Will I Need A Procedure As Part Of My Left
A procedure may be necessary if:
- Your symptoms dont improve.
- Your testing or labs show signs of worsening heart failure.
Your care may include:
- Cardiac resynchronization therapy : An implantable device that uses a gentle electrical current to stimulate your hearts pumping action. Its also called a biventricular pacemaker.
- Electrical cardioversion: This procedure helps restore a normal rhythm.
- Implantable cardioverter defibrillator : This implantable device detects arrhythmias and sends a gentle electrical current to restore a normal rhythm.
- Left ventricular assist device : An implantable pump that helps the heart circulate blood.
- Heart transplant: Procedure to replace a worn-out heart with a healthy one from a donor. This treatment is for patients with the most severe forms of left-sided heart failure.
Discuss An Exercise Plan And Get Started
Your doctor may advise you to treat exercise as part of your overall plan to manage heart failure. Talk to your doctor about the right level of exercise for you, and how you can get started. Depending on your condition, they may recommend a cardiac rehabilitation program.
For many people, a great exercise for getting started is simply walking. You can build up gradually, walking for longer periods of time and at a quicker pace as your fitness level improves. If youre finding moderate activity difficult, let your doctor know and see what they suggest.
Surprisingly, some programs might use high intensity interval training . This form of exercise alternates very intense cardio exercise with short breaks.
You May Like: Frequently, What Is The Earliest Symptom Of Left-sided Heart Failure
What Is Cardiac Rehabilitation
Cardiac rehabilitation is an important program for anyone recovering from a heart attack, heart failure, or some types of heart surgery. Cardiac rehab is a supervised program that includes
- Physical activity
- Education about healthy living, including healthy eating, taking medicine as prescribed, and ways to help you quit smoking
- Counseling to find ways to relieve stress and improve mental health
A team of people may help you through cardiac rehab, including your health care team, exercise and nutrition specialists, physical therapists, and counselors or mental health professionals.
Test your knowledge of heart disease!
Read Also: Aspirin For Heart Attacks
Comorbidities: Anemia Iron Deficiency Kidney Failure Diabetes Frailty
Moderate anemia is often prevalent in patients with heart failure regardless of HFrEF or HFpEF . The incidence is higher in women, elderly and diabetic patients as well as in patients with renal failure. Increased blood loss in patients treated with oral anticoagulants , aspirin or both as well as decreased absorption of vitamin and/or iron may favor anemia. Similar as in other chronic illnesses iron deficiency is common in heart failure and may influence prognosis worse. Whether anemia and/or iron deficiency are markers of heart failure severity or whether they affect outcome of heart failure disease and thus should be treated is not entirely clear. In patients with heart failure with as well as without anemia intravenous ferric carboxymaltose has improved quality of life and NYHA class but not prognosis .
Heart failure and chronic kidney disease frequently coexist and share many risk factors also. CKD worsen prognosis in heart failure patients however, patients with severe CKD often have been excluded from randomized clinical trials and thus there is limited evidence-based therapy available.
Comorbidities and aging via influencing cognitive and self-care ability affect management of heart failure patients. Also, polypharmacy is present often. In addition, frailty is common in these patients. In consequence, a multidisciplinary team is needed to take care especially for older heart failure patients to reduce hospitalizations and improve outcome.
European Society Of Cardiology’s Guidelines For Diagnosis Of Heart Failure
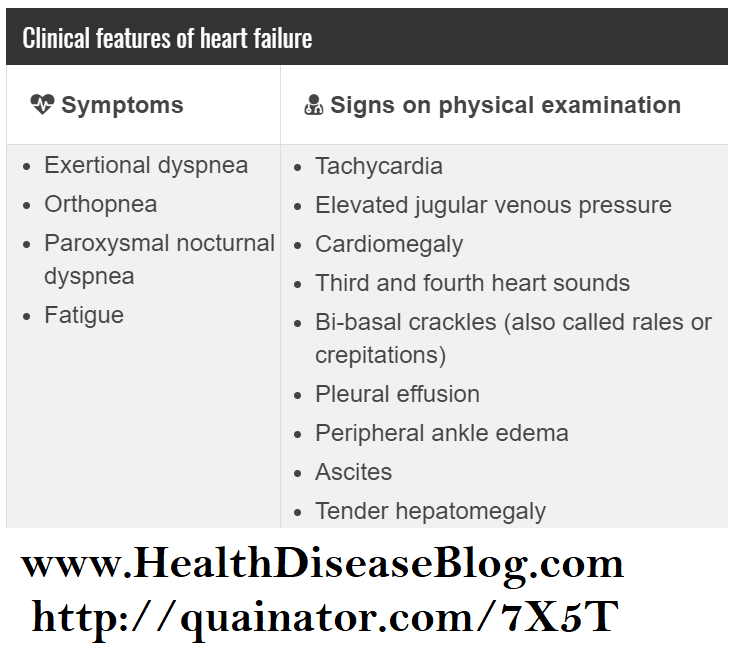
Essential features
- ArrhythmiasAtrial fibrillation ventricular arrhythmias bradyarrhythmias
- ThromboembolismStroke peripheral embolism deep venous thrombosis pulmonary embolism
- GastrointestinalHepatic congestion and hepatic dysfunction malabsorption
- MusculoskeletalMuscle wasting
- RespiratoryPulmonary congestion respiratory muscle weakness pulmonary hypertension
Recent observational data from the studies of left ventricular dysfunction and vasodilator heart failure trials indicate that mild to moderate heart failure is associated with an annual risk of stroke of about 1.5% , rising to 4% in patients with severe heart failure. In addition, the survival and ventricular enlargement study recently reported an inverse relation between risk of stroke and left ventricular ejection fraction, with an 18% increase in risk for every 5% reduction in left ventricular ejection fraction this clearly relates thromboembolism to severe cardiac impairment and the severity of heart failure. As thromboembolic risk seems to be related to left atrial and left ventricular dilatation, echocardiography may have some role in the risk stratification of thromboembolism in patients with chronic heart failure.
Also Check: How To Help Heart Palpitations
Left Ventricular Assist Device
A left ventricular assist device is a mechanical pump operated by a battery thats implanted via open-heart surgery. There are different types, but they all have four parts, including:
Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction Treatment
Diuretics are a mainstay of HFpEF treatment. For these medications to be helpful, however, you need to also make changes to your diet and overall lifestyle.
If you have HFpEF, your doctor will likely suggest you follow a treatment regimen that includes a combination of:
- Diet and lifestyle changes
- For some patients, a device to protect the heart from abnormal rhythms
Diet and Lifestyle Changes
If you have heart failure, the following lifestyle changes may help you manage your symptoms:
- Regular low-intensity aerobic exercise to strengthen the heart
- Cutting back on salt
- Limiting your alcohol consumption
- Quitting smoking
Reducing your salt intake is especially important. Too much salt in your diet can cause fluid retention. This will counteract the drugs that help relieve fluid accumulation.
The effectiveness of medication in the treatment of diastolic heart failure is inconclusive. Therefore, the best way to manage HFpEF is to treat its underlying cause, such as hypertension, diabetes, or coronary artery disease.
SGLT2 inhibitor medications are antidiabetic drugs that may be used to treat HFpEF in people with or without diabetes. In people with heart failure, taking this medication can help prevent heart failure episodes. Your doctor can determine whether you are able to use an SGLT2 inhibitor.
Management by Stage
The American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association recommend that cardiologists manage heart failure by stage.
Read Also: Have Statins Reduced Heart Attacks
Heart Failure Treatment Is A Team Effort
Heart failure management is a team effort, and you are the key player on the team. Your heart doctor will prescribe your medications and manage other medical problems. Other team members — including nurses, dietitians, pharmacists, exercise specialists, and social workers — will help you achieve success. But it is up to YOU to take your medications, make dietary changes, live a healthy lifestyle, keep your follow-up appointments, and be an active member of the team.
If you notice anything unusual, don’t wait until your next appointment to discuss it with your doctor. Call them right away if you have:
- Unexplained weight gain
- Swelling in your ankles, feet, legs, or belly that gets worse
- Shortness of breath that gets worse or happens more often, especially if you wake up feeling that way
- Bloating with a loss of appetite or nausea
- Extreme fatigue or more trouble finishing your daily activities
- A lung infection or a cough that gets worse
- Fast heart rate
- New irregular heartbeat
What Can I Do To Recover After A Heart Attack
Take our quiz to see how much you know about cardiac rehabilitation.
If youve had a heart attack, your heart may be damaged. This could affect your hearts rhythm and its ability to pump blood to the rest of the body. You may also be at risk for another heart attack or conditions such as stroke, kidney disorders, and peripheral arterial disease .
You can lower your chances of having future health problems following a heart attack with these steps:
- Physical activityTalk with your health care team about the things you do each day in your life and work. Your doctor may want you to limit work, travel, or sexual activity for some time after a heart attack.
- Lifestyle changesEating a healthier diet, increasing physical activity, quitting smoking, and managing stressin addition to taking prescribed medicinescan help improve your heart health and quality of life. Ask your health care team about attending a program called cardiac rehabilitation to help you make these lifestyle changes.
- Cardiac rehabilitationCardiac rehabilitation is an important program for anyone recovering from a heart attack, heart failure, or other heart problem that required surgery or medical care. Cardiac rehab is a supervised program that includes
- Physical activity
- Education about healthy living, including healthy eating, taking medicine as prescribed, and ways to help you quit smoking
- Counseling to find ways to relieve stress and improve mental health
Also Check: Is 200 Heart Rate Bad
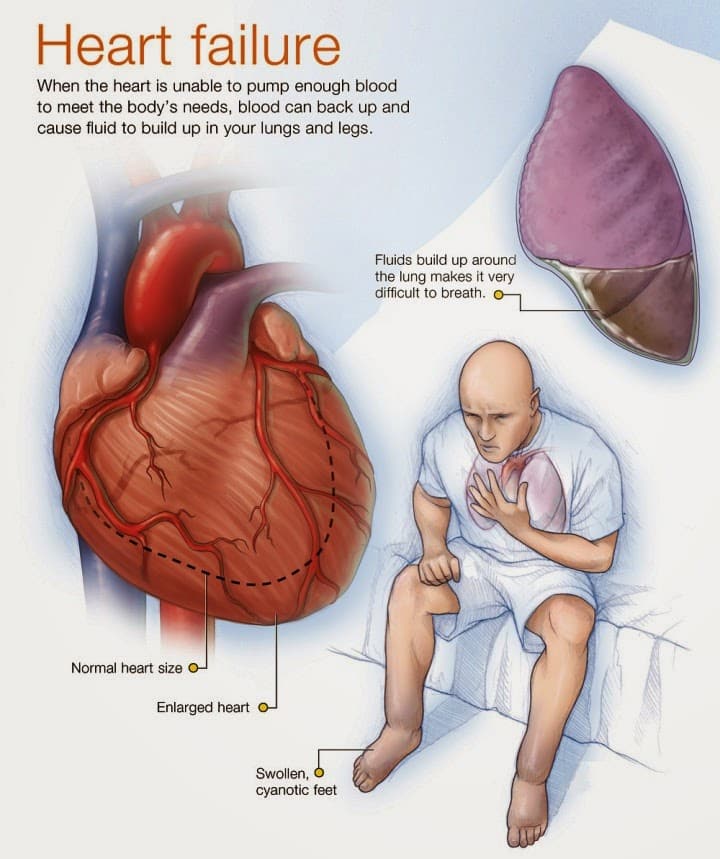
How Does Heart Failure Affect The Body
Heart failure can affect the right side of the heart, the left side of the heart, or both sides.
When the right side of the heart begins to function less efficiently, it is unable to pump much blood forward into the vessels of the lungs. Because of the congestion in the right side of the heart, blood flow begins to back up into the veins. Eventually, swelling is noticed in the feet, ankles, lower legs, eyelids, and abdomen due to fluid retention.
When the left side of the heart fails, it is unable to pump blood forward out to the body efficiently. Blood begins to back up into the vessels in the lungs, and the lungs become stressed. Breathing becomes faster and more difficult. Also, the body does not receive enough blood to meet its needs, resulting in fatigue and poor growth in children.
When Should I Get Emergency Care
Go to the ER or call 911 if you have:
- New, unexplained, and severe chest pain that comes with shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, or weakness
- Fast heart rate , especially if you are short of breath
- Shortness of breath that doesn’t get better if you rest
- Sudden weakness, or you can’t move your arms or legs
- Sudden, severe headache
- Fainting spells
Don’t Miss: What Dose Of Aspirin For Heart Attack
Can Surgery Be Used To Treat Heart Failure
In heart failure, surgery may sometimes prevent further damage to the heart and improve the heart’s function. Procedures used include:
- Coronary artery bypass grafting surgery. The most common surgery for heart failure caused by coronary artery disease is . Although surgery is more risky for people with heart failure, new strategies before, during, and after surgery have reduced the risks and improved outcomes.
- Heart valve surgery. Diseased heart valves can be treated both surgically and non-surgically .
- Implantable left ventricular assist device . The LVAD is known as the “bridge to transplantation” for patients who haven’t responded to other treatments and are hospitalized with severe systolic heart failure. This device helps your heart pump blood throughout your body. It allows you to be mobile, sometimes returning home to await a heart transplant. It may also be used as destination therapy for long-term support in patients who are not eligible for transplant.
- Heart transplant. A heart transplant is considered when heart failure is so severe that it doesn’t respond to all other therapies, but the person’s health is otherwise good.
What Are The Risk Factors For Heart Disease
High blood pressure, high blood cholesterol, and smoking are key risk factors for heart disease. About half of people in the United States have at least one of these three risk factors.2 Several other medical conditions and lifestyle choices can also put people at a higher risk for heart disease, including
Don’t Miss: Symptoms For Heart Attack In Woman
Nyha Functional Classification System
The New York Heart Association functional classification considers heart failure symptoms that happen during exercise to determine stage. Patients can go back and forth between stages depending on how well-controlled symptoms are on a given day.
- Stage 1: The person has heart disease, but it isnt yet causing symptoms or limiting activities.
- Stage 2: The person has mild symptoms that only slightly limit activity.
- Stage 3: The person has significant limitations to activities. He or she is only comfortable when resting.
- Stage 4: The person has major limitations and experiences symptoms when at rest.
Systolic And Diastolic Failure
Systolic and diastolic heart failure each result in a decrease in stroke volume. This leads to activation of peripheral and central baroreflexes and chemoreflexes that are capable of eliciting marked increases in sympathetic nerve traffic.
Although there are commonalities in the neurohormonal responses to decreased stroke volume, the neurohormone-mediated events that follow have been most clearly elucidated for individuals with systolic heart failure. The ensuing elevation in plasma norepinephrine directly correlates with the degree of cardiac dysfunction and has significant prognostic implications. Norepinephrine, while directly toxic to cardiac myocytes, is also responsible for a variety of signal-transduction abnormalities, such as downregulation of beta1-adrenergic receptors, uncoupling of beta2-adrenergic receptors, and increased activity of inhibitory G-protein. Changes in beta1-adrenergic receptors result in overexpression and promote myocardial hypertrophy.
Recommended Reading: Watches With Heart Rate
Types Of Heart Failure
The main types of heart failure are named for where they occur in the heart:
- Left-sided heart failure
- Biventricular heart failure
Clinicians also may classify heart failure as:
- Acute: You have active symptoms of heart failure, with either a new diagnosis or with long-term heart failure.
- Chronic: You have a history of heart failure, but your condition is relatively stable with no symptoms or with manageable symptoms.
Refractory Heart Failure And Pulmonary Edema
Patients presenting with acute heart failure include those who develop heart failure de novo as a consequence of another cardiac event, usually a myocardial infarction,6 and those who present for the first time with decompensation of previously asymptomatic and often unrecognized cardiac dysfunction . However, because of frequent recurrences, most episodes of decompensation occur in patients with established, chronic heart failure that has worsened as a result of the unavoidable natural progression of the syndrome, with an intercurrent cardiac or noncardiac event, or as a consequence of an avoidable reason, such as nonadherence with treatment or use of an agent that can alter renal function. Although it is not always identified, searching for a reversible precipitant is an important aspect of the initial therapy plan . Many patients with decompensated heart failure experience worsening over a period of days or weeks before presenting to their doctor.
Noninvasive ventilation using a tight-fitting mask to provide positive-pressure ventilation reduces respiratory distress and metabolic disturbances more rapidly than standard oxygen therapy but has not reduced short-term mortality. Intravenous infusion of a nitrate may also be valuable in patients with hypertension or myocardial ischemia .
Also Check: Congestive Heart Failure And Afib
What Is The Outlook For People With Heart Failure
With the right care, heart failure may not stop you from doing the things you enjoy. Your prognosis or outlook for the future will depend on how well your heart muscle is functioning, your symptoms, and how well you respond to and follow your treatment plan.
Everyone with a long-term illness, such as heart failure, should discuss their desires for extended medical care with their doctor and family. An “advance directive” or “living will” is one way to let everyone know your wishes. A living will expresses your desires about the use of medical treatments to prolong your life. This document is prepared while you are fully competent in case you are unable to make these decisions at a later time.
Show Sources
What Medications Should I Avoid If I Have Heart Failure
There are several different types of medications that are best avoided in those with heart failure including:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications such as Motrin or Aleve. For relief of aches, pains, or fever take Tylenol instead.
- Most calcium channel blockers
- Some nutritional supplements, such as salt substitutes, and growth hormone therapies
- Antacids that contain sodium
If youâre taking any of these drugs, discuss them with your doctor.
Itâs important to know the names of your medications, what theyâre used for, and how often and at what times you take them. Keep a list of your medications and bring them with you to each of your doctor visits. Never stop taking your medications without discussing it with your doctor. Even if you have no symptoms, your medications decrease the work of your heart so that it can pump more effectively.
You May Like: How Long Does It Take Atenolol To Lower Heart Rate
Treatments For Heart Failure
Treatment for heart failure usually aims to control the symptoms for as long as possible and slow down the progression of the condition.
How youre treated will depend on what is causing your heart failure.
Common treatments include:
- lifestyle changes including eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly and stopping smoking
- medicine a range of medicines can help many people need to take 2 or 3 different types
- devices implanted in your chest these can help control your heart rhythm
- surgery such as a or a heart transplant
Treatment will usually be needed for life.
A cure may be possible when heart failure has a treatable cause. For example, if your heart valves are damaged, replacing or repairing them may cure the condition.
How Is Heart Failure Diagnosed
Your doctor will ask you many questions about your symptoms and medical history. Youâll be asked about any conditions you have that may cause heart failure . Youâll be asked if you smoke, take drugs, drink alcohol , and about what drugs you take.
Youâll also get a complete physical exam. Your doctor will listen to your heart and look for signs of heart failure as well as other illnesses that may have caused your heart muscle to weaken or stiffen.
Your doctor may also order other tests to determine the cause and severity of your heart failure. These include:
Other tests may be ordered, depending on your condition.
Recommended Reading: How Does Alcohol Affect The Heart Rate
