How Is Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia Diagnosed
If you have an episode of fast heartbeats during an examination, your doctor will be able to measure your heart rate. If its very high, they may suspect PSVT.
To diagnose PSVT, your doctor will order an electrocardiogram . This is an electrical tracing of the heart. It can help determine which type of rhythm problem is causing your fast heart rate. PSVT is only one of many causes of abnormally fast heartbeats. Your doctor will also likely order an echocardiogram, or ultrasound of the heart, to evaluate the size, movement, and structure of your heart.
If you have an abnormal heart rhythm or rate, your doctor may refer you to a specialist who is an expert in electrical problems of the heart. They are known as electrophysiologists or EP cardiologists. They may perform an electrophysiology study . This will involve threading wires through a vein in your groin and up into your heart. This will allow your doctor to evaluate your hearts rhythm by checking the electrical pathways of your heart.
Your doctor may also monitor your heart rate over a period of time. In this case, you may wear a Holter monitor for 24 hours or longer. During that time, youll have sensors attached to your chest and will wear a small device that records your heart rate. Your doctor will assess the recordings to determine if you have PSVT or some other type of abnormal rhythm.
When To Contact A Medical Professional
If you have never had heart palpitations before, see your provider.
- Loss of alertness
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- You often feel extra heartbeats .
- You have risk factors for heart disease, such as high cholesterol, diabetes, or high blood pressure.
- You have new or different heart palpitations.
- Your pulse is more than 100 beats per minute .
- You have related symptoms, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, feeling faint, or loss of consciousness.
Svt Symptoms Causes And Diagnosis
Some patients with SVT, which generally first arises in people in their teens and 20s, may have no symptoms, going in and out of the arrhythmia quickly. Others have symptoms, such as palpitations, a racing heart, sweating and feeling lightheaded or dizzy. SVT can become a problem requiring treatment if it lasts a long time or causes shortness of breath or chest pain.
Though most episodes of SVT are caused by the hearts electrical system, other causes include certain drugs, health conditions, surgery and familial disorders, such as Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.
SVT can be diagnosed by your doctor through a physical exam and questions about what triggers your fast or irregular heart rate. Tests include X-rays or an electrocardiogram to measure the heart’s electrical activity and record SVT events. You may have to temporarily wear a portable EKG to pick up events as they occur.
You May Like: Claritin Heart Racing
What Does Fetal Tachycardia Indicate
Fetal tachyarrhythmia is an abnormally fast fetal heart rate. In some cases the fast heartbeat may also have an irregular rhythm. Tachyarrhythmia is one of several types of fetal cardiac arrhythmias, congenital heart conditions involving an abnormal heartbeat. The condition is also sometimes referred to as tachycardia.
What Is Lee Health’s Approach
Lee Health has extensive expertise in diagnosing and treating tachycardias using the latest technique appropriate for each individual.
Our integrated team includes doctors trained in medical and surgical diagnosis and treatment for diseases of the heart including, cardiologists, electrophysiologists, and cardiac and cardiovascular surgeons.
Recommended Reading: Does Ibs Cause Heart Palpitations
What Causes Atrial Tachycardia
Atrial tachycardia occurs most commonly in elderly patients and those with other types of heart disease, though it occasionally appears in children, younger people and those with healthy hearts. Causes include:
- A “stretched” atrium resulting from high blood pressure or from cardiomyopathy
- A previous heart attack
- Excessive use of alcohol, cocaine and other stimulants
- An “irritable focus,” when cells outside the sinus node start generating an electrical impulse automatically on their own
Sometimes, atrial tachycardia is idiopathic, meaning doctors can find no specific cause.
How A Heart Attack Affects Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the inside walls of your arteries as it circulates throughout the body. Just as heart rate changes are unpredictable during a heart attack, so too are blood pressure changes.
Because blood flow in the heart is blocked and a portion of heart tissue is denied oxygen-rich blood, your heart may not be able to pump as strongly as it normally does, thus lowering your blood pressure.
A heart attack may also trigger a response from your parasympathetic nervous system, causing your heart and the rest of your body to relax and not fight while your heart struggles to keep blood circulating. This can also cause a dip in blood pressure.
On the other hand, the pain and stress from the heart attack can raise the blood pressure during a heart attack.
Blood pressure-lowering medications, such as diuretics or angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, can keep your blood pressure low during a heart attack, too.
Risk factors for a heart attack include modifiable factors, such as your weight, as well as those beyond your control, such as your age. Some of the most common conditions that raise your risk for a heart attack include:
- advancing age
Read Also: How To Calculate Target Heart Rate Zone
What Causes Ventricular Tachycardia
Your heart rate is controlled by electrical signals that move across the heart muscle. When something goes wrong and signals are sent too quickly, it can cause tachycardia. Most patients with ventricular tachycardia have another heart problem, such as coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, an enlarged heart or heart valve disease. The condition can also develop after a heart attack or heart surgery because of scar tissue that forms on the heart. Other, non-heart-related causes of ventricular tachycardia include some medications, an imbalance in electrolytes , too much caffeine or alcohol, recreational drugs, exercise, and certain genetically transmitted conditions. Sometimes the cause is unknown. You are also more likely to have ventricular tachycardia as you get older or if you have a family history of heart rhythm disorders.
How Is Tachycardia Treated
The treatment for tachycardia depends on the type, but could include:
- changes to your lifestyle:
Some people will need a defibrillator to help get the heart into the right rhythm. Some will need radioablation a surgical procedure that inactivates the tiny parts of the heart causing electrical signal problems.
Recommended Reading: Ibs And Palpitations
Normal Resting Heart Rate For Kids
Childrens heart rates are normally faster than those of adults. According to Cleveland Clinic, the normal resting heart rate for a child aged six to 15 is between 70 to 100 beats per minute.
Many factors can affect your resting heart rate, including your level of physical activity. In fact, highly trained athletes can have a resting heart rate of around 40 beats per minute!
Other factors that can affect resting heart rate include:
- Age. You may find that your resting heart rate decreases as you get older.
- Temperature. Your heart rate may increase slightly when youre exposed to hot temperatures.
- Medication side effects. For example, medications such as beta-blockers can lower your resting heart rate.
- Emotions. If youre anxious or excited, your heart rate may increase.
- Weight. People who are obese may have a higher resting heart rate. This is because the heart has to work harder to supply the body with blood.
- Body positioning. Heart rate can increase temporarily when you move from a sitting to a standing position
- Smoking. Smokers tend to have a higher resting heart rate. Quitting smoking can help bring it back down.
Treating Supraventricular Tachycardia In Hospital
SVT is rarely life threatening. But you may need treatment in hospital if you keep having long episodes.
This may include:
- medicines to control the episodes of SVT given as tablets or through a vein
- cardioversion a small electric shock to the heart to help it get back to a normal rhythm
- catheter ablation a treatment where thin tubes are placed through a vein or artery into your heart to correct the problem with the electrical system this permanently cures the problem in most patients
Find out more about:
Don’t Miss: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
How The Heart Works
The heart has two upper chambers and two lower chambers .
The atria and ventricles have walls of muscle. A heartbeat happens when this muscle suddenly contracts so that the chambers become smaller and the blood inside is squeezed out.
The control of the heartbeat starts with a small clump of cells in the right atrium, called the sinoatrial node . This sends out electrical impulses through the atrial muscle to another clump of cells called the atrioventricular node, found between the atria and ventricles. The impulse then continues through the AV node down fibres that conduct the impulse into the muscle of the ventricles.
The AV node determines the rate of contraction of the ventricles. The pulse felt at the wrist is due to the contraction of the ventricles.
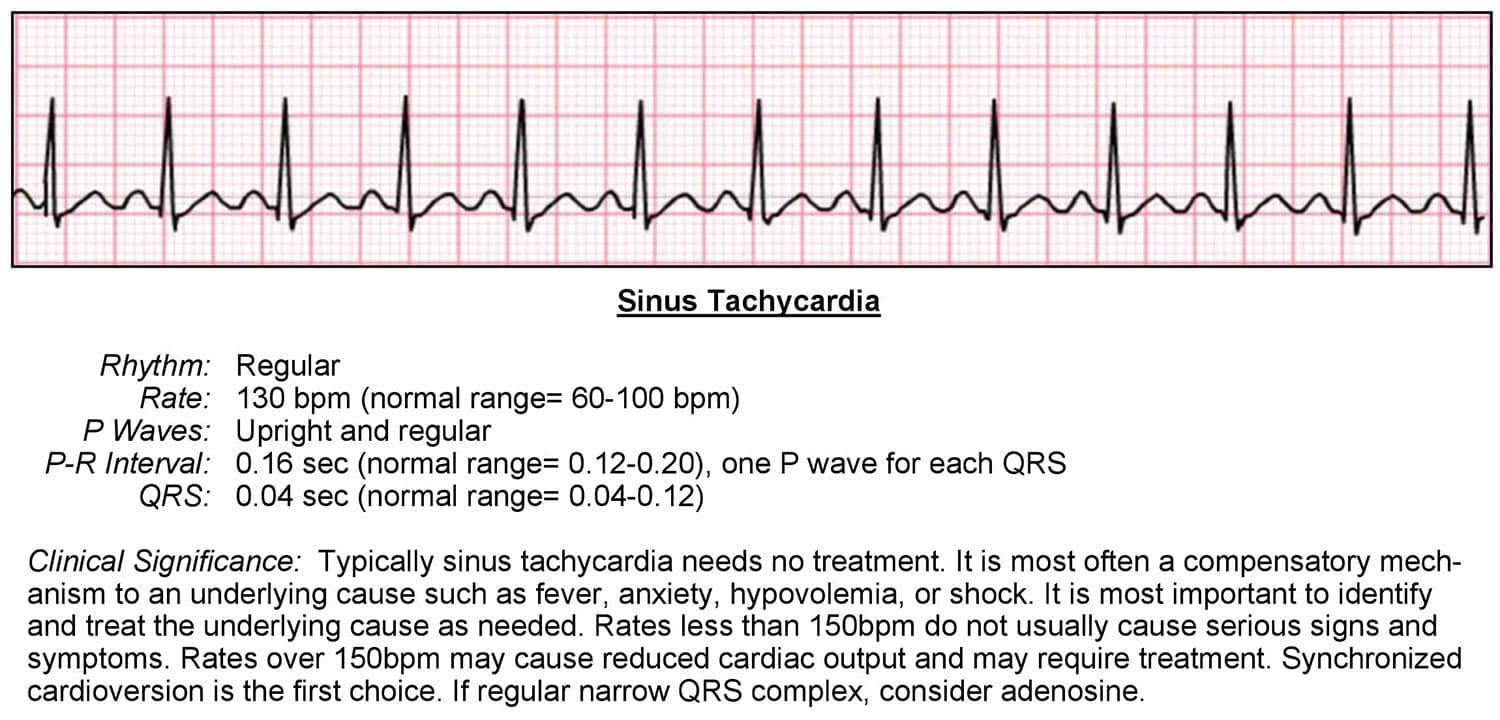
Key Points About Tachycardia Arrhythmia
Tachycardia, or fast heartbeat, is when there are rapid electrical signals to the heart, causing faster than normal contractions and goes above 100 beats per minute.
There are many types of tachycardia. Common types are:
- Atrial fibrillation : A Fib is the most common type of tachycardia associated with heart disease, high blood pressure, heart valve disorder, hyperthyroidism, or heavy alcohol use.
- Atrial flutter: Atrial flutter occurs when the hearts atria are beating fast but at a regular rate resulting in the contractions in the atria being weak. Typically, those who have experienced atrial fibrillation can experience atrial flutter as well.
- Supraventricular tachycardia : Originating somewhere above the ventricles, SVT is an abnormally fast heartbeat that is usually present at birth.
- Ventricular tachycardia: A ventricular tachycardia originates from rapid electrical signals in the lower chambers . Due to the rapid heart rate, the ventricles cant efficiently pump enough blood to the body.
- Ventricular fibrillation: Ventricular fibrillation occurs when rapid and chaotic electrical impulses to the ventricles cause the ventricles to quiver and become ineffective in pumping blood to the body. Typically, those with underlying heart disease or have experienced serious trauma can experience ventricular fibrillation.
Don’t Miss: Does Flonase Help With Shortness Of Breath
Influences From The Central Nervous System
Cardiovascular centres
The heart rate is rhythmically generated by the sinoatrial node. It is also influenced by central factors through sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves. Nervous influence over the heart rate is centralized within the two paired cardiovascular centres of the medulla oblongata. The cardioaccelerator regions stimulate activity via sympathetic stimulation of the cardioaccelerator nerves, and the cardioinhibitory centers decrease heart activity via parasympathetic stimulation as one component of the vagus nerve. During rest, both centers provide slight stimulation to the heart, contributing to autonomic tone. This is a similar concept to tone in skeletal muscles. Normally, vagal stimulation predominates as, left unregulated, the SA node would initiate a sinus rhythm of approximately 100 bpm.
Norepinephrine binds to the beta1 receptor. High blood pressure medications are used to block these receptors and so reduce the heart rate.
Input to the cardiovascular centres
Increased metabolic byproducts associated with increased activity, such as carbon dioxide, hydrogen ions, and lactic acid, plus falling oxygen levels, are detected by a suite of chemoreceptors innervated by the glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves. These chemoreceptors provide feedback to the cardiovascular centers about the need for increased or decreased blood flow, based on the relative levels of these substances.
Possible Treatment For Post
Current treatment of postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome includes the selective sinus node inhibitor ivabradine, beta-blockers, and compression garments to stabilize cardiovascular regulation. Other pharmacological options to reduce associated symptoms are midodrine , pyridostigmine and modafinil . A structured, regular, and supervised rehabilitation program is also recommended. Immunomodulation and drugs targeting possible associated mast cell activation syndrome have not been systematically evaluated in postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome, but might be considered ex iuvantibus if the typical clinical manifestation is present.
Although postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome in the context of COVID-19 may be different from the traditional postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome , we suggest starting patients with post-acute COVID-19 syndrome and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome on heart rate-lowering drugs and a rehabilitation program. Other pharmacological interventions may also be considered but should be carefully monitored.
Whether patients with post-COVID-19 tachycardia syndrome are responsive to heart rate-lowering drugs and other symptomatic treatment previously used in postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome remains to be established.
Also Check: Does A Higher Heart Rate Burn More Calories
What To Expect At Your Office Visit
Your provider will examine you and ask questions about your medical history and symptoms.
You may be asked:
- Do you feel skipped or stopped beats?
- Does your heart rate feel slow or fast when you have the palpitations?
- Do you feel a racing, pounding, or fluttering?
- Is there a regular or irregular pattern to the unusual heartbeat sensations?
- Did the palpitations begin or end suddenly?
- When do the palpitations occur? In response to reminders of a traumatic event? When you are lying down and resting? When you change your body position? When you feel emotional?
- Do you have any other symptoms?
An electrocardiogram may be done.
If you go to an emergency room, you will be connected to a heart monitor. However, most people with palpitations do not need to go to an emergency room for treatment.
If your provider finds you have an abnormal heart rhythm, other tests may be done. This may include:
- Holter monitor for 24 hours, or another heart monitor for 2 weeks or longer
Is Your Racing Heart A Sign Of Supraventricular Tachycardia
Approximately 2 in every 1,000 people have SVT, a type of arrhythmia that can often be cured. Learn more about symptoms, diagnosis and treatment.
If youve ever experienced a sudden racing heartbeat, you know how unsettling the feeling can be.
While there are many potential causes of a fast heartbeat, one of the more common forms is supraventricular tachycardia, or SVT.
LISTEN UP: Add the new Michigan Medicine News Break to your Alexa-enabled device, or subscribe to our daily audio updates on iTunes, and Stitcher.
SVT symptoms heart palpitations, chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness or lightheadedness can be alarming, but the condition is usually treatable and can often be cured, says Michigan Medicine electrophysiologist Rakesh Latchamsetty, M.D.
First, he says, the type of arrhythmia responsible for the symptoms needs to be determined since different arrhythmias can be treated very differently and some can be more serious than others.
A person experiencing a rapid heartbeat should consult with their physician, and anyone experiencing unrelenting palpitations or severe symptoms should be seen in the emergency room, says Latchamsetty.
Recommended Reading: Flonase Chest Pain
How Is It Treated
If you have tachycardia, your treatment team will work with you to offer appropriate treatment options that can restore your heart to normal rhythm, regulate your heart rate and prevent blood clots.
Your treatment will depend on the specific type of tachycardia you have and may include:
- Medication. Your doctor may prescribe drugs alone or in combination with other treatments. You may need a medicine that slows your heart rate, restores normal rhythm, prevents blood clots or thins your blood.
- Implantable cardioverter defibrillator . If you’re diagnosed with ventricular tachycardia, your doctor may recommend an implantable cardioverter defibrillator. This small device monitors your heart’s rhythm and delivers bursts of electrical energy to restore a normal heart rhythm.
- Catheter radiofrequency ablation. In cardiac catheter ablation you get a mild sedative and a local anesthetic. Then your doctor threads thin, flexible tubes through your blood vessels. Radiofrequency energy given through the catheter removes abnormal tissue.
- Open-heart maze procedure. If you have atrial fibrillationthe most common kind of tachycardiayour doctor may recommend a maze procedure to regulate your heartbeat.
- Follow-up care. If you’re recovering from heart surgery or medical device implantation, your doctor may recommend cardiac rehabilitation. Cardiac rehabilitation consists of monitored exercise sessions during your recovery period.
How Is This Problem Diagnosed
Clinical features: As described above, infants may be diagnosed because of symptoms of congestive heart failure including poor feeding, unusual sleepiness, irritability, vomiting, rapid breathing, and/or pale skin color. In children, the problem is found because of symptoms of “heart racing” that may be associated with dizziness, lightheadedness, chest pain, shortness of breath, and/or fainting. Physical findings: Most of the time the physical exam is normal when the child is not having an episode. Rarely, the problem is associated with a heart defect. In this case, the child has the physical findings associated with that defect. Medical tests: One of the first tests usually done is an electrocardiogram . However, unless the child has WPW or is having an episode at the time, the ECG at rest is usually normal. In this case, a device called a transtelephonic ECG recorder is used to record an ECG at the time of symptoms. Other tests that may be done include a Holter monitor, echocardiogram, and/or exercise test. If further information is needed a special type of heart catheterization called an electrophysiologic study may be done.
You May Like: Why Do Av Nodal Cells Not Determine The Heart Rate
How Is Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia Treated
You might not need treatment if your symptoms are minimal or if you only have episodes of rapid heart rate occasionally. Treatment may be necessary if you have an underlying condition causing the PSVT or more severe symptoms like heart failure or passing out.
If you have a rapid heart rate but your symptoms arent severe, your doctor can show you techniques to return your heart rate to normal. Its called the Valsalva maneuver. It involves closing your mouth and pinching your nose while trying to exhale and straining as if you were trying to have a bowel movement. You should do this while sitting and bending your body forward.
You can perform this maneuver at home. It may work up to 50 percent of the time. You can also try coughing while sitting and bending forward. Splashing ice water on your face is another technique to help lower your heart rate.
Treatments for PSVT include medications, such as or flecainide or propafenone, to help regulate your heartbeat. A procedure called radiofrequency catheter ablation is a common way to correct PSVT permanently. Its performed in the same way as an EPS. It allows your doctor to use electrodes to disable the electrical pathway thats causing the PSVT.
If your PSVT doesnt respond to other treatments, your doctor may surgically implant apacemaker into your chest to regulate your heart rate.
