Stage B Treatment Options
While stage A CHF is managed with lifestyle changes, the treatment plan for stage B typically includes taking medications regularly. People at this stage should still make the same lifestyle changes as those appropriate for stage A. However, your doctor may also prescribe additional treatments such as:
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers, if you arent taking any as part of your stage A treatment plan
- Beta blockers if youve had a heart attack and your EF is 40% or lower, if you arent taking any as part of your stage A treatment plan
- Possible surgery or intervention as a treatment for coronary artery blockage, heart attack, valve disease, or congenital heart disease
Quality Of Patient Care
Brigham and Womens Hospital is committed to providing all of our patients with the safest, highest-quality, most-satisfying care possible and follow established protocols that have been shown to improve patient outcomes. Our inpatient satisfaction survey, sent to patients to assess their total care experience, helps us to monitor what we are doing well and areas for improvement. We pride ourselves in the quality of patient care we provide and how we are measured compared with other hospitals.
How Is Heart Failure Treated
Your treatment will depend on the type of heart failure you have and, in part, what caused it. Medications and lifestyle behaviors are part of every treatment plan. Your healthcare provider will talk to you about the best treatment plan for you. Treatment is the same, regardless of gender.
As heart failure gets worse, your heart muscle pumps less blood to your organs, and you move toward the next stage of heart failure. Since you cant move backward through the heart failure stages, the goal of treatment is to keep you from moving forward through the stages or to slow down the progression of your heart failure.
Stage A treatment
The usual treatment plan for people with Stage A heart failure includes:
- Regular exercise, being active, walking every day.
- Stopping the use of tobacco products.
- Treatment for high blood pressure .
- Treatment for high cholesterol.
- Not drinking alcohol or using recreational drugs.
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or an angiotensin II receptor blocker if you have coronary artery disease, diabetes, high blood pressure, or other vascular or cardiac conditions.
- Beta-blocker if you have high blood pressure.
Stage B treatment
The usual treatment plan for people with Stage B heart failure includes:
Stage C treatment
The usual treatment plan for people with Stage C HF-rEF includes:
If the treatment causes your symptoms to get better or stop, you still need to continue treatment to slow the progression to Stage D.
Stage D treatment
Don’t Miss: How To Bring Down Heart Rate
Signs Of Heart Failure
Signs associated with heart failure depend on the causes of the heart failure and the heart chamber that is affected. With left-sided congestive heart failure, signs are associated with a backup of pressure in the vessels delivering blood to the left ventricle. This causes fluid to accumulate within the lungs . Coughing, difficulty breathing, and exercise intolerance are the most common signs. Many dogs with left-sided congestive heart failure faint due to lack of blood flow and oxygen to the brain. They may also have a low heart rate and low blood pressure and may collapse. Dogs with left-side congestive heart failure often breathe faster than healthy dogs. Your veterinarian may direct you to count the number of breaths your dog takes within a minute when it is sleeping or resting. This sleeping respiratory rate can then be regularly monitored to identify early heart failure and assess whether your dog is responding to treatment.
Right-sided congestive heart failure results in increased pressure in the vessels delivering blood to the right atrium and the bodys veins and capillaries. This may cause fluid to build up in the abdomen , the chest cavity, liver, and the limbs.
Congestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology

Definition: According to Mayo Clinic Heart failure, sometimes known as congestive heart failure, occurs when your heart muscle doesnât pump blood as well as it should. Certain conditions, such as narrowed arteries in your heart or high blood pressure, gradually leave your heart too weak or stiff to fill and pump efficiently. Not all conditions that lead to heart failure can be reversed, but treatments can improve the signs and symptoms of heart failure and help you live longer. Lifestyle changes such as exercising, reducing salt in your diet, managing stress and losing weight can improve your quality of life. One way to prevent heart failure is to control conditions that cause heart failure, such as coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, diabetes or obesity.
Manifestations : Shortness of breath when you exert yourself or when you lie down Fatigue and weakness Swelling in your legs, ankles and feet Rapid or irregular heartbeat Reduced ability to exercise Persistent cough or wheezing with white or pink blood-tinged phlegm Increased need to urinate at night Swelling of your abdomen Sudden weight gain from fluid retention Lack of appetite and nausea Difficulty concentrating or decreased alertness Sudden, severe shortness of breath and coughing up pink, foamy mucus Chest pain if your heart failure is caused by a heart attack
Also Check: What Is Ideal Resting Heart Rate
Diagnostic Tests And Procedures
This animation discusses some of the tests used to diagnose heart failure. These tests may include an electrocardiogram to look at your hearts electrical activity, an echocardiogram to measure how well your heart is working and look at the structure, and a chest X-ray to see if your heart is enlarged or there is fluid in your lungs. Other tests may include blood tests and an exercise, or stress test. .
Respiratory Manifestations Of Chf
A nurse performing a respiratory assessment on an individual with congestive heart failure would expect the presence of pulmonary edema, dyspnea and fatigue, and paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea. When the left ventricle is weak, it causes blood to back flow into the pulmonary veins. Pulmonary edema is when fluid backs up into the lungs, making it difficult for the lungs to perform gas exchange. Mrs. S specified that she has an occasional productive wet cough for pink frothy sputum. When body attempts to removes blood from the respiratory tract and forces the person to cough, this is known as hemoptysis. . Furthermore, the nurse would hear crackles in the patients lungs, indicating the movement of air through fluid. Additionally, as a result of blood preventing adequate gas exchange, Mrs. S. suffers from shortness of breath, followed with fatigue. That being said, the nurse would notice the patient struggling to take full deep breathes. Lastly, Mrs. S has been unable to lie flat in bed and has added three pillows to allow her to sit up higher to sleep. Lewis et al. mentioned paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea is another symptom of CHF It is when an individual cannot breathe, especially at night when lying down for long periods of time. This is due to the pressure put on the chest when lying flat from the blood back up.
Also Check: Frequently, What Is The Earliest Symptom Of Left-sided Heart Failure
Third And Fourth Heart Sounds
A double apical impulse can represent an auscultated third heart sound . Just as with the displaced point of maximal impulse, a third heart sound is not sensitive for heart failure, but it is highly specific .14 Patients with heart failure and left ventricular hypertrophy can also have a fourth heart sound . The physician should be alert for murmurs, which can provide information about the cause of heart disease and also aid in the selection of therapy.
Heart Replacement Therapies: Heart Transplantation Ventricular Assist Devices And Artificial Heart
Heart transplantation
Patients who should be considered for heart transplantation are those with severe symptoms of heart failure with no alternative form of treatment and with a poor prognosis. The introduction of new treatments has probably modified the prognostic significance of the variables traditionally used to identify heart transplant candidates i.e. VO2 max . The patient must be willing and capable to undergo intensive medical treatment, and be emotionally stable so as to withstand the many uncertainties likely to occur both before and after transplantation. The contraindications for heart transplantation are shown in Table .
-
Heart transplantation is an accepted mode of treatment for end stage heart failure. Although controlled trials have never been conducted, it is considered to significantly increase survival, exercise capacity, return to work and quality of life compared with conventional treatment, provided proper selection criteria are applied .
Besides shortage of donor hearts, the main problem of heart transplantation is rejection of the allograft, which is responsible for a considerable percentage of deaths in the first postoperative year. The long-term outcome is limited predominantly by the consequences of immuno-suppression .
Ventricular assist devices and artificial heart
You May Like: What To Eat After Open Heart Surgery
How Long Can An 85 Year Old Live With Heart Failure
In a recent study, it was reported that patients hospitalized with moderate systolic heart failure faced a median expected survival time of 2.4 years if they were aged 71 to 80 years and 1.4 years if they were aged 80 years or more. In patients with more advanced systolic dysfunction, life expectancy was even shorter.
Blood Tests For Heart Disease
- LDL , the so-called “bad” cholesterol
- HDL , the so-called “good” cholesterol
Recommended Reading: Does Diltiazem Lower Heart Rate
Arterial And Venous Blood Gases
Although arterial blood gas measurement is more accurate than pulse oximetry for measuring oxygen saturation, it is unclear if ABG results add any clinical utility to pulse oximetry. In the setting of acute heart failure, ABG measurement is rarely performed. Indications include severe respiratory distress, documented hypoxemia by pulse oximetry not responsive to supplemental oxygen, and evidence of acidosis by serum chemistry findings or elevated lactate levels.
In general, heart failure patients who do not have comorbid lung disease do not manifest hypoxemia except in severe acute decompensation. Patients with severe heart failure may have signs and symptoms ranging from severe hypoxemia, or even hypoxia, along with hypercapnia, to decreased vital capacity and poor ventilation.
Mixed venous oxygen saturation is a good marker of the blood circulation time and thus of the cardiac output and cardiac performance. Patients who have advanced heart failure have low cardiac output and slower circulation time, which translate into an increased oxygen extraction by the tissues and therefore lower oxygen .
How Is Chf Diagnosed
After reporting your symptoms to your doctor, they may refer you to a heart specialist, or cardiologist.
The cardiologist will perform a physical exam, which will involve listening to your heart with a stethoscope to detect abnormal heart rhythms.
To confirm an initial diagnosis, a cardiologist might order certain diagnostic tests to examine your hearts valves, blood vessels, and chambers.
There are a variety of tests used to diagnose heart conditions. Because these tests measure different things, your doctor may recommend a few to get a full picture of your current condition.
Also Check: How Does Your Heart Pump Blood
Physical Exam For Heart Failure
First, your doctor will want to know if you:
- Have other conditions such as diabetes, kidney disease, angina, high blood pressure, or other heart problems
- Drink alcohol, and how much
- Take medications, and which ones
Your doctor will also do a physical exam. They’ll look for signs of heart failure as well as other illnesses that may have weakened your heart.
During your visit, your doctor will:
- Listen to your heart
- Check your blood pressure
Theyâll also look at your appearance while you sit, do mild activity, and lie flat. People with mild or moderate heart failure may appear comfortable at rest, but when active, they often become short of breath. Those with heart failure may be uncomfortable if they lie flat for a few minutes.
Your doctor may check for fluid in your lungs with a stethoscope. People with heart failure may also have neck veins that are larger than normal, swelling of the legs or abdomen, or an enlarged liver.
Congestive Heart Failure: Prevention Treatment And Research
Congestive heart failure is a serious condition in which the heart doesnt pump blood as efficiently as it should. Despite its name, heart failure doesnt mean that the heart has literally failed or is about to stop working. Rather, it means that the heart muscle has become less able to contract over time or has a mechanical problem that limits its ability to fill with blood. As a result, it cant keep up with the bodys demand, and blood returns to the heart faster than it can be pumped outit becomes congested, or backed up. This pumping problem means that not enough oxygen-rich blood can get to the bodys other organs.
The body tries to compensate in different ways. The heart beats faster to take less time for refilling after it contractsbut over the long run, less blood circulates, and the extra effort can cause heart palpitations. The heart also enlarges a bit to make room for the blood. The lungs fill with fluid, causing shortness of breath. The kidneys, when they dont receive enough blood, begin to retain water and sodium, which can lead to kidney failure. With or without treatment, heart failure is often and typically progressive, meaning it gradually gets worse.
More than 5 million people in the United States have congestive heart failure. Its the most common diagnosis in hospitalized patients over age 65. One in nine deaths has heart failure as a contributing cause.
Read Also: How To Raise Resting Heart Rate
Medical History And Physical Exam
If you are experiencing symptoms, your NYU Langone cardiologist gathers information about your medical history. Your doctor also asks about your family history, because your risk for some types of cardiomyopathy increases if family members have had these conditions.
Next, your doctor conducts a physical exam, in which he or she uses a stethoscope to listen to your heart and lungs for sounds that occur when a person has cardiomyopathy and heart failure. He or she also looks for swelling in your legs and abdomen, which may be due to a buildup of fluid.
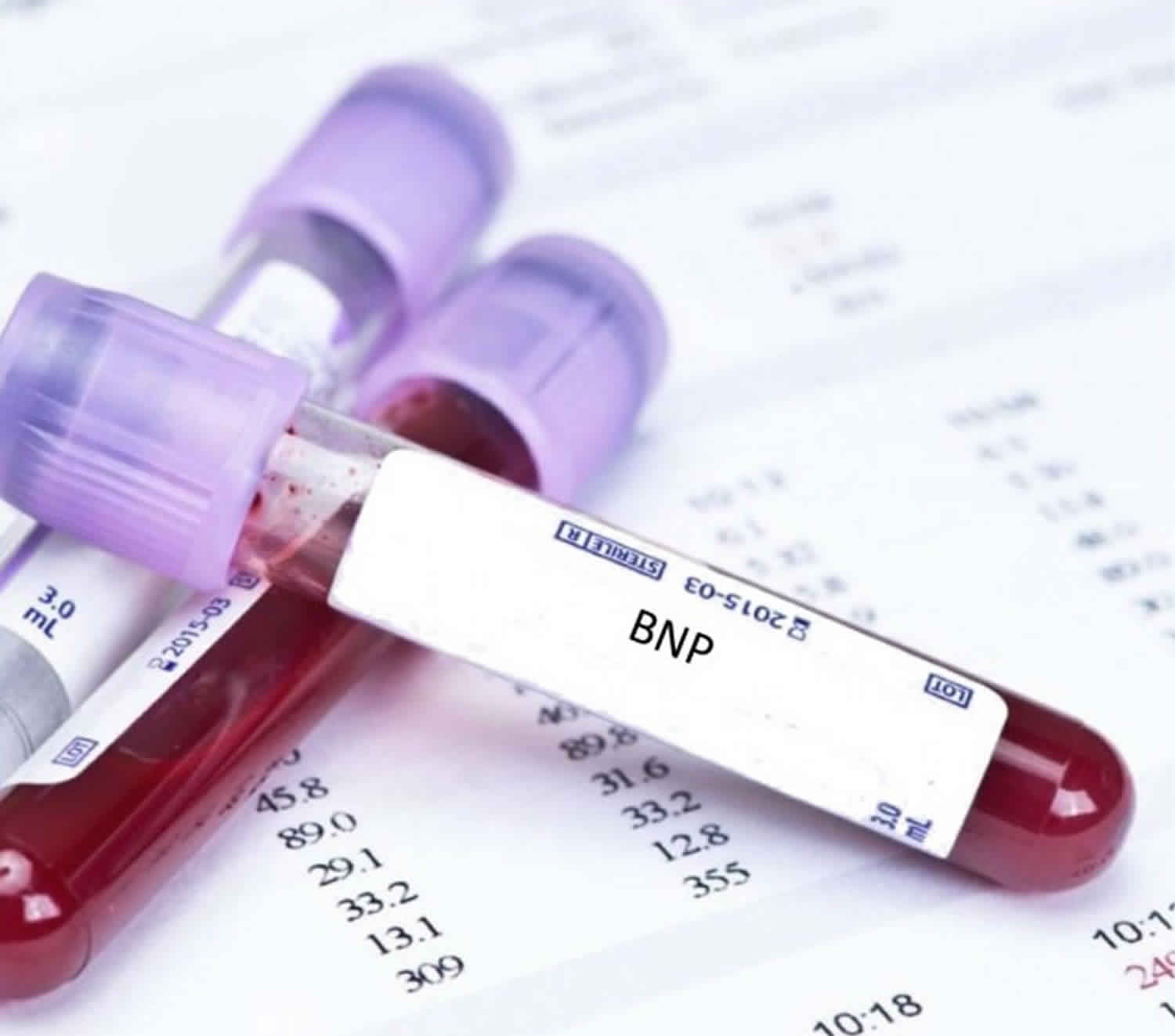
Natriuretic Peptides: Bnp Or Nt
- Plasma concentrations of NPs are recommended as initial diagnostic tests in patients with symptoms suggestive of HF to rule out the diagnosis.
- Elevated concentrations support a diagnosis of HF.
- Other causes of an elevated NP include atrial fibrillation, increasing age, and acute or chronic kidney disease.
- NP concentrations may be low in obesepatients.
- The upper limits of normal in the non-acute setting are 35 pg/mL for BNP, and 125 pg/mL for NT-proBNP.
The CoDE-HF decision support tool may help diagnose heart failure. The CoDE-HF interprets the N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide in various settings including obesity.
| Causes of elevated concentrations of natriuretic peptides |
- BNP or its amino-terminal cleavage equivalent is generated by cardiomyocytes in the context of numerous triggers, most notably myocardial stretch.
- BNP levels may be useful in the initial establishment of the diagnosis of heart failure in the patient with dyspnea of unclear etiology. In a meta-analysis, BNP was superior N-terminal pro-BNP and was associated with a sensitivity of 85% and specificity of 84% in the diagnosis of heart failure in the primary care setting.
- These biomarkers have been studied for the detection of elevated cardiac pressures., low ejection fraction, or both.
- Clinical practice guidelines suggest their measurement is helpful for diagnosis or ruling out heart failure especially in the acute settings.
Don’t Miss: What Should Your Heart Rate Be At Rest
How Does Heart Failure Affect The Quality Of Life And Lifestyle
With the right care and treatment plan, many adults still enjoy life even though heart failure limits their activities. How well you feel depends on:
- How well your heart muscle is working.
- How well you respond to your treatment plan.
- How well you follow your treatment plan.
This includes caring for yourself by:
- Taking your medications.
Expert Care For Patients With Chf
An estimated 8 million people in the U.S. have congestive heart failure , a condition where the heart is unable to pump an adequate amount of blood to the rest of the body. Symptoms include shortness of breath, swelling of the legs, chest tightness and difficulty doing day-to-day tasks.
The Congestive Heart Failure Program at Montefiore Nyack Hospital, which brings you the same world-renowned care provided at Montefiore Einsteins main campus in New York City, specializes in diagnosing heart failure and offers a variety of effective treatments that can improve heart function and help you live longer. Every heart failure patient is differentand your condition can change over timeso routine follow-ups will be an important part of your care plan.
In addition to CHF, the Program treats women with heart disease during pregnancy, as well as patients with heart valve disease, arrhythmias, heart muscle disease, pericardial disease and pulmonary hypertension.
If CHF is suspected, your cardiologist will order a comprehensive study of your heart muscle. This will likely include an echocardiography or other imaging tests to measure your ejection fraction. Your ejection fraction is the percent of blood in the lower left chamber of your heart that is pumped out of your heart with each heartbeat. Ejection fraction measures how well your heart pumps. This helps diagnose the type of heart failure you have and guides your treatment.
You May Like: What Causes Slow Heart Rate
