How Does Heart Failure Affect Quality Of Life And Lifestyle
With the right care and treatment plan, heart failure may limit your activities, but many adults still enjoy life. How well you feel depends on how well your heart muscle is working, your symptoms and how well you respond to and follow your treatment plan. This includes caring for yourself and living a healthy lifestyle .
Because heart failure is a chronic long-term illness, talk to your doctor and your family about your preferences for medical care. You can complete an advance directive or living will to let everyone involved in your care know your desires. A living will details the treatments you do or dont want to prolong your life. It is a good idea to prepare a living will while you are well in case you arent able to make these decisions at a later time.
Reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional.
References
Types Of Heart Failure
Systolic heart failure happens when your heart muscle doesn’t squeeze with enough force. When that’s the case, it pumps less oxygen-rich blood through your body.
With diastolic heart failure, your heart squeezes normally, but the ventricle — the main pumping chamber — doesn’t relax properly. Less blood can enter your heart, and the blood pressure in your lungs goes up. When that happens, you get fluid in your lungs, legs, and belly.
What Are The Main Causes Of Heart Failure
Heart failure can have many causes. The most common causes are:
- Coronary heart disease this is where the arteries that supply blood to the heart become clogged up with fatty substances called atherosclerosis which may cause symptoms of chest discomfort called angina or heart damage from a heart attack.
- Hypertension high blood pressure can put extra strain on the heart, which over time can lead to heart failure.
- Cardiomyopathy conditions affecting the heart muscle and can be hereditary or acquired condition that causes the changes in the heart muscle tissue leading to failure of function.
- Arrhythmias heart rhythm problems such as atrial fibrillation which impairs the contraction strength of the heart by the persistent fast heart rate is one of the many rhythm disturbances causing the heart to pump less efficiently.
- Heart valve disease valve defects and damage will increase volume and strain on the heart and weaken it.
- Congenital heart disease birth defects that affect the normal workings of the heart.
- Metabolic hyperthyroid with overactive thyroid and diabetes are endocrine causes of heart failure.
- Toxicity alcohol and certain chemotherapy drugs can be toxic to the muscle cells and damage their function.
You May Like: Does Lack Of Sleep Increased Heart Rate
What Do The Numbers Mean
Ejection Fraction 55% to 70%
- Pumping Ability of the Heart: Normal.
- Level of Heart Failure/Effect on Pumping: Heart function may be normal or you may have heart failure with preserved EF .
Ejection Fraction 40% to 54%
- Pumping Ability of the Heart: Slightly below normal.
- Level of Heart Failure/Effect on Pumping: Less blood is available so less blood is ejected from the ventricles. There is a lower-than-normal amount of oxygen-rich blood available to the rest of the body. You may not have symptoms.
Ejection Fraction 35% to 39%
- Pumping Ability of the Heart: Moderately below normal.
- Level of Heart Failure/Effect on Pumping: Mild heart failure with reduced EF .
Ejection Fraction Less than 35%
- Pumping Ability of the Heart: Severely below normal.
- Level of Heart Failure/Effect on Pumping: Moderate-to-severe HF-rEF. Severe HF-rEF increases risk of life-threatening heartbeats and cardiac dyssynchrony/desynchronization .
Normal Heart. A normal left ventricular ejection fraction ranges from 55% to 70%. An LVEF of 65%, for example means that 65% of total amount of blood in the left ventricle is pumped out with each heartbeat. Your EF can go up and down, based on your heart condition and how well your treatment works.
HF-pEF. If you have HF-pEF, your EF is in the normal range because your left ventricle is still pumping properly. Your doctor will measure your EF and may check your heart valves and muscle stiffness to see how severe your heart failure is.
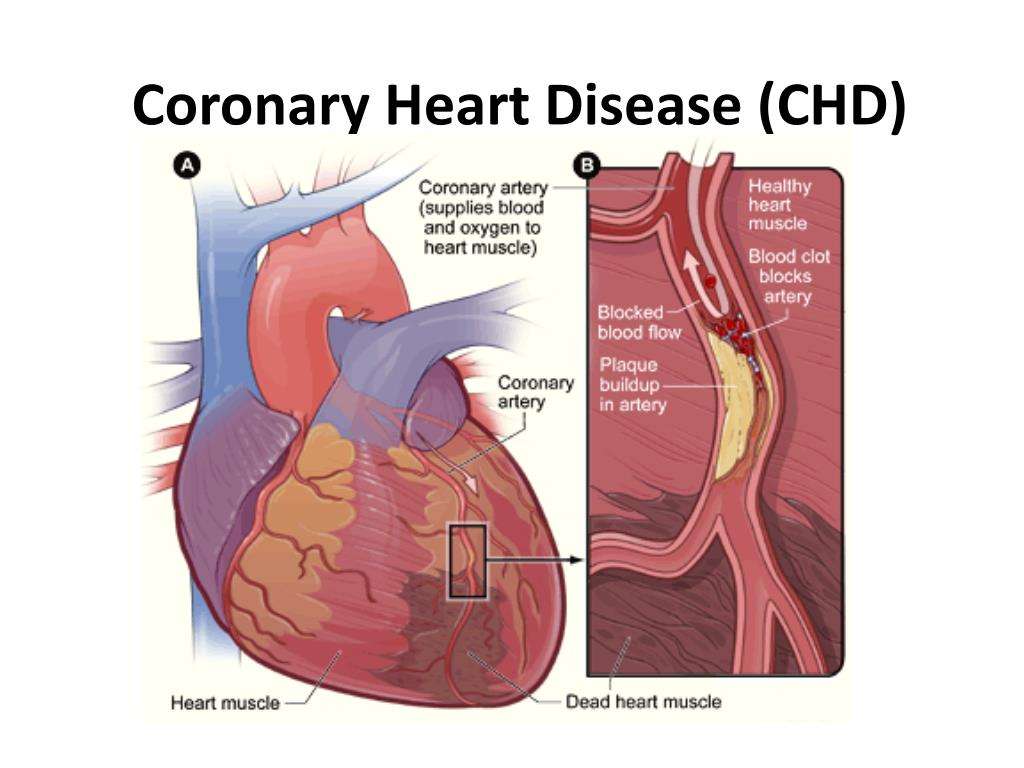
What Is Coronary Artery Disease
Most heart attacks are caused by coronary artery disease . This is when a gradual build-up of fatty streaks form in the coronary arteries. These are the arteries that deliver oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. The build-up of fatty streaks makes the coronary arteries narrow and stiffen over time.
As the coronary arteries narrow, it becomes more difficult for oxygenated blood to reach the heart muscle, sometimes causing pain and discomfort known as angina.
If a piece of plaque cracks, it may cause a blood clot to form and block a coronary artery, cutting off the blood supply to a part of the heart muscle. This causes a heart attack.
The heart attack symptoms you feel during a heart attack are caused by your heart muscle being starved of oxygen. This prevents your heart from beating as normal.
Also Check: Where Does Oxygenated Blood Enter The Heart
Symptoms Of Severe Heart Failure
When heart failure is advanced, Cheyne-Stokes respiration may develop. In this unusual pattern of breathing, a person has a period of not breathing for a few seconds, and then begins to breathe progressively faster and deeper, then slower and shallower until they again briefly stop breathing and repeat the cycle over and over. Cheyne-Stokes respiration develops because blood flow to the brain is reduced and the areas of the brain that control breathing therefore do not receive enough oxygen. Cheyne-Stokes respiration is considered a form of central sleep apnea.
Obstructive sleep apnea is a different and more common breathing disorder that can occur in people with heart failure. Severe obstructive sleep apnea can make heart failure worse.
Acute pulmonary edema is a sudden accumulation of a large amount of fluid in the lungs. It causes extreme difficulty breathing, rapid breathing, bluish skin, and feelings of restlessness, anxiety, and suffocation. Some people have severe spasms of the airways and wheezing. Acute pulmonary edema is a life-threatening emergency that can occur when people with heart failure develop very high blood pressure, have a heart attack, or sometimes just stop taking their heart failure drugs or eat salty food.
Depression and decline in mental function are common in people with severe heart failure, particularly the elderly, and require careful evaluation and treatment.
What Diet And Lifestyle Management Techniques Help Heart Failure
Many lifestyle and diet factors can improve, or even reverse, congestive heart failure. Cardiac rehabilitation programs can teach people how to make lifestyle changes, as can integrative cardiology clinics. Some of the lifestyle factors that make a difference include:
- Manage stress by doing mind-body practices such as Tai Chi, yoga, Qi Gong, and meditation
- Take dietary supplements including CoQ10, L-carnitine, Crataegus , magnesium, and fish oil
- Avoiding salt and excess fluids
Talk to your doctor before taking any herbs or supplements.
Recommended Reading: What Causes Left Sided Heart Failure
What Are The Complications Of Heart Failure
Untreated heart failure can eventually lead to congestive heart failure , a condition in which blood builds up in other areas of your body. In this potentially life threatening condition, you may experience fluid retention in your limbs as well as in your organs, such as the liver and lungs.
Additional complications of heart failure can include:
- stroke
- arrhythmias, like atrial fibrillation
When To Call The Doctor
- You are tired or weak.
- You feel short of breath when you are active or when you are at rest.
- You feel short of breath when you lie down, or an hour or two after falling asleep.
- You are wheezing and having trouble breathing.
- You have a cough that does not go away. It may be dry and hacking, or it may sound wet and bring up pink, foamy spit.
- You have swelling in your feet, ankles, or legs.
- You have to urinate a lot, particularly at night.
- You have gained or lost weight.
- You have pain and tenderness in your belly.
- You have symptoms that you think might be from your medicines.
- Your pulse, or heartbeat, gets very slow or very fast, or it is not steady.
You May Like: Does Tylenol Increase Heart Rate
What Happens After A Heart Failure Diagnosis
Your hospital stay, where your cardiologist told you that your heart was failing, has come to an end. Youre ready to – finally – return home with a handful of prescriptions, for drugs and for several lifestyle changes sanctioned by the doctor. Instead, the cardiologist strongly recommends a pitstop at a skilled nursing facility, ensuring you that after a certain amount of time – days, weeks, months – youll be ready to go home.
But is the pitstop truly necessary? Even more important, is a stay at a skilled nursing facility negatively affecting the health of heart failure patients? These are the questions experts from Mayo Clinic set out to answer definitively, hoping to understand the complete experience of heart failure patients traveling between the hospital, nursing facilities, and home.
“This required linked data from across the community and across the lives of these patients, explained first author of their study published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings, Sheila Manemann.
1,498 patients diagnosed with heart failure and living in Minnesota became the subjects of the Mayo Clinic study. Researchers took into account several risk factors and preexisting conditions that could potentially confound the results, and then they began to learn the truth about the effects on patients who spend time in a skilled nursing facility after being in the hospital, instead of returning to their homes.
What Are The Types Of Heart Failure
There are many causes of heart failure, but the condition is generally broken down into two types:
Heart failure with reduced left ventricular function The lower left chamber of the heart gets bigger and cannot squeeze hard enough to pump the right amount of oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body.
Heart failure with preserved left ventricular function The heart contracts and pumps normally, but the bottom chambers of the heart are thicker and stiffer than normal. Because of this, the ventricles can’t relax properly and fill up all the way. Because there’s less blood in the ventricles, less blood is pumped out to the rest of the body when the heart contracts.
You May Like: Does Tylenol Raise Your Blood Pressure
Other Causes Of Heart Failure
Pulmonary hypertension and heart failure
Heart failure can be caused by pulmonary hypertension . This condition can damage the right side of your heart, leading to heart failure. In some cases, the pulmonary hypertension itself is caused by an existing heart condition.
- Find out more about pulmonary hypertension on NHS Choices and PHA UK.
Amyloidosis
Amyloidosis happens when abnormal proteins, called amyloid, build up in organs and tissues. This affects how your organs work. If amyloidosis affects the heart it’s called cardiac amyloidosis or stiff heart syndrome and can lead to heart failure.
- Read more about amyloidosis treatment.
How Is Heart Failure Treated/managed
Treatment of heart failure depends on the underlying cause and this will direct the main treatment to prevent further deterioration. Heart failure can be cured if it has a treatable cause.
If the causes are due to coronary heart disease then the patient may require coronary stents or . If there is a heart valve cause, then the defective valve will need surgery to repair or replace the valve.
All heart failure patients will need:
- Lifestyle changes including eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly and stopping smoking and watching fluid intake and reduce alcohol consumption.
- Medicine a range of medicines can help many people need to take three to four different types which have evidence to show they strengthen the heart and improve prognosis. This includes beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, ARNI and SGLT2 inhibitors. Other medicines, such as diuretics, may be used to help with the symptoms.
In cases where patients are seen to be experiencing continued deteriorating heart function despite the best and optimal medication, the following may be considered:
- Cardiac resynchronising therapy In very severe heart failure conditions, a specialised type of pacemaker has shown to benefit and improve symptoms as well as prolonging life by resynchronising the contractility of the two main pumping chambers of the heart.
- Cardiac transplant If there is no scope for recovery and the condition deteriorates then in suitable patients, a heart transplant may be considered.
Also Check: What Are The Early Signs Of Congestive Heart Failure
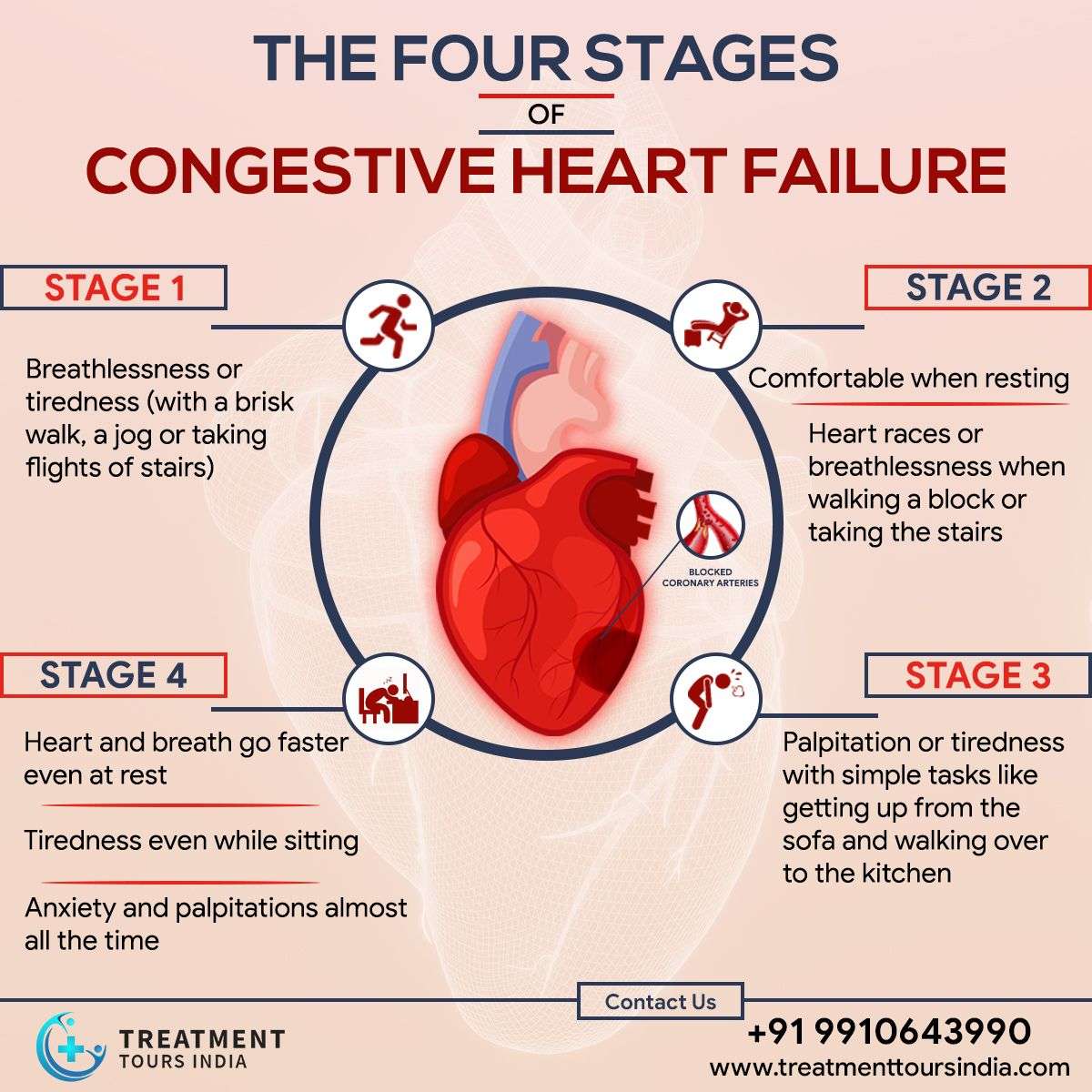
What Are The 4 Stages Of Heart Failure
There are four stages of heart failure – stage A, B, C and D – which range from high risk of developing heart failure to advanced heart failure.
The four stages of heart failure are different to the four classes of heart failure symptoms also described in New York Heart Association , which illustrates the severity of symptoms, ranging from class one to the most severe, which is class four .
Congestive Heart Failure: Prevention Treatment And Research
Congestive heart failure is a serious condition in which the heart doesnt pump blood as efficiently as it should. Despite its name, heart failure doesnt mean that the heart has literally failed or is about to stop working. Rather, it means that the heart muscle has become less able to contract over time or has a mechanical problem that limits its ability to fill with blood. As a result, it cant keep up with the bodys demand, and blood returns to the heart faster than it can be pumped outit becomes congested, or backed up. This pumping problem means that not enough oxygen-rich blood can get to the bodys other organs.
The body tries to compensate in different ways. The heart beats faster to take less time for refilling after it contractsbut over the long run, less blood circulates, and the extra effort can cause heart palpitations. The heart also enlarges a bit to make room for the blood. The lungs fill with fluid, causing shortness of breath. The kidneys, when they dont receive enough blood, begin to retain water and sodium, which can lead to kidney failure. With or without treatment, heart failure is often and typically progressive, meaning it gradually gets worse.
More than 5 million people in the United States have congestive heart failure. Its the most common diagnosis in hospitalized patients over age 65. One in nine deaths has heart failure as a contributing cause.
Also Check: How Does Heart Rate Affect Blood Pressure
When To Get Medical Advice
See a GP if you experience persistent or gradually worsening symptoms of heart failure.
Call 999 for an ambulance or go to your nearest A& E department as soon as possible if you have sudden or very severe symptoms.
A number of tests can be used to help check how well your heart is working, including blood tests, an ECG and an echocardiogram.
Clinicians Show Gender Racial Biases In Treatment Decisions For Heart Failure Patients
The Black community as a whole has a higher rate of heart disease, as well as a higher rate of many of the main risk factors for heart disease and heart failure, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and obesity. While there is no one-size-fits all explanation for this increased risk, researchers believe a combination of socioeconomic factors, environment, education, stress levels, and culture are all at play, according to UT Southwestern Medical Center.
Researchers suggest Hispanic Americans are at a greater risk of heart failure, as well. A study published in 2016 in the American Heart Associations journal Circulation: Heart Failure found that about one-half of the middle-aged Hispanic adults studied had heart problems that could lead to heart failure. However, fewer than 1 in 20 participants knew they had a health issue. The researchers found these individuals also had higher rates of obesity, high blood pressure, and diabetes.
Don’t Miss: Flonase Chest Pain
Articles On Heart Failure Types & Stages
The name of this condition can be a little confusing. When you have heart failure, it doesn’t mean your ticker stopped beating. What’s really going on is that your heart can’t pump blood as well as a healthy one.
The chambers of your heart may respond by stretching to carry more blood to pump through your body. They may become stiffer and thicker. This helps keep blood moving for a while, but in time, your heart muscle walls may get weaker.
Your kidneys react by causing your body to hold on to water and salt. Fluid may start to build up in your arms, legs, ankles, feet, lungs, or other organs.
The American Heart Association and American College of Cardiology have defined four stages of heart failure to help people understand how the condition changes over time and the kinds of treatments that are used for each.
Prevention Of Congestive Heart Failure
The best way to prevent heart failure is to control your risk factors. The good news is you can reduce or eliminate many of the risk factors that lead to heart disease, such as high blood pressure. Lifestyle changes and adhering to any medication your doctor prescribes can go a long way in preventing heart failure.
These lifestyle changes include:
Also Check: What Causes Low Blood Pressure And High Heart Rate
Tips For Managing Congestive Heart Failure End
You may be asking, How can I provide comfort to my loved one as they experience the end-of-life signs of congestive heart failure? Its only natural that you as a loved one and/or caregiver will want to be as helpful as possible, and ensure that your loved one is experiencing as little pain as possible. Heres some ways you can help:
- Communicate with the doctors and healthcare professionals: Your loved one may be too weak, or simply forget, to communicate their symptoms to the doctors and nurses. You can help by sharing this information with them in order to make sure your loved one gets what they need.
- Provide comfort: Sometimes it is just as simple as spending time with your loved one while watching a TV show, or talking about things they love. These conversations can help in alleviating some of their depression and anxiety.
- Help them remember to take their medicine: There will likely be various pills and medications that your loved one needs to take. You can help by assisting your loved one in staying on schedule.
