Symptoms Of Reduced Pumping Capability
The most prominent symptoms are:
- Extreme weakness and fatigue
- Muscle weakness and muscle wasting
- Lethargy and inanition
- Extreme weight loss
Obviously, symptoms like this are not compatible with a long life. Unless the cardiac function can be improved, or unless cardiac transplantation or a ventricular assist device can be used, once a person with heart failure develops these kinds of symptoms, death usually follows relatively soon.
Also Check: Is Congestive Heart Disease Hereditary
What Do You Do When You Develop Pneumonia And Congestive Heart Failure
Former Bodybuilder- Pro Wrestler-Host Ric’s Corner, Designer of the Iconic Gold’s Gym and World Gym Logos, former training Partner of Arnold Schwarzenegger, Demi Hulk – Incredible Hulk TV Series
Last week I was in the gym feeling strong but still felt something was wrong with my breathing and tiredness. Heavy chest and walking block and getting tired however the weight workouts were fine and had one of my strongest days ever.
Then a few days later I end up in the hospital after seeing three doctors and last day was almost the end of the line for me. I was admitted and tested for everything.
Trust me the hospital was the last place I wanted to be. I can’t lay in a bed for days. They found fluid around my lungs with blood in it. Two liters full as they drained it out of my back with a tube.
It wasn’t painful but I was shocked at what they found. Plus it was what they call pleural effusion which fluid surrounds the heart making it hard to pump and the heart rate increases rapidly.
The lungs get compressed and if it’s for any length of time, they take more time to open up and then you have to practice breathing deeper to open them more. This is all very uncomfortable. I do not like being chained to the house with oxygen following me everywhere but this is what i have to do if I don’t want the alternative.
I’ve got my eye on this again.
What Causes Congestive Heart Failure
Several factors can cause congestive heart failure. They include:
- Presence of other diseases like diabetes and high blood pressure
- Addictions like smoking and alcohol
Although heart failure is a serious condition, it does not mean that the heart stops functioning altogether. With proper management, persons who have congestive heart failure can lead nearly normal lives, depending on its severity. Besides the required medical and surgical interventions, it is important to eat healthy, stay active as possible, and refrain from alcohol, smoking, and drug abuse. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , almost half of the patients with congestive heart failure live beyond five years.
Don’t Miss: End Stage Heart Failure Life Expectancy
Strengths And Limitations Of Study
The putative role of community acquired pneumonia on heart failure, and cardiac disease in general, is still evolving. Pneumonia increases systematic oxidative stress and inflammatory markers , in both the short term and the long term, leading to an increased risk of thrombogenesis, destabilisation of atherosclerotic plaques, and endothelial dysfunction, potentially leading to increased rates of ischaemic heart disease, atrial fibrillation, and reduced ventricular function.61637 Furthermore, this increased host response to infection has been shown to occur even in those with less severe infections and to persistent long after a patient clinically recovers from the acute infection.31 Whether community acquired pneumonia truly causes heart failure in itself or whether heart failure is simply the endgame in the cardiac cascade triggered by acute pneumonia event is not fully elucidated. Other factors, which are common to both pneumonia and heart failure, are also likely at play, including advanced age, reduced renal function, and the presence of other major comorbidities , and collectively are likely to contribute to the increased risk of heart failure in patients with pneumonia.6 A major limitation of our study is that we could not examine these potential mechanisms and causes of heart failure related to pneumonia.
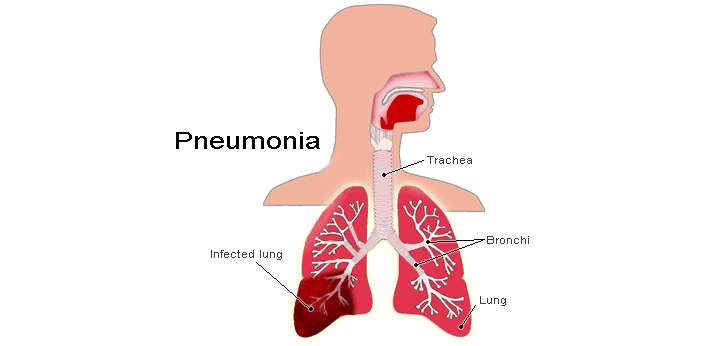
Congestive Heart Failure And Pneumonia In The Elderly
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Read Also: What Is Your Target Heart Rate
If You’re Over 65 Be Sure To Follow The Latest Pneumonia Vaccine Guidelines
Each year, about a million people in the United States end up in the hospital with pneumonia, a serious lung infection that can be caused by an array of different viruses, bacteria, and even fungi. New research suggests that older people hospitalized with pneumonia face four times their usual risk of a having a heart attack or stroke or dying of heart disease in the month following the illness.
The risk declines over the following year, according to the report, published in the Jan. 20, 2015, Journal of the American Medical Association. Infections put added stress on your heart, forcing it to work harder. Your body’s efforts to fight the infection also trigger unhealthy changes inside your arteries, such as releasing chemicals that can make blood more likely to clot, which can lead to a heart attack or stroke.
“Serious infections like pneumonia are linked to a higher risk of heart attack as well as worsening heart failure in people with that condition,” says Dr. Scott Solomon, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School. For older people, the pneumonia vaccine may help prevent these dangerous complications, but an annual flu shot is also important, he notes. The same virus that causes the flu can also cause viral pneumonia in some people and nudge others to develop bacterial pneumonia.
Congestive Heart Failure Can Be Mistaken For Pneumonia
DEAR DR. DONOHUE At first, doctors thought I had pneumonia. Then they decided I had congestive heart failure. How can such a mistake be made? I am now taking all sorts of medicines. Before, I wasn’t taking any. Will I ever get off them? I am 79.
— N.N.
Pneumonia and congestive heart failure have two things in common Both fill the lungs with fluid, and both make a person short of breath. With pneumonia, the fluid in the lungs is filled with white blood cells trying to fight off the infection. With congestive heart failure, the fluid in the lungs is fluid that has leaked from the circulation due to a backup of blood in lung blood vessels. The two can be mistaken, but the error is usually quickly corrected.
Congestive heart failure results when the heart is no longer a good pump. Its muscle has become so feeble that it can’t empty all the blood in it. Pressure inside lung blood vessels rises and forces fluid into the lungs’ air sacs. Air can’t get into or out of the lungs. Slight effort makes a person pant for air. Lying down often precipitates an attack of breathlessness. When heart failure becomes more severe, people waken from sleep gasping for breath.
Causes of heart failure are many. A heart attack can weaken heart muscle and its ability to pump. Deformed heart valves are another cause. Uncontrolled blood pressure can bring on heart failure.
before I die? I am 58.
— J.F.
— C.N.
Most vitamins are digested and absorbed.
Many major brands of vitamins &
Recommended Reading: Where Do You Feel Heart Palpitations
Medications Used To Treat Congestive Heart Failure
Treatment of congestive heart failure also includes medications. Doctors prescribe medicine to manage symptoms and to make it easier for the heart to function, which will improve symptoms and reduce the risk of complications.
Medications include:
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors , which lower blood pressure and reduce strain on the heart
- Angiotensin-II receptor blockers , which are an alternative to lower blood pressure for those who canât tolerate ACE inhibitors. Examples include losartan and valsartan .
- Combination valsartan-sacubitril , which is used in place of an ARB or ACE inhibitor
- Aldosterone blockers , which may be used for severe congestive heart failure
- Anticoagulants , which prevent the formation of blood clots that can lead to and stroke
- Beta-blockers , which lower blood pressure, control heart rate, and reduce strain on the heart
- Cholesterol-lowering medications , which can reduce the risk of heart attack and . Cholesterol-lowering medications also reduce the risk of recurrent heart attack and stroke.
- Digitalis drugs , which slow and strengthen the beating of the heart to make the heart muscle more effective in pumping blood
- Diuretics , which pull excess fluid out of the lungs and tissues of the body by increasing urine production
Pneumonia Risk Soars In Heart Failure Patients Especially Hfpef
FROM JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
Patients with heart failure get pneumonia at a rate almost three times greater than expected and, once they do get pneumonia, have about a fourfold greater risk of death, investigators for a retrospective analysis of 13,000 patients from two landmark randomized HF trials have found.
Dr. John J.V. McMurray
The investigators also found that HF patients with preserved ejection fraction are at the highest risk of developing pneumonia. The findings underscore the importance of patients with HF getting a pneumonia vaccination, they found.
The analysis showed that 6.3% of patients in the PARADIGM-HF trial and 10.6% of those in the PARAGON-HF trial developed pneumonia, reported the study authors, led by John J.V. McMurray, MD, of the British Heart Foundation Cardiovascular Research Center at the University of Glasgow in Scotland .
The main reason for doing this study was the fact that many heart failure patients are not vaccinated, as they should be, against pneumonia both pneumococcus and influenza vaccination, Dr. McMurray said in an interview. We wanted to document the frequency and consequences of pneumonia in patients with heart failure to help highlight this deficiency in care.
Dr. McMurray said he believes this is the first study to document the incidence of pneumonia and pneumonia-related outcomes according to the two major ejection fraction phenotypes.
Recommended Reading: Swollen Ankles Heart Failure
Heart Failure Treatments And Covid
The key to managing heart failure is adhering to a treatment strategy that includes medications and lifestyle changes. In severe cases, implants or surgeries may be required. Some common prescription medications used to treat heart failure include:
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors like captopril, lisinopril, enalapril, and ramipril
- Angiotensin receptor blockers like valsartan and losartan
- Beta-blockers like carvedilol, metoprolol succinate, and bisoprolol
- Angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor
- Aldosterone antagonists like spironolactone
- Diuretics like furosemide and torsemide
- SGLT2 inhibitors like empagliflozin
Many of these medications carry a risk of side effects like dizziness, low blood pressure, shortness of breath, and difficulty breathing. These symptoms can be exacerbated by COVID-19 or make a coronavirus infection feel worse.
People with heart failure should stick to the medication regimen prescribed by their healthcare providereven if they have COVID-19. Call your practitioner before making any medication changes on your own.
Heart Failure And Covid
People with a pre-existing heart problem like heart failure are about 10% to 20% more likely to experience severe illness from COVID-19 compared to people with healthy hearts. They are also more likely to get much sicker and even die because of COVID-19.
Research has shown that people who have a history of heart failure who are hospitalized for COVID-19 are nearly twice as likely to die than those who don’t. COVID-19 patients with heart failure had hospital stays averaging about two days longer than those without the condition, and they were twice as likely to require mechanical ventilation.
Also Check: What Should My Heart Rate Be While Working Out
Congestive Heart Failure In Children With Pneumonia And Respiratory Failure
Department of Pediatrics, Suratthani Hospital, Suratthani, Thailand
Department of Pediatrics, Suratthani Hospital, Suratthani, Thailand
Get access to the full version of this article.You previously purchased this article through ReadCube.
Institutional Login
Log in to Wiley Online Library
If you have previously obtained access with your personal account, please log in.
- View the article/chapter PDF and any associated supplements and figures for a period of 48 hours.
- Article/Chapter can not be printed.
- Article/Chapter can not be downloaded.
- Article/Chapter can not be redistributed.
- Unlimited viewing of the article/chapter PDF and any associated supplements and figures.
- Article/Chapter can not be printed.
- Article/Chapter can not be downloaded.
- Article/Chapter can not be redistributed.
- Unlimited viewing of the article/chapter PDF and any associated supplements and figures.
- Article/chapter can be printed.
Data On Hospitalizations For Pneumonia
We identified patients aged at least 15 years of age, with a first-time hospitalization for pneumonia during the three data collection periods, using counties hospital discharge registries merged into a research database, as previously described 13. The registries contain key information on all patient discharges from non-psychiatric hospitals in the counties since 1977 . Data include patients civil registration numbers, admission and discharge dates, and up to 20 discharge diagnoses coded exclusively by physicians according to the International Classification of Diseases . The ICD-10 codes used for pneumonia hospitalizations were J12-J18, A481, and A709.
Also Check: Which Is A Manifestation Of Right-sided Heart Failure
Complications Of Heart Failure And Covid
People with heart failure are at a greater risk of becoming severely ill with COVID-19. One study found that among patients who were hospitalized with a COVID-19 infection, there was a 50% mortality rate among those with pre-existing heart failure compared with a mortality rate of 10% in individuals without heart failure.
Treatment for COVID-19 can also lead to serious complications for people with heart failure due to several contributing factors:
- Breathing can be difficult for people with heart failure even without a COVID-19 infection. Fluid can accumulate in the body, particularly in the lungs, since blood that can’t be pumped throughout the body causes a backup. This can further reduce the much-needed oxygen supply in people with heart failure. Additionally, COVID-19 usually results in pneumonia and decreased movement of oxygen across the cells in the lung to the bloodstream.
- As COVID-19 and heart failure create difficulty for the body to breathe and pump blood, a person’s chances of requiring mechanical ventilation increase. This may seem like the fix. However, especially for people with heart failure, there has been evidence that the high pressure required to support the breathing of people with COVID-19 on mechanical ventilation can further increase pressure in the pulmonary vessels. This creates even greater strainand damageto the heart.
- Severe COVID-19 infection has also been known to cause kidney damage, which can further increase the workload of the heart.
What Are The Stages Of Heart Failure
Heart failure is a chronic long-term condition that gets worse with time. There are four stages of heart failure . The stages range from âhigh risk of developing heart failureâ to âadvanced heart failure,â and provide treatment plans. Ask your healthcare provider what stage of heart failure you are in. These stages are different from the New York Heart Association clinical classifications of heart failure that reflect the severity of symptoms or functional limits due to heart failure.
As the condition gets worse, your heart muscle pumps less blood to your organs, and you move toward the next stage of heart failure. You cannot go backwards through the stages. For example, if you are in Stage B, you cannot be in Stage A again. The goal of treatment is to keep you from progressing through the stages or to slow down the progression.
Treatment at each stage of heart failure may involve changes to medications, lifestyle behaviors and cardiac devices. You can compare your treatment plan with those listed for each stage of heart failure. The treatments listed are based on current treatment guidelines. The table outlines a basic plan of care that may apply to you. If you have any questions about any part of your treatment plan, ask a member of your healthcare team.
Read Also: Apple Watch Heart Rate Monitor Accuracy
Recommended Reading: Bypass Heart Surgery Recovery
Does Pneumonia Have Cardiovascular Risk
Pneumonia is an infection that can cause inflammation throughout the body. This inflammation can lead to other complications, including an increased risk that bits of plaque can break free from your vessel walls and lead to heart attack or stroke.
Even without existing coronary artery disease or plaque buildup, the body-wide inflammation that pneumonia triggers can cause its own problems.
Inflammation can interfere with the normal function of all kinds of systems in your body especially the heart. This makes heart failure one of the most common complications of pneumonia.
About 30% of people hospitalized with community-acquired pneumonia develop heart failure and other cardiovascular problems, but the risk isnt always immediate. Research indicates that the greatest risk of heart complications occurs in the month after a pneumonia diagnosis, and the risk can continue for up to a decade.
How Pulmonary Edema Happens In Case Of Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive Heart failure gives rise to pulmonary edema. The initial stage of congestive heart failure may not be that problematic for lungs, but when the heart is unable to pump blood properly and insufficiently to the whole part of the body for a long term, the blood starts backing up in the veins which carry blood through the lungs. With the increase in the pressure, the blood in these vessels leak and the fluid is pushed in the alveoli or the air sacs of the lungs. As the heart failure worsens and slowly fluid starts accumulating in lungs. The fluid accumulates in the other parts of the body and produces edema especially in the legs, ankles and feet.
To prevent pulmonary edema, it is important to check, diagnose and correct the congestive heart failure diseases, if it is present. Below are few symptoms which are indicative of a Congestive Heart Failure:
- Impaired thinking, delirium and confusion.
- Appetite loss.
- Tiredness, fatigue.
If these occur, it is important to get it diagnosed and treated on proper time or else it can be fatal in the near future. Fortunately there are improvements and advancements in the treatment of congestive heart failure, but only 50% of the patients will have an average expectancy of about five years or less. Those who have serious CHF have more risk of life and 90% of patients may die within one year.
Read Also: Which Type Of Fat May Help Lower The Risk Of Heart Disease
