Newborn Survival By Stat Category
HIGHER IS BETTER
What it means:
At Childrens Colorado, our surgeons have extensive experience correcting heart defects in even the youngest patients some just a few hours old. Our survival rates for STAT 1, STAT 2 and STAT 5 cases are higher than the national averages. Across all STAT categories, Children’s Colorado has a newborn survival rate of 94.4% compared to a national average of 92.5%
What Did This Study Do
This systematic review identified 93 observational studies including a total 53,884 adults undergoing bioprosthetic aortic valve replacement for severe aortic stenosis. Only studies published after 2006 were included to ensure relevance to current technologies. Patients were enrolled between 1977 and 2013. Average patient age was 53 to 92 years.
The researchers carried out several subgroups analyses to examine the influence of different factors. These included patient age, whether the study also included mechanical valves, and risk of study bias.
Overall the risk of bias was assessed as low in 51 studies, moderate for 21, and high risk for 21 studies.
Newark Beth Israel Medical Center Heart Transplant Survival/life Expectancy
The Newark Beth Israel Heart Transplant team notes that a heart transplant is considered the gold standard treatment option for end-stage heart failure. It is only recommended when conservative treatment options fail. The worldwide heart transplant survival rate is greater than 85 percent after one year and 69 percent after 5 years for adults, which is excellent when compared to the natural course of end-stage heart failure.
The first year after surgery is the most important in regards to heart transplant survival rate. The annual death rate after the first year is only 4 percent. Recent improvements to the heart transplant survival rate can be attributed to an increased rate of survival after the first year, and specifically to improvements seen with immunosuppressant medications.
Immunosuppressant medications suppress the immune system, thereby decreasing its ability to attack foreign invaders. These medications are given to heart transplant patients to prevent the immune system from attacking the new donor heart. Immunosuppressant therapy is now tailored to the individual patient.
Also Check: Icd 10 For Congestive Heart Failure
Why Can Data About Survival Be Difficult To Interpret
Heart disease covers a wide range of disorders, from relatively minor to more severe conditions. Some hospitals take on more complicated conditions and tend to operate on children with a lower chance of survival. Also, every child is unique and may respond differently to treatment .
We therefore would not expect all hospitals to have the same survival rate: we should take into account how ill the children were that the hospitals treated. In other words, if one hospital has a higher survival rate than another hospital this is not necessarily evidence that one hospital is better than the other it could indicate that the second hospital treated children with more severe problems.
Purpose Of Quadruple Bypass
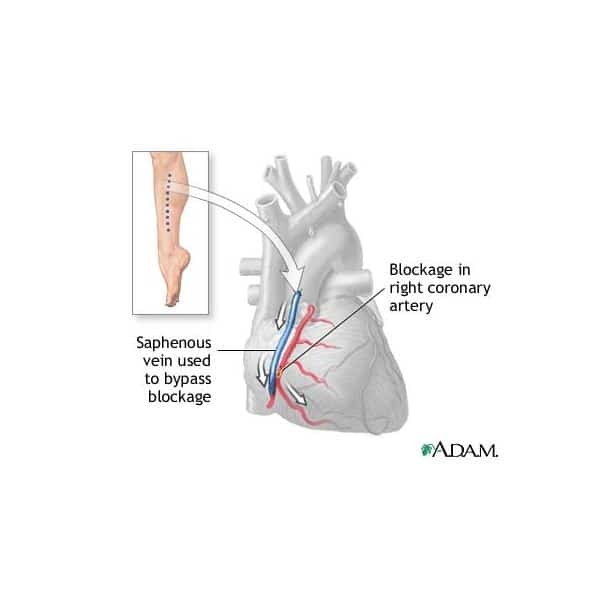
The coronary arteries can become blocked when plaque builds up inside the blood vessels. This condition is known as coronary artery disease.
If the blockage in the coronary artery is severe, it can interfere with blood flow to a section of the heart muscle and cause chest pain, also known as angina. It is possible to have several arteries blocked at the same time, which can pose a significant risk to the heart.
Usually, the chest pain occurs during physical exertion. This is because the demand for oxygen in the heart is greater. The narrowed vessels are not able to meet the increase in the heart muscle’s needs. That is when the chest pain will begin.
If the blockage severely or completely prevents blood from flowing to a part of the heart muscle, a heart attack may occur.
In many cases, coronary artery disease can be treated with medication or lifestyle changes. It also may be treated with surgery that is less invasive than a quadruple bypass, such as angioplasty. A stent, a tube that holds the artery open to restore blood flow, may be placed in the artery.
In general, if one or two vessels need to be repaired, or if the blockage is too long to place a stent, then surgery is likely to be recommended. At the time of bypass surgery, all of the blocked vessels will usually be treated at the same time.
You May Like: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
Proteolysis Metalloproteinases And Inflammation
In AAA, the aortic media appears to degrade by way of a proteolytic process. This implies an increase in the concentration of proteolytic enzymes relative to the concentration of their inhibitors in the abdominal aorta as the individual ages.
Some research has focused on the role of the metalloproteinases, a group of zinc-dependent enzymes responsible for tissue remodeling. Reports have documented increased expression and activity of matrix metalloproteinases in people with AAAs. MMPs and other proteases have been shown to be secreted into the extracellular matrix of AAAs by macrophages and aortic smooth-muscle cells.
MMPs and their inhibitors are present in normal aortic tissue and are responsible for vessel-wall remodeling. Aneurysmal tissue tends to demonstrate increased MMP activity and decreased inhibitor activity, which favor the degradation of elastin and collagen. The mechanism that tips the balance in favor of degradation of elastin and collagen in the aortic wall of AAAs by MMPs and other proteases is not yet known.
Upon histologic examination, AAAs demonstrate a chronic adventitial and medial inflammatory infiltrate. Infiltration of AAAs with lymphocytes and macrophages may trigger protease activation via various cytokines .
What Is The Adequate Follow
Having shown the differences between the mortality measures and the effects on benchmarking, the next question is to decide which measure to choose. Considering the arguments mentioned above, it would be logical to take the longest follow-up possible before benchmarking is performed. However, a long follow-up has several downsides. First, the follow-up of patients after discharge is time-consuming and requires effort and money. This problem should not be underestimated, since an incomplete follow-up might lead to biased results . Secondly, the question is what it is that needs to be measured different mortality rates might reflect other processes. For instance, patient compliance to medication, quality of home care, extent of involvement of the cardiologist and many other factors have an increasing effect on the risk of mortality after discharge. On the contrary, the effect of the initial care provided around the intervention in the hospital is likely to decrease in time. Therefore, it seems less adequate to measure mortality after 1 year or longer, when it is the process surrounding the cardiac surgery in which one is interested. In 1986, Blackstone et al. suggested that the hazard can be subdivided into an early, constant and a late phase . In benchmarking of outcomes, the early phase reflects the part of the process of care that we want to evaluate.
Read Also: New Heart Surgery Without Opening Chest
You May Be Interested To Read
A study of developmental problems in young children: Hoskote AU, and others. Neurodevelopmental status and follow-up in preschool children with heart disease in London, UK. Arch Dis Child. 2021 106:263-271
Outcomes after childrens heart surgery in a quality improvement scheme: Gaies M, and others. Improvement in Pediatric Cardiac Surgical Outcomes Through Interhospital Collaboration. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 74:2786-2795
Research to identify the children most likely to have developmental problems after heart surgery: Bucholz EM, and others. Trajectories in Neurodevelopmental, Health-Related Quality of Life, and Functional Status Outcomes by Socioeconomic Status and Maternal Education in Children with Single Ventricle Heart Disease. J Pediatr. 2021 229:289-293
Patient information on congenital heart disease from the Royal Brompton and Harefield hospital: Congenital heart disease in children
Funding: This project was funded by the NIHR Health Services and Delivery Research programme.
Conflicts of Interest: The study authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Disclaimer: NIHR Alerts are not a substitute for professional medical advice. They provide information about research which is funded or supported by the NIHR. Please note that views expressed in NIHR Alerts are those of the author and reviewer and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR or the Department of Health and Social Care.
What To Expect On The Day Of Surgery
General anesthesia is started right before the surgical procedure. Then the cardiothoracic surgeon starts harvesting veins from the legs or arms. These vessels are used for bypass grafts.
The surgical team will confirm that the vessels are healthy enough to be used to bypass the diseased coronary arteries. Meanwhile, the surgeon opens the chest and begins preparing the heart. They may also remove another vessel from the left chest, to supplement the other veins already harvested.
During the vast majority of quadruple bypass surgeries, the heart is stopped to prevent motion. A heart-lung bypass machine is used to allow both the heart and lungs to be still.
This helps the surgical team complete the graft portion of the surgery safely and quickly. The machine supplies oxygen to the blood instead of the lungs doing so. It pumps the oxygenated blood through the body as the heart would normally do.
During surgery, the blood vessels are attached to the existing heart vessel, around the areas of blockage. It’s similar to a quick detour you might take to avoid traffic, with the blood literally rerouted around the blocked portion of the cardiac artery.
You May Like: When Was The First Open Heart Surgery
Uk Heart Surgery Survival Rates Exceptionally Good
26 June, 2008By NT Contributor
Survival rates for patients undergoing heart surgery in the UK remain consistently high, according to figures published today by the Healthcare Commission .
Over 35,000 heart operations were performed at 37 heart units across the UK between April 2006 and March 2007.
The national survival rate for all types of heart operations was 96.6%, up by 0.1% from last years figure.
Based on the percentage range of patients expected to survive – taking into account patient risk factors the HCC said the rate of survival for all heart surgery in the UK is as good as, or better, than rates of survival in other developed countries.
According to the data, survival rates at 32 centres were as expected and five centres performances were better than expected.
Of the 20,474 heart bypass operations performed, 98.32% of patients survived nationally, as did 98.01% of the 3,522 patients who underwent aortic valve replacement.
Leslie Hamilton, president of The Society for Cardiothoracic Surgery, said the quality of care in the UK is now exceptionally and uniformly good.
Sir Ian Kennedy, chairman of The Healthcare Commission, added: Some feared that surgeons may take on fewer high-risk operations but this has not proved to be the case. In fact, the opposite is true.
Making this information available has increased patients confidence in heart surgeons. It is a fine example for other surgical specialities to follow.
Survival Rate After Nhs Heart Surgery Is Higher Than European Average
Patients undergoing bypass surgery in the NHS have a better chance of surviving than almost anywhere in Europe, shows the first study to compare outcomes from heart operations across the continent.
Findings from the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery show that, after adjustment for risk, the in-hospital mortality rate after coronary artery bypass graft surgery in England was 1.8% between 2006 and 2008. In Wales the rate was 1.1% and in Scotland it was 2.2%. By comparison the average rate across 25 European countries was 2.4%.
Although it is the fourth time the association has published a report
You May Like: How Does Heart Attack Occur
Other Frequently Asked Questions
- Is there such a thing as too old? What about aortic valve replacement in a 90-year-old? Ultimately, theres two people who matter when making this decision: the senior and their doctor. There are risks associated with any medical procedure, but you may decide that the cost of inaction outweighs the risks.
- If I had heart valve replacement at 65, will I need another later? Possibly, depending on a number of factors, including the health of your other valves at the time. Its not uncommon for those with heart valve issues to live long lives with the help of modern medicine, nutrition and fitness.
What Procedures And Tests Diagnose Aortic Aneurysms
Most aortic aneurysms cause no symptoms and are found when a person undergoes a medical test or procedure for some other reason. Others are found only when the individual has symptoms .
The typical symptoms of an abdominal aortic aneurysm are not specific. This means that they could be caused by a number of different conditions.
- The doctor will probably not know at first what is causing symptoms. He or she will rapidly consider the possibilities and develop a plan for systematically ruling each one out.
- This evaluation will start with the most serious conditions, and ruptured aneurysm is near the top of the list.
- If the person is able, they can help by giving a focused, detailed description of how the symptoms started, how they were feeling before the symptoms started, and how the situation once the symptoms started. Because some patients cannot communicate or remember items, it is helpful to arrive in an emergency department with someone who knows or who has access to the patients medical and surgical history. This is especially helpful if the patient has a documented history of an aortic aneurysm or conditions that might predispose them to aneurysms .
A full exam, with special attention to the cardiovascular system and abdomen, will give clues to the diagnosis.
- The doctor may be able to feel a pulsating bulge in the abdomen or hear a loud pulse or other signs of aortic enlargement with the stethoscope.
- The exam findings will guide the rest of the evaluation.
Don’t Miss: How Blood Flows Through The Heart
What Happens Before Heart Surgery
Preparation for your surgery can take weeks or months. Before your heart surgery is scheduled, your medical care team will evaluate your condition. Your care team will likely include your primary care doctor and cardiologist. Youll also consult with a cardiothoracic surgeon .
Your care team will give you a medical evaluation. This includes:
- Talking about your symptoms and how long theyve been going on.
- Talking about your medical history and your biological familys medical history.
- Blood tests to check your cholesterol and other important numbers.
Your team will also run some diagnostic tests. These tests provide a detailed picture of your heart function and any problems. They also help you and your care team decide if you need surgery and what type you need.
If you need surgery, your care team will tell you exactly how to prepare and what to expect. Its important to follow their recommendations about:
- When to stop taking any medications.
- When to begin fasting the day before your surgery.
- Quitting smoking or tobacco use and reducing alcohol consumption to lower your risk of complications.
Be sure to ask any questions you have, even if they seem small or you think you asked them already. Its better to double-check to make sure youre as prepared as possible for your surgery.
What to expect after youre admitted to the hospital
- Tests like an EKG or chest X-ray.
- Hair shaved from the spot where youll have your incision.
- Glasses and contact lenses.
Recovery After Open Heart Surgery
Open heart surgery is a serious procedure that necessitates constant monitoring and post-operative care. After the procedure, a person may need to stay in the intensive care unit for a few days to receive further treatment. A breathing tube will be left in place for a while after the operation to help with breathing. In addition, a line is left in the vein to provide pain treatment. A person could be connected up to a variety of various monitoring devices. A person will most likely stay in the hospital for roughly a week after exiting ICU. After leaving the hospital, it normally takes 4 to 6 weeks to recover at home. Take your time and be patient. Returning to normal levels of activity can take weeks or months. As part of a specific cardiac rehabilitation programme, some doctors may provide specialist support for daily activities and other aspects of recovery. Blood tests, heart scans, and stress testing may be part of the aftercare for each patient. During a treadmill activity, the heart is monitored as part of a stress test.
Donât Miss: Does Pain Increase Heart Rate
Read Also: Fluid In The Lungs After Heart Surgery
Cardiac Surgery Survival By Procedure
Cardiac surgery programs can also report survival rates by each specific operation. These are called benchmark operations, and they are one of the ways surgical centers can compare outcomes. Note that these data do not include a patients specific risk factors prior to surgery.
In the table below, we report the total number of benchmark operations at Childrens Colorado, as well as the survival rates here compared to the national average.
What we measure:
Index case survival shows the percentage of patients who received a specific operation and were alive 30 days after their operation. It also includes patients who needed to be in the hospital longer than 30 days who were alive and successfully able to go home.
Index case survival
| 98.8% |
What it means:
For the majority of the open-heart surgeries listed above, our survival rates are higher than the national average.
It is challenging to compare outcomes by procedure alone. The procedure-alone data does not include important health-related factors such as age, other health conditions , and genetic conditions that can make procedures riskier. This is why pediatric heart surgery programs should report a wide range of outcomes, including how well patients do when they are at higher risk due to other health conditions.
Recommended Reading: How Do I Know If I M Having Heart Attack
Who Is In Theater For Open Heart Surgery
A team of doctors and other health professionals work together in the operating theater during open heart surgery.
The team is likely to include:
- the lead surgeon who will direct others surgeons who will assist during the operation
- the anesthesiologist, who is in charge of giving and anesthesia and monitoring vital signs
- the pump team, also known as perfusionists, operate the heart-lung machine and other technical equipment that supports open heart surgery
- nurses and technicians, who assist the surgical team and prepare the operating theater for surgery
Recommended Reading: What Are Some Heart Disease
