Blood Vessels Of The Heart
The blood vessels of the heart include:
- venae cavae deoxygenated blood is delivered to the right atrium by these two veins. One carries blood from the head and upper torso, while the other carries blood from the lower body
- pulmonary arteries deoxygenated blood is pumped by the right ventricle into the pulmonary arteries that link to the lungs
- pulmonary veins the pulmonary veins return oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart
- aorta this is the largest artery of the body, and it runs the length of the trunk. Oxygenated blood is pumped into the aorta from the left ventricle. The aorta subdivides into various branches that deliver blood to the upper body, trunk and lower body
- coronary arteries like any other organ or tissue, the heart needs oxygen. The coronary arteries that supply the heart are connected directly to the aorta, which carries a rich supply of oxygenated blood
- coronary veins deoxygenated blood from heart muscle is ‘dumped’ by coronary veins directly into the right atrium.
Blood Flow Between Capillaries And Tissues
The blood flow via capillaries are majorly regulated by hydrostatic pressure and oncontic pressure. The blood flowing through the capillary applies pressure on the capillary wall due to the pressure of blood flowing from the arteriole. Blood pressure develops hydrostatic pressure that helps in the flow of the blood from capillary pores to the interstitial compartment. The hydrostatic pressure developed in the capillary will be higher at the end of the arterial side and lower at the venous side.
Oncontic pressure is another force influencing the blood flow. The major principle being this pressure is osmosis. The plasma proteins in the blood which cannot pass through the walls of the capillary will develop the osmotic pressure. This pressure pulls the blood from the surrounding tissue into the capillary . This whole pressure is called oncontic pressure.
Another major factor that plays a vital part in the blood pressure is the design of the capillaries that differs depending upon the location in the body and affects the permeability.
How Does Blood Return From To The Heart Against Gravity
Venous return is the flow of blood back to the heart. Under steady-state conditions, venous return must equal cardiac output , when averaged over time because the cardiovascular system is essentially a closed loop. Otherwise, blood would accumulate in either the systemic or pulmonary circulations. Although cardiac output and venous. George Washington University researcher Narine Sarvazyan, Ph.D., has invented a new organ to help return blood flow from veins lacking functional valves.A rhythmically contracting cuff made of cardiac muscle cells surrounds the vein acting as a ‘mini heart’ to aid blood flow through venous segments
Also Check: Can Ibs Cause Heart Palpitations
What Helps Return Blood To The Heart
Inklusive Fachbuch-Schnellsuche. Jetzt versandkostenfrei bestellen There are other mechanisms that aid in the return of blood flow to the heart. The muscle pumps that are present in our thighs, calves, and feet all help return blood to the heart. Therefore exercise, even something as simple as walking, is good for circulation and vein health Muscle contraction in our extremities help squeeze blood back to the heart as the veins are under much lower pressure than the arteries. Additionally, the veins have one-way valves to keep blood.. The respiratory pump refers to the alterations in pressure that take place during the process of breathing. This pump actually helps the blood to return to the heart because it increases the difference in pressure that occurs between the thoracic and abdominal veins during inspiration
Vitamin C with bioflavonoids, B complex, calcium, magnesium and omega 3 fish oil are especially important for heart health and good blood circulation flow. Exercise at least 30 minutes a day. Whether you walk, do yoga or ride a bike, regular physical activity greatly improves blood circulation. Exercise doesn’t have to be extreme, just regular Blood passing through the external iliac vein continues onward into the common iliac vein and inferior vena cava, which returns it to the heart. Blood flowing through the veins of the lower limbs is under very little pressure and must fight the pull of gravity to return to the heart
What Are The Parts Of The Circulatory System
Two pathways come from the heart:
- The pulmonary circulation is a short loop from the heart to the lungs and back again.
- The systemic circulation carries blood from the heart to all the other parts of the body and back again.
In pulmonary circulation:
- The pulmonary artery is a big artery that comes from the heart. It splits into two main branches, and brings blood from the heart to the lungs. At the lungs, the blood picks up oxygen and drops off carbon dioxide. The blood then returns to the heart through the pulmonary veins.
In systemic circulation:
Also Check: Where Does Oxygenated Blood Enter The Heart
Blood Supply Of The Liver
Blood leaves the liver through the hepatic veins. This blood is a mixture of blood from the hepatic artery and from the portal vein. The hepatic veins carry blood to the inferior vena cavathe largest vein in the bodywhich then carries blood from the abdomen and lower parts of the body to the right side of the heart.
Blood vessel disorders of the liver usually result from inadequate blood flowwhether into or out of the liver. If the problem is blood flow out of the liver, blood backs up in the liver, causing congestion which can result in an enlarged liver Congestive Hepatopathy Congestive hepatopathy is a backup of blood in the liver, resulting from heart failure. Severe heart failure causes blood to back… read more . In either case, liver cells do not receive enough blood and thus are deprived of oxygen and nutrients. In ischemic cholangiopathy Ischemic Cholangiopathy Ischemic cholangiopathy is damage to one or more bile ducts caused by inadequate blood flow. Bile ducts (such as the hepatic ducts… read more , it is the bile ducts that do not receive enough blood.
The Four Chambers Of The Heart
Your heart has a right and left side separated by a wall called the septum. Each side has a small collecting chamber called an atrium, which leads into a large pumping chamber called a ventricle. There are four chambers: the left atrium and right atrium , and the left ventricle and right ventricle .The right side of your heart collects blood on its return from the rest of our body. The blood entering the right side of your heart is low in oxygen. Your heart pumps the blood from the right side of your heart to your lungs so it can receive more oxygen. Once it has received oxygen, the blood returns directly to the left side of your heart, which then pumps it out again to all parts of your body through an artery called the aorta. Blood pressure refers to the amount of force the pumping blood exerts on arterial walls.
Recommended Reading: Does Tylenol Raise Your Blood Pressure
What Are The Heart And Blood Vessels
Blood vessels form the living system of tubes that carry blood both to and from the heart. All cells in the body need oxygen and the vital nutrients found in blood. Without oxygen and these nutrients, the cells will die. The heart helps to provide oxygen and nutrients to the body’s tissues and organs by ensuring a rich supply of blood.
Not only do blood vessels carry oxygen and nutrients, they also transport carbon dioxide and waste products away from our cells. Carbon dioxide is passed out of the body by the lungs most of the other waste products are disposed of by the kidneys. Blood also transports heat around your body.
Anatomy of the heart and blood vessels
What Is The Vascular System
The vascular system, also called the circulatory system, is made up of the vessels that carry blood and lymph through the body. The arteries and veins carry blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to the body tissues and taking away tissue waste matter. The lymph vessels carry lymphatic fluid . The lymphatic system helps protect and maintain the fluid environment of the body by filtering and draining lymph away from each region of the body.
The vessels of the blood circulatory system are:
-
Arteries. Blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body.
-
Veins. Blood vessels that carry blood from the body back into the heart.
-
Capillaries. Tiny blood vessels between arteries and veins that distribute oxygen-rich blood to the body.
Blood moves through the circulatory system as a result of being pumped out by the heart. Blood leaving the heart through the arteries is saturated with oxygen. The arteries break down into smaller and smaller branches to bring oxygen and other nutrients to the cells of the body’s tissues and organs. As blood moves through the capillaries, the oxygen and other nutrients move out into the cells, and waste matter from the cells moves into the capillaries. As the blood leaves the capillaries, it moves through the veins, which become larger and larger to carry the blood back to the heart.
Also Check: What Does Heart Rate Mean
What Are The 3 Mechanisms That Assist In Venous Return
4.9/5Skeletal Muscle Pumplimbis here
Respiration During inspiration, venous return increases as the pressure in the thoracic cavity becomes more negative. This reduced intrathoracic pressure draws more blood into the right atrium. Venous Compliance Increased sympathetic activity will reduce venous compliance.
Beside above, how does vasoconstriction increase venous return? In the venous system, constriction increases blood pressure as it does in arteries the increasing pressure helps to return blood to the heart. In addition, constriction causes the vessel lumen to become more rounded, decreasing resistance and increasing blood flow.
In this regard, which of the following is the mechanism in which skeletal muscles assist venous return of blood to the heart?
The return of blood to the heart is assisted by the action of the skeletal-muscle pump and by the thoracic pump action of breathing during respiration. As muscles move, they squeeze the veins that run through them.
What is the importance of venous return?
Venous Return. Venous return to the right atrium is the most important factor determining cardiac output, provided both ventricles and the pulmonary circulation are normal. Venous return to the right atrium from the systemic venous reservoir occurs along the venous pressure gradient.
Chemical Signals Involved In Autoregulation
Chemical signals work at the level of the precapillary sphincters to trigger either constriction or relaxation. As you know, opening a precapillary sphincter allows blood to flow into that particular capillary, whereas constricting a precapillary sphincter temporarily shuts off blood flow to that region. The factors involved in regulating the precapillary sphincters include the following:
- Opening of the sphincter is triggered in response to decreased oxygen concentrations increased carbon dioxide concentrations increasing levels of lactic acid or other byproducts of cellular metabolism increasing concentrations of potassium ions or hydrogen ions inflammatory chemicals such as histamines and increased body temperature. These conditions in turn stimulate the release of NO, a powerful vasodilator, from endothelial cells .
- Contraction of the precapillary sphincter is triggered by the opposite levels of the regulators, which prompt the release of endothelins, powerful vasoconstricting peptides secreted by endothelial cells. Platelet secretions and certain prostaglandins may also trigger constriction.
Recommended Reading: What Causes Left Sided Heart Failure
Overview Of Blood Vessel Disorders Of The Liver
, MD, University of Colorado School of Medicine
The liver receives the oxygen and nutrients it needs in blood that comes from two large blood vessels:
-
Portal vein
-
Hepatic artery
The portal vein provides about two thirds of the blood. This blood contains oxygen and many nutrients brought to the liver from the intestines for processing. The hepatic artery provides the remaining one third of blood. This oxygen-rich blood comes from the heart and provides the liver with about half of its oxygen supply. Receiving blood from two blood vessels helps protect the liver: If one of these blood vessels is damaged, the liver can often continue to function because it receives oxygen and nutrients from the other blood supply.
Clinical Relevance Chronic Varicose Veins
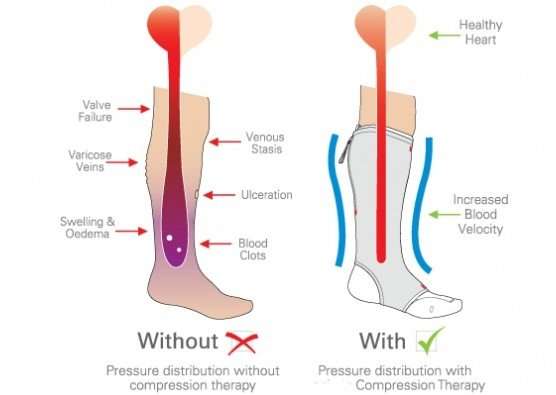
In this condition, the competency of the valves in veins in compromised. This means the valves do not sufficiently close, allowing blood in the veins to flow backwards and accumulate in the veins. This can decrease the venous return.
This commonly affects the superficial veins of the legs, which look engorged and twisted. Blood can pool in the veins to cause bruising and ulceration of the tissue if the pressure becomes excessive.
Fig 2 Diagram showing the difference between normal veins and varicose veins.
Also Check: Can Ibs Cause Heart Palpitations
Understanding The Circulation System : By What
About The Heart And Blood Vessels
The heart is the hardest working muscle in the human body. Located almost in the center of the chest, a healthy adult heart is the size of a clenched adult fist. By age 70, the human heart will beat more than 2.5 billion times. The heart is always working. It pumps about 2,000 gallons of blood daily.
A child’s heart works just as hard as an adult’s heart. In fact, at rest, a baby’s heart may beat up to 130 to 150 times a minute. An adult’s heart often beats between 60 and 100 times a minute. The rate at which the heart pumps gradually slows down from birth to teen years.
The cardiovascular system is made up of the heart and blood vessels. It circulates blood throughout the body. A healthy cardiovascular system is vital to supplying the body with oxygen and nutrients.
You May Like: Ibs And Palpitations
Blood Supply Of The Heart
Like all organs, the heart needs a constant supply of oxygen-rich blood.
The coronary circulation, a system of arteries and veins, supplies the heart muscle with oxygen-rich blood and then returns oxygen-depleted blood to the right atrium.
The right coronary artery and the left coronary artery branch off the aorta to deliver oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle. These two arteries branch into other arteries that also supply blood to the heart. The cardiac veins collect blood from the heart muscle and empty it into a large vein on the back surface of the heart called the coronary sinus, which returns the blood to the right atrium. Because of the great pressure exerted in the heart as it contracts, most blood flows through the coronary circulation only while the ventricles are relaxing between beats .
Tech Savvy Not Required
About 30% to 50% of patients do not receive optimal medical treatment for hypertension and hypercholesterolemia, even though most treatments are generic, Blood noted.
Their program aimed to improve this while ensuring equitable access to care.
“Many patients are not comfortable with apps and smartphones and for them we use standard telephone calls and the cellular BP devices that don’t require any setup,” Scirica said.
“For more tech-savvy patients, we use text, emails, or secure patient messaging, based on their preference.”
Navigators who spoke Spanish or Creole and translators who spoke other languages were available. The educational materials were multilingual.
“With this approach,” he said, “we can reach a broad spectrum of the population including the elderly, non-English speakers, and traditionally underserved communities.”
Between January 2018 and October 2021, the researchers screened 28,473 patients and enrolled 6887 of these in the lipid program and 3367 patients in the hypertension program . Participants did not have to pay for the program.
A total of 12% of the patients were older than age 75 years, 55% were female, 29% were non-White, and 8% were non-English speaking.
In the lipid group, patients either had established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease , diabetes , LDL > 190 mg/dL or were being given primary prevention because they were at high risk with roughly 25% of patients in each of the four categories.
You May Like: What Is A Dangerously High Heart Rate
How Does Blood Return From The Feet Back To The Heart
