightly. Most of the tissue between the atria and ventricles does not conduct the impulse. However, a thin band of conducting fibres called the atrioventricular bundle acts like ‘wires’ and carries the impulse from the AV node to the ventricles.
- The AV bundle splits into two – a right and a left branch. These then split into many tiny fibres which carry the electrical impulse throughout the ventricles. The ventricles contract and pump blood through one-way valves into large arteries:
- The arteries going from the right ventricle take blood to the lungs.
- The arteries going from the left ventricle take blood to the rest of the body.
Don’t Miss: How Is A Heart Attack Treated
Vasculature Of The Head
Blood is carried from your heart to the rest of your body through a complex network of arteries, arterioles, and capillaries. Blood is returned to your heart through venules and veins.
The one-way vascular system carries blood to all parts of your body. This process of blood flow within your body is called circulation. Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood away from your heart, and veins carry oxygen-poor blood back to your heart.
In pulmonary circulation, though, the roles are switched. It is the pulmonary artery that brings oxygen-poor blood into your lungs and the pulmonary vein that brings oxygen-rich blood back to your heart.
In the diagrams, the vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood are colored red, and the vessels that carry oxygen-poor blood are colored blue.
Difference Between Blood Vessels And Veins
There are multiple functions going on in our bodies simultaneously. For smooth functioning and better coordination between organs, each work inside the body is differentiated so that the whole body works flawlessly.
One of the main functions of our body is the transportation of blood to and from the heart. There are two types of blood vessels; arteries and veins in the circulatory system involved in carrying blood to the heart and away from the heart.
Arteries and veins, though they belong to the circulatory system, differs in their functionality and speciality. In this article, we will be looking at what exactly arteries and veins are and what are their significant differences.
Recommended Reading: Is Your Pulse And Heart Rate The Same Thing
Introduction To The Major Blood Vessels Of The Heart:
The major blood vessels of the heart are the larger arteres and veins that attach to the atria and ventricles and transport blood to and from the
Blood is delivered to the right atrium from the systemic circulatory system by two veins:
- The superior vena cava transports oxygen-depleted blood from the upper extremities, head, and neck.
Learning about the cardiovascular system? You may like this cardiovascular system revision guide complete with diagrams, quizzes and free worksheets.
Veins Carry Blood Back Toward The Heart
After the capillaries release oxygen and other substances from blood into body tissues, they feed the blood back toward the veins. First the blood enters microscopic vein branches called venules. The venules conduct the blood into the veins, which transport it back to the heart through the venae cavae. Vein walls are thinner and less elastic than artery walls. The pressure pushing blood through them is not as great. In fact, there are valves within the lumen of veins to prevent the backflow of blood.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does End Stage Heart Failure Last
Biology Of The Blood Vessels
, MD, Michigan Medicine at the University of Michigan
The heart and blood vessels constitute the cardiovascular system. The blood circulating in this system delivers oxygen and nutrients to the tissues of the body and removes waste products from the tissues.
The blood vessels consist of
-
Arteries
All blood is carried in these vessels.
There Are Three Main Types Of Blood Vessels
Arteries
The arteries carry oxygen and nutrients away from your heart, to your body’s tissues.The veins take oxygen-poor blood back to the heart.
- Arteries begin with the aorta, the large artery leaving the heart.
- They carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to all of the body’s tissues.
- They branch several times, becoming smaller and smaller as they carry blood further from the heart.
Capillaries
- Capillaries are small, thin blood vessels that connect the arteries and the veins.
- Their thin walls allow oxygen, nutrients, carbon dioxide and waste products to pass to and from the tissue cells.
Veins
- These are blood vessels that take oxygen-poor blood back to the heart.
- Veins become larger and larger as they get closer to the heart.
- The superior vena cava is the large vein that brings blood from the head and arms to the heart, and the inferior vena cava brings blood from the abdomen and legs into the heart.
This vast system of blood vessels – arteries, veins, and capillaries – is over 60,000 miles long. That’s long enough to go around the world more than twice!
Blood flows continuously through your body’s blood vessels. Your heart is the pump that makes it all possible.
You May Like: What Causes Low Blood Pressure And High Heart Rate
How Does Blood Flow Through Your Body
- Veins bring blood to the right side of your heart.
- Pulmonary arteries carry the blood to your lungs, where it receives oxygen.
- Pulmonary veins move the blood oxygen-rich blood to the left side of your heart.
- The aorta carries the blood from the left side of your heart to the rest of your body through many branches of arteries.
- Capillaries have thin walls that allow oxygen, nutrients, carbon dioxide and waste products to pass through, to and from the tissue cells.
- Veins then carry the blood back to your heart, and the process begins again.
How Does The Blood Circulatory System Work
The blood circulatory system delivers nutrients and oxygen to all cells in the body. It consists of the heart and the blood vessels running through the entire body. The arteries carry blood away from the heart; the veins carry it back to the heart. The system of blood vessels resembles a tree: The trunk the main artery branches into large arteries, which lead to smaller and smaller vessels. The smallest arteries end in a network of tiny vessels known as the capillary network.
There isn’t only one blood circulatory system in the human body, but two, which are connected: The systemic circulation provides organs, tissues and cells with blood so that they get oxygen and other vital substances. The pulmonary circulation is where the fresh oxygen we breathe in enters the blood. At the same time, carbon dioxide is released from the blood.
Blood circulation starts when the heart relaxes between two heartbeats: The blood flows from both atria into the ventricles , which then expand. The following phase is called the ejection period, which is when both ventricles pump the blood into the large arteries.
Read Also: Who Invented Open Heart Surgery
Outside View Of The Back Of The Heart
Coronary veins -take oxygen-poor blood that has already been “used” by muscles of the heart and returns it to the right atrium.
Circumflex artery – supplies blood to the left atrium and the side and back of the left ventricle.
Left coronary artery – divides into two branches .
Left anterior descending artery – supplies blood to the front and bottom of the left ventricle and the front of the septum.
Pulmonary veins -bring oxygen-rich blood back to the heart from the lungs.
Right coronary artery – supplies blood to the right atrium, right ventricle, bottom portion of the left ventricle and back of the septum.
What Are Blood Vessels
Blood vessels are channels that carry blood throughout your body. They form a closed loop, like a circuit, that begins and ends at your heart. Together, the heart vessels and blood vessels form your circulatory system. Your body contains about 60,000 miles of blood vessels.
There are three types of blood vessels:
- Arteries carry blood away from your heart.
- Veins carry blood back toward your heart.
- Capillaries, the smallest blood vessels, connect arteries and veins.
Also Check: Is 190 Heart Rate Bad
What Causes Vascular Disease
Causes of vascular disease include:
-
Atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is the most common cause of vascular disease.;It is unknown exactly how atherosclerosis starts or what causes it. Atherosclerosis is a slow, progressive, vascular disease that may start as early as childhood. However, the disease has the potential to progress rapidly. It is generally characterized by the buildup of fatty deposits along the innermost layer of the arteries. If the disease process progresses, plaque may form. This thickening narrows the arteries and can decrease blood flow or completely block the flow of blood to organs and other body tissues and structures.
-
Blood clots. A blood vessel may be blocked by an embolus or a thrombus .
-
Inflammation. In general, inflammation of blood vessels is referred to as vasculitis, which includes a range of disorders. Inflammation may lead to narrowing and blockage of blood vessels.
-
Trauma or injury. Trauma or injury involving the blood vessels may lead to inflammation or infection, which can damage the blood vessels and lead to narrowing and blockage.
-
Genetic. Certain conditions of the vascular system are inherited.
The Constant Pumping Of The Heart Maintains Blood Pressure And Supply Throughout The Body
The blood moving through the circulatory system puts pressure on the walls of the blood vessels. Blood pressure results from the blood flow force generated by the pumping heart and the resistance of the blood vessel walls. When the heart contracts, it pumps blood out through the arteries. The blood pushes against the vessel walls and flows faster under this high pressure. When the ventricles relax, the vessel walls push back against the decreased force. Blood flow slows down under this low pressure.
Also Check: Can This 10 Second Trick Prevent Your Heart Attack
What Are The Two Main Blood Vessels That Carry Blood To The Heart
aortaarteriesarteries
The arteries carry oxygen and nutrients away from your heart, to your body’s tissues. The veins take oxygen-poor blood back to the heart. Arteries begin with the aorta, the large artery leaving the heart. They carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to all of the body’s tissues.
Furthermore, which two vessels carry blood at the highest pressure? Blood Vessels and Blood PressureBlood pressure is highest in arteries and lowest in veins.
Herein, what are the major blood vessels of the heart?
Key Points
- Five great vessels enter and leave the heart: the superior and inferior vena cava, the pulmonary artery, the pulmonary vein, and the aorta.
- The superior vena cava and inferior vena cava are veins that return deoxygenated blood from circulation in the body and empty it into the right atrium.
Which blood vessels carry blood back to the heart quizlet?
Systemic arteries carry oxygenated blood from the left ventricle of the heart to the rest of the body, while systemic veins return deoxygenated blood back to the heart via the right atrium.
