When Should I Get Emergency Care
Go to the ER or call 911 if you have:
- New, unexplained, and severe chest pain that comes with shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, or weakness
- Fast heart rate , especially if you are short of breath
- Shortness of breath that doesn’t get better if you rest
- Sudden weakness, or you can’t move your arms or legs
- Sudden, severe headache
- Fainting spells
Can Surgery Be Used To Treat Heart Failure
In heart failure, surgery may sometimes prevent further damage to the heart and improve the heart’s function. Procedures used include:
- Coronary artery bypass grafting surgery. The most common surgery for heart failure caused by coronary artery disease is . Although surgery is more risky for people with heart failure, new strategies before, during, and after surgery have reduced the risks and improved outcomes.
- Heart valve surgery. Diseased heart valves can be treated both surgically and non-surgically .
- Implantable left ventricular assist device . The LVAD is known as the “bridge to transplantation” for patients who haven’t responded to other treatments and are hospitalized with severe systolic heart failure. This device helps your heart pump blood throughout your body. It allows you to be mobile, sometimes returning home to await a heart transplant. It may also be used as destination therapy for long-term support in patients who are not eligible for transplant.
- Heart transplant. A heart transplant is considered when heart failure is so severe that it doesn’t respond to all other therapies, but the person’s health is otherwise good.
History And Physical Exam
A clinician listens to your heart and lungs and measures your blood pressure and weight. They will also ask about your:
- Familys medical history, especially previous cardiac problems
- Medications, including prescriptions, over-the-counter drugs and supplements
- Personal medical history
Blood tests can measure several things related to heart failure:
- Sodium and potassium levels
- Creatinine, which helps measure how well your kidneys are working
- B-type natriuretic peptide , a hormone released from the ventricles in response to increased wall tension that occurs with heart failure
Recommended Reading: Can Iron Supplements Cause Heart Palpitations
Heart Failure Treatment Is A Team Effort
Heart failure management is a team effort, and you are the key player on the team. Your heart doctor will prescribe your medications and manage other medical problems. Other team members — including nurses, dietitians, pharmacists, exercise specialists, and social workers — will help you achieve success. But it is up to YOU to take your medications, make dietary changes, live a healthy lifestyle, keep your follow-up appointments, and be an active member of the team.
If you notice anything unusual, don’t wait until your next appointment to discuss it with your doctor. Call them right away if you have:
- Unexplained weight gain
- Swelling in your ankles, feet, legs, or belly that gets worse
- Shortness of breath that gets worse or happens more often, especially if you wake up feeling that way
- Bloating with a loss of appetite or nausea
- Extreme fatigue or more trouble finishing your daily activities
- A lung infection or a cough that gets worse
- Fast heart rate
- New irregular heartbeat
Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction
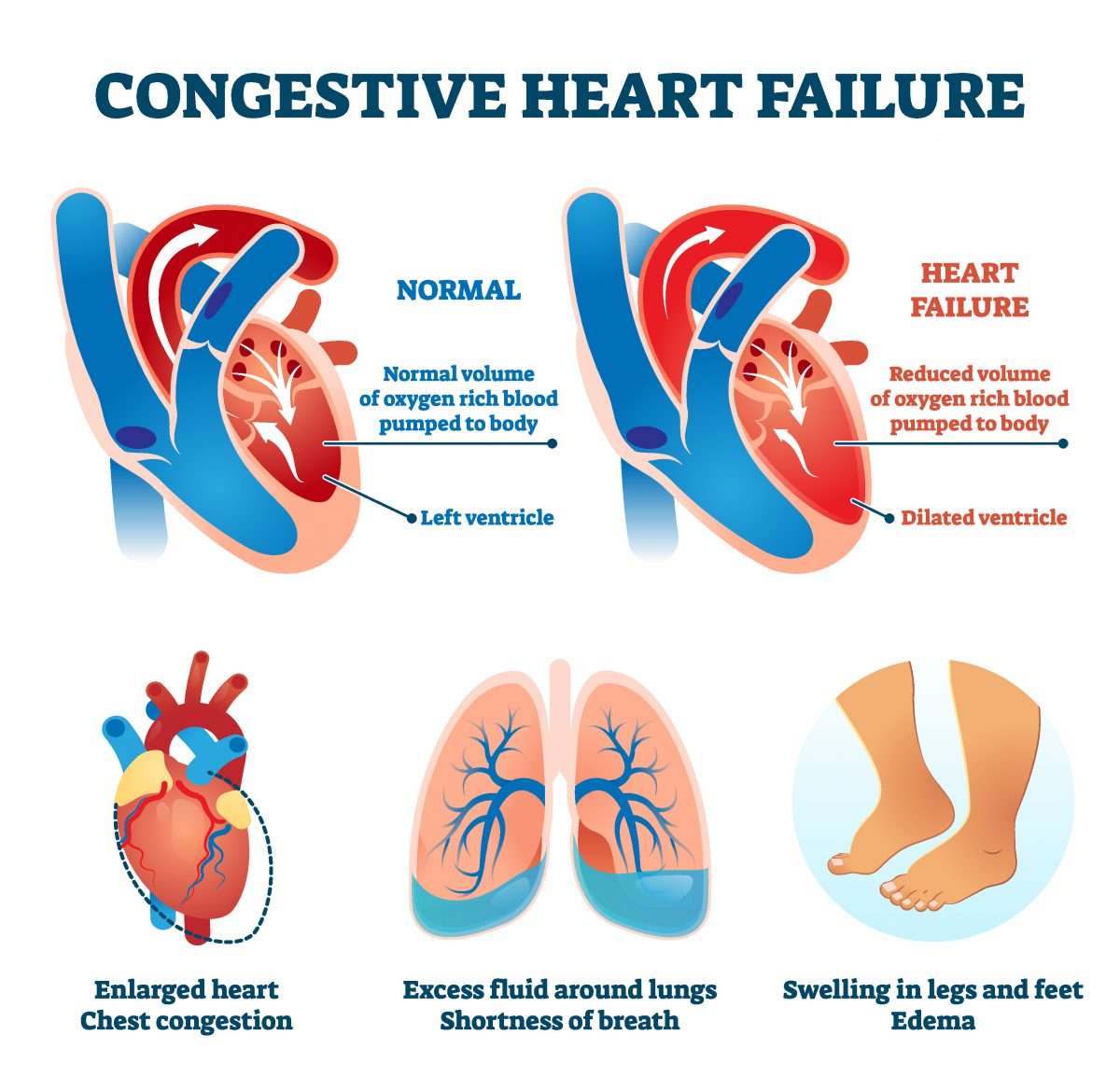
In diastolic heart failure , the same pathophysiologic processes occur that lead to decreased cardiac output in systolic heart failure, but they do so in response to a different set of hemodynamic and circulatory environmental factors that depress cardiac output.
In HFpEF, altered relaxation and increased stiffness of the ventricle occur in response to an increase in ventricular afterload . The impaired relaxation of the ventricle then leads to impaired diastolic filling of the left ventricle .
Morris et al found that right venticular subendocardial systolic dysfunction and diastolic dysfunction, as detected by echocardiographic strain rate imaging, are common in patients with HFpEF. This dysfunction is potentially associated with the same fibrotic processes that affect the subendocardial layer of the LV and, to a lesser extent, with RV pressure overload. It may play a role in the symptomatology of patients with HFpEF.
You May Like: How To Differentiate Between Anxiety And Heart Attack
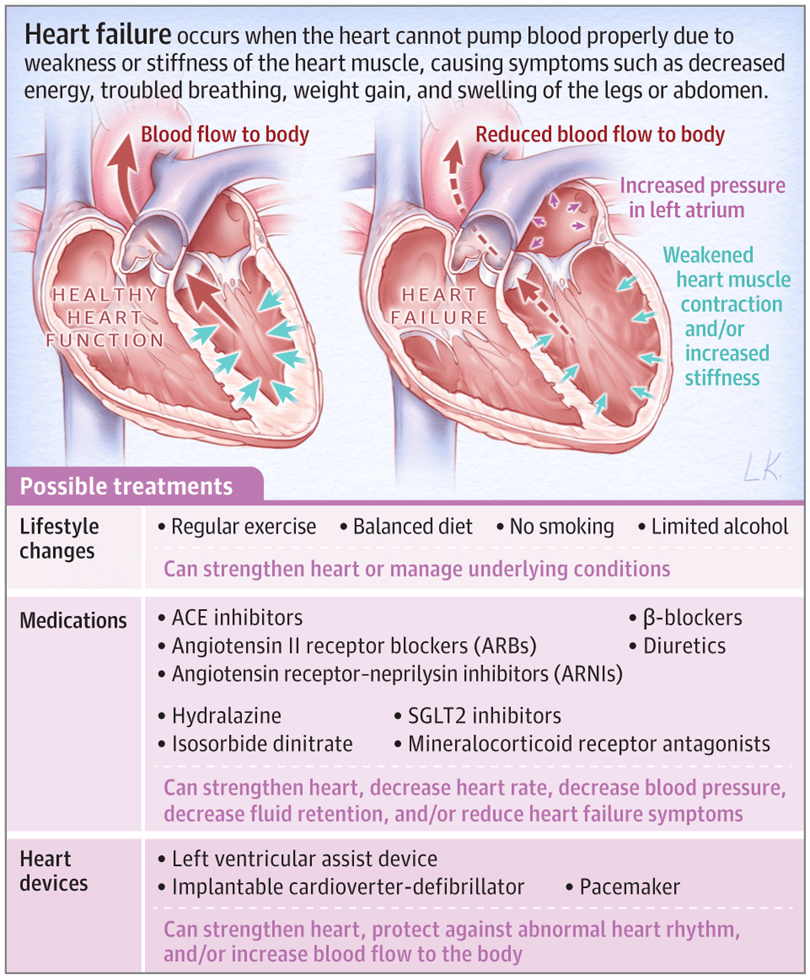
Causes Of Heart Failure
The heart is a double pump made up of four chambers. Deoxygenated blood from the veins enters the right upper chamber , is passed to the right lower chamber , and then pumped to the lungs.
Oxygenated blood from the lungs enters the left upper chamber and then enters the left lower chamber . The blood is then pumped around the body, under pressure, via arteries.
In a person with heart failure, one or both ventricles dont empty properly. This leads to increased pressure in the atria and the nearby veins. This backlog of blood can affect the kidneys and lungs interfering with their function and leading to a build-up of fluid in the lungs, abdominal organs and legs.
In some people with heart failure, rather than failed pumping of the blood from the ventricle, there is failed relaxation of the ventricle.
If the heart is not pumping and becomes stiff and unable to relax, it can cause the blood to pool in the hearts ventricles. This can cause pressure build up and can put strain on the heart.
Heart failure can be caused by several conditions, including:
How Can I Improve My Quality Of Life With Heart Failure
There are several things you can do to improve your quality of life if you have heart failure. Among them:
- Eat a healthy diet. Limit your consumption of sodium to less than 1,500 milligrams each day. Eat foods high in fiber. Limit foods high in trans fat, cholesterol, and sugar. Reduce total daily intake of calories to lose weight if necessary.
- Exercise regularly. A regular cardiovascular exercise program, prescribed by your doctor, will help improve your strength and make you feel better. It may also decrease heart failure progression.
- Don’t overdo it. Plan your activities and include rest periods during the day. Certain activities, such as pushing or pulling heavy objects and shoveling may worsen heart failure and its symptoms.
- Prevent respiratory infections. Ask your doctor about flu and pneumonia vaccines.
- Take your medications as prescribed. Do not stop taking them without first contacting your doctor.
- Get emotional or psychological support if needed. Heart failure can be difficult for your whole family. If you have questions, ask your doctor or nurse. If you need emotional support, social workers, psychologists, clergy, and heart failure support groups are a phone call away. Ask your doctor or nurse to point you in the right direction.
Also Check: How To Slow Down Your Heart Rate From Anxiety
Systolic And Diastolic Failure
Systolic and diastolic heart failure each result in a decrease in stroke volume. This leads to activation of peripheral and central baroreflexes and chemoreflexes that are capable of eliciting marked increases in sympathetic nerve traffic.
Although there are commonalities in the neurohormonal responses to decreased stroke volume, the neurohormone-mediated events that follow have been most clearly elucidated for individuals with systolic heart failure. The ensuing elevation in plasma norepinephrine directly correlates with the degree of cardiac dysfunction and has significant prognostic implications. Norepinephrine, while directly toxic to cardiac myocytes, is also responsible for a variety of signal-transduction abnormalities, such as downregulation of beta1-adrenergic receptors, uncoupling of beta2-adrenergic receptors, and increased activity of inhibitory G-protein. Changes in beta1-adrenergic receptors result in overexpression and promote myocardial hypertrophy.
What Causes Congestive Heart Failure In Dogs
Heart disease, which can develop into heart failure, is commonly seen in older dogs. According to veterinary cardiologist Dr. Bonnie Lefbom, Dipl. ACVIM, incidence of heart disease varies from between 15% to 30% of older, small dogs and 5% to 15% of giant breed dogs.
Congestive heart failure, which can occur as heart disease progresses, is less common thanks to the veterinary treatments available today, but some dogs with heart disease will go on to develop heart failure. Dr. Lefbom says small breed dogs with a long-standing heart murmur are the most common patients with CHF. Large and giant breed dogs more commonly develop a weakened heart muscle.
One of the most common causes of heart failure in dogs is chronic degenerative valve disease . Just like in older people, the heart valves can start to break down and leak, causing backflow in the heart and a heart murmur, says Dr. Lefbom, who practices at the Regional Veterinary Referral Center in Springfield, Virginia. Over time, with continued backflow through the valves, the heart enlarges. When the heart gets too big, fluid backs up in the lungs.
Some breeds at higher risk for developing CVD include Cavalier King Charles Spaniels
You May Like: What Are Signs Of A Heart Attack
Congestive Heart Failure In Dogs Life Expectancy
Make sure to bring your dog for regular visits with your vet and stick with your treatment plan. Unchecked heart problems can make things harder on your dog and even shorten their life. With the right treatments, care, and monitoring, your dog can live a long, comfortable life.
Unfortunately, treating congestive heart failure in dogs is not curative. Your dog’s treatment will be aimed primarily at improving quality of life and making your dog comfortable and happy. Advances in medications used to treat this condition have vastly improved the overall prognosis. Vigilant home care and lifestyle management may help to extend survival from months to years. The sooner this condition can be identified and treatment is started, the better the chances are of extending your dog’s life.
Myocytes And Myocardial Remodeling
In the failing heart, increased myocardial volume is characterized by larger myocytes approaching the end of their life cycle. As more myocytes drop out, an increased load is placed on the remaining myocardium, and this unfavorable environment is transmitted to the progenitor cells responsible for replacing lost myocytes.
Progenitor cells become progressively less effective as the underlying pathologic process worsens and myocardial failure accelerates. These featuresnamely, the increased myocardial volume and mass, along with a net loss of myocytesare the hallmark of myocardial remodeling. This remodeling process leads to early adaptive mechanisms, such as augmentation of stroke volume and decreased wall stress and, later, to maladaptive mechanisms such as increased myocardial oxygen demand, myocardial ischemia, impaired contractility, and arrhythmogenesis.
As heart failure advances, there is a relative decline in the counterregulatory effects of endogenous vasodilators, including nitric oxide , prostaglandins , bradykinin , atrial natriuretic peptide , and B-type natriuretic peptide . This decline occurs simultaneously with the increase in vasoconstrictor substances from the RAAS and the adrenergic system, which fosters further increases in vasoconstriction and thus preload and afterload. This results in cellular proliferation, adverse myocardial remodeling, and antinatriuresis, with total body fluid excess and worsening of heart failure symptoms.
Read Also: Left Sided Vs Right Sided Heart Failure
Nyha Functional Classification System
The New York Heart Association functional classification considers heart failure symptoms that happen during exercise to determine stage. Patients can go back and forth between stages depending on how well-controlled symptoms are on a given day.
- Stage 1: The person has heart disease, but it isnt yet causing symptoms or limiting activities.
- Stage 2: The person has mild symptoms that only slightly limit activity.
- Stage 3: The person has significant limitations to activities. He or she is only comfortable when resting.
- Stage 4: The person has major limitations and experiences symptoms when at rest.
Sign And Symptoms Of Cardiac Heart Failure
- Metabolic disorders like beriberi,
- Disorders of the rhythm e.g. atrial fibrillation and flutter.
2. Increased workload on the heart: Increased mechanical load on the heart results in increased myocardial demand resulting in myocardial failure. Increased load on the heart may be in the form of pressure load or volume load.
Increased pressure load may occur in the following states:
- Systemic and pulmonary arterial hypertension.
- Valvular disease e.g. mitral stenosis, aortic stenosis, pulmonary stenosis.
- Chronic lung diseases. Increased volume load occurs when a ventricle is required to eject more than normal volume of the blood resulting in cardiac failure. This is seen inthe following conditions:
- Hypoxia due to lung diseases.
3. Impaired filling of cardiac chambers: Decreased cardiac output and cardiac failure may result from extra cardiac causes or defect in filling of the heart in pericarditis.
You May Like: Female Sign Of Heart Attack
When To Get Medical Advice
See a GP if you experience persistent or gradually worsening symptoms of heart failure.
Call 999 for an ambulance or go to your nearest A& E department as soon as possible if you have sudden or very severe symptoms.
A number of tests can be used to help check how well your heart is working, including blood tests, an ECG and an echocardiogram.
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide And B
ANP and BNP are endogenously generated peptides activated in response to atrial and ventricular volume/pressure expansion. ANP and BNP are released from the atria and ventricles, respectively, and both promote vasodilation and natriuresis. Their hemodynamic effects are mediated by decreases in ventricular filling pressures, owing to reductions in cardiac preload and afterload. BNP, in particular, produces selective afferent arteriolar vasodilation and inhibits sodium reabsorption in the proximal convoluted tubule. It also inhibits renin and aldosterone release and, therefore, adrenergic activation. ANP and BNP are elevated in chronic heart failure. BNP especially has potentially important diagnostic, therapeutic, and prognostic implications.
For more information, see the Medscape Drugs & Diseases article Natriuretic Peptides in Congestive Heart Failure.
Don’t Miss: How To Connect Heart Rate Monitor To Peloton App
Congestive Heart Failure Symptoms Causes Diagnosis Treatments & Preventions
Congestive Heart Failure Symptoms Cardiovascular diseases are a big problem for the world. It is among the leading causes of death. The World Health Organization believes cardiovascular disease takes 17.9 million lives each year.
Even the Centers for Disease Control and prevention of the United States have several programs to teach the general public about cardiovascular health. The rising population of obese and overweight people in the United States is also becoming one of the biggest reasons for the rising numbers of people with cardiovascular diseases.
As per the latest data points released by the Centers for Disease control and prevention, The United States can have more than 45% obese population by the year 2025. That is why today we are here to discuss congestive heart failure symptoms. Obesity is among the biggest causes of the condition, and you need to learn everything about it.
What Is Ejection Fraction
The ejection fraction is a measurement your doctor will use to determine the type of heart failure and to assess the stage of heart disease.
The ejection fraction represents the percentage of blood pumped out of the left ventricle when the heart contracts. When blood leaves the left ventricle, it moves into the aorta to deliver blood loaded with oxygen to the rest of the body.
In a healthy heart, the ejection fraction ranges from around 52%74%. When the ejection fraction drops below 52%, its considered low. Your healthcare professional may use your ejection fraction to determine the severity of heart failure.
You May Like: Drugs To Lower Heart Rate
What Is The Outlook With Heart Failure
With the right care, congestive heart failure wont stop you from doing the things you enjoy. Your prognosis, or outlook for the future, will depend on:
- How well your heart muscle is working.
- How well you respond to your treatment plan.
- How well you follow your treatment plan.
One study says that people with heart failure have a life span 10 years shorter than those who dont have heart failure. Another study showed that the survival rates of people with chronic heart failure were 80% to 90% for one year, but that dropped to 50% to 60% for year five and down to 30% for 10 years.
A different study found that people who had heart failure and were discharged from the hospital had expected life spans ranging from three to 20 years, depending on various factors like age and gender. Its important to look at your specific situation when considering your prognosis.
Facts About Heart Failure In The United States
- About 6.2 million adults in the United States have heart failure.1
- In 2018, heart failure was mentioned on 379,800 death certificates .1
- Heart failure costs the nation an estimated $30.7 billion in 2012.2 This total includes the cost of health care services, medicines to treat heart failure, and missed days of work.
Read Also: Heart Blockage Treatment Without Surgery
Congestive Heart Failure: Etiology Pathogenesistypes Treatment And More
Congestive Cardiac failure is a condition associated with heart disorders leading to impairment of the heart to supply sufficient blood to meet the body requirements. Cardiac Failure may be associated with the failure of the right or left ventricle or both. Cardiac failure causes the blood to move through the heart and body at a slower rate, leading to increased pressure in the heart. As a result, the heart is unable to pump enough oxygen and nutrients to meet the body’s requirements. The heart chambers thus respond by stretching in order to hold more blood to pump through the body or by becoming more stiff and thickened. Such mechanism helps to keep the blood moving for a short while, but the heart muscle walls tend to weaken with time and then are unable to pump with enough strength.
Fluid Retention And Swelling:
Puffy swelling in the legs, the feet, and the ankles may occur,particularly at the end of the day or after prolonged sitting. Often, the swelling is more noticeable in the ankles or on the lower leg in the front where the bone, the tibia, is close to the skin.
Pitting edema can occur when pressing down on the skin in the puffy areas. The indentation where the finger pressed may be visible for a few minutes. Pitting edema is not synonymous with heart failure it can have other causes, including liver and kidney failure.Nonpitting edema is generally not caused by heart failure.
Swelling may be so severe as to reach upto the hips, scrotum, abdominal wall,and eventually, the abdominal cavity .
Daily weight checks are necessary in persons with heart failure because the amount of fluid retention is usually reflected by the amount of weight gain and increasing shortness of breath.
Persons with heart failure should know their dry weight, which is what they weigh when they feel good with no pitting edema.
Read Also: Can You Recover From Congestive Heart Failure
