Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction
In diastolic heart failure , the same pathophysiologic processes occur that lead to decreased cardiac output in systolic heart failure, but they do so in response to a different set of hemodynamic and circulatory environmental factors that depress cardiac output.
In HFpEF, altered relaxation and increased stiffness of the ventricle occur in response to an increase in ventricular afterload . The impaired relaxation of the ventricle then leads to impaired diastolic filling of the left ventricle .
Morris et al found that right venticular subendocardial systolic dysfunction and diastolic dysfunction, as detected by echocardiographic strain rate imaging, are common in patients with HFpEF. This dysfunction is potentially associated with the same fibrotic processes that affect the subendocardial layer of the LV and, to a lesser extent, with RV pressure overload. It may play a role in the symptomatology of patients with HFpEF.
Summary Right Sided Vs Left Sided Heart Failure
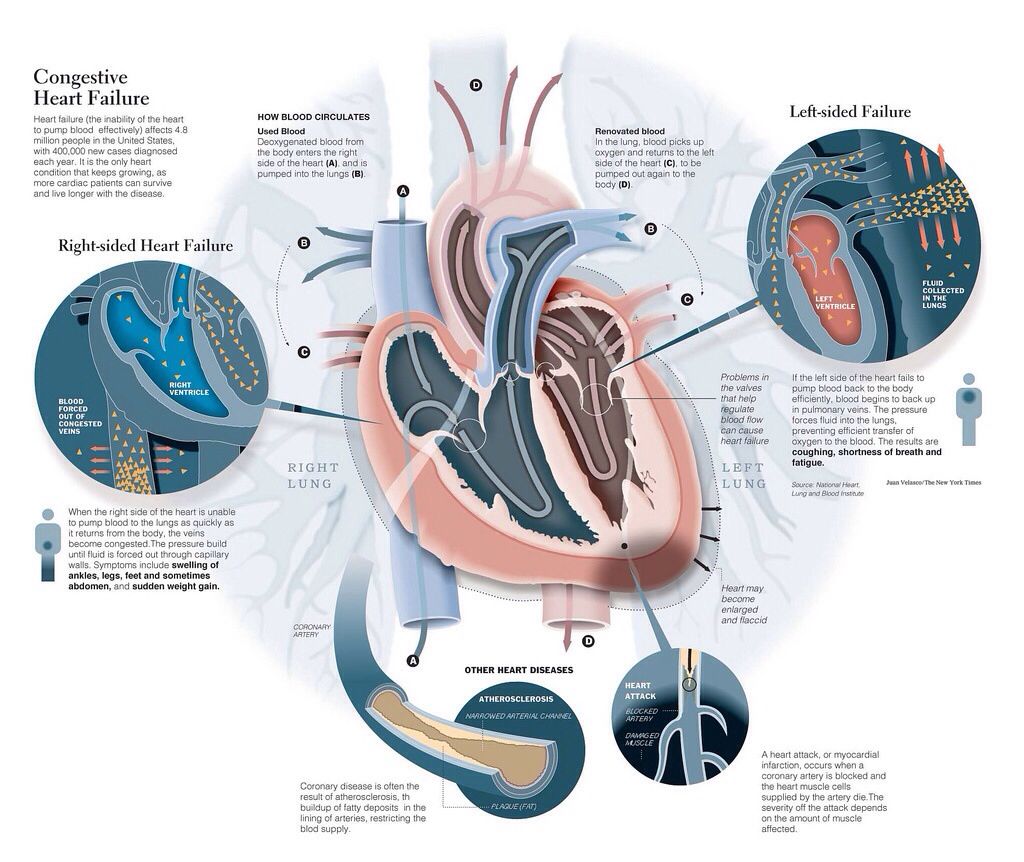
When the heart fails to pump blood adequately to the body tissues, owing to the decrease in the pumping capacity of right heart chambers, that condition is identified as the right heart failure. On the other hand, when the heart failure is due to the faltering of the pumping capacity of the left heart chambers, it is known as left sided heart failure. Thus, the difference between right sided and left sided heart failure is that in right heart failure, the function of right heart chambers is impaired whereas the function of left heart chambers is impaired in the left heart failure.
Read Also: Why Does Heart Rate Increase During Running
The Flow Of Blood Through Your Heart
To understand the different types of heart failure, it helps to know how your heart pumps blood:
You May Like: How Much Do Beta Blockers Lower Heart Rate
Comorbidities: Anemia Iron Deficiency Kidney Failure Diabetes Frailty
Moderate anemia is often prevalent in patients with heart failure regardless of HFrEF or HFpEF . The incidence is higher in women, elderly and diabetic patients as well as in patients with renal failure. Increased blood loss in patients treated with oral anticoagulants , aspirin or both as well as decreased absorption of vitamin and/or iron may favor anemia. Similar as in other chronic illnesses iron deficiency is common in heart failure and may influence prognosis worse. Whether anemia and/or iron deficiency are markers of heart failure severity or whether they affect outcome of heart failure disease and thus should be treated is not entirely clear. In patients with heart failure with as well as without anemia intravenous ferric carboxymaltose has improved quality of life and NYHA class but not prognosis .
Heart failure and chronic kidney disease frequently coexist and share many risk factors also. CKD worsen prognosis in heart failure patients however, patients with severe CKD often have been excluded from randomized clinical trials and thus there is limited evidence-based therapy available.
Comorbidities and aging via influencing cognitive and self-care ability affect management of heart failure patients. Also, polypharmacy is present often. In addition, frailty is common in these patients. In consequence, a multidisciplinary team is needed to take care especially for older heart failure patients to reduce hospitalizations and improve outcome.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Heart Failure
The signs and symptoms depend on how severe your heart failure is. The signs and symptoms you have may be due to the backup of fluid and blood in your tissues. It may also be due to decreased oxygen in your blood. You may have any of the following:
- Trouble breathing with activity that worsens to trouble breathing at rest
- Shortness of breath while lying flat
- Severe shortness of breath and coughing at night that usually wakes you
- Feeling lightheaded when you stand up
- Purple color around your mouth and nails
- Confusion or anxiety
- Periods of no breathing, then breathing fast
- Lack of energy , or trouble sleeping
- Swelling in your ankles, legs, or abdomen
- Heartbeat that is fast or not regular
- Fingers and toes feel cool to the touch
Recommended Reading: Can 30 Year Olds Have Heart Attacks
Classification Based On Course Of The Disease
Heart failure can develop suddenly, for instance after a heart attack or due to certain heart rhythm problems. This is known as acute heart failure.
But it usually develops gradually over time as a result of a different medical problem, such as permanently high blood pressure. This is known as chronic heart failure.
Anemia And Iron Deficiency
Anemia is common among patients with chronic heart failure and is frequently multifactorial. Anemia is associated with worse symptoms and outcomes in HF and so reversible causes should be sought and treated. Iron deficiency Iron Deficiency Anemia Iron deficiency is the most common cause of anemia and usually results from blood loss malabsorption, such as with celiac disease, is a much less common cause. Symptoms are usually nonspecific… read more is among the most common causes of anemia in HF, and iron replacement therapy should be considered once treatable causes such as blood loss have been excluded. Oral iron replacement is often less effective due to poor absorption and other reasons, thus intravenous iron replacement is preferred.
You May Like: What Is A Stemi Heart Attack
How Is Heart Failure Diagnosed
Tell your healthcare provider about your health history and the medicines you take. Tell him or her if you have a family history of heart failure or cardiomyopathy. He or she will ask about your shortness of breath and other symptoms. Your provider will make a diagnosis based on your physical exam, symptoms, and tests. The diagnosis may be left-sided or right-sided heart failure, or heart failure that affects both sides. You may need any of the following:
What Can I Do To Manage Swelling From Extra Fluid
- Elevate your legs above the level of your heart. This will help with fluid that builds up in your legs or ankles. Elevate your legs as often as possible during the day. Prop your legs on pillows or blankets to keep them elevated comfortably. Try not to stand for long periods of time during the day. Move around to keep your blood circulating.
- Limit sodium . Ask how much sodium you can have each day. Your healthcare provider may give you a limit, such as 2,300 milligrams a day. Your provider or a dietitian can teach you how to read food labels for the number of mg in a food. He or she can also help you find ways to have less salt. For example, if you add salt to food as you cook, do not add more at the table.
- Drink liquids as directed. You may need to limit the amount of liquid you drink within 24 hours. Your healthcare provider will tell you how much liquid to have and which liquids are best for you. He or she may tell you to limit liquid to 1.5 to 2 liters in a day. He or she will also tell you how often to drink liquid throughout the day.
- Weigh yourself every morning. Use the same scale, in the same spot. Do this after you use the bathroom, but before you eat or drink. Wear the same type of clothing each time. Write down your weight and call your healthcare provider if you have a sudden weight gain. Swelling and weight gain are signs of fluid buildup.
You May Like: Heart Disease Death Rate
Classification Based On Pumping Ability
Nowadays, heart failure is increasingly being classified based on the pumping ability of the heart. This is because the pumping ability plays an important role when choosing the most suitable medication. There are two types of heart failure here:
- Heart failure with reduced pumping ability: The heart muscle has become weaker, and no longer pumps enough blood around the body when it contracts . As a result, the organs in the body dont get enough oxygen. The medical term for this is heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
- Heart failure with preserved pumping ability: Although the heart muscle is still strong, it can no longer relax and widen enough after it has squeezed blood out, so it doesnt fill up with blood properly. Despite pumping strongly enough, not enough blood is pumped out into the body as a result, especially during physically strenuous activities. Doctors call this heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.
Heart failure with reduced pumping ability is sometimes referred to as systolic heart failure, and heart failure with preserved pumping ability is also known as diastolic heart failure. The systolic phase of the cardiac cycle is the phase when the heart contracts , and the diastolic phase is when the heart relaxes and widens.
How Is Heart Failure Treated
Your healthcare providers will help you manage any other health conditions that may be causing your heart failure. The goals of treatment are to manage, slow, or reverse heart damage. Treatment may include the following:
- Medicines may be given to help regulate your heart rhythm and lower your blood pressure. You may also need medicines to help decrease extra fluid. Medicines, such as NSAIDs, may be stopped if they are making your heart failure worse. Do not stop any of your medicines on your own.
- Cardiac rehab is a program run by specialists who will help you safely strengthen your heart. In the program you will learn about exercise, relaxation, stress management, and heart-healthy nutrition. Cardiac rehab may be recommended if your heart failure is not severe.
- Oxygen may help you breathe easier if your oxygen level is lower than normal. A CPAP machine may be used to keep your airway open while you sleep.
- Surgery can be done to implant a pacemaker or another device in your chest to regulate your heart rhythm. Other types of surgery can open blocked heart vessels, replace a damaged heart valve, or remove scar tissue.
Don’t Miss: Who Performed The First Open Heart Surgery In The World
Systolic And Diastolic Failure
Systolic and diastolic heart failure each result in a decrease in stroke volume. This leads to activation of peripheral and central baroreflexes and chemoreflexes that are capable of eliciting marked increases in sympathetic nerve traffic.
Although there are commonalities in the neurohormonal responses to decreased stroke volume, the neurohormone-mediated events that follow have been most clearly elucidated for individuals with systolic heart failure. The ensuing elevation in plasma norepinephrine directly correlates with the degree of cardiac dysfunction and has significant prognostic implications. Norepinephrine, while directly toxic to cardiac myocytes, is also responsible for a variety of signal-transduction abnormalities, such as downregulation of beta1-adrenergic receptors, uncoupling of beta2-adrenergic receptors, and increased activity of inhibitory G-protein. Changes in beta1-adrenergic receptors result in overexpression and promote myocardial hypertrophy.
Dont Miss: What Is Target Heart Rate Definition
Whats The Outlook For People With Right

For many people, the right combination of therapies and lifestyle changes can slow or stop the disease and improve symptoms. They can lead full, active lives.
About 1 in 10 American adults who live with heart failure have advanced heart failure. That means treatments arent working, and symptoms are getting worse. You may feel symptoms, such as shortness of breath, even when youre sitting. If you have advanced heart failure, talk with your care team about important care decisions and next steps.
Also Check: How To Take Your Heart Rate
Diagnosis Of Heart Failure
A clinical suspicion of heart failure is confirmed through the following investigations.
This includes FBC, liver biochemistry, cardiac enzymes released in acute cardiac failure and BNP.
- Electrocardiogram
- Cardiac MRI. This is also called CMR
- Cardiac biopsy. This is carried out only when a cardiac myopathy is suspected
- Cardiopulmonary exercise testing
When To See A Doctor
Its a good idea to speak with your doctor to check your heart health if you:
- Notice swelling in your legs
- Become winded easily with normal activities
There is no cure for heart failure. Still, with treatment, you can slow the progression of it and stay feeling better for longer.
You should seek immediate medical attention or call 911 if you or a loved one is experiencing:
- Sudden shortness of breath, irregular heartbeat, or chest pain
- Trouble breathing and blood-tinged phlegm
- Fainting or loss of consciousness
You May Like: How To Tell The Difference Between Heartburn And Heart Attack
Read Also: What Is A Dangerously Low Heart Rate
What Are The Treatments For Heart Failure
Your treatment will depend on the type of heart failure you have and how serious it is. There’s no cure for heart failure. But treatment can help you live longer with fewer symptoms.
Even with treatment, heart failure usually gets worse over time, so you’ll likely need treatment for the rest of your life.
Most treatment plans include:
You may need heart surgery if:
- You have a congenital heart defect or damage to your heart that can be fixed.
- The left side of your heart is getting weaker and putting a device in your chest could help. Devices include:
- A biventricular pacemaker .
- A mechanical heart pump or a total artificial heart).
As part of your treatment, you’ll need to pay close attention to your symptoms, because heart failure can worsen suddenly. Your provider may suggest a cardiac rehabilitation program to help you learn how to manage your condition.
Diagnosis Of Heart Failure Of Acute Onset
|
Data from Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, et al: 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: The Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association of the ESC. European Heart Journal 37:2129-2200, 2016. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw128 |
You May Like: Heart Failure Early Signs
What Are The Symptoms
Your feet, legs, and ankles will likely to swell because blood is backing up in your veins. This symptom is called edema.
- If it backs up into your stomach or liver, you may notice that your abdomen is distended, too.
- You might find that you have to go to the bathroom more, especially at night. This is caused by fluid buildup, too.
As your heart failure gets worse, you may also see some of these symptoms:
- Itâs hard to breathe.
- Your neck veins are swollen.
- Your pulse is fast or feels âoff.â
- Your chest hurts.
- Youâre gaining weight from excess fluid.
- You donât feel like eating.
- Your skin is cold and sweaty.
- Youâre very tired.
What Are The Symptoms Of Heart Failure
The symptoms of heart failure depend on which side of your heart is affected and how serious your condition has become. Most symptoms are caused by reduced blood flow to your organs and fluid buildup in your body.
Fluid buildup happens because the flow of blood through your heart is too slow. As a result, blood backs up in the vessels that return the blood to your heart. Fluid may leak from the blood vessels and collect in the tissues of your body, causing swelling and other problems.
Symptoms of heart failure may include:
- Feeling short of breath when you do things like climbing stairs. This may be one of the first symptoms you notice.
- Fatigue or weakness even after rest.
Recommended Reading: Which Arm Hurts With Heart Attack
What Are The Different Types Of Chf
Heart failure can occur on the left side of the heart, the right side, or both. Most commonly, it begins in the heartâs primary pumping chamber â the left ventricle. Each specific type of CHF is accompanied by its own distinct characteristics:
- Right-sided CHF âRight-sided CHF develops when the right ventricle struggles to deliver blood to the lungs. As blood backs up into the blood vessels, the body begins to retain fluid in the abdomen and lower body.
- Left-sided CHF âLeft-sided CHF is the most common form of CHF and begins when the left ventricle cannot effectively deliver blood throughout the body. Eventually, this can lead to fluid retention throughout the body, particularly around the lungs.
Cases of left-sided CHF can be further classified into one of two sub-types, characterized by the manner in which the ventricle is affected:
- Systolic CHF â Systolic CHF occurs when the left ventricle is unable to contract with enough force to circulate blood properly.
- Diastolic CHF âDiastolic CHF occurs when the heart muscle becomes stiff. Because the chamber must relax in order to fill with blood between contractions, this stiffness means that an inadequate amount of blood is available to pump out to the rest of the body.
What Is The Difference Between Left And Right
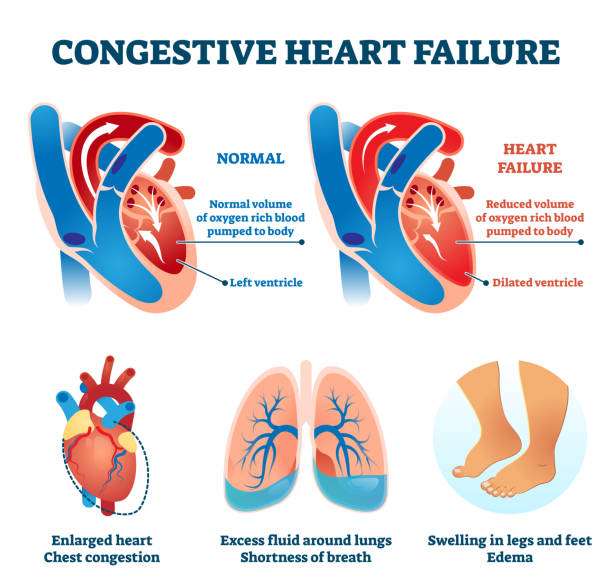
Heart failure can occur in the left side of the heart, the right side of the heart or on both sides. The major difference between left-sided heart failure and right-sided heart failure is in the side of the heart that is weakened. In left-sided heart failure, the left side of the heart is weakened and results in reduced ability for the heart to pump blood into the body. In right-sided heart failure, the right side of the heart is weakened and results in fluid in your veins, causing swelling in the legs, ankles, and liver.
To understand these conditions, it is important to know a little about how blood flows through the heart.
The heart is made up of four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria and the lower chambers are called ventricles. Each side of the heart has paired upper and lower chambers. Blood returns from the body and enters the right atrium. From there it moves to the right ventricle, which pumps it to the lungs where it is oxygenated. Blood moves from the lungs into the left atrium, down to the left ventricle and then out to the body to supply organs and tissues with oxygen and nutrients.
Recommended Reading: What Does Your Heart Rate Tell You
