Deterrence And Patient Education
Effective treatment of comorbidities and risk factor reduction can decrease the chance of developing heart failure. Patient education should be focused on ensuring compliance with prescribed evidence-based treatments.
- Hypertension – effective treatment of systolic and diastolic hypertension can reduce the risk of heart failure by approximately 50%
- Diabetes – is directly associated with the development of heart failure, independent of other associated clinical conditions
- Alcohol – heavy alcohol use is associated with heart failure
- Metabolic syndromes – important to keep up treatment based on evidence-based guidelines to decrease the risk of heart failure
- Patient education regarding dietary salt restriction and fluid restriction is imperative
Difference Between Pneumonia And Congestive Heart Failure
Categorized under Disease | Difference between Pneumonia and Congestive heart failure
Pneumonia vs congestive heart failure
Coughing is one of the commonest symptoms of any condition affecting the respiratory system, right from the nose to the lungs. Occasionally, it may be a symptom of a medical condition of the cardio-vascular system too. Few signs and accompanying symptoms will give the diagnosis to a qualified doctor. Pneumonia and a congestive heart failure are two very different medical conditions that might present just with a cough. Heres how the two differ.
Pneumonia is an infection of the lung tissue. It affects the air sacs called alveoli that form the lung tissue. It is most commonly caused by bacteria and viruses. Rarely is it caused by a fungus or due to an autoimmune disorder. Congestive heart failure is a serious medical condition where there is failure of the pumping action of the heart, leading to accumulation of blood within the heart and deficiency of it everywhere else in the body. Both of these have cough as a leading symptom and often the only one.
The cause of pneumonia commonly is an infectious agent like a virus, bacteria or a fungus. Causes of congestive heart failure are plenty. The leading cause of heart failures is ischaemic heart disease followed by smoking, diabetes, obesity, hypertension and congenital heart diseases.
Read Also: Fluticasone Heart Palpitations
Complications Of Heart Failure And Covid
People with heart failure are at a greater risk of becoming severely ill with COVID-19. One study found that among patients who were hospitalized with a COVID-19 infection, there was a 50% mortality rate among those with pre-existing heart failure compared with a mortality rate of 10% in individuals without heart failure.
Treatment for COVID-19 can also lead to serious complications for people with heart failure due to several contributing factors:
- Breathing can be difficult for people with heart failure even without a COVID-19 infection. Fluid can accumulate in the body, particularly in the lungs, since blood that cant be pumped throughout the body causes a backup. This can further reduce the much-needed oxygen supply in people with heart failure. Additionally, COVID-19 usually results in pneumonia and decreased movement of oxygen across the cells in the lung to the bloodstream.
- As COVID-19 and heart failure create difficulty for the body to breathe and pump blood, a persons chances of requiring mechanical ventilation increase. This may seem like the fix. However, especially for people with heart failure, there has been evidence that the high pressure required to support the breathing of people with COVID-19 on mechanical ventilation can further increase pressure in the pulmonary vessels. This creates even greater strainand damageto the heart.
- Severe COVID-19 infection has also been known to cause kidney damage, which can further increase the workload of the heart.
Also Check: Left Sided Vs Right Sided Heart Failure
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
The treatment of heart failure and acute decompensated heart failure is challenging despite the use of maximal evidence-based therapy based on the stage of heart failure. Given the limited effect that current treatment strategies have on the progression of heart failure, it is important to identify ways to maximize patient outcomes and quality of care by the interprofessional team.
Patients at potential risk for heart failure based on comorbidities or other identified risk factors should receive appropriate evidence-based preventative counseling and treatments. When appropriate, the primary care providers who may be the most involved in the management of the patients’ risk factors should consult other specialists, including cardiologists, endocrinologists, pharmacists, cardiology nurses, and nutritionists, to ensure that they are providing the best advice and treatment for their patients. Nurses monitor patients, provide education, and collaborate with the physicians and the rest of the team to improve outcomes. Pharmacists review medications, inform patients and their families about side effects and monitor compliance.
Given the propensity of heart failure patients to require re-current admissions, often because of non-heart failure related conditions, the collaboration between inpatient and outpatient services can be of benefit in the continuity of care and helping promote improved outcomes.
Data On Heart Failure
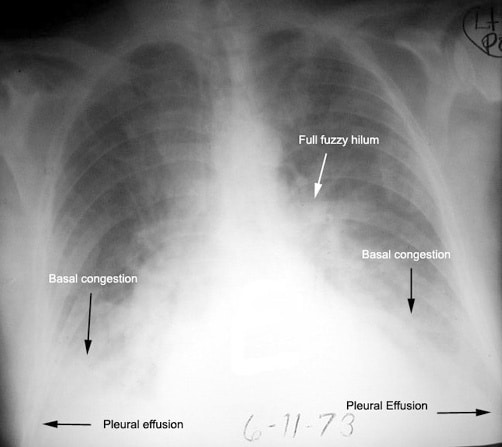
Data on markers for heart failure among study patients were obtained from the counties hospital discharge registries. Heart failure was defined as a previous hospital discharge diagnosis or outpatient diagnosis of congestive heart failure pulmonary edema left ventricular failure unspecified heart failure cardiomyopathy or hypertensive heart disease with congestive heart failure . We considered diagnoses recorded within five years preceding the date of hospitalization for pneumonia . We further disaggregated patients with heart failure into five categories of heart failure-related conditions: 1) cardiomyopathy 2) heart valve disease 3) myocardial infarction , 4) atrial fibrillation only 5) none of the above diagnoses.
You May Like: High Blood Pressure And High Heart Rate
Symptoms Of Reduced Pumping Capability
The most prominent symptoms are:
- Extreme weakness and fatigue
- Muscle weakness and muscle wasting
- Lethargy and inanition
- Extreme weight loss
Obviously, symptoms like this are not compatible with a long life. Unless the cardiac function can be improved, or unless cardiac transplantation or a ventricular assist device can be used, once a person with heart failure develops these kinds of symptoms, death usually follows relatively soon.
Also Check: Is Congestive Heart Disease Hereditary
Cardiovascular Complication After Cap
Involvement of the cardiovascular system after developing CAP is as an important short- and long-term co-morbidity., Corrales-Medina et al. performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies, and found that CC occurred in 18% of CAP patients. Most of the studies showed that the rate of CC is higher among hospitalized patients than outpatients.
Several risk factors are associated with the development of CC in patients with pneumonia. The strongest associated risk factor is preexistent CVD preceding the pneumonia event. Patients with CAP older than 65âyears tend to have higher rates of co-morbidities. The most common co-morbidities include chronic obstructive pulmonary disease , ischaemic heart disease, congestive heart failure, diabetes and stroke. However, all these conditions seem to be overrepresented among hosts with compromised immunological status, potentially leading to poor clinical outcomes. In addition, many of these co-morbidities are associated with poor functional and disability status, usually requiring admission to long-term care facilities.,
You May Like: Why Do Fit People Have Heart Attacks
What Do You Do When You Develop Pneumonia And Congestive Heart Failure
Former Bodybuilder- Pro Wrestler-Host Rics Corner, Designer of the Iconic Golds Gym and World Gym Logos, former training Partner of Arnold Schwarzenegger, Demi Hulk Incredible Hulk TV Series
Last week I was in the gym feeling strong but still felt something was wrong with my breathing and tiredness. Heavy chest and walking block and getting tired however the weight workouts were fine and had one of my strongest days ever.
Then a few days later I end up in the hospital after seeing three doctors and last day was almost the end of the line for me. I was admitted and tested for everything.
Trust me the hospital was the last place I wanted to be. I cant lay in a bed for days. They found fluid around my lungs with blood in it. Two liters full as they drained it out of my back with a tube.
It wasnt painful but I was shocked at what they found. Plus it was what they call pleural effusion which fluid surrounds the heart making it hard to pump and the heart rate increases rapidly.
The lungs get compressed and if its for any length of time, they take more time to open up and then you have to practice breathing deeper to open them more. This is all very uncomfortable. I do not like being chained to the house with oxygen following me everywhere but this is what i have to do if I dont want the alternative.
Ive got my eye on this again.
Congestive Heart Failure: Prevention Treatment And Research
Congestive heart failure is a serious condition in which the heart doesnt pump blood as efficiently as it should. Despite its name, heart failure doesnt mean that the heart has literally failed or is about to stop working. Rather, it means that the heart muscle has become less able to contract over time or has a mechanical problem that limits its ability to fill with blood. As a result, it cant keep up with the bodys demand, and blood returns to the heart faster than it can be pumped outit becomes congested, or backed up. This pumping problem means that not enough oxygen-rich blood can get to the bodys other organs.
The body tries to compensate in different ways. The heart beats faster to take less time for refilling after it contractsbut over the long run, less blood circulates, and the extra effort can cause heart palpitations. The heart also enlarges a bit to make room for the blood. The lungs fill with fluid, causing shortness of breath. The kidneys, when they dont receive enough blood, begin to retain water and sodium, which can lead to kidney failure. With or without treatment, heart failure is often and typically progressive, meaning it gradually gets worse.
More than 5 million people in the United States have congestive heart failure. Its the most common diagnosis in hospitalized patients over age 65. One in nine deaths has heart failure as a contributing cause.
Read Also: Is Green Tea Good For Heart Attack Patients
Prognosis Of Patients With Pre
A paper in the Journal of General Internal Medicine states: Thirty-day mortality from pneumonia was 24.4% among heart failure patients vs. 14.4% among other pneumonia patients.
The paper adds, We identified 33,736 patients with a first-time hospitalization for pneumonia, of whom 3,210 had a previous diagnosis of heart failure. The median age was 73 years
In addition: We were able to adjust for a wide range of prognostic factors assumed to be important for pneumonia, including cardiovascular disease, chronic lung disease, liver cirrhosis, and renal disease.
The paper also says that Our data indicated that pneumonia mortality increased with preadmission heart failure severity. treatment
Lorra Garrick has been covering medical, fitness and cybersecurity topics for many years, having written thousands of articles for print magazines and websites, including as a ghostwriter. Shes also a former ACE-certified personal trainer.
Treatment For Pneumonia In A Heart Failure Patient: What To Expect
An elderly person with pneumonia, who has pre-existing heart failure, presents a tricky situation to doctors.
My very elderly father, who has congestive heart failure, was diagnosed with pneumonia at an urgent care center. The doctor wanted him admitted to a hospital.
When my mother was diagnosed with pneumonia for the first time at an elderly age, she too, had congestive heart failure, but was not admitted, and instead, sent home with a prescription for antibiotics and recovered.
A few years later she developed pneumonia a second time and was admitted overnight in the observation unit, but discharged the next day with a prescription for antibiotics and recovered.
I anticipated that my father, whose heart was seemingly stronger than my mothers, would be discharged the next day with a prescription for antibiotics.
But he was discharged from the hospital seven days later.
Heres a summary of how the pneumonia treatment went down, due to the pre-existing heart failure.
The pneumonia treatment involved an IV infusion of fluids. Due to the pre-existing heart failure, my father was on Lasix, a diuretic that promotes fluid excrement from the body.
Early on in his admission, my fathers weight went up, which meant unwanted fluid retention.
It was not clear exactly how much of this was being caused by the IV infusion of fluids any fluid buildup in the lungs from the pneumonia or the pre-existing heart failure being worsened by the infection.
Peripheral edema. Shutterstock/AppleDK
Also Check: Why Is Resting Heart Rate Important
Telling The Difference Between Dog Congestive Heart Failure And Pneumonia
My dog has an enlarged heart,a murmur and is coughing.An echo and an x-ray were taken in nov 2009 and the cardiologist said her heart is not in congestive failure so no medication was prescribed.She is still coughing but the cough now sounds like she has fluid in her lungs. how do i know if she is now in congestive heart failure or could it be something else like phnemonia? Thanks for your help.
-
By: Erin Broersma El Segundo, CA
Replied on 04/19/2011
If she has an enlarged heart and a murmur, there are medications that help the heart pump more efficiently. I would say if she saw a cardiologist, I would ask them about products such as Enalapril and Digoxin. If she is coughing due to her heart murmur, there are also medications that help open airways and pull fluid from the chest Theophylline, and Lasix . If she has pneumonia, she will be running a fever. She also will not feel well. If she is lethargic and not wanting to eat/drink, I would be concerned that she has pneumonia. It seems more likely, with her medical history, that she may be coughing due to the fact her heart is not working as well as it could be and fluid is forming around her heart and in her lungs. This is a normal side-effect of such a diagnosis and medications tend to alleviate the excess fluid and allow her to breathe much better, while reducing or eliminating the coughing.
Data On Hospitalizations For Pneumonia
We identified patients aged at least 15 years of age, with a first-time hospitalization for pneumonia during the three data collection periods, using counties hospital discharge registries merged into a research database, as previously described 13. The registries contain key information on all patient discharges from non-psychiatric hospitals in the counties since 1977 . Data include patients civil registration numbers, admission and discharge dates, and up to 20 discharge diagnoses coded exclusively by physicians according to the International Classification of Diseases . The ICD-10 codes used for pneumonia hospitalizations were J12-J18, A481, and A709.
Also Check: Can Turmeric Cause Heart Palpitations
Pneumonia Risk Soars In Heart Failure Patients Especially Hfpef
FROM JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
Patients with heart failure get pneumonia at a rate almost three times greater than expected and, once they do get pneumonia, have about a fourfold greater risk of death, investigators for a retrospective analysis of 13,000 patients from two landmark randomized HF trials have found.
Dr. John J.V. McMurray
The investigators also found that HF patients with preserved ejection fraction are at the highest risk of developing pneumonia. The findings underscore the importance of patients with HF getting a pneumonia vaccination, they found.
The analysis showed that 6.3% of patients in the PARADIGM-HF trial and 10.6% of those in the PARAGON-HF trial developed pneumonia, reported the study authors, led by John J.V. McMurray, MD, of the British Heart Foundation Cardiovascular Research Center at the University of Glasgow in Scotland .
The main reason for doing this study was the fact that many heart failure patients are not vaccinated, as they should be, against pneumonia both pneumococcus and influenza vaccination, Dr. McMurray said in an interview. We wanted to document the frequency and consequences of pneumonia in patients with heart failure to help highlight this deficiency in care.
Dr. McMurray said he believes this is the first study to document the incidence of pneumonia and pneumonia-related outcomes according to the two major ejection fraction phenotypes.
Recommended Reading: Swollen Ankles Heart Failure
Pneumonia As A Cardiovascular Disease
Division of Pulmonary Diseases and Critical Care Medicine, South Texas Veterans Health Care System, San Antonio, TX, USA
Department of Medicine, University of Texas Health at San Antonio, San Antonio, TX, USA
Luis F. Reyes
Division of Pulmonary Diseases and Critical Care Medicine, South Texas Veterans Health Care System, San Antonio, TX, USA
Department of Medicine, University of Texas Health at San Antonio, San Antonio, TX, USA
Division of Pulmonary Diseases and Critical Care Medicine, South Texas Veterans Health Care System, San Antonio, TX, USA
Department of Medicine, University of Texas Health at San Antonio, San Antonio, TX, USA
Luis F. Reyes
Division of Pulmonary Diseases and Critical Care Medicine, South Texas Veterans Health Care System, San Antonio, TX, USA
Department of Medicine, University of Texas Health at San Antonio, San Antonio, TX, USA
Recommended Reading: What Should Heart Rate Be When Running
What Are The Stages Of Congestive Heart Failure
The New York Heart Association has developed a scale that commonly is used to determine the functional capabilities of heart failure.
New York Heart Association Functional Classification of Heart Failure
