Measuring Congenital Cardiac Surgery Survival
Open heart surgeries can be risky, and some deaths and complications are inevitable. Unfortunately, no program has a 100% survival rate. When researching a pediatric heart surgery center, its also important to compare the survival rate by patient age, type of operation and STAT category . This is because these rates can be much different than the programs overall survival rate.
Heart Surgery Survival Rates By Type Of Procedure
The Cardiac Center team performs more than 850 pediatric heart surgeries a year, including open heart and closed heart procedures and heart transplants. Open heart procedures, which represent a major portion of our volume, require cardiopulmonary bypass and are usually the most complicated and complex procedures.
Pediatric heart surgery survival rates reflect the number of patients who survived within 30 days of the surgery or until the time they were discharged, whichever period is longer.
We track outcomes from common procedures as Quality Indicators for congenital heart surgery. The following data shows CHOP’s outcomes for these procedures.
The cardiac surgery indicators are included in the Society of Thoracic Surgeons Congenital Heart Surgery Database and in the National Quality Forum standards for pediatric heart surgery. The STS Congenital Heart Surgery Database contains data from over 100 congenital heart surgery centers in North America. The NQF is a nonprofit organization that sets or endorses standards to measure quality in healthcare.
How Often Is Sts Data Updated
Childrens Colorado and other centers submit data to the STS twice per year. The STS then verifies the data and generates reports that allow us to compare our results with our peers.
We publish our outcomes data on this website as soon as possible following the STS data release, also twice per year.
Recommended Reading: Which Feature Is The Hallmark Of Systolic Heart Failure
What Is The Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery Procedure
In general, the CABG procedure begins with general anesthesia and intubation followed by sawing through the breastbone.
- The heart is cooled with a preservative and then a cardiopulmonary bypass machine that takes over as a pump for the heart and also functions as a lung) is started .
- The bypass machine is placed so the aorta can be clamped off to allow bypass grafts to be attached to the aorta in a bloodless surgical field.
- Then bypass grafts are attached to a coronary artery beyond the blockage.
- The heart/lung machine is taken off and the heart takes over after rewarming as the pump that moves the blood.
- The breastbone is then wired back together.
- Other items like breathing tube and chest tubes are removed as the patient continues with recovery.
- Statistics suggest about 5% of new CABG patients need a redo or exploration due to bleeding after surgery.
What Happens After Open
When you wake up after surgery, you will have two or three tubes in your chest. These are to help drain fluid from the area around your heart. You may have intravenous lines in your arm to supply you with fluids, as well as a catheter in your bladder to remove urine.
You will also be attached to machines that monitor your heart. Nurses will be nearby to help you if something should arise.
You will usually spend your first night in the intensive care unit . You will then be moved to a regular care room for the next three to seven days.
Taking care of yourself at home immediately after the surgery is an essential part of your recovery.
Don’t Miss: How To Increase Heart Rate Immediately
When Do You Need Heart Valve Replacement Surgery
A heart valve disease develops when the valve becomes either stiff, narrow , or leaky . These two disease states of the valve disrupt the flow of blood in and out of the heart.
Heart valve diseases can be present by birth or occur as a complication of other health conditions, such as rheumatic heart disease.
Many people who have heart valve disease may never experience any symptoms. Sometimes, the valve disease is diagnosed when a woman is pregnant. Doctors may still recommend heart valve replacement surgery to prevent the worsening of the heart condition.
With a diseased valve, heart valve replacement surgery becomes an emergency if you experience:
Why It’s Carried Out
Like all organs in the body, the heart needs a constant supply of blood.
This is supplied by 2 large blood vessels called the left and right coronary arteries.
Over time, these arteries can become narrowed and hardened by the build-up of fatty deposits called plaques.
This process is known as atherosclerosis.
People with atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries are said to have coronary heart disease.
Your chances of developing coronary heart disease increase with age.
You’re also much more likely to be affected if:
- you smoke
- you’re overweight or obese
- you have a high-fat diet
Coronary heart disease can cause angina, which is chest pain that happens when the supply of oxygen-rich blood to the heart becomes restricted.
While angina can often be treated with medicine, severe angina may require a coronary artery bypass graft to improve the blood supply to the heart.
Another risk associated with coronary heart disease is the possibility of one of the plaques in the coronary artery rupturing , creating a blood clot.
If the blood clot blocks the blood supply to the heart, it can trigger a heart attack.
A coronary artery bypass graft may be recommended to reduce your chances of having a heart attack.
Read Also: Heart Attacks And Headaches
Pediatric Heart Surgery Volumes
Finally, when it comes to congenital heart surgery, volume matters. Studies show that kids who need heart surgery do better when they are treated by medical teams that perform a high number of surgeries. This is because surgeons in high-volume centers get more experience and see a wider range of heart defects than surgeons who perform only a handful of surgeries per year.
Performing hundreds of surgeries each year indicates that the hospital is a high-volume center and is likely to have better patient outcomes. This is particularly true for patients with complex heart defects.
Feeling Better About Heart Valve Surgery
It is true and unfortunate that a very, very, very small percentage of patients do not make it through the surgery. But, as they say, “Life is risk!” From the moment you wake up in the morning, you are in a risky situation. Just consider the act of driving.
I dont know about you… But I live in Los Angeles. The drivers here are crazy!!! At least once a week I yell out to someone, What are you trying to kill me???!!!
Recommended Reading: What Is The Difference Between Heart Rate And Blood Pressure
Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy And Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Defibrillator Device
If you have heart failure, you may need a special type of device called cardiac resynchronisation therapy device. As well as treating heart arrhythmias, this device also synchronises your hearts chambers to contract and relax in a regular way, which improves the pumping action of your heart.
There is also a type of CRT that can be used as above and in addition can deliver a “shock” to treat dangerous heart arrhythmias and then synchronise your hearts chambers to normal rhythm once more. This is CRT-D .
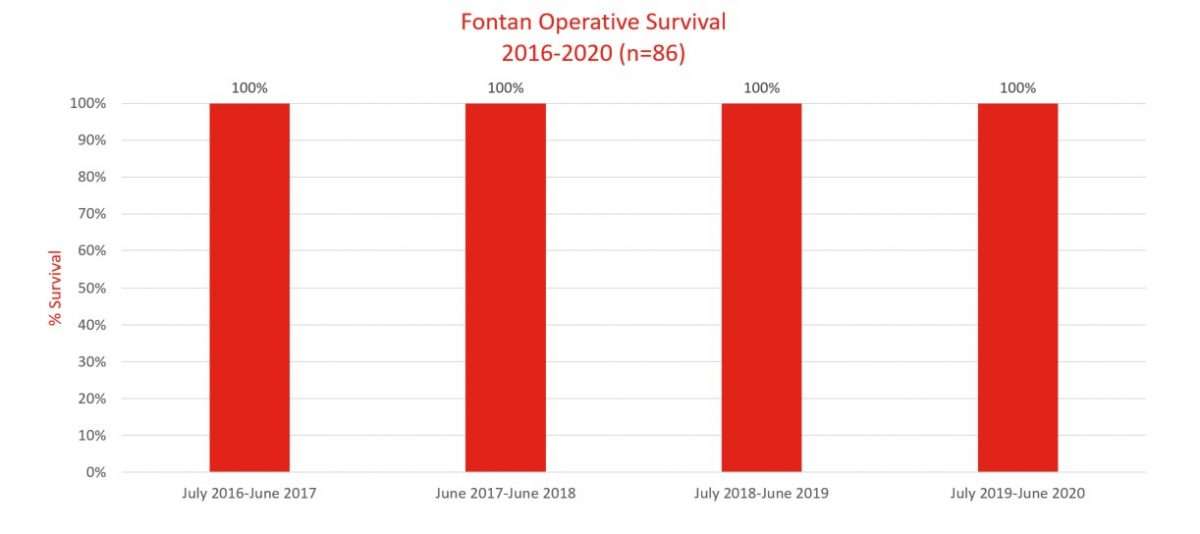
What Are Pediatric Cardiac Surgery Outcomes
In the medical world, the term outcomes means success rates. Many but not all pediatric cardiology centers measure and report their surgical outcomes to help parents make the best decision about where to take their child for heart surgery.
Here, we evaluate our success by monitoring and comparing our cardiac surgery statistics with other top pediatric hospitals. We also routinely check and publish other quality and patient safety metrics and heart transplant outcomes to ensure that families have the latest information when deciding who should care for their child.
Read Also: What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Congestive Heart Failure
Left Ventricular Assist Device
A VAD – also known as an LVAD for Left Ventricular Assist Device – is a circulatory support device. It takes blood from the left ventricle and pumps it into the aorta , helping the heart in pumping blood round the body.
It was originally designed to support the work of the heart while someone was waiting for a heart transplant. However, its now also used as a long-term support therapy for people who are not candidates for transplant and have end-stage heart failure.
Learn more about left ventricular assist devices through the British Heart Foundation.
How To Dispell The Fear Of Heart Surgery
Let me start by providing you with a few, well-documented facts about heart valve repair and heart valve replacement procedures.
Fact #1 and #2 According to the American Heart Association, each year over 700,000 heart surgeries take place across the world. Of those surgeries, more than 250,000 are valve repairs and valve replacements.
So what does that tell you? First, it tells you that you are not alone. There are many, many, many people out there that are just like you! So, dont feel like you are alone. Support groups and cardiac rehabilitation centers are waiting to support you before-and-after the heart valve replacement or repair.
Second, I share this fact because it should make you feel better about the medical procedure that awaits you. Whichever procedure you choose, please know that you are most likely not the first one to test it out. The odds are pretty high that your medical staff has performed this operation not once but hundreds of times.
Fact #3 The mortality rate for heart valve surgery is about 1.5%, according to The Society of Thoracic Surgeons.
Thats right. I did just provide you with the real big truth about heart valve surgery. Now, its your turn to process the mortality rate for operations like aortic valve replacement and mitral valve repair.
But… Wait!!!
And… Wait some more!!!
Recommended Reading: Does Baby Aspirin Help Prevent Heart Attacks
Data Analysis And Outcomes
The POCMA analysis was performed by a multidisciplinary and technical group composed of cardiologist, cardiac surgeon, intensive care physician, nurse and a perfusionist from the coordinating center. Using POCMA, the identified seminal event was then categorized according to the phase of the event during peri-operative care . A list of categories and subcategories capable of triggering mortality was developed based on POCMA for each perioperative phase. When multiple contributing factors were found, the first potential event was chosen, representing the best time for systematic correction of the course of mortality. Death of cardiac surgery patients was defined as avoidable if the chance of survival with better care or in the absence of contributing factors was> 50%. When there were no identifiable factors for a sudden death of a patient, it was defined as unavoidable death .
Preparing For The Surgery
Preparation for open heart surgery starts the night before. A person should eat an evening meal as usual but must not consume any food or drink after midnight.
It is a good idea to wear loose, comfortable clothing to assist with restricted movement following surgery, but wear whatever is comfortable.
Be sure to have all personal medical information on hand. This might include a list of medications, recent illness, and insurance information.
It is normal to feel anxious before an anesthetic, and people should not hesitate to seek reassurance from the healthcare team.
The doctor may request that the person washes their upper body with antibacterial soap. A member of the healthcare team may need to shave the persons chest area before they can have the anesthetic.
The doctors may also need to run tests before surgery, such as monitoring the heart or taking blood samples. A doctor or nurse might place a line into a vein to enable the delivery of fluids.
After the medical team has completed the preliminary tasks, the anesthesiologist will administer general anesthesia.
Don’t Miss: How Does Obesity Cause Heart Disease
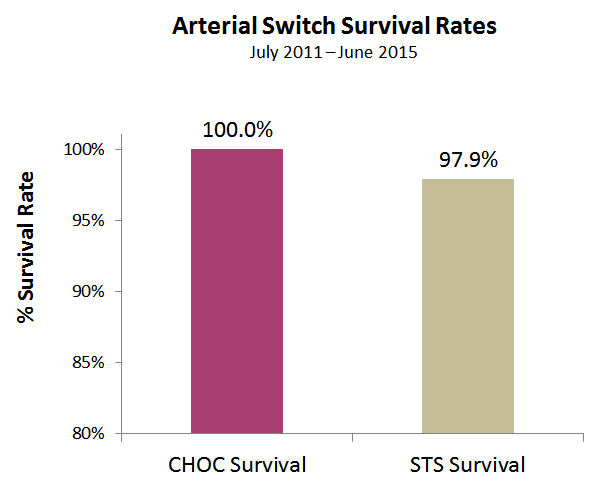
Newborn Cardiac Surgery Survival
Performing heart surgery on newborn babies is more challenging due to the young age and small size of the patients. By comparing newborn survival rates along with STAT category, parents can get an idea of how well the surgeons perform in the most challenging cases.
What we measure:
We compare our survival rates for newborn patients with national averages by the complexity of the surgery.
What it means:
At Childrens Colorado, our surgeons have extensive experience correcting heart defects in even the youngest patients some just a few hours old. Our survival rates for STAT 1, STAT 2 and STAT 5 cases are higher than the national averages.
Cardiac Surgery Survival By Procedure
Cardiac surgery programs can also report survival rates by each specific operation. These are called benchmark operations, and they are one of the ways surgical centers can compare outcomes. Note that these data do not include a patients specific risk factors prior to surgery.
In the table below, we report the total number of benchmark operations at Childrens Colorado, as well as the survival rates here compared to the national average.
What we measure:
Index case survival shows the percentage of patients who received a specific operation and were alive 30 days after their operation. It also includes patients who needed to be in the hospital longer than 30 days who were alive and successfully able to go home.
Index case survival
| 98.8% |
What it means:
For the majority of the open-heart surgeries listed above, our survival rates are higher than the national average.
It is challenging to compare outcomes by procedure alone. The procedure-alone data does not include important health-related factors such as age, other health conditions , and genetic conditions that can make procedures riskier. This is why pediatric heart surgery programs should report a wide range of outcomes, including how well patients do when they are at higher risk due to other health conditions.
Read Also: What Exactly Is A Heart Attack
Details About The Studies
Two separate studies presented at the March 2019 American College of Cardiology conference supported similar findings: After one to two years of follow-up, TAVR outcomes were found to be similar to surgical aortic valve replacement outcomes in patients with aortic stenosis and low surgical risk.
In a TAVR procedure, a doctor can repair a diseased aortic valve without open heart surgery. The new heart valve is inserted via catheter through an incision in the groin, guided inside the affected valve, and expanded to reopen it. Approximately half of patients with aortic stenosis today are considered to have low surgical risk hence the excitement about those studies.
Medtronics trial studied the CoreValve platform. Researchers assessed two endpoints after two years: death and disabling stroke. This study found that 5.3 percent of patients who had TAVR died or suffered a disabling stroke compared to 6.7 percent of patients who had surgery. All-cause mortality rates were the same for both procedures. Disabling stroke affected 1.1 percent of TAVR patients and 3.5 percent of surgery patients. The mean age of participants was 74.
The two competing medical device companies have both since published two-year results, which are in line with the initial reported findings.
What Are The Four Types Of Heart Valves
The heart is made up of four pumping chambers:
- Two atria: Upper chambers of the heart
- Two ventricles: Lower chambers of the heart
There are valves between each of the heart’s pumping chambers that open and close in coordination with each other. Their action keeps blood flowing forward through the heart. There are four valves in the heart:
- Tricuspid valve: Between the right atrium and the right ventricle
- Pulmonary valve: Between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery
- Aortic valve: Between the left ventricle and the aorta
You May Like: How Do I Lower My Heart Rate
Tavr Is Not The Beginning Of The End For Aortic Stenosis Open Heart Surgery
In March 2019, media outlets hailed two new studies on transcatheter aortic valve replacement as potentially signaling the beginning of the end of open heart surgery for aortic stenosis. Data from these studies supported the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s approval of TAVR for low-risk individuals replacing a narrowed aortic valve through a small incision in a procedure performed in the cardiac catheterization laboratory or hybrid operating room, as opposed to open heart surgery for patients with low surgical risk. As many as 50 percent of patients with aortic stenosis are low-surgical risk patients.
After the presentation of those landmark studies and the FDA approval of TAVR for low-risk individuals, many predicted the beginning of the end of open heart surgery. Some were concerned about how open heart surgery is portrayed in the media, such as in this article in The New York Times that referred to cracking open the ribs and stopping the heart. While medically accurate, that type of verbiage is likely to be scary to patients and overly dramatic. However, two years have passed, and surgery still remains a viable and important treatment for aortic valve disease.
How Long Will I Have To Wait For Surgery

The length of time you’ll have to wait to have a coronary artery bypass graft will vary from area to area.
Your GP or cardiac surgeon should be able to tell you what the waiting lists are like in your area or at the hospital you have chosen.
Ideally, you should be treated within 3 months of the decision to operate.
Don’t Miss: What Time Of Day Are Heart Attacks Most Common
Once Scary Heart Bypass Surgery Has Become Common And Safer
Frank Vignuli couldnt be having a heart attack, could he?
He wasnt short of breath. His chest didnt feel tight. But on the morning of Aug. 4, 2004, the 47-year-old from Wilmington, Del., didnt feel normal. His jaw was burning, his shoulder was in pain. But he didnt want to wake up his family. The port operations manager wasnt in the habit of going to the doctor or asking for help about his health.
Finally, concerned about the ongoing sensation in his jaw, Vignuli woke his wife. Soon, he was in an emergency room, where a doctor told him he had just had a heart attack and needed quadruple bypass surgery immediately.
Hours later, he awoke in the cardiac intensive care unit at Christiana Hospital in Newark, Del. Since then, Vignuli has lived a successful and active life once thought impossible for people with clogged arteries, which can lead to stroke, infections and heart attacks.
He has done so thanks to a procedure once considered risky: More than 9 percent of the first 150 patients to receive the procedure at one hospital in 1966 and 1967 died before they were able to be sent home. That figure went down to 3 percent in 1999 for a large comparable group of American and Canadian patients. Today, 14 years after Vignulis surgery, deaths before being discharged from the hospital are between 1 and 3 percent, and surgeons have refined the procedure and the rehab that follows even more.
It would take 50 more years for the surgery to succeed in a human.
