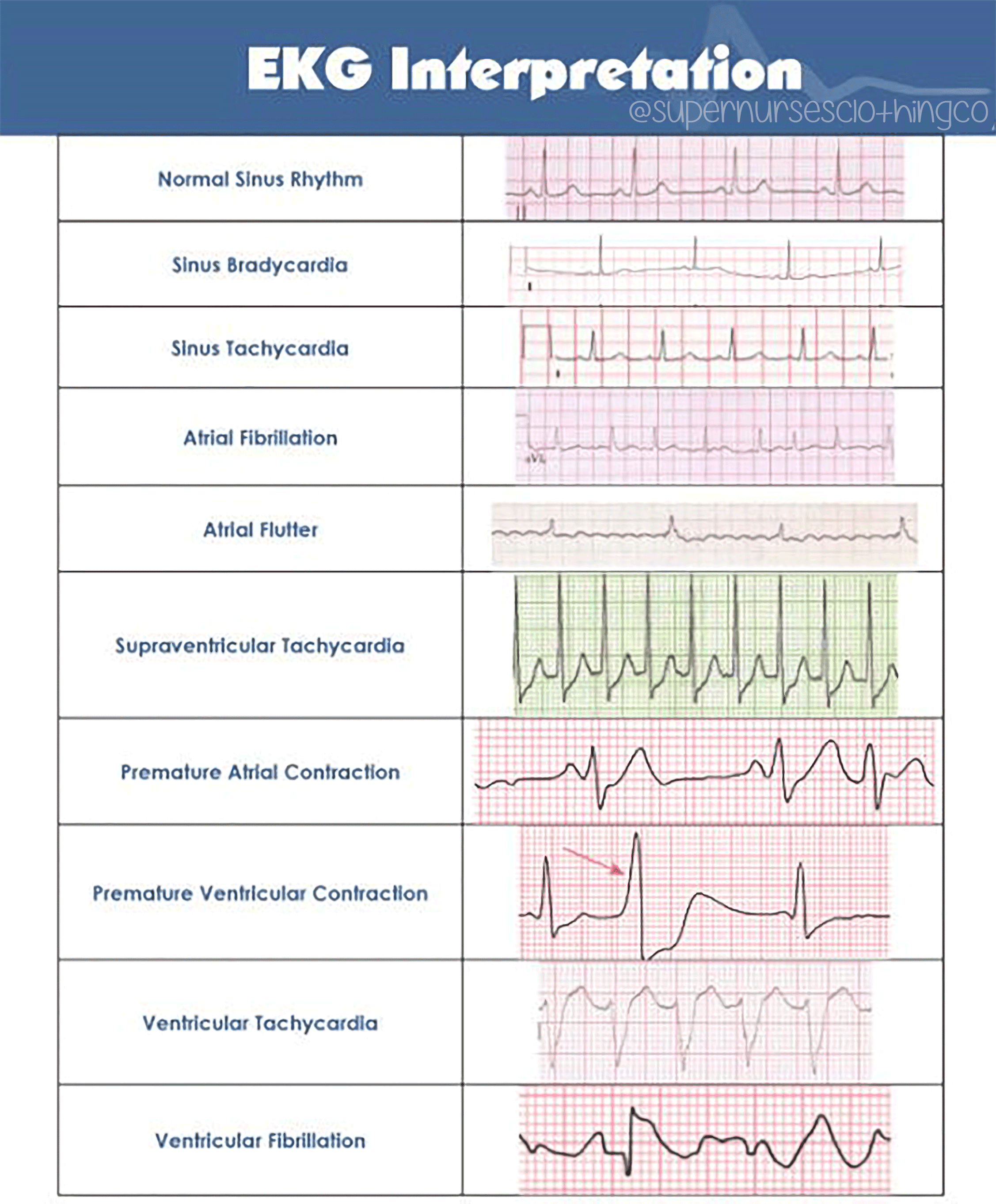
Atrial Or Supraventricular Tachycardia
Atrial or supraventricular tachycardia is a fast heart rate that starts in the upper chambers of the heart. Some forms of this particular tachycardia are paroxysmal atrial tachycardia or paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia .
With atrial or supraventricular tachycardia, electrical signals in the hearts upper chambers fire abnormally. This interferes with electrical impulses coming from the sinoatrial node, the hearts natural pacemaker.
The disruption results in a faster than normal heart rate. This rapid heartbeat keeps the hearts chambers from filling completely between contractions, which compromises blood flow to the rest of the body.
A profile for atrial or SVT
In general, those most likely to have atrial or supraventricular tachycardia are:
- Women, to a greater degree than men
- Anxious young people
In extreme cases, those suffering with atrial or SVT may also experience:
- Unconsciousness
Treatment for Atrial or SVT
If you have atrial or SVT, its possible that you wont need treatment.
But if the episodes are prolonged, or recur often, your doctor may recommend treatment, including:
- Some medicinal and street drugs
Other, less common causes may include:
- Heart muscle damage from heart attack or heart failure
- Severe bleeding
Approach to treatment
What Is A Supraventricular Tachycardia
In some hearts, an abnormal heart rhythm develops in the top part of the heart when an electrical impulse either starts from a different location other than the SA node, or follows a route that is not normally present. When this occurs the heart will suddenly start racing. The heart rate is usually over 150 beats per minute and often over 200 beats per minute. Certain things in some people can trigger episodes. These include caffeine, alcohol, anxiety, exercise or sudden movements such as bending over. However, often these episodes can occur at any time without a trigger. During an episode, you will usually be aware of the rapid beating of your heart.
Other symptoms might include dizziness , shortness of breath, sweating, chest pain and anxiety. After an episode it is usual to feel very tired.
What Causes Atrial Fibrillation And Supraventricular Tachycardia
AFib is quite common. It affects about 2.3 million American adults. The biggest risk factor is age. Most people who develop AFib are over the age of 65. In AFib, your atria donât work correctly because of abnormal electrical activity. Your heart canât move blood out of your heartâs upper chambers as quickly, which raises your risk for blood clots that can lead to a stroke.
Besides age, there are other risk factors for AFib:
- Mild shortness of breath, especially when you work out
More severe symptoms include trouble breathing, especially during exercise, fainting, chest pain, and severe fatigue.
If you have SVT, you are more likely to notice that your heart is racing. Many people have a fast heartbeat thatâs more than 100 beats per minute, even when they are at rest. This can last for hours. Serious SVT can cause you to pass out or go into cardiac arrest.
You May Like: How To Avoid Congestive Heart Failure
Testing And Diagnosis Of Svt
Supraventricular tachycardia is suspected when a doctor or nurse counts a very rapid heart rate during an attack. To confirm the diagnosis, your childs pediatrician might perform an electrocardiogram . An ECG is a test which records the electrical activity of the heart. An echocardiogram or echo may also be performed in the cardiologists office. This is a type of ultrasound that captures moving pictures of the heart.
An ECG, echocardiogram and a physical exam are usually normal if they are performed after the tachycardia stops, so it is important to obtain an ECG while your child is having the symptoms. If thats not possible, your child may be sent home with a Holter monitor or another heart monitor that can be used to continuously record your childs heart rhythm over the course of at least 24 hours. An accurate ECG will allow for the correct diagnosis and appropriate treatment for your child.
Your doctor may also refer your child to an electrophysiologist, a cardiologist who has additional education and training in the diagnosis and treatment of abnormal heart rhythms.
Signs And Symptoms Of Supraventricular Tachycardia
Symptoms of supraventricular tachycardia in children may include:
- Heart palpitations an uncomfortable sensation caused by the heart beating hard and fast.
- Rapid heartbeats that occur suddenly and randomly
- Syncope , which rarely happens with SVT
- Symptoms of heart failure may develop if an episode lasts more than 24 hours before the patient receives medical care. This is especially true in newborns and infants who cannot communicate the sensation of palpitations. Symptoms of SVT in babies are subtle and often involve poor feeding, vomiting, or a general decrease in the babys activity level and alertness.
Supraventricular tachycardia virtually never causes sudden death. Patients with SVT usually do not have any symptoms when they are not having these attacks.
Recommended Reading: What Is A Normal Resting Heart Rate For A 50 Year Old Woman
What Are The Symptoms Of Arrhythmia
Some patients have no associated symptoms with arrhythmia, while others may notice symptoms but not have a life-threatening arrhythmia. It is important to have regular check-ups with your GP, especially if you are concerned.
Common symptoms of a heart arrhythmia include:
- Fluttering feeling in the chest
- Racing heartbeat
Is Your Racing Heart A Sign Of Supraventricular Tachycardia
Approximately 2 in every 1,000 people have SVT, a type of arrhythmia that can often be cured. Learn more about symptoms, diagnosis and treatment.
If youve ever experienced a sudden racing heartbeat, you know how unsettling the feeling can be.
While there are many potential causes of a fast heartbeat, one of the more common forms is supraventricular tachycardia, or SVT.
LISTEN UP: Add the new Michigan Medicine News Break to your Alexa-enabled device, or subscribe to our daily audio updates on iTunes, and Stitcher.
SVT symptoms heart palpitations, chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness or lightheadedness can be alarming, but the condition is usually treatable and can often be cured, says Michigan Medicine electrophysiologist Rakesh Latchamsetty, M.D.
First, he says, the type of arrhythmia responsible for the symptoms needs to be determined since different arrhythmias can be treated very differently and some can be more serious than others.
A person experiencing a rapid heartbeat should consult with their physician, and anyone experiencing unrelenting palpitations or severe symptoms should be seen in the emergency room, says Latchamsetty.
Read Also: Heart Surgery Through Leg
How Is Svt Treated
You may not need treatment. Some people may feel better after resting more, drinking less coffee or alcohol or after quitting smoking.
These treatments may be the first things to try:
- Have your healthcare provider apply pressure to specific areas of your face and neck.
- Do the Valsalva maneuver .
- Put an ice cold towel on your face.
People who require therapy in the form of a catheter ablation to eliminate the areas responsible for the abnormal electricity can have cure rates close to 95% depending on the specific SVT.
Risk Factors Of Supraventricular Tachycardia
Risk factors that increase your risk of experiencing supraventricular tachycardia include:
- Coronary artery disease, previous heart surgery, or other heart conditions.
- Congenital heart disease.
- Anxiety, physical fatigue, or emotional stress.
- OTC and prescription drugs and supplements.
- Uncontrolled diabetes. Recreational drug use
- Overactive or underactive thyroids.
Read Also: Which Arm Is Heart Attack Sign
How Does Svt Compare To Ventricular Tachycardia
SVT is different from a condition called ventricular tachycardia .
The main difference is that SVT begins above the ventricles, and VT starts in the hearts lower chambers.
The other key difference is that VT can have more severe and life threatening symptoms because it originates in the hearts primary pumping chambers.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Paroxysmal SVT is usually managed by an interprofessional team of healthcare workers dedicated to cardiac arrhythmias. Since these arrhythmias cannot be prevented, the focus is on treatment. Besides the cardiologist, the role of the nurse and pharmacist is indispensable. The patient should be educated about this arrhythmia and the potential risk of sudden death if left untreated. For patients with SVT managed with medications, the pharmacist should assist the team by educating the patient on potential adverse effects, drug interactions and the need for close follow-up. The patient should also be educated on the option of radiofrequency ablation, which has a much higher success rate compared to medications.
Outcomes
For the most part, patients with paroxysmal SVT have a good outcome with treatment. However, a small number of patients with WPW do have a tiny risk of sudden death. In patients with SVT arising due to a structural defect in the heart, the prognosis depends on the severity of the defect, but in healthy people with no structural defects, the prognosis is excellent. Pregnant women who develop SVT do have a slightly higher risk of death if there is an unrepaired heart defect.
You May Like: Is Heart Failure Curable
Common Signs And Symptoms
Infants are not able to tell you if the following signs or symptoms happen. They are not unique to SVT. They can occur with other illness.
- baby sweats a lot with feeding
- pale or generally ill appearing
Toddlers and older children may be able to tell you if they are having the following symptoms:
- feels a rapid or irregular heartbeat
- feeling pulses in their throat
Things You Can Do To Help With Supraventricular Tachycardia
If your episodes of SVT only last a few minutes and do not bother you, you may not need treatment.
You can make changes to your lifestyle to reduce your chances of having episodes, such as:
- cutting down on the amount of caffeine or alcohol you drink
- stopping or cutting back on smoking
- making sure you get enough rest
Your doctor may also be able to recommend some simple techniques to help stop episodes when they happen.
Recommended Reading: Best Fat Burning Heart Rate
How Are Afib And Svt Diagnosed
Both conditions are usually diagnosed via an electrocardiogram . This is a test that measures your heartâs electrical activity. Your doctor may want you to wear a Holter monitor for a couple of days. Itâs an EKG device that monitors your heart activity. Some smartwatches may also be able to monitor your heart rhythm.
Your doctor may also run the following tests if you have AFib to see if you have an underlying medical condition thatâs causing symptoms:
- Echocardiogram. This is a heart ultrasound to look for heart failure or heart valve problems.
- Blood tests to screen for thyroid disorders.
- Sleep studies and lung function tests to look for sleep apnea or lung disease.
What You Need To Know About Supraventricular Tachycardia
Supraventricular tachycardia is a very rapid heartbeat and can cause a number of serious health issues. Its seen in just over 2 out of every 1,000 people, affecting children and adults alike.
There are several types of SVT, with each involving a different part of the heart or having a unique origin. Signs of SVT include a racing heart rate and other symptoms that can cause discomfort, pain, or feeling faint.
A cardiac monitor is used to record the heart to identify an abnormal rhythm. Treatment for SVT ranges from tips you can apply at home to procedures that can get rid of or bypass the source of this condition.
Recommended Reading: Resting Heart Rate Chart By Age
What Happens During Psvt
A normal heartbeat begins with an electrical impulse from the sinus node, a small area in the heart’s right atrium . PSVT occurs because of a short circuit an abnormal electrical pathway made of heart cells that allows electricity to speed around in a circle and repeat the signal over and over. As a result, the chambers contract rapidly, which may impair heart function and cause symptoms such as lightheadedness or shortness of breath.
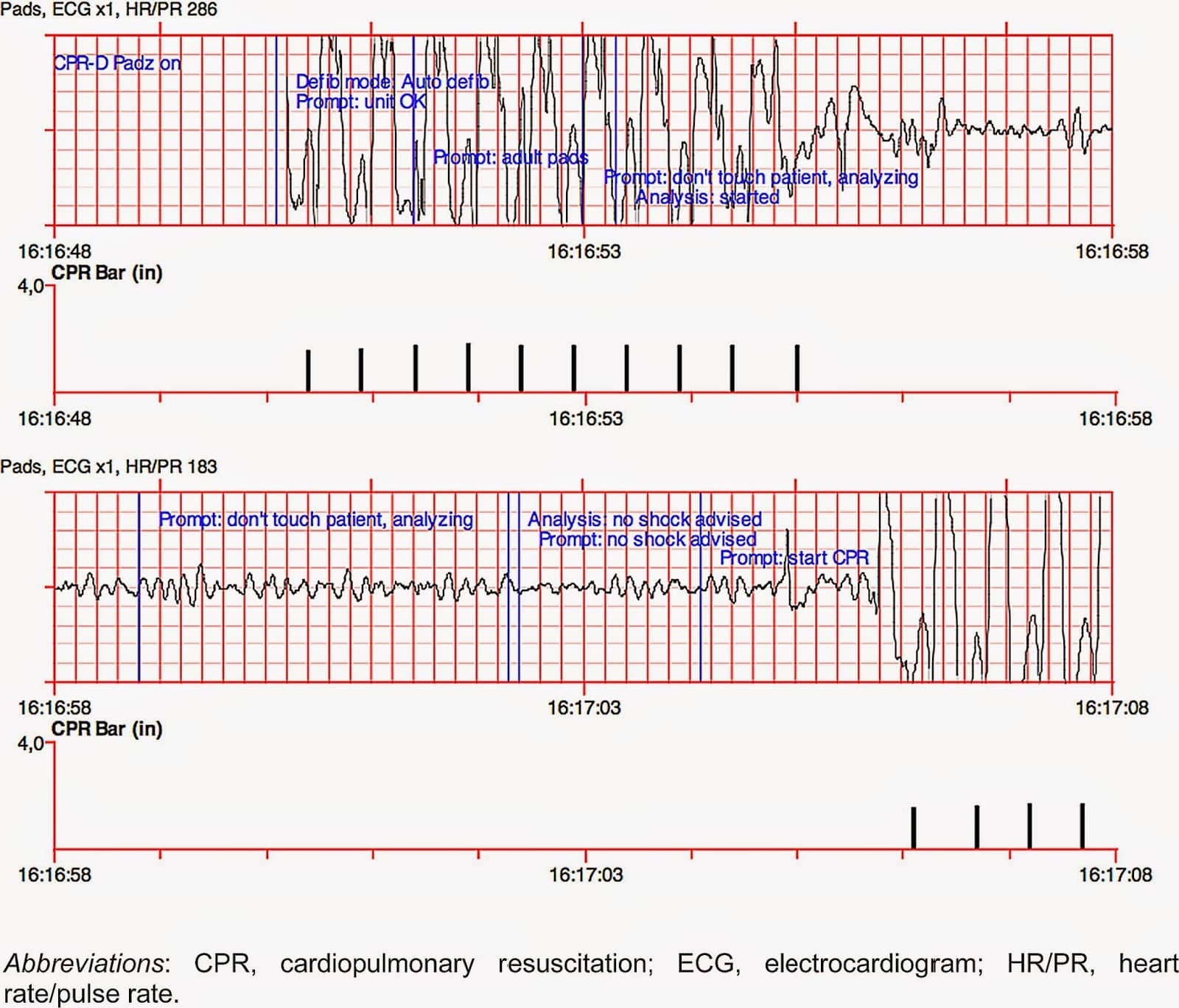
Pediatric Heart Rates During Supraventricular Tachycardia
Posted: October 4, 2019
It is important to understand that sometimes a recorded heart rate can confirm if a child or teenager is in supraventricular tachycardia , but not always.
SVT is a common cause of abnormally fast heartbeats in children and teenagers, but the range of heart rates in SVT is pretty broad. In addition, there is a wide range of heart rates in otherwise healthy children, depending on things like age and activity level. As it turns out, there is substantial overlap in the heart rates in SVT and what is actually normal for any given child at any given time.
For example, at the high end of normal heart rates, heart rates of 200 to 220 beats per minute often are recorded in a healthy child who is running around or playing hard, and up to 230 beats per minute in a really angry or febrile baby. At the low end, heart rates can be as slow as in the 30s to 50s beats per minute in a resting or sleeping teenager and are usually in the 70s to 110s in resting young children and infants.
The range of heart rates in SVT depends on a number of factors, including the childs age, the type of SVT activity level, medications and other things. Heart rates in childhood SVT range from around 140 beats per minute to up to 350 beats per minute.
So, how do fast heart rates alone help sort out whats going on in a child or teen?
Also Check: Sglt2 Inhibitors Heart Failure Guidelines
What Treatments Are Available For Supraventricular Tachycardia
There are 3 main options for people with SVT.
Causes Of Supraventricular Tachycardia
An episode of supraventricular tachycardia occurs when abnormal electrical impulses suddenly start in the upper chambers of the heart, and override the heart’s natural rhythm.
SVT is sometimes called paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia . Paroxysm means a sudden temporary disturbance of heart rhythm.
PSVT is usually caused by a short circuit in the electrical system of the heart, which causes an electrical signal to travel rapidly and continuously around in a circle, forcing the heart to beat each time it completes the circuit.
Another type of SVT is called Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, where an abnormal electrical connection occurs between the atria and ventricles . People with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome are born with a strand of extra muscle tissue between these chambers. This produces a short circuit, which causes the fast heartbeat.
Recommended Reading: Open Heart Surgery Bypass
How Does The Heart Beat
The heart has four chambers. The two upper ones are the atria and the two lower ones are the ventricles. People refer to the sinoatrial node, which is in the right atrium, as the pacemaker.
In a typical heartbeat, the electrical signal that controls heart rate begins in the SA node. The signal travels through the atria to the atrioventricular node in the lower right atrium. From there, it passes into the ventricles, allowing them to contract and pump blood.
In people with SVT, the electrical signal that initiates the heartbeat comes from somewhere above the ventricle other than the SA node. As a result, the heart rate accelerates, shortening the time the ventricles have to fill with blood. This prevents the heart from pumping blood efficiently to the body.
These episodes of abnormal heart rhythm may last for just a few seconds or go on for several hours. They can also occur often or only once in a while.
What Can You Do At Home To Prevent Svt
You can try some things at home to help prevent SVT by avoiding the things that trigger it.
- Limit or do not drink alcohol.
- Avoid over-the-counter decongestants, herbal remedies, diet pills, and “pep” pills.
- Don’t use illegal drugs, such as cocaine, ecstasy, or methamphetamine.
To find your triggers, keep a diary of your heart rate and your symptoms. You might find, for example, that smoking or alcohol causes your SVT episodes.
For most people, moderate amounts of caffeine do not trigger SVT. So most people do not have to avoid chocolate or caffeinated coffee, tea, or soft drinks.
Read Also: Childrens Heart Rate
Who Does Svt Affect
Children and adults can get SVT . Women get it more than men. Others are more likely to get this condition because they:
- Drink more alcohol than recommended by your provider.
- Smoke or use tobacco products.
- Drink more than the recommended amount of coffee or other drinks with caffeine.
Young people who are exercising or training hard are more likely to get short-lived paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia . AV nodal reentrant tachycardia is common in young adults and the elderly. Accessory pathway tachycardias are common in children younger than 12.
Older adults and people who are anxious or have too much caffeine are more likely to have premature atrial contractions . Youre more likely to get atrial flutter if you have lung disease, are an older adult or have diabetes. Lung disease, heart disease, caffeine and alcohol put you more at risk for atrial tachycardia. People with lung and heart diseases are also more likely to get atrial fibrillation.
Treating Supraventricular Tachycardia In Hospital
SVT is rarely life threatening. But you may need treatment in hospital if you keep having long episodes.
This may include:
- medicines to control the episodes of SVT given as tablets or through a vein
- cardioversion a small electric shock to the heart to help it get back to a normal rhythm
- catheter ablation a treatment where thin tubes are placed through a vein or artery into your heart to correct the problem with the electrical system this permanently cures the problem in most patients
Find out more about:
Recommended Reading: Cure To Heart Attack
