Usmle Step 2 Style Questions Usmle
A previously healthy one-month-old infant is admitted to the hospital because of respiratory distress. He was born at term following an uncomplicated pregnancy and delivery. He had been well until 2 days ago when he developed fever and malaise. His is 162/min, respirations are 54/min, and is 64/48 mm Hg. Examination shows evidence of . A viral infection is suspected as the etiology of his acute heart failure. Which of the following is the most likely virus?
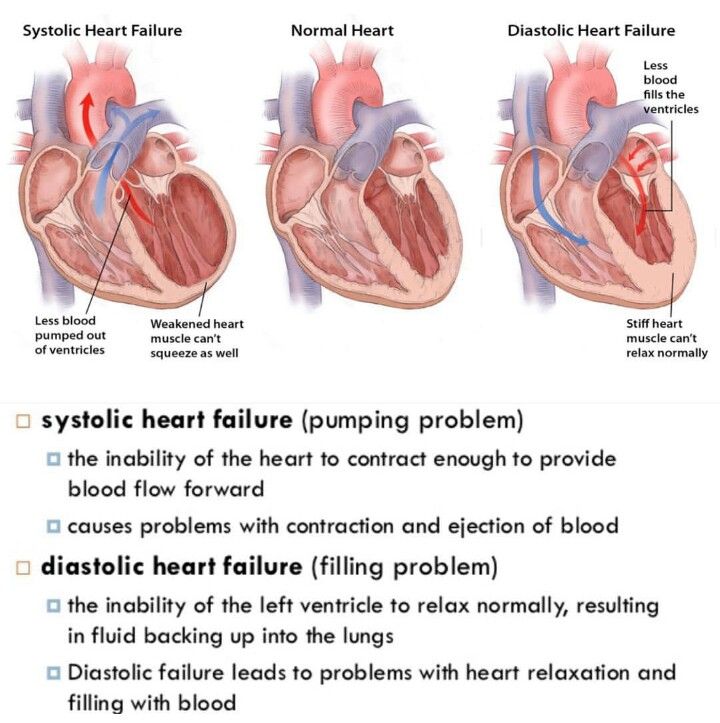
s used to describe a point at which the heart cant supply enough blood to meet the s demands.
This can happen in two ways, either the hearts ventricles cant pump blood hard enough during systole, called , or not enough blood fills into the ventricles during diastole, called .
In both cases, blood backs up into the lungs, causing congestion or fluid buildup, which is why its also often known as , or just CHF.
Congestive heart failure affects millions of people around the world and since it means that the s needs are not being met, it can ultimately lead to death.
Part of the reason why so many people are affected by heart failure, is that there are a wide variety of like and valvular disease that can impair the hearts ability to pump out blood andover timecan ultimately cause the heart to fail.
The heart rate is pretty intuitive, but the stroke volumes a little tricky.
So notice that not all the blood was pumped out right?
And the stroke volume is only a fraction of the total volume.
Cms National Coverage Policy
An ICD is an electronic device designed to diagnose and treat life-threatening ventricular tachyarrhythmias.
Indications and Limitations of Coverage
B. Nationally Covered Indications
Effective for services performed on or after February 15, 2018, CMS has determined that the evidence is sufficient to conclude that the use of ICDs, is reasonable and necessary:
ICD-10-CM codes which describe the above: I46.2, I46.9, I47.20, I47.29, I49.01, I49.02, I49.3, I49.9, Z45.02 or Z86.74.
Treatment For Systolic Heart Failure
If you have systolic heart failure, your doctor will offer treatments to address the underlying causes, relieve your symptoms and improve your overall health. Treatment often involves a combination of therapies that may include:
- Lifestyle changes
- Recognize small warning signs in your body, such as swelling or weight gain.
Recommended Reading: Heart Valve Replacement Surgery Cost In India
Treatments For Heart Failure
Treatment for heart failure usually aims to control the symptoms for as long as possible and slow down the progression of the condition.
How youâre treated will depend on what is causing your heart failure.
Common treatments include:
- lifestyle changes including eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly and stopping smoking
- medicine a range of medicines can help many people need to take 2 or 3 different types
- devices implanted in your chest these can help control your heart rhythm
- surgery such as a or a heart transplant
Treatment will usually be needed for life.
A cure may be possible when heart failure has a treatable cause. For example, if your heart valves are damaged, replacing or repairing them may cure the condition.
Chf Icd 10 Codes And Guidelines
Most of the heart failure codes include in chapter 9 of ICD-10 CM manual, diseases of circulatory system, code range I00-I99.
- Combination code If patient has any type of heart failure and hypertension, it should be combined and coded as I11.0 eventhough physician has not linked both. It should not be coded combined if the medical record states the conditions are unrelated.
- Heart failure should be coded additionally when coding I11.0
- Do not code I11.9 when coding I11.0 .
- When coding biventricular heart failure it is necessary to code the type of left heart failure also according to the code also note with I50.82
Go by Failure, Heart to find correct codes for heart failure in ICD-10 CM manual index.
Look at the below scenarios to clearly understand the coding concepts of CHF.
CHF ICD 10 Code Example 1
Elizabeth is a 65 year old female who comes to emergency department for shortness of breath and leg edema from past 2 days. She came to visit doctor as the symptoms are getting worse. She has hypertension and takes Lisinopril for the same. She does not have chest pain or palpitation. She is not a smoker. Her family history includes heart disease for her mother and brother. Vitals showed temperature 97.3 F, heart rate 72 bpm, respiratory rate 25, BP 150/96 mmHg. Physical exam showed pitting edema on both the extremities, shortness of breath and dry skin. Physician ordered for blood tests, EKG and chest X-ray. This case was diagnosed as acute diastolic heart failure.
Don’t Miss: How To Tell If You’ve Had A Heart Attack
Causes And Symptoms Of Acute Heart Failure
The most common cause of acute heart failure is a heart attack . This is caused by blockages in the arteries supplying blood to the heart muscle. Other causes include viruses, severe infections, allergic reactions, blood clots in the lungs, certain medications, or an illness that can attack the heart muscle.1
Shortness of breath is the most common symptom of AHF. Acute heart failure can also present with symptoms of rapid swelling and fluid retention characterized by sudden weight gain, up to several pounds in a 24-hr period. Coughing, wheezing, difficulty laying flat to sleep, as well as an irregular heartbeat can also be symptoms. In some cases, it is related to pre-existing cardiomyopathy. AHF often requires unexpected hospital admission. This tends to have a poor prognosis, with a high risk of readmission and death post-discharge.1 Seek emergency medical treatment if sudden or painful symptoms develop.
Medications For Systolic Heart Failure
Depending on the severity of systolic heart failure and its underlying cause, your doctor may prescribe medications. Some of the drug options for treating systolic heart failure include:
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers relax the blood vessels to lower blood pressure.
- Beta blockers make the heart beat more slowly and with less force.
- Aldosterone blockers help the body release sodium and water.
- Angiotensin receptorneprilysin inhibitors reduce excess fluid in the body and relax blood vessels, making it easier for your heart to pump blood.
Also Check: How To Slow Your Heart Rate When Nervous
What Is Acute On Chronic Chf
When heart muscles are damaged chronically, the term Chronic is used to define such a condition but sometimes, a chronically damaged heart can get a viral infection, certain vessels blockage, or shortness of breath leading to acute heart failure of chronic CHF. Medical professionals call it acute on chronic heart failure. The simple definition could be Sudden onset of chronic heart condition.
Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction
In diastolic heart failure , the same pathophysiologic processes occur that lead to decreased cardiac output in systolic heart failure, but they do so in response to a different set of hemodynamic and circulatory environmental factors that depress cardiac output.
In HFpEF, altered relaxation and increased stiffness of the ventricle occur in response to an increase in ventricular afterload . The impaired relaxation of the ventricle then leads to impaired diastolic filling of the left ventricle .
Morris et al found that right venticular subendocardial systolic dysfunction and diastolic dysfunction, as detected by echocardiographic strain rate imaging, are common in patients with HFpEF. This dysfunction is potentially associated with the same fibrotic processes that affect the subendocardial layer of the LV and, to a lesser extent, with RV pressure overload. It may play a role in the symptomatology of patients with HFpEF.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Feel After A Heart Attack
Acute On Chronic Systolic Heart Failure
- 20162017201820192020202120222023Billable/Specific Code
- I50.23 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2023 edition of ICD-10-CM I50.23 became effective on October 1, 2022.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I50.23 – other international versions of ICD-10 I50.23 may differ.
- Applicable To annotations, or
What Are The Treatments For Heart Failure
Your treatment will depend on the type of heart failure you have and how serious it is. Thereâs no cure for heart failure. But treatment can help you live longer with fewer symptoms.
Even with treatment, heart failure usually gets worse over time, so youâll likely need treatment for the rest of your life.
Most treatment plans include:
You may need heart surgery if:
- You have a congenital heart defect or damage to your heart that can be fixed.
- The left side of your heart is getting weaker and putting a device in your chest could help. Devices include:
- A biventricular pacemaker .
- A mechanical heart pump or a total artificial heart).
As part of your treatment, youâll need to pay close attention to your symptoms, because heart failure can worsen suddenly. Your provider may suggest a cardiac rehabilitation program to help you learn how to manage your condition.
Donât Miss: 100 Resting Heart Rate
Recommended Reading: What Causes A Heart Attack
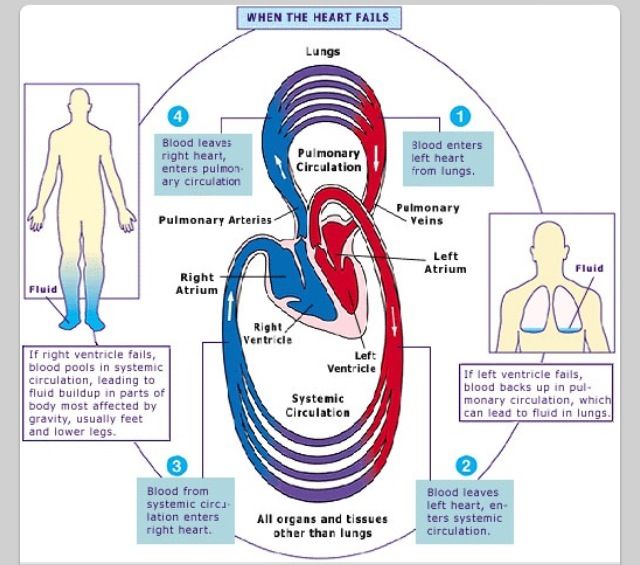
Liver Size And Hepatojugular Reflux
The key component of the abdominal examination is the evaluation of liver size. Hepatomegaly may occur because of right-sided heart failure and venous congestion.
The hepatojugular reflux can be a useful test in patients with right-sided heart failure. This test should be performed while the patient is lying down with the upper body at a 45-degree angle from the horizontal plane. The patient keeps the mouth open and breathes normally to prevent Valsalva’s maneuver, which can give a false-positive test. Moderate pressure is then applied over the middle of the abdomen for 30 to 60 seconds. Hepatojugular reflux occurs if the height of the neck veins increases by at least 3 cm and the increase is maintained throughout the compression period.18
Articles On Heart Failure Types & Stages
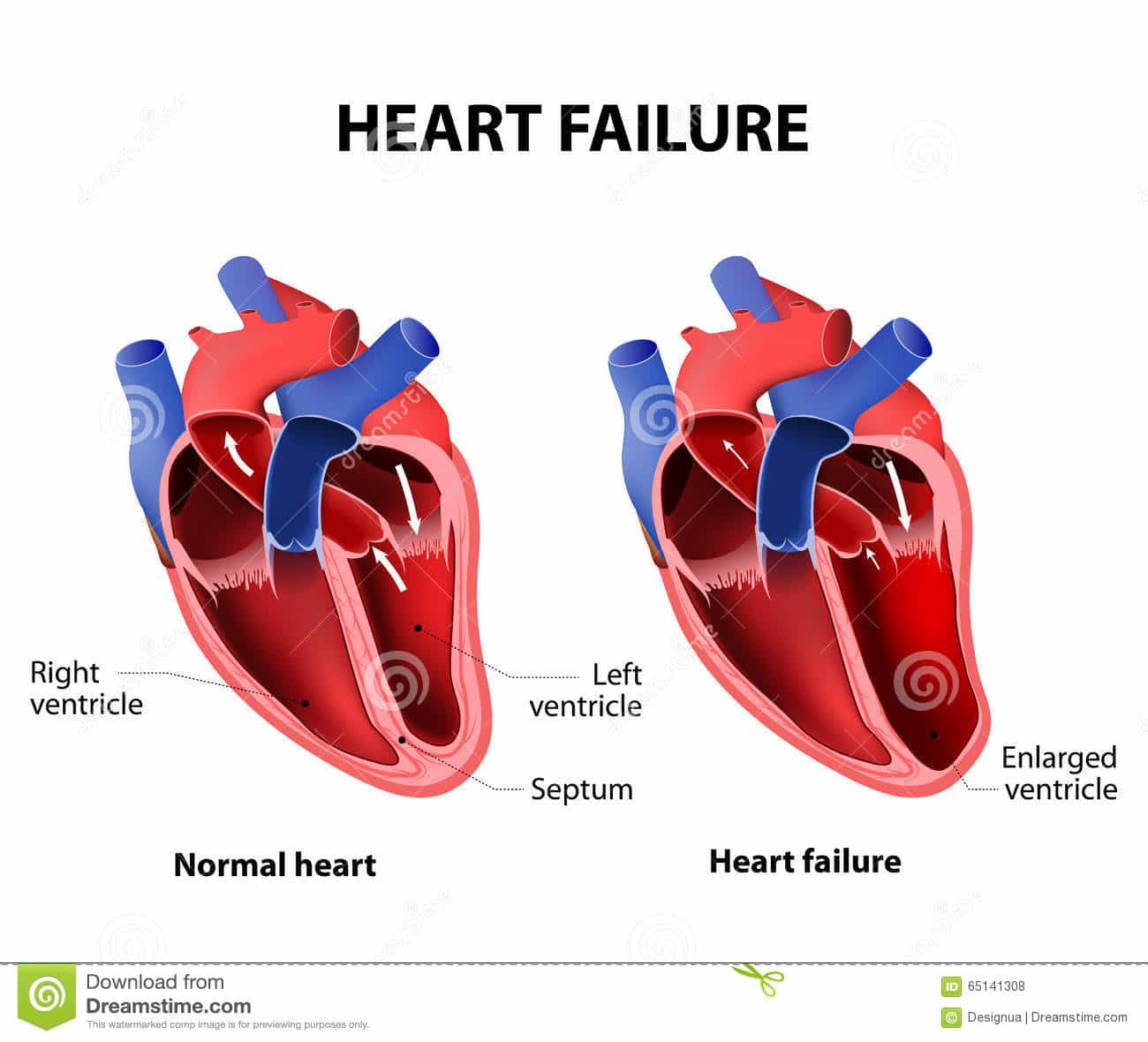
If you have systolic heart failure, the left ventricle of your heart, which pumps most of the blood, has become weak. This may happen because it’s gotten bigger. Since it’s larger, the ventricle can’t contract the way it should. Because of that, your heart doesn’t pump with enough force to push blood throughout your body.
Read Also: What Causes Heart Palpitations After Eating
Treatment Options For People With Acute Heart Failure
There is no cure for heart failure, but treatment can help improve your quality of life. Acute heart failure can have lasting effects on your body. Because of this, treatment is centered on managing symptoms and preventing future heart failure.
If you experience acute heart failure, youll likely stay in the hospital until youre in stable condition. During this time, you may need oxygen therapy. You might also need supplemental oxygen after you leave the hospital.
The cause of your acute heart failure will determine your treatment plan. In some cases, acute heart failure can be caused by undiagnosed chronic heart failure. Treatment for acute heart failure and chronic heart failure is often the same.
Treatment options for acute heart failure include medications, medical devices, and surgery.
Classification Of Acute Heart Failure
The definition of AHF presented here is broad and there have been many attempts to stratify this further . Although characterised by a distinctive set of signs and symptoms, a major challenge in classifying AHF as a single entity is that the patient population is not uniform. Patients admitted with HF exhibit a wide spectrum of disease and range from those with severe LV systolic dysfunction and low cardiac output to those with severe hypertension and normal or near-normal LV systolic function. The majority of patients with AHF lie between these extremes and therefore also demonstrate a distribution of underlying pathology and precipitants, leading to the common endpoint of fluid overload.
This is a neat classification system and focusses the treating physician towards the management of the underlying cause of AHF. However, given patients often present with a range of co-morbidities, the reasons for decompensation may not be apparent at initial presentation or indeed, there may be multiple contributing factors. Practically speaking, therefore, it may be more prudent to stratify patients with AHF based on their initial clinical presentation. This allows the attending physician to identify those most at risk in order to direct specific interventions such as instituting ionotropic agents and/or mechanical circulatory support.
You May Like: Recovery From Open Heart Surgery
How To Prevent Acute Heart Failure
Some risk factors, such as aging, cant be avoided. The key to preventing heart failure is to reduce the risk factors that you can control.
Many of the lifestyle measures recommended for heart failure recovery can also reduce or eliminate conditions that lead to heart failure. These conditions include high blood pressure and high cholesterol.
If youre at risk for heart failure, you should consider these measures to promote heart health:
- maintain a healthy weight, if overweight or obesity is a concern
- get regular physical activity
Etiology Congestive Heart Failure
There are numerous causes for systolic heart failure, but the most common is related to coronary artery disease and prior myocardial infarctions. This entity is termed an ischemic cardiomyopathy and accounts for nearly half of systolic heart failure cases in the United States.
Dilated cardiomyopathy is the second leading cause of systolic HF. This can be idiopathic , a viral cardiomyopathy, peripartum and hypertensive heart disease . These include doxorubicin therapy, stress-induced , alcohol-related, selenium or thiamine deficiency, tachycardia-mediated, giant cell arteritis, hyperthyroidism, cocaine use, obstructive sleep apnea and familial cardiomyopathies.
The third leading cause of systolic HF is valvular heart disease. This includes aortic valve stenosis, aortic valve regurgitation, mitral valve stenosis and mitral regurgitation. In many developing nations, the most common cause of systolic HF is Chagas disease, which is related to Trypanosoma cruzi and transmitted by triatomine bugs.
Recall that right heart failure and diastolic heart failure are different entities from the left-sided systolic heart failure reviewed here. The most common cause of right HF is pressure overload related to left HF. Diastolic HF is most commonly caused by hypertension as a part of hypertensive heart disease. Aging of the heart contributes to diastolic HF as well.
You May Like: Cough With Congestive Heart Failure
Description Of The Problem
Chronic heart failure is common. Over 5 million people in the United States alone carry this diagnosis, and each year over 600,000 patients are newly diagnosed. At the same time, the morbidity and mortality associated with this disease process is staggering there are over 1 million hospitalizations each year, nearly 300,000 annual deaths, and it is the largest Medicare expenditure.
Chronic heart failure can be caused by a number of clinical conditions most commonly, it is the result of coronary artery disease. That being said, there are a number of non-ischemic etiologies, including myocarditis, hypertension, valvular disorders, genetic cardiomyopathies, drug and toxins, and connective tissue diseases, to name a few. In fact, nearly half of all patients with chronic heart failure have an idiopathic cardiomyopathy, in which a common etiology cannot be identified.
Patients can present with chronic heart failure in a variety of ways. Some patients will have absolutely no symptoms, and only have evidence of structural heart disease identified by screening study . Some patients experience mild symptoms exacerbated by conditions of increased myocardial demand symptoms include dyspnea with exertion, orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, peripheral edema, and fatigue. Other patients will present in an acutely decompensated state, with or without hemodynamic stability, due to volume overload and/or low cardiac output.
Key management points
What Causes Heart Failure
Heart failure can start suddenly after a medical condition or injury damages your heart muscle. But in most cases, heart failure develops slowly from long-term medical conditions.
Conditions that can cause heart failure include:
You May Like: Heart Surgery Charity Organizations
Prognosis Of Systolic Heart Failure
In general, a diagnosis of heart failure is serious, since it can cause life-threatening arrhythmias and organ failure.
Taking medications as prescribed, monitoring fluid status, and close follow-up with a healthcare provider can help people with heart failure stay out of the hospital and improve quality of life.
Advanced treatments and heart transplant are also options for those with very severe heart failure.
Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction
Systolic heart failure is also called heart failure with reduced ejection fraction .
Ejection fraction is the percentage of blood the left ventricle pumps out with every beat. A normal, healthy ejection fraction is 55% to 65%. If its higher or lower, that can indicate a heart problem.
With systolic heart failure, the ejection fraction is usually less than 50%.
Read Also: How To Get My Heart Rate Down
