What Procedures And Tests Diagnose Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive heart failure CHF can be confused with other illnesses that cause breathing difficulties, such as bronchitis, pneumonia, emphysema, and asthma. Talking to a medical professional, along with receiving a physical exam and tests available only at a medical office or hospital, are necessary to make an definitive diagnosis. Some of the most useful tests are mentioned below.
Chest X-ray: This is very helpful in identifying the buildup of fluid in the lungs. Also, the heart usually enlarges in congestive heart failure, and this may be visible on the X-ray film. In addition, other disorders may be diagnosed.
- An electrocardiogram is a painless test that measures the electrical activity of the heart. For this test, which takes just a few minutes, one lies on a table with electrodes attached to the skin of the chest, arms, and legs. The ECG can reveal several different heart problems that can cause heart failure, including heart attacks, rhythm disorders, long-standing strain on the heart from high blood pressure, and certain valve problems.
- However, the ECG result may be normal in heart failure.
Blood tests: People may have blood drawn for lab tests.
Echocardiogram : This is a type of ultrasound that shows the beating of the heart and the various cardiac structures. It is safe, painless, and one of the most important tests for diagnosing and following patients with heart failure over time.
MRI :
What Is Congestive Heart Failure
This is a type of disease the heart is not able to pump enough oxygenated blood to other parts of the body. The body tries to compensate for this problem in different ways.
The heartbeats get faster and take less time to refill after it contracts, but extra efforts can cause heart palpitations for longer. In some cases, the heart can also enlarge in size and bit to make room for the blood. The lungs fill with fluid, which causes shortness of breath. It also affects the kidney and can cause kidney failure when they do not receive enough blood.
Without and with treatment, heart failure is often and most progressive, which means it gradually gets worse. The best way to overcome this disease is the proper treatment, maintaining a healthy weight, a healthy lifestyle, good heart health, and a healthy diet. All these help in the treatment of heart disease.
More than around 5 million people in the United States of America have congestive heart failure. It is a very common diagnosis in hospitalized patients over age 65 years.
Heart Failure Treatment Is A Team Effort
Heart failure management is a team effort, and you are the key player on the team. Your heart doctor will prescribe your medications and manage other medical problems. Other team members — including nurses, dietitians, pharmacists, exercise specialists, and social workers — will help you achieve success. But it is up to YOU to take your medications, make dietary changes, live a healthy lifestyle, keep your follow-up appointments, and be an active member of the team.
If you notice anything unusual, don’t wait until your next appointment to discuss it with your doctor. Call them right away if you have:
- Unexplained weight gain
- Swelling in your ankles, feet, legs, or belly that gets worse
- Shortness of breath that gets worse or happens more often, especially if you wake up feeling that way
- Bloating with a loss of appetite or nausea
- Extreme fatigue or more trouble finishing your daily activities
- A lung infection or a cough that gets worse
- Fast heart rate
- New irregular heartbeat
Recommended Reading: Which Of The Following Would Lead To A Decreased Heart Rate
Menopause And Hormone Therapy
Menopause does not cause heart disease. But the decline in estrogen after menopause may be one of several factors in the increase in heart disease risk.
Other risks, such as weight gain, may also increase around the time of menopause.
Hormone therapy can be used to treat some of the problems women have during menopause. However, the FDA has not approved any estrogen hormone replacement therapy for reduction of heart disease. Learn more about menopause and hormones.
How Could I Get It
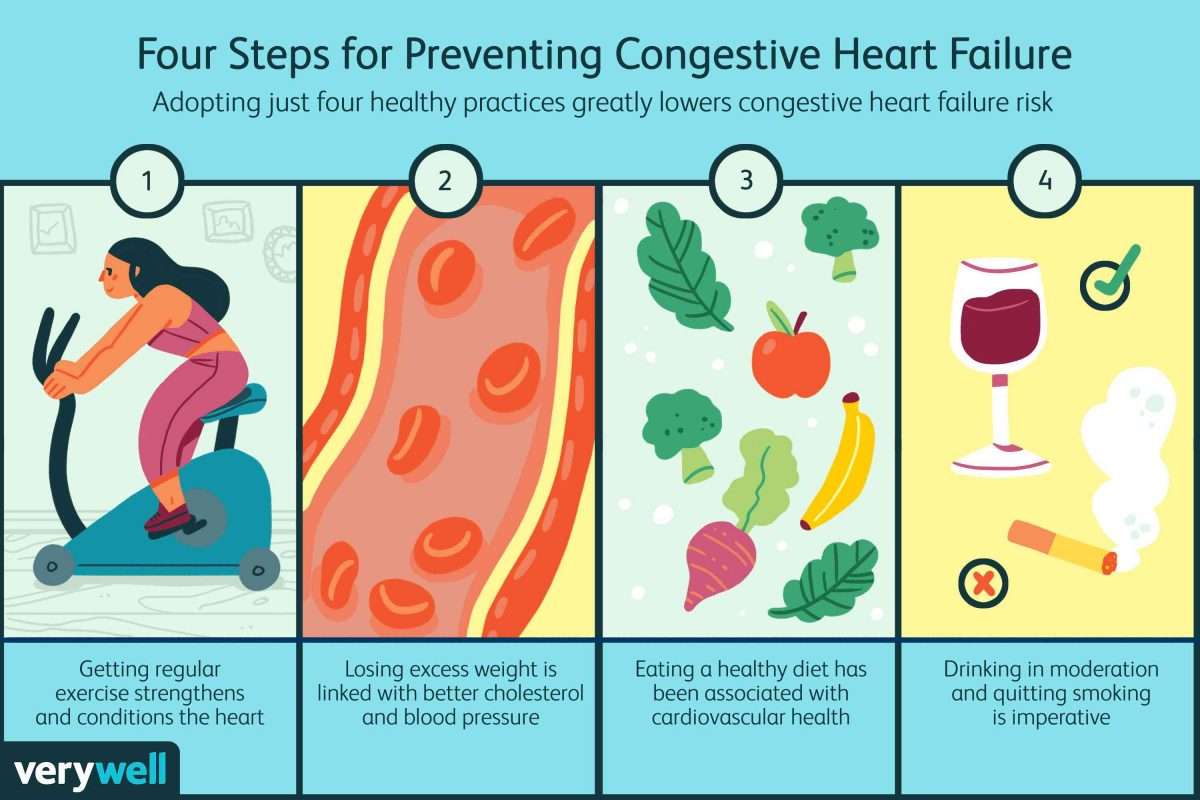
Certain problems can make your heart work harder than it should and weaken the muscle. Some of these are:
- High blood pressure
- Past heart attack
- Being too overweight
Things like drinking too much alcohol, smoking, and using illegal drugs are all known to damage your heart.
Some things that raise your chances of heart failure are out of your control, including:
- Race
- Heart defects you’re born with
- Age
Read Also: Does High Heart Rate Mean High Blood Pressure
Here Are More Unsettling Facts:
- Heart disease causes 1 in 3 womens deaths each year, killing approximately one woman every minute.
- 90 percent of women have one or more risk factors for developing heart disease.
- Since 1984, more women than men have died each year from heart disease and the gap between men and womens survival continues to widen.
- The symptoms of heart disease can be different in women vs. men, and are often misunderstood.
- While 1 in 31 American women dies from breast cancer each year, 1 in 3 dies of heart disease.
Types Of Heart Failure
There are several anatomical types of heart failure that can lead to CHF. Both the right and left sides of the heart can fail, but left-sided heart failure is much more common than right-sided heart failure.
Most of the hearts pumping power comes from the left side. The left side of the heart receives oxygenated blood from the lungs and pumps it to the rest of the body. If the large and powerful chambers of the left ventricle and left atrium begin to fail, the left side of the heart has to work harder to pump blood.
Over time, blood can build up in the pulmonary veins, leading to shortness of breath and trouble breathing, especially during physical activity. If left untreated, the right side of the heart may begin to fail as well.
There are two types of left-sided heart failure: heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction .
Don’t Miss: Bayer Aspirin And Heart Attacks
Know The Top 5 Heart Attack Warning Signs
- Chest discomfort, such as pain, pressure, squeezing or fullness in the center of your chest, lasting more than a few minutes or going away and then coming back
- Discomfort elsewhere in the upper body, such as in one or both arms, back, neck, jaw or stomach
- Lightheadedness
- Nausea
- Shortness of breath
Note: While the most common symptom among both sexes is chest discomfort, women suffering a heart attack are more likely than men to experience nausea, shortness of breath and back or jaw pain.
What Is The Importance Of Ejection Fraction
Your ejection fraction is one way to measure the severity of your condition. If its below normal, it can mean that you have heart failure. Your ejection fraction tells your healthcare provider how good of a job your left or right ventricle is doing at pumping blood. Usually, your EF number is talking about how much blood your left ventricle is pumping out because its your heart’s main pumping chamber.
Several non-invasive tests can measure your EF. With this information, your healthcare provider can decide how to treat you or find out if a treatment is working as it should.
A normal left ventricular ejection fraction is 53% to 70%. An LVEF of 65%, for example, means that 65% of the total amount of blood in your left ventricle is pumped out with each heartbeat. Your EF can go up and down, based on your heart condition and how well your treatment works.
Also Check: Why Does My Heart Rate Increase After Drinking Alcohol
What Causes Heart Failure
Although the risk of heart failure doesnt change as you get older, youre more likely to have heart failure when youre older.
Many medical conditions that damage the heart muscle can cause heart failure. Common conditions include:
- Tobacco and recreational drug use.
- Medications. Some drugs used to fight cancer can lead to heart failure.
Know Your Risk Factors
Certain populations have a higher risk for heart failure than others. Adults who are 65 or older have a higher risk than younger people. However, children and adolescents can have heart failure as well, particularly those who have a congenital heart defect. Men have a slightly higher risk for heart failure than women, and African-Americans have a higher risk than other races or ethnicities.
People who are overweight or obese also have a high risk for heart failure, as do people who have previously had a heart attack. Those suffering from coronary artery disease, in which narrowed arteries limit the heart’s supply of oxygen-rich blood, also have a high risk. Diabetes and some diabetes medications can increase the risk for congestive heart failure.
Other risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption.
You May Like: What Is Your Heart Rate Supposed To Be
Signs And Symptoms Of Congestive Heart Failure
During heart failure, the body tries to compensate for reduced blood flow in other ways, including:
- Enlarging the Heart Chamber This is the bodys attempt to get the heart to contract more strongly, in order to pump more blood. Initially, it may help the heart function more efficiently, but ultimately it causes the heart to not pump as effectively and causes fluid retention, leading to congestion in the lungs.
- Developing More Heart Muscle Mass The contracting cells in the heart get bigger, which initially lets the heart pump more strongly.
- Increasing Heart Rate This causes the heart to pump faster and increase its output.
- Increasing Fluid and Salt Retention and Tightening Some Blood Vessels This helps maintain the hearts normal output.
These compensations may mask heart failure temporarily, but eventually heart failure gets worse, and people start to experience symptoms.
- F: Fatigue
How Is Congestive Heart Failure Treated
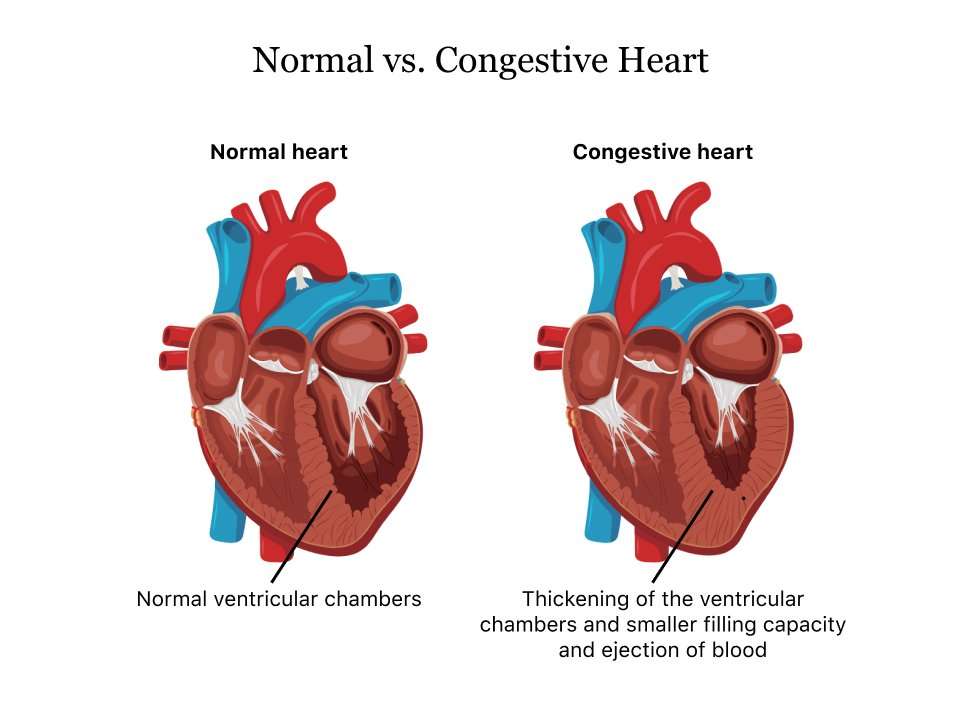
Doctors will assess the current health status of the patient to establish a baseline, and develop a long-term health plan with the goal of improving the patients health. This may involve the optimization of medicines and therapies, adding new medication, or possibly enrollment in a clinical trial.
Stabilizing and/or reversing a patients condition often involves long-term, collaborative follow-up with a referring cardiologist or physician.
In serious situations, advanced therapies, which include mechanical solutions, a heart transplant, or hospice, may be offered.
Read Also: Is Pulse Rate And Heart Rate The Same Thing
Early Intervention In Patients At Risk For Coronary Heart Failure
The patient with a dilated left ventricle already has a reduced life expectancy that can only modestly be prolonged with ACE inhibitor therapy.13 Identification of high-risk patients and early intervention before ventricular dysfunction has developed is an attractive public health strategy. This strategy has already been demonstrated to be effective in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Some patients, especially those who develop infarcts of the anterior wall, develop late ventricular dilation, which significantly increases morbidity and reduces survival rate. Early intervention with ACE inhibitors has been demonstrated to slow the progression of left ventricular enlargement and reduce morbidity and mortality.14,15
Other interventions, including the early administration of nitroglycerin and the early administration of beta blockers, have also been tested in patients with acute myocardial infarction with varying results. Some studies have shown early administration of nitrates to be beneficial18 and others have not.19 It is likely that selective administration of these drugs would be effective in responsive patient populations, but the criteria for identifying these populations are not yet available.
Heart Failure Vs Congestive Heart Failure: What’s The Difference
Heart failure affects people of all ages, from children and young adults to the middle-aged and older adults. About 6.2 million adults in the United States are currently living with heart failure, and over 64 million people are dealing with some form of heart failure worldwide.
Approximately 550,000 new cases are diagnosed in the United States each year, but many more remain undiagnosed as the initial symptoms of heart failure can be subtle and mimic similar symptoms seen in other conditions.
Congestive heart failure refers to the inadequate functioning of the heart muscle such that fluid builds up in the lungs, abdomen, feet, and arms . The condition can either be acute or chronic .
Untreated heart disease can be aggressive and fatal. The five-year survival rate is about 50% for all stages. In 2018, heart failure led to nearly 400,000 deaths, according to death certificate data, with the highest prevalence of disease primarily in the South and Midwest.
Also Check: How To Check Resting Heart Rate
Take Charge Of Your Medical Conditions
If you have high cholesterol, high blood pressure, or diabetes, you can take steps to lower your risk for heart disease.
Your health care team should test your blood levels of cholesterol at least once every 4 to 6 years. If you have already been diagnosed with high cholesterol or have a family history of the condition, you may need to have your cholesterol checked more often. Talk with your health care team about this simple blood test. If you have high cholesterol, medicines and lifestyle changes can help reduce your risk for heart disease.
High blood pressure usually has no symptoms, so have it checked on a regular basis. Your health care team should measure your blood pressure at least once every 2 years if you have never had high blood pressure or other risk factors for heart disease.
If you have been diagnosed with high blood pressure, also called hypertension, your health care team will measure your blood pressure more often to make sure you have the condition under control. Talk with your health care team about how often you should check your blood pressure. You can check it at a doctors office, at a pharmacy, or at home.
If you have high blood pressure, your health care team might recommend some changes in your lifestyle, such as lowering the sodium in your diet your doctor may also prescribe medicine to help lower your blood pressure.
Maintain A Healthy Weight
Extra pounds can interfere with blood circulation and put excess pressure and stress on the heart. Losing a few of those pounds can make a big difference in preventing heart failure and promoting general heart health.
Studies have shown that even a modest weight loss of 5% to 10% can lead to significant improvements in blood pressure, cholesterol, and co-morbidities associated with increased weight.
Recommended Reading: What Is A Normal.resting Heart Rate
What Are The Heart Disease Risk Factors That I Cannot Change
- Age. Your risk of heart disease increases as you get older. Men age 45 and older and women age 55 and older have a greater risk.
- Sex. Some risk factors may affect heart disease risk differently in women than in men. For example, estrogen provides women some protection against heart disease, but diabetes raises the risk of heart disease more in women than in men.
- Race or ethnicity. Certain groups have higher risks than others. African Americans are more likely than whites to have heart disease, while Hispanic Americans are less likely to have it. Some Asian groups, such as East Asians, have lower rates, but South Asians have higher rates.
- Family history. You have a greater risk if you have a close family member who had heart disease at an early age.
What Makes Yale Medicines Approach To Treating Congestive Heart Failure Unique
Yale Medicines multidisciplinary team comprises heart failure cardiologists and cardiac surgeons, dedicated advanced-practice, registered nurses and nurse coordinators, dietitians, exercise physiologists, financial counselors, immunologists specializing in transplants, psychologists, and specialists in palliative care.
With a multidisciplinary approach, Yale Medicine physicians include the patients desires as well as input from the family to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that’s right for them.
Also Check: What Are The Final Stages Of Congestive Heart Failure
What Is The Treatment For Congestive Heart Failure
The treatment of heart failure depends on the exact cause, but it can usually be treated effectively. The overall goals are to correct underlying causes, to relieve symptoms, and to prevent worsening of the condition. Symptoms are relieved by removing excess fluid from the body, improving blood flow, improving heart muscle function, and increasing delivery of oxygen to the body tissues. This can be done by the various congestive heart failure treatments listed in this sections.
If the underlying cause of heart failure is not correctable by surgery or catheterization procedures, medical treatment is composed of lifestyle changes and medications.
What Are The Complications Of Heart Failure

Some of the complications from heart failure include:
- Irregular heartbeat.
- History of taking drugs that can damage your heart muscle, such as some cancer drugs.
Stage B
Stage B is considered pre-heart failure. It means your healthcare provider has given you a diagnosis of systolic left ventricular dysfunction but youve never had symptoms of heart failure. Most people with Stage B heart failure have an echocardiogram that shows an ejection fraction of 40% or less. This category includes people who have heart failure and reduced EF due to any cause.
Stage C
People with Stage C heart failure have a heart failure diagnosis and currently have or previously had signs and symptoms of the condition.
There are many possible symptoms of heart failure. The most common are:
- Shortness of breath.
- Need to urinate while resting at night.
- Rapid or irregular heartbeats .
- A dry, hacking cough.
- A full or hard stomach, loss of appetite or upset stomach .
There may be times that your symptoms are mild or you may not have any symptoms at all. This doesn’t mean you no longer have heart failure. Symptoms of heart failure can range from mild to severe and may come and go.
Unfortunately, heart failure usually gets worse over time. As it worsens, you may have more or different signs or symptoms.Its important to let your doctor know if you have new symptoms or if your symptoms get worse.
Recommended Reading: What Is Bpm Heart Rate
