What Is The Link Between Diabetes Heart Disease And Stroke
High blood glucose from diabetes can damage your blood vessels and the nerves that control your heart and blood vessels. Over time, this damage can lead to heart disease.1
People with diabetes tend to develop heart disease at a younger age than people without diabetes. Adults with diabetes are nearly twice as likely to have heart disease or stroke as adults without diabetes.2,3
The good news is that the steps you take to manage your diabetes also help lower your chances of having heart disease or stroke.
Manage Stress And Get Help For Depression
- Manage stress. Stress can hurt your heart. Keep stress low by talking about your problems and feelings, rather than keeping your feelings hidden. Try different ways to reduce stress, such as exercise, deep breathing, meditation, or yoga.
- Get help for depression. Getting treatment for depression can help you stay healthy.
What Is Angina And Why Is Unstable Angina A Concern
Angina is a symptom of coronary artery disease. Angina occurs when there is not enough blood flow to the heart. Angina can be dangerous. So it is important to pay attention to your symptoms, know what is typical for you, learn how to control it, and know when to call for help.
Symptoms of angina include chest pain or pressure, or a strange feeling in the chest. Some people feel pain, pressure, or a strange feeling in the back, neck, jaw, or upper belly, or in one or both shoulders or arms.
There are two types of angina:
- Stable angina means that you can usually predict when your symptoms will happen. You probably know what things cause your angina. For example, you know how much activity usually causes your angina. You also know how to relieve your symptoms with rest or nitroglycerin.
- Unstable angina means that your symptoms have changed from your typical pattern of stable angina. Your symptoms do not happen at a predictable time. For example, you may feel angina when you are resting. Your symptoms may not go away with rest or nitroglycerin.
Unstable angina is an emergency. It may mean that you are having a heart attack.
Read Also: How Does Heart Disease Affect The Skeletal System
Is All Chest Pain A Heart Attack
No. One very common type of chest pain is called angina. Its a recurring discomfort that usually lasts only a few minutes. Angina occurs when your heart muscle doesnt get the blood supply and oxygen that it needs.
The difference between angina and a heart attack is that angina attacks dont permanently damage the heart muscle.
There are different types of angina, including:
- Stable angina, or angina pectoris Stable angina often occurs during exercise or emotional stress when your heart rate and blood pressure increase, and your heart muscle needs more oxygen. Learn more about stable angina.
- Unstable angina, sometimes referred to as acute coronary syndrome Unstable angina occurs while you may be resting or sleeping, or with little physical exertion. It comes as a surprise. Unstable angina can lead to a heart attack and it should be treated as an emergency. Learn more about unstable angina.
Take Other Steps To Live Healthier
After a heart attack, it’s also important to:
- Take your medicines exactly as directed. Do not stop taking your medicine unless your doctor tells you to.
- Do not take any over-the-counter medicines or natural health products without talking to your doctor first.
- If you are a woman and have been taking hormone therapy, talk with your doctor about whether you should continue taking it.
- Keep your blood sugar in your target range if you have diabetes.
- Get a flu vaccine every year. It can help you stay healthy and may prevent another heart attack.
- Get the pneumococcal vaccine. If you have had one before, ask your doctor whether you need another dose.
- If you drink alcohol, drink in moderation. Ask your doctor how much, if any, is okay for you.
- Seek help for sleep problems. Your doctor may want to check for sleep apnea, a common sleep problem in people who have heart disease. For more information, see the topic Sleep Apnea.
You May Like: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of A Heart Attack
- Chest pain, tightness, or heaviness that can last 30 minutes or longer
- Pressure, crushing, squeezing, or burning in your chest
- Discomfort that spreads to your neck, jaw, shoulders, back, or arms
- Heartburn, abdominal pain, nausea, or vomiting
- Feeling weak, dizzy, or like you are going to faint
- Trouble catching your breath or taking a deep breath
- Feeling cold and sweaty
- Fast heartbeat
- You may not have typical symptoms if you are a woman or an older adult, or have diabetes or heart failure. You may only have shortness of breath and no other symptoms. You may have no symptoms at all.
Heart Attack Recovery Faqs
Most people survive their first heart attack and return to their normal lives to enjoy many more years of productive activity. But having a heart attack does mean you need to make some changes in your life.
Your doctor will advise you of medications and lifestyle changes according to how badly your heart was damaged and what degree of heart disease you have.
It’s up to you to follow your doctor’s recommendations to make a full recovery.
You May Like: List The Steps Of How To Calculate Your Target Heart Rate Zone
Control Cholesterol And Blood Pressure
To reduce your risk of a heart attack, you will need to control your cholesterol and manage your blood pressure. Quitting smoking, changing the way you eat, and getting more exercise can help. But if these things don’t work, you may also need to take medicines.
Prevention Of A Heart Attack
You can help prevent a heart attack by managing certain risk factors and making healthy lifestyle choices.
Its important to keep tabs on your blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and body weight, and to take action when any of these reaches an unhealthy level. If you have diabetes, its also important to manage your blood sugar well.
A heart-healthy lifestyle involves not smoking, getting enough physical activity, and following a healthy diet thats rich in fruits, vegetables, fiber, healthy fats, and lean . You should drink in moderation, if at all, and try to reduce or manage stress.
You May Like: Can Too Much Vitamin D Cause Heart Palpitations
How Is Heart Attack Diagnosed
You may need several tests to determine the cause of your symptoms.
- Electrocardiogram. This test records the electrical activity of your heart. It can help diagnose heart rhythm problems. It can also find damage from a decrease in blood flow.
- Blood tests.When blood flow decreases, special proteins leak into the blood system. A blood test can detect these proteins. Your doctor will want to test your blood several times during the first 24 to 48 hours after yours symptoms start.
Other tests your doctor may want you to have include:
- Echocardiogram. This test uses sound waves to create pictures of your heart. The pictures show how well your heart is pumping. It can show if there are problems with your heart valves.
- Chest X-ray.This looks at the size and shape of your heart. It can show if there is any fluid in your lungs.
- Nuclear imaging.This test injects a tiny radioactive substance into your blood. This substance travels to your heart to create pictures of it. It shows how well your heart is pumping. The radioactive substance is safe and leaves your body after the test is finished.
- Coronary angiography. This test is sometimes called cardiac catheterization. It involves inserting a long tube into a blood vessel. The tube is guided to the heart or arteries that carry blood to the heart. A substance is injected into the tube that makes it visible by X-ray. It allows your doctor to see where the blockage that caused the decrease in blood flow to your heart is located.
Preventing A Heart Attack
There are 5 main steps you can take to reduce your risk of having a heart attack :
- smokers should quit smoking
- lose weight if you’re overweight or obese
- do regular exercise adults should do at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity each week, unless advised otherwise by the doctor in charge of your care
- eat a low-fat, high-fibre diet, including wholegrains and at least 5 portions of fruit and vegetables a day
- moderate your alcohol consumption
You May Like: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
Have An Emergency Action Plan
Make sure that you have an emergency action plan in case you or someone in your family has a heart attack. This is very important if youre at high risk for, or have already had, a heart attack.
Write down a list of medicines you are taking, medicines you are allergic to, your health care providers phone numbers , and contact information for a friend or relative. Keep the list in a handy place.
Talk with your doctor about the signs and symptoms of a heart attack, when you should call 911, and steps you can take while waiting for medical help to arrive.
When Should I See My Doctor
If calling triple zero does not work on your mobile, try calling 112. Early treatment could save a life.
See your doctor regularly to manage your general health, test for heart disease risk factors and help you take steps to prevent a heart attack.
Recommended Reading: Does Tylenol Increase Heart Rate
Complications Of A Heart Attack
Complications of a heart attack can be serious and possibly life threatening.
These include:
- arrhythmias these are abnormal heartbeats. 1 type is where the heart begins beating faster and faster, then stops beating
- cardiogenic shock where the heart’s muscles are severely damaged and can no longer contract properly to supply enough blood to maintain many body functions
- heart rupture where the heart’s muscles, walls or valves split apart
These complications can happen quickly after a heart attack and are a leading cause of death.
Many people die suddenly from a complication of a heart attack before reaching hospital or within the 1st month after a heart attack.
The outlook often depends on:
- age serious complications are more likely as you get older
- the severity of the heart attack how much of the heart’s muscle has been damaged during the attack
- how long it took before a person received treatment treatment for a heart attack should begin as soon as possible
What Are The Risks
All medical procedures come with a certain amount of risk. Just like many other types of invasive procedures, you may have an allergic reaction to the anesthetic, the dye, or some of the materials used in the angioplasty. Some other risks associated with coronary angioplasty include:
- bleeding, clotting, or bruising at the point of insertion
- scar tissue or blood clots forming in the stent
- an irregular heartbeat, or arrhythmia
- damage to a blood vessel, heart valve, or artery
- kidney damage, especially in people who have preexisting kidney problems
- an infection
This procedure is also associated with the risk of stroke, but the risk is low.
The risks of an emergency angioplasty after a heart attack are greater than those of an angioplasty performed under different circumstances.
Angioplasty isnt a cure for blocked arteries. In some cases, arteries can become narrow again if plaque builds up again in the artery or in a previously placed stent. This is called restenosis. The risk of restenosis is higher when your doctor doesnt use a stent.
Recommended Reading: How Accurate Is Fitbit Charge 2 Heart Rate
Symptoms And Signs Of A Stemi
A STEMI has the classic symptom of pain in the center of the chest. This chest discomfort may be described as a pressure or tightness rather than a sharp pain. Some people who experience STEMIs also describe feeling pain in one or both arms or their back, neck, or jaw.
Other symptoms that may accompany chest pain include:
- nausea
- lightheadedness
- breaking out in a cold sweat
Other Factors That Affect Atherosclerosis
Other factors also may raise your risk for atherosclerosis, such as:
- Sleep apnea. Sleep apnea is a disorder that causes one or more pauses in breathing or shallow breaths while you sleep. Untreated sleep apnea can raise your risk for high blood pressure, diabetes, and even a heart attack or stroke.
- Stress. Research shows that the most commonly reported “trigger” for a heart attack is an emotionally upsetting event, especially one involving anger.
- Alcohol. Heavy drinking can damage the heart muscle and worsen other risk factors for atherosclerosis. Men should have no more than two drinks containing alcohol a day. Women should have no more than one drink containing alcohol a day.
Also Check: How Much Blood Does The Heart Pump
What Are The Symptoms Of A Heart Attack
Symptoms of a heart attack include:
- Angina: Chest pain or discomfort in the center of the chest also described as a heaviness, tightness, pressure, aching, burning, numbness, fullness or squeezing feeling that lasts for more than a few minutes or goes away and comes back. It is sometimes mistakenly thought to be indigestion or heartburn.
- Pain or discomfort in other areas of the upper body including the arms, left shoulder, back, neck, jaw, or stomach.
- Trouble breathing or feeling shortness of breath.
- Sweating or “cold sweat.”
- Rapid or irregular heart beats.
If you are having any of these symptoms and they last for more than 5 minutes, SEEK EMERGENCY TREATMENT WITHOUT DELAY. These symptoms could be the signs of a heart attack and you need to get treatment as soon as possible.
Are There Other Causes Of Heart Attack Besides Blockage
Sometimes a coronary artery temporarily contracts or goes into spasm. When this happens the artery narrows, and blood flow to part of the heart muscle decreases or stops.
The causes of spasms are unclear. A spasm can occur in normal-appearing blood vessels as well as in vessels partly blocked by atherosclerosis. A severe spasm can cause a heart attack.
Another rare cause of heart attack is spontaneous coronary artery dissection, which is a spontaneous tearing of the coronary artery wall.
Recommended Reading: Can Constipation Cause Heart Palpitations
What Increases Your Risk
Coronary artery disease is the major cause of heart attacks. So the more risk factors you have for CAD, the greater your risk for unstable angina or a heart attack. The main risks for CAD are:
- Smoking.
- Family history of early CAD.
- Age. The risk increases in men after age 45 and in women after age 55.
Reducing Your Risk For A Heart Attack

Lowering your risk factors for ischemic heart disease can help you prevent a heart attack. Even if you already have heart disease, you still can take steps to lower your risk for a heart attack. These steps involve making heart-healthy lifestyle changes and getting ongoing medical care for related conditions that make a heart attack more likely. Talk to your doctor about whether you may benefit from aspirin primary prevention, or using aspirin to help prevent your first heart attack.
Also Check: Tylenol Heart Rate
What Are The Symptoms Of Heart Attack
The major symptoms of a heart attack are
- Chest pain or discomfort. Most heart attacks involve discomfort in the center or left side of the chest that lasts for more than a few minutes or that goes away and comes back. The discomfort can feel like uncomfortable pressure, squeezing, fullness, or pain.
- Feeling weak, light-headed, or faint. You may also break out into a cold sweat.
- Pain or discomfort in the jaw, neck, or back.
- Pain or discomfort in one or both arms or shoulders.
- Shortness of breath. This often comes along with chest discomfort, but shortness of breath also can happen before chest discomfort.
Other symptoms of a heart attack could include unusual or unexplained tiredness and nausea or vomiting. Women are more likely to have these other symptoms. Learn more about women and heart disease.
Every 40 seconds, someone in the United States has a heart attack.1Learn more facts about heart attack and heart disease.
Diagnosis Of A Heart Attack
Tests to help diagnose a heart attack include:
- a blood test to measure levels of enzymes released into the blood when the heart muscle is damaged
- cardiac catheterisation a tube, or catheter, is threaded into the coronary arteries via a blood vessel in the groin. A special dye is then injected into the coronary artery. This outlines the artery while movie x-rays are taken. Narrowings and blockages within the artery are outlined by the dye
- electrocardiogram a reading of the hearts electrical impulses.
Also Check: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
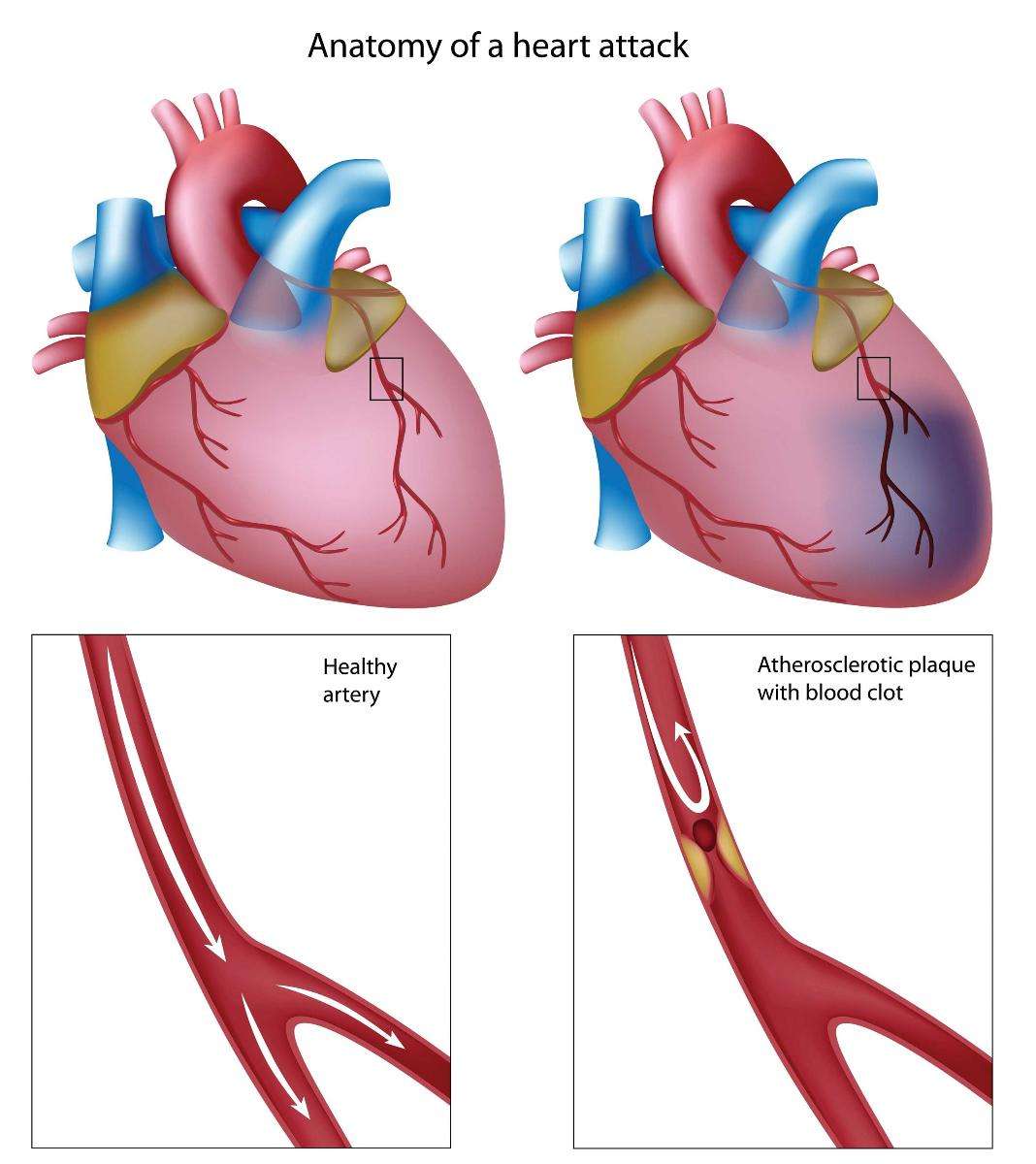
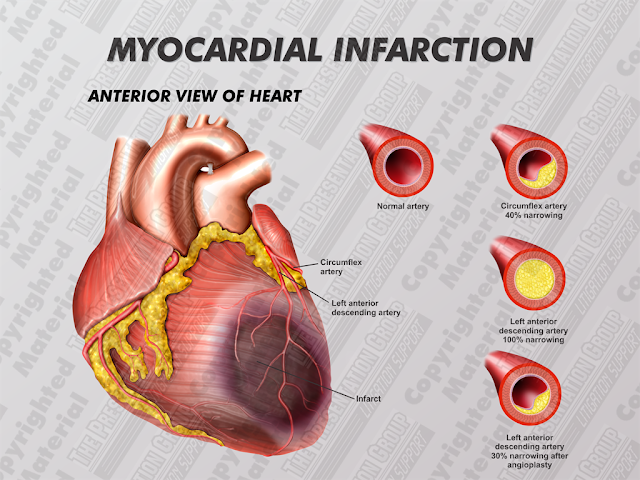
Causes And Risk Factors Of Heart Attacks
Most heart attacks are caused by coronary artery disease , in which your arteries become narrowed and hardened due to the buildup of a fatty substance called plaque.
Plaque is a combination of fat, cholesterol, and other substances that can build up in the inner lining of your artery walls.
This buildup is known as atherosclerosis, or “hardening of the arteries.”
Blood flow to your heart can become completely cut off or severely reduced when a blood clot gets lodged in any artery that has been previously narrowed by a buildup of plaque.
Less commonly, heart attacks may be caused by a spasm, or tightening, of a coronary artery. Spasms may be related to smoking, high blood pressure, alcohol withdrawal, recreational stimulant drugs, or exposure to extreme cold or stress.
There are three common risk factors for heart disease that can put you at greater risk for a heart attack:
- High blood pressure
