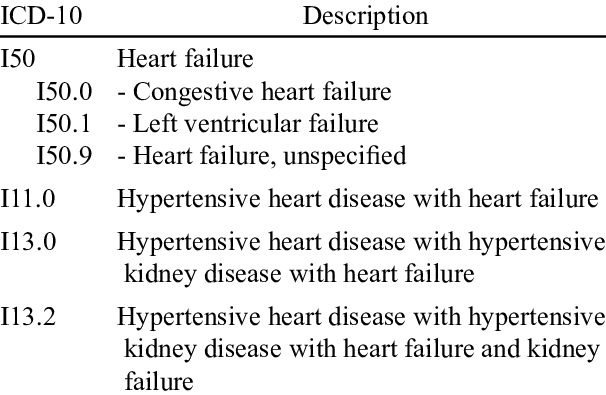
Unspecified Combined Systolic And Diastolic Heart Failure
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- Edema of lung with heart disease NOS
- Edema of lung with heart failure
- Left heart failure
- Pulmonary edema with heart disease NOS
- Pulmonary edema with heart failure
- edema of lung without heart disease or heart failure
- pulmonary edema without heart disease or failure
What Is The Code For Congestive Heart Failure
codecongestiveheart failurecodeheart failure
Keeping this in consideration, what is ICD 10 code for congestive heart failure?
I50.20
Furthermore, what are the 4 stages of congestive heart failure? There are 4 stages of heart failure . The stages range from “high risk of developing heart failure” to “advanced heart failure,” and provide treatment plans. Ask your healthcare provider what stage of heart failure you are in.
Also, what is the code for heart failure?
ICD-10 Code: I50. 9 Heart Failure, Unspecified. Code I50. 9 is the diagnosis code used for Heart Failure, Unspecified.
What is the difference between acute and chronic congestive heart failure?
Share on Pinterest Acute heart failure is heart failure that occurs suddenly and sometimes without warning. Heart failure is the inability of the heart to pump enough blood to serve the body’s needs. Chronic heart failure develops slowly, while acute occurs suddenly.
How To Code If No Cause For Heart Failure Is Documented
If no cause for heart failure is spcified in the note, it is better to code just the heart failure diagnosis alone , even if a secondary diagnosis is present in the note, such as hypertension. In other words, the medical coder does not have the liberty to makes the connection between another condition and heart failure, unless it is already present in the chart. In such a case, the coder should assign separate codes for the two conditions.
You May Like: Does Tylenol Increase Heart Rate
Right Heart Failure Due To Left Heart Failure
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- Right ventricular failure secondary to left ventricular failure
- the type of left ventricular failure, if known
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I50.2
- 2016201720182019202020212022Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code
- Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction
- Systolic left ventricular heart failure
- end stage heart failure, if applicable
The Icd Code I50 Is Used To Code Acute Decompensated Heart Failure
Acute decompensated heart failure is a sudden worsening of the signs and symptoms of heart failure, which typically includes difficulty breathing , leg or feet swelling, and fatigue. ADHF is a common and potentially serious cause of acute respiratory distress. The condition is caused by severe congestion of multiple organs by fluid that is inadequately circulated by the failing heart. An attack of decompensation can be caused by underlying medical illness, such as myocardial infarction, infection, or thyroid disease.
| Specialty: |
Also Check: 10 Second Trick To Prevent Heart Attack
Symptoms Of Congestive Heart Failure
Heart failure can be ongoing , or your condition may start suddenly . Heart failure signs and symptoms may include shortness of breath when you exert yourself or when you lie down, fatigue and weakness, swelling in your legs, rapid or irregular heartbeat, reduced ability to exercise, persistent cough or wheezing with white or pink blood-tinged phlegm, increased need to urinate at night, swelling of your abdomen , very rapid weight gain from fluid retention, lack of appetite and nausea, difficulty concentrating or decreased alertness, sudden or severe shortness of breath and coughing up pink and foamy mucus, and chest pain if your heart failure is caused by a heart attack
Symptoms Tests And Diagnosis
There may be one or multiple symptoms like shortness of breath, leg edema, fatigue, rapid heartbeat or chest pain. Doctor will verify the patients medical history as conditions like CAD, angina, hypertension, heart valve diseases and diabetes are risk factors for heart failure. After doing a physical examination, physicians may do cholesterol check, BNP blood test, chest X-ray, EKG, stress test, CT scan, MRI or coronary angiogram.
Recommended Reading: How Does Blood Move Through The Heart
Coding For Congestive Heart Failure
April 23, 2021 / By Rebecca Caux-Harry
I was reading an article the other day about a young man who developed severe biventricular heart failure after consuming a large quantity of an energy drink every day for 2 years. I remember my days as a college student and the need to be mentally alert for my classes and studies. We didnt have energy drinks at that time, but there were, and still are, caffeine pills. I tried them once or twice and found myself so overwhelmed by the caffeine side effects that there was no benefit. I guess I was lucky in that way.
While the young British student is expected to make a partial to full recovery with ongoing treatment, the article got me thinking about the ICD-10 codes for congestive heart failure . CHF is when the heart muscle doesnt pump blood to the rest of the body as it should. The condition is usually progressive, meaning most people arent cured, but rather managed with medication and lifestyle changes.
When I first started coding, we only had 3 ICD-9 codes for CHF: 428.0, 428.1 and 428.9. A few years later, those codes were expanded with specificity for acuity and type . Now, with ICD-10 we have a wide variety of codes to choose from, but as always, selection of the most accurate and specific code depends entirely on the physicians documentation.
Rebecca Caux-Harry, CPC, is a professional fee coding specialist with 3M Health Information Systems.
Tabular List Of Diseases And Injuries
The Tabular List of Diseases and Injuries is a list of ICD-10 codes, organized “head to toe” into chapters and sections with coding notes and guidance for inclusions, exclusions, descriptions and more. The following references are applicable to the code I50.9:
Inclusion Terms
- Cardiac, heart or myocardial failure NOS
- Congestive heart disease
- fluid overload unrelated to congestive heart failure E87.70
Read Also: Can Ibs Cause Palpitations
Determine The Cause Of Heart Failure
One of the most important things you understand, when coding for heart failure, is that there can be many very different reasons why somebody can develop heart failure, and the ICD-10-CM coding system, as complex as it is, allows for very fine granuation in this respect. Therefore, your first decision to make, when looking for a code to use, is to determine, from the note, what is the underlying cause for heart failure. To illustrate, I am listing a few of the more common ICD-10 codes for heart failure based on cause:
- I11.0 – Hypertensive heart disease with heart failure
- I09.81 – Rheumatic heart failure
- I97.131 – Postprocedural heart failure following other surgery
- I97.130 – Postprocedural heart failure following cardiac surgery
- I13.0 – Hypertensive heart and chronic kidney disease with heart failure and stage 1 through stage 4 chronic kidney disease, or unspecified chronic kidney disease
- P29.0 – Neonatal cardiac failure
Note that none of the above conditions where heart failure is present use the root “I50” for buidling the ICD-10 code.
Assumptive Coding For Heart Disease A Coders Perspective
Official guidance on ICD-10-CM coding raises questions regarding how to document cardiac care.
The first step in choosing the proper ICD-10-CM code is reading the medical documentation to identify the diagnosis the provider has documented and confirmed. If there is no confirmed diagnosis, look for the sign or symptom that brought the patient in for the encounter.
Well, at least that is what we have been taught, and have had hammered into our thinking not only with ICD-9, but with the launching of ICD-10 in 2015, and its platform of coding to the highest specificity. That is why I am at a loss when it comes to the 2018 instructions for coding hypertensive heart disease in the ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Reporting for FY 2018.
I have had many coders ask me, are we supposed to assume a disease has a causal relationship when it is not documented as such by the physician?
What coders are referring to are the stated ICD-10-CM guidelines on this topic, and how they have coders scratching their heads, having to go against everything they have been taught about code selection.
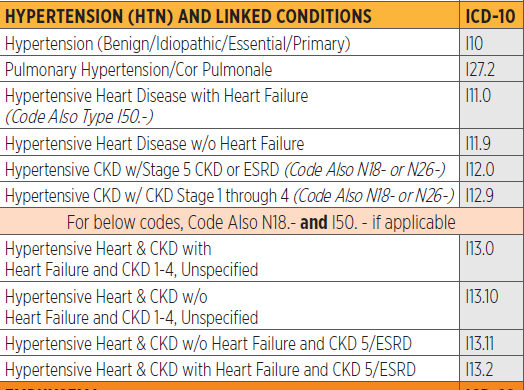
First, lets look at what hypertensive heart disease is.
Hypertensive heart disease refers to heart conditions caused by high blood pressure.
The heart working under increased pressure may cause some different heart disorders. Hypertensive heart disease includes heart failure, thickening of the heart muscle, coronary artery disease, and other conditions.
Narrowing of the Arteries
Complications
Also Check: What Heart Chamber Pushes Blood Through The Aortic Semilunar Valve
Types Of Heart Failure
The types are based on which part of the heart is affected.
Left sided heart failure : This is the most common type of heart failure found in medical record. It is related to the pumping of blood by left ventricle. This can be either Systolic or Diastolic.
Systolic It is also called HFrEF which means heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
Diastolic Another term for this is HFpEF which means heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.
Right sided heart failure : It is related to the pumping of blood by right ventricle.
Biventricular heart failure : This is a type of heart failure in which ventricles of both the sides are unable to pump enough blood.
Hypertensive Heart Disease With Heart Failure
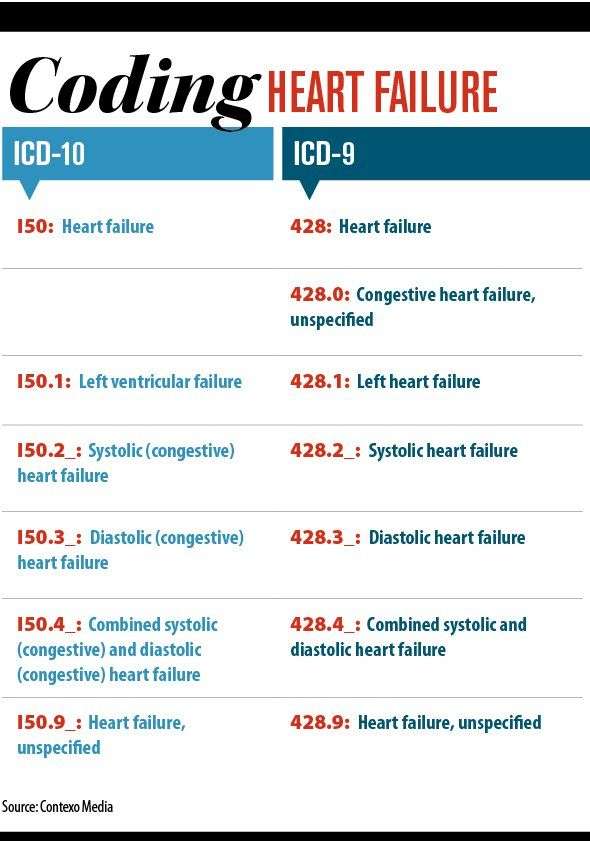
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- I11.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I11.0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I11.0 – other international versions of ICD-10 I11.0 may differ.
“use additional code”
- code to identify type of heart failure (ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I50
Don’t Miss: Does Tylenol Increase Heart Rate
What Is The Icd 10 Code For Acute Decompensated Heart Failure
3.9/5codeheart failureheart failureheart failureCodingacute
Consequently, what is the ICD 10 code for decompensated heart failure?
Acute on chronic diastolic heart failureI50. 33 is a billable/specific ICD–10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD–10-CM I50. 33 became effective on October 1, 2019.
Likewise, what is the code for congestive heart failure? ICD-10 has no code for congestiveheart failure the term is included in code I50. 9 – Unspecified heart failure.
Beside this, what does decompensated mean in heart failure?
Specialty. Cardiology. Acute is a sudden worsening of the signs and symptoms of heart failure, which typically includes difficulty breathing , leg or feet swelling, and fatigue. ADHF is a common and potentially serious cause of acute respiratory distress.
What is stage a heart failure?
Stage A is considered pre-heart failure. It means you are at high risk of developing heart failure because you have a family history of heart failure or you have one of more of these medical conditions: Hypertension. Diabetes. Coronary artery disease.
Index To Diseases And Injuries
The Index to Diseases and Injuries is an alphabetical listing of medical terms, with each term mapped to one or more ICD-10 code. The following references for the code I50.9 are found in the index:
- – cardiac – See Also: Failure, heart – I50.9
- – cardiovascular – See Also: Failure, heart – I50.9
- – heart – See Also: Failure, heart – I50.9
- – myocardial – See Also: Failure, heart – I50.9
- – cardiac – See Also: Failure, heart – I50.9
Don’t Miss: How To Calculate Target Heart Rate Zone
Treatment For Congestive Heart Failure
There are several medications that can be used to treat CHF. The first is ACE inhibitors. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors open up narrowed blood vessels to improve blood flow. Vasodilators are another option if you cannot tolerate ACE inhibitors. ACE inhibitors shouldnt be taken with the following medications without consulting with a doctor, because they may cause an adverse reaction. The second type of medication is beta-blockers. Beta-blockers can reduce blood pressure and slow rapid heart rhythm. Beta-blockers should be taken with caution with the following medications, as they may cause an adverse reaction. The third type of medication is diuretics. Diuretics reduce your bodys fluid content. CHF can cause your body to retain more fluid than it should. Thiazide diuretics cause blood vessels to widen and help the body remove any extra fluid. Loop diuretics cause the kidneys to produce more urine. This helps remove excess fluid from your body. Potassium-sparing diuretics help get rid of fluids and sodium while still retaining potassium. If medications arent effective on their own, more invasive procedures may be required. Angioplasty, a procedure to open up blocked arteries, is one option. Your cardiologist may also consider heart valve repair surgery to help your valves open and close properly.
The table below includes the most commonly used ICD-10 codes for Congestive Heart Failure:
| ICD-10 Chapter |
|---|
Chronic Diastolic Heart Failure
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I50.3
- 2016201720182019202020212022Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code
- Diastolic left ventricular heart failure
- Heart failure with normal ejection fraction
- Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
- end stage heart failure, if applicable
Don’t Miss: How Long Can Someone Live With Heart Failure
Diseases Of The Circulatory Systemtype 2 Excludes
- 2016201720182019202020212022Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code
Code First
Unspecified Systolic Heart Failure
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- I50.20 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I50.20 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I50.20 – other international versions of ICD-10 I50.20 may differ.
- Applicable To annotations, or
You May Like: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
Chf Icd 10 Codes And Guidelines
Most of the heart failure codes include in chapter 9 of ICD-10 CM manual, diseases of circulatory system, code range I00-I99.
- Combination code If patient has any type of heart failure and hypertension, it should be combined and coded as I11.0 eventhough physician has not linked both. It should not be coded combined if the medical record states the conditions are unrelated.
- Heart failure should be coded additionally when coding I11.0
- Do not code I11.9 when coding I11.0 .
- When coding biventricular heart failure it is necessary to code the type of left heart failure also according to the code also note with I50.82
Go by Failure, Heart to find correct codes for heart failure in ICD-10 CM manual index.
Look at the below scenarios to clearly understand the coding concepts of CHF.
CHF ICD 10 Code Example 1
Elizabeth is a 65 year old female who comes to emergency department for shortness of breath and leg edema from past 2 days. She came to visit doctor as the symptoms are getting worse. She has hypertension and takes Lisinopril for the same. She does not have chest pain or palpitation. She is not a smoker. Her family history includes heart disease for her mother and brother. Vitals showed temperature 97.3 F, heart rate 72 bpm, respiratory rate 25, BP 150/96 mmHg. Physical exam showed pitting edema on both the extremities, shortness of breath and dry skin. Physician ordered for blood tests, EKG and chest X-ray. This case was diagnosed as acute diastolic heart failure.
Unspecified Diastolic Heart Failure
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- 2016201720182019202020212022Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code
- I50.1 Left ventricular failure, unspecified
- I50.2 Systolic heart failure
- I50.20 Unspecified systolic heart failu…
- I50.21 Acute systolic heart failure
- I50.22 Chronic systolic heart failure
- I50.23 Acute on chronic systolic heart …
Don’t Miss: How To Find Thrz
