Why Are Heart Disease And Stroke Important
Currently more than 1 in 3 adults live with 1 or more types of cardiovascular disease.2 In addition to being the first and fifth leading causes of death, heart disease and stroke result in serious illness and disability, decreased quality of life, and hundreds of billions of dollars in economic loss every year.
The burden of cardiovascular disease is disproportionately distributed across the population. There are significant disparities in the following based on gender, age, race/ethnicity, geographic area, and socioeconomic status:7,8
- Prevalence of risk factors
How Are Ear Creases Associated With Heart Attacks
There is no definitive answer on the association between ear creases and heart attacks. Some experts theorize that the underlying process that causes the two are similar.
End-arteries supply the heart and ears. This means that once they lose blood supply, no other arteries can take over, causing damage to the tissue.
One theory suggests that ear lobe crease is associated with the loss of elastin and elastic fibers, the same process that damages blood vessels in CAD.
There is also a link between heart attack and ear creases across different ethnic populations, supporting the idea that a common genetic factor may be involved.
older study found that appearing older for ones age may be a marker of poor cardiovascular health. Specifically, visible signs including earlobe crease, male pattern baldness, and cholesterol deposits in the eyes , whether alone or in combination, are associated with an increased risk of ischemic heart disease and heart attack.
While the exact mechanism linking DELC and CAD still needs further research, a 2016 study stated that DELCs are a simple and feasible way to identify CAD.
The study suggests that DELC is independently associated with a risk of CAD. It also suggested a positive association with age, gender, and smoking status.
A 2017 study found that DELC could predict ischemic cerebrovascular events such as transient ischemic attack and stroke.
Another
What Are The Symptoms Of Heart Disease In Women
Women often experience different signs and symptoms of heart disease than men, specifically with regards to CAD and other cardiovascular diseases.
In fact, a 2003 study looked at the symptoms most often seen in women whod experienced a heart attack. The top symptoms didnt include classic heart attack symptoms such as chest pain and tingling. Instead, the study reported that women were more likely to say they experienced anxiety, sleep disturbances, and unusual or unexplained fatigue.
Whats more, 80 percent of the women in the study reported experiencing these symptoms for at least one month before their heart attack occurred.
Symptoms of heart disease in women can also be confused with other conditions, such as depression, menopause, and anxiety.
Common heart disease symptoms in women include:
- dizziness
- existing heart damage or disease
Also Check: Can Too Much Exercise Cause Heart Attack
How Heart Attack Symptoms Vary Between Men And Women
We use women and men in this article to reflect the terms that have been historically used to gender people. But your gender identity may not align with how your body experiences symptoms of a heart attack. Your doctor can better help you understand how your specific circumstances will translate into symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment.
Many people experience a mix of heart attack symptoms regardless of sex or gender. However, there are sex-specific differences in the presentation, biology, and outcomes of heart attacks.
A women , the pain is often described as tightness, squeezing, or pressure in the chest, while men tend to describe it as a heavy weight on the chest.
According to the American Heart Association , women are somewhat more likely than men to experience the following heart attack symptoms:
- shortness of breath
- pain in the upper back or jaw
- dizziness or lightheadedness
- extreme fatigue
Higher levels of estrogen can reduce the risk of a heart attack. As a result, women have a greater risk of a heart attack after menopause than before menopause.
However, women who have a heart attack are more at risk of underdiagnosis and undertreatment.
For example, a 2018 Swiss study found that women tend to wait longer to contact emergency services after experiencing typical heart attack symptoms. Researchers also found that women tend to experience greater delays in receiving treatment in emergency settings.
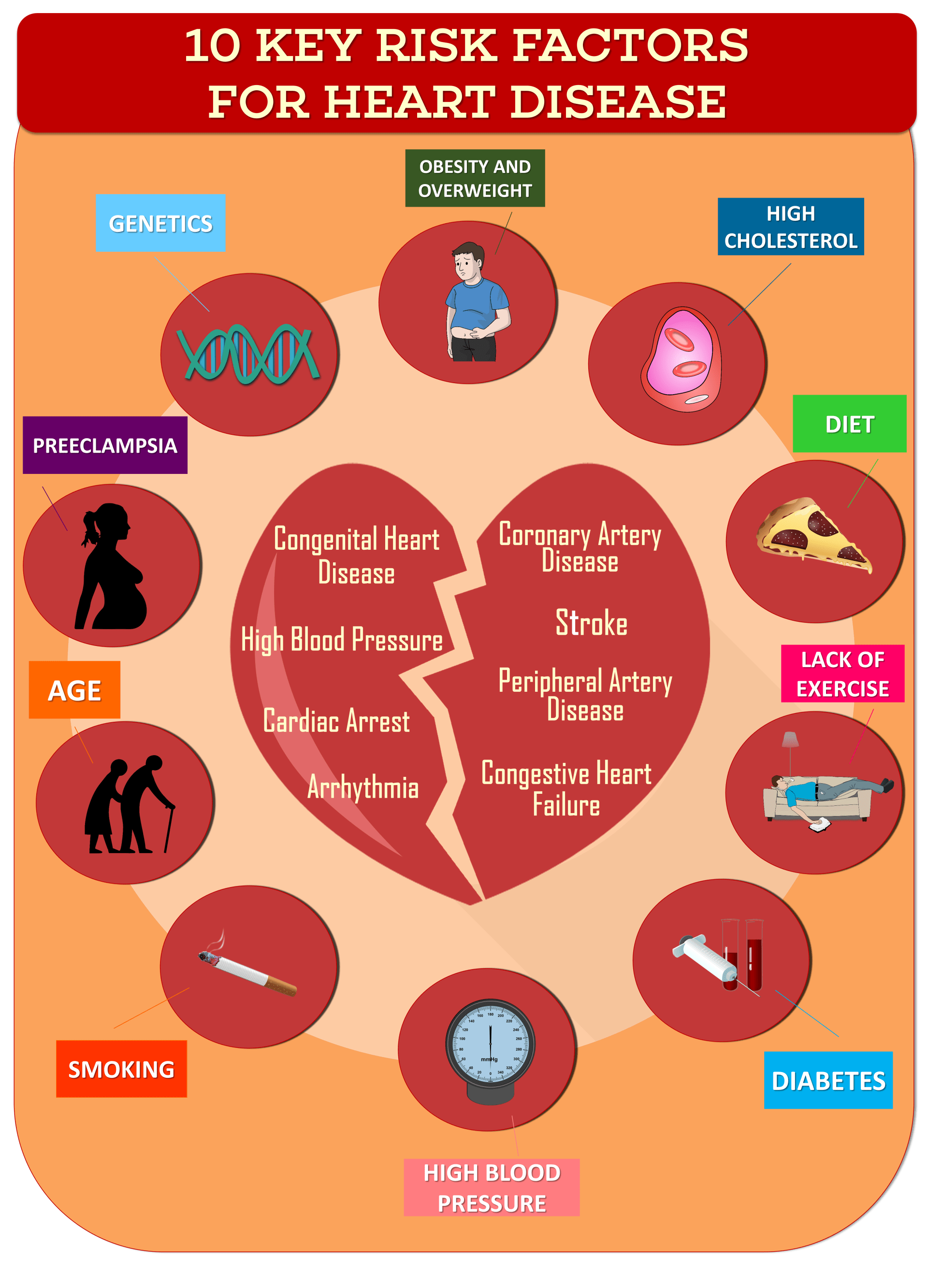
Major Risk Factors You Can Modify Treat Or Control

Tobacco smoke
The risk that smokers will develop coronary heart disease is much higher than that for nonsmokers.
Cigarette smoking is a powerful independent risk factor for sudden cardiac death in patients with coronary heart disease. Cigarette smoking also interacts with other risk factors to greatly increase the risk for coronary heart disease. Exposure to other peoples smoke increases the risk of heart disease even for nonsmokers.
Learn about smoking and cardiovascular disease
High blood cholesterol
As your blood cholesterol rises, so does your risk of coronary heart disease. When other risk factors are also present, this risk increases even more. A persons cholesterol level is also affected by age, sex, heredity and diet. Heres the lowdown on:
Learn more about managing your cholesterol.
High blood pressure
High blood pressure increases the hearts workload, causing the heart muscle to thicken and become stiffer. This stiffening of the heart muscle is not normal and causes the heart to function abnormally. It also increases your risk of stroke, heart attack, kidney failure and congestive heart failure.
When high blood pressure is present alongside obesity, smoking, high blood cholesterol levels or diabetes, the risk of heart attack or stroke increases even more.
Learn more about managing your blood pressure.
Physical inactivity
Learn more about getting active.
Obesity and being overweight
Learn more about managing your weight.
Diabetes
Read Also: What Happens To Your Heart Rate When You Exercise
Surgery Or Invasive Procedures
In some cases of heart disease, surgery or a medical procedure is necessary to treat the condition and prevent worsening symptoms.
For example, if you have arteries that are blocked entirely or almost completely by plaque buildup, your doctor may insert a stent in your artery to return regular blood flow. The procedure your doctor will perform depends on the type of heart disease you have and the extent of damage to your heart.
Some risk factors for heart disease cant be controlled, like your family history, for example. But its still important to lower your chance of developing heart disease by decreasing the risk factors that you can control.
How Can You Lower Your Heart Disease Risk
Research shows heart disease may be preventable more than half the time with simple changes in lifestyle. Besides lowering your risk for heart attack and stroke, these changes often can improve your overall physical and mental health. Here are some ways you can change lifestyle factors to reduce your risk of heart disease:
Quit smoking. Smoking is the most preventable risk factor. Smokers have more than twice the risk of heart attack as nonsmokers and are much more likely to die from them. If you smoke, quit. Better yet, donât start smoking in the first place. Even if you donât smoke, constant exposure to other peopleâs cigarette smoke raises your risk of heart disease.
Improve cholesterol levels. Your risk for heart disease increases with unhealthy cholesterol numbers. The right levels can vary somewhat depending on your age, sex, overall health, and family health history. Ask your doctor about the right levels for you. In general though, your levels should be as follows:
- Total cholesterol: less than 200 mg/dL
- âGood,â or HDL, cholesterol: 60 mg/dL or greater
- âBad,â or LDL, cholesterol: less than 100 mg/dL
- Triglycerides: less than 150 mg/dL
A diet low in cholesterol, saturated and trans fats, and simple sugars, and high in complex carbohydrates can help lower cholesterol levels in some people. Regular exercise will also help lower “bad” cholesterol and raise “good” cholesterol in some cases.
Show Sources
Don’t Miss: When Does A Heart Attack Occur
Symptoms Of Heart Attacks And Strokes
Often, there are no symptoms of the underlying disease of the blood vessels. A heart attack or stroke may be the first sign of underlying disease. Symptoms of a heart attack include:
- pain or discomfort in the centre of the chest and/or
- pain or discomfort in the arms, the left shoulder, elbows, jaw, or back.
In addition the person may experience difficulty in breathing or shortness of breath nausea or vomiting light-headedness or faintness a cold sweat and turning pale. Women are more likely than men to have shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, andback or jaw pain.
The most common symptom of a stroke is sudden weakness of the face, arm, or leg, most often on one side of the body. Other symptoms include sudden onset of:
- numbness of the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body
- confusion, difficulty speaking or understanding speech
- difficulty seeing with one or both eyes
- difficulty walking, dizziness and/or loss of balance or coordination
- severe headache with no known cause and/or
- fainting or unconsciousness.
People experiencing these symptoms should seek medical care immediately.
Are Heart Attacks Preventable
In the perfect world, all heart attacks could potentially be prevented. The requirement is being forewarned of who is at risk and being in the position to strategize how to reduce the risk.
The opportunity to undertake 3-D scanning of the heart and literally look at the health of the arteries before a patient develops any symptoms at all is a golden opportunity to literally identify the high-risk people in our community who could then receive the best possible risk reduction care with appropriate clinical evaluation and avoid a heart attack altogether.
We are completely comfortable with the idea of bowel cancer screening to identify bowel cancer early and save lives, we are also completely comfortable with the idea of mammography to identify breast cancer early and again save lives. It is a matter of awareness that we need to become comfortable with looking at the health of the heart arteries using 3-D scanning to save lives from heart attacks in the Australian community.
Read Also: Is 200 Heart Rate Bad
What Raises Your Risk For Heart Disease
There are risk factors for heart disease that you have control over and others that you donât. Uncontrollable risk factors for heart disease include:
- Being male
- Family history of heart disease
- Being postmenopausal
- Race
Heart disease risk factors that you can control revolve around lifestyle. These include:
- Unhealthy cholesterol numbers
- Uncontrolled high blood pressure
- Obesity
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- Uncontrolled stress, depression, and anger
- Poor diet
- Alcohol use
Being Overweight Or Obese
Being overweight or obese increases your risk of developing diabetes and high blood pressure, both of which are risk factors for CVD.
You’re at an increased risk of CVD if:
- your body mass index is 25 or above use the BMI healthy weight calculator to work out your BMI
- you’re a man with a waist measurement of 94cm or more, or a woman with a waist measurement of 80cm or more
Read more about obesity.
Don’t Miss: How To Calculate Heart Rate
Smoking And Secondhand Smoke Exposure
Smoking is a major cause of heart disease and stroke and causes 1 in every 4 deaths from these conditions. Smoking can damage the body several ways by:
- Raising triglycerides and lowering high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, also called good cholesterol.
- Making blood sticky and more likely to clot, which can block blood flow to the heart and brain.
- Damaging cells that line the blood vessels.
- Increasing the buildup of plaque in blood vessels.
- Causing thickening and narrowing of blood vessels.
About 34 million US adults smoke cigarettes, and every day, about 1,600 young people under age 18 try their first cigarette.
CDCs Response
CDCs is at the forefront of the nations efforts to reduce deaths and prevent chronic diseases that result from commercial* tobacco use, including heart disease and stroke. OSH prioritizes health equity by creating resources and opportunities for all people to be as healthy as possible.
CDC and its partners promote efforts to:
- Prevent young people from starting to use tobacco.
- Promote quitting among adults and young people.
- Reduce peoples exposure to secondhand smoke.
- Advance health equity by identifying and eliminating tobacco-related disparities.
Tips connects people who smoke with resources to help them quit, including 1-800-QUIT-NOW, which directs people to free services from their state quitlines.
What Lifestyle Changes Does Heart Disease Require
If youve recently received a heart disease diagnosis, talk to your doctor about steps you can take to stay as healthy as possible. You can prepare for your appointment by creating a detailed list of your everyday habits. Possible topics include:
- medications you take
- losing weight if youre overweight
- eating healthy
Making these changes all at once might not be possible. Discuss with your healthcare provider which lifestyle changes will have the biggest impact. Even small steps toward these goals will help keep you at your healthiest.
Don’t Miss: Is It Normal To Have Heart Palpitations Every Day
Actions For This Page
- There is no single thing that causes heart disease and stroke, but there are several risk factors that contribute to it.
- You can reduce your risk of developing cardiovascular disease by choosing healthy foods, quitting smoking, being physically active, managing conditions managing your weight and avoiding social isolation.
- Medicines are often used to help prevent cardiovascular disease , depending on your level of risk and other health conditions.
What Early Detection Can Help Prevent Heart Attacks
Will this require government funding? A very exciting and relatively new development is the opportunity to undertake 3-D scanning of the heart to literally look at the health of the arteries in someone who is fit and well before they have a problem. This imaging of the heart is done with CT scanning and can be an incredibly invaluable early detection tool, helping to plan the best possible strategies for an individual based on their specific results.
In many situations, this sort of testing becomes appropriate for men as they reach 50 years of age or just beyond or for women at 60 years of age or just beyond. There is no Medicare rebate for this testing however it does represent an excellent investment in health care and if one wanted to compare prices, it would cost less than a new set of tyres for your car.
Don’t Miss: How Do They Do Heart Bypass Surgery
How Does Heart Disease Affect Men
- Heart disease is the leading cause of death for men in the United States, killing 382,776 men in 2020thats about 1 in every 4 male deaths.1
- Heart disease is the leading cause of death for men of most racial and ethnic groups in the United States, including African Americans, American Indians or Alaska Natives, Hispanics, and whites. For Asian American or Pacific Islander men, heart disease is second only to cancer.2
- About 1 in 13 white men and 1 in 14 black men have coronary heart disease. About 1 in 17 Hispanic men have coronary heart disease.3
- Half of the men who die suddenly of coronary heart disease had no previous symptoms.4 Even if you have no symptoms, you may still be at risk for heart disease.
How Can The Burden Of Cardiovascular Diseases Be Reduced
The key to cardiovascular disease reduction lies in the inclusion of cardiovascular disease management interventions in universal health coverage packages, although in a high number of countries health systems require significant investment and reorientationto effectively manage CVDs.
Evidence from 18 countries has shown that hypertension programmes can be implemented efficiently and cost-effectively at the primary care level which will ultimately result in reduced coronary heart disease and stroke. Patients with cardiovascular diseaseshould have access to appropriate technology and medication. Basic medicines that should be available include:
- aspirin
Recommended Reading: How To Measure Max Heart Rate
Heart Disease And Stroke Risk Factors
There is no single cause for CVD, but there are risk factors that increase your chance of a heart attack or stroke. There are modifiable factors and non-modifiable factors .
Heart disease and stroke risk factors that you can change include:
- Management of depression.
Social isolation and lack of social support are risk factors for CVD that can be changed, although it can seem challenging. One way to help with loneliness is to learn how to improve your social connections.
Risk factors you canât change include increasing age, being male, being post-menopausal and having a family history of CVD. Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people are also at increased risk of CVD.
The good news is that you can reduce your overall risk of developing CVD by leading a healthy lifestyle and taking medicines as prescribed by your doctor.
How Is A Heart Attack Diagnosed
Doctors typically diagnose a heart attack after they perform a physical exam and review your medical history. Your doctor will likely conduct an electrocardiogram to check your hearts electrical activity.
An echocardiogram, which uses sound waves to create an image of the hearts chambers and valves, can reveal how blood is flowing through the heart and what parts of the heart, if any, have been damaged.
Your doctor may also order a cardiac catheterization. This is a probe inserted into the blood vessels through a flexible tube called a catheter. It allows your doctor to view areas in and around your heart where plaque may have built up. They can also inject dye into your arteries, order an X-ray to see how the blood flows, and view any blockages.
Your healthcare team will likely also take a sample of your blood or perform other tests to see if theres evidence of heart muscle damage.
A commonly used blood test checks for levels of troponin T, a protein found in the heart muscle. Elevated levels of troponin T in the bloodstream is associated with a heart attack.
If youve had a heart attack, your doctor may recommend a procedure . These procedures can relieve pain and help prevent another heart attack from occurring.
Common procedures include:
Your doctor may also prescribe medications to treat your heart attack, including:
- aspirin
- blood pressure medication
- beta-blockers
You May Like: How To Wear Peloton Heart Rate Monitor
