Ibuprofen Can Raise Risk Of Heart Attack
Doctors have warned that the painkiller ibuprofen can raise the risk of having a heart attack.
A study by British researchers suggests regular use of the drug increases the chances of an attack by almost a quarter.
Other painkillers in the same family of anti- inflammatory drugs used by millions of arthritis patients are even more hazardous, raising the risk by up to 55 per cent, according to the study.
Researcher Professor Julia Hippisley-Cox, who is also a GP, said the findings meant there should be an investigation into the safety of all this group of painkillers.
Ibuprofen is one of the most popular over-the-counter painkillers available from pharmacists and supermarkets with 46 tons sold here each year. Sales of Nurofen have risen 15 per cent in the past year.
Increasing risk
We have identified an increasing risk, which rises with the dosage of ibuprofen and the time it is used, said Professor Hippisley-Cox. We want to see this study followed up.
However, she did not recommend that people stop taking it.
The latest study was undertaken after concern raised last year over a range of anti-inflammatory drugs called Cox-2s used by 1.4 million Britons.
A safety review by European regulators found these painkillers were linked with an increased risk of heart disease and stroke, and those at high risk were advised not to take them.
The new generation of anti-inflammatory drugs Cox-2s was also linked to higher rates of firsttime heart attacks.
Stress Effect Stronger Than Thought
Rounding out the list of risk factors were diabetes, high blood pressure, sedentary life style, and a diet that doesn’t include generous servings of fruits and vegetables. On the positive side, a good diet, regular exercise, and moderate alcohol intake did reduce the risk of heart disease — again the reduction was the same regardless of race or ethnicity.
Richard Horton, MD, editor of The Lancet, says that the study demonstrates the potential for real health benefits that can be achieved without pills or surgery. Horton says the results indicate the need for “political action. I think it is really time to consider political moves to control the food industry.” Among the possible options would be special taxes on foods known to contribute to obesity or limits on where such foods can be sold. Horton was not involved in the study.
Yusuf agrees that a concerted, international effort could greatly reduce what he calls a pandemic of heart disease. “We need to build healthier environments,” he says. “Shopping, work, and residence should be concentrated in the same area so that people can walk to a store or walk to work or school.”
The study received funding from 39 institutions including the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Ontario as well as a number of pharmaceutical companies.
Show Sources
The Lancet
What Did The Abstract Say
Researchers used something called the Protein Unstable Lesion Signature Cardiac Test in 566 people visiting a cardiac clinic. All of these individuals had recently received the second dose of one of the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines .
The PULS Cardiac Test claims to predict heart attack risk over a 5-year period by measuring nine different markers in a blood sample. After the marker levels are determined, a score is generated. A higher PULS score may indicate an increased heart attack risk.
In the individuals tested, three of the nine markers had increased following vaccination. These markers were associated with inflammation. The increase boosted the PULS score by a predicted 11 percent compared to pre-vaccination levels.
Also Check: What Is A Dangerously Low Heart Rate
Other Factors That Contribute To Heart Disease Risk
Stress
Individual response to stress may be a contributing factor for heart attacks.
Some scientists have noted a relationship between coronary heart disease risk and stress in a persons life, along with their health behaviors and socioeconomic status. These factors may affect established risk factors.
For example, people under stress may overeat, start smoking or smoke more than they otherwise would.
Get stress management tips and tools.
Alcohol
Drinking too much alcohol can raise blood pressure, and increase your risk for cardiomyopathy, stroke, cancer and other diseases. It can also contribute to high triglycerides, and produce irregular heartbeats. Additionally, excessive alcohol consumption contributes to obesity, alcoholism, suicide and accidents.
All that said, there is a protective benefit to moderate alcohol consumption.
If you drink, limit your alcohol consumption to no more than two drinks per day for men and no more than one drink per day for women. The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism defines one drink as 1 1/2 fluid ounces of 80-proof spirits , 5 fl. oz. of wine or 12 fl. oz. of regular beer.
It is not recommended that nondrinkers start using alcohol or that drinkers increase the amount they drink.
Read our recommendation on alcohol and cardiovascular disease.
Diet and nutrition
To maintain a healthy weight, coordinate your diet with your physical activity level so youre using up as many calories as you take in.
What Should Patients Do
Doctors are already aware from previous studies that non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs could increase the risk of heart problems and strokes.
And current UK guidelines state that Nsaids must be used carefully in people with heart problems and in some cases they should not be used at all.
Dr Mike Knapton of the British Heart Foundation, suggests patients and doctors weigh up the risks and benefits of taking high doses of these common painkillers, particularly if they have survived a heart attack or are at higher risk.
Meanwhile, GP leader Prof Helen Stokes-Lampard said it was important that any decision to prescribe was based on a patients individual circumstances and medical history, and was regularly reviewed.
She said that as new research was published, it was important that it was taken on board to help inform guidelines.
But she added: The use of Nsaids in general practice to treat patients with chronic pain is reducing, and some of the drugs in this study are no longer routinely prescribed in the UK, such as coxibs, as we know that long-term use can lead to serious side-effects for some patients.
Read Also: How Does A Pulse Oximeter Measure Heart Rate
Changing Your Lifestyle Can Reduce Your Risk Of Heart Attack
Dealing with the lifestyle factors that contribute to CVD, which you can change, can help reduce your risk of heart attack. Things you can do include:
- take medicines as prescribed
- eat plenty of vegetables, fruits and wholegrains
- eat a variety of healthy protein sources especially fish and seafood, legumes , nuts and seeds. Smaller amounts of eggs and lean poultry can also be included in a heart healthy diet. If choosing red meat, make sure the meat is lean and limit to 1 to 3 times a week
- unflavoured milk, yoghurt and cheese if you have high blood cholesterol you should choose reduced fat varieties
- healthy fat choices with nuts, seeds, avocados, olives and their oils for cooking
- herbs and spices to flavour foods, instead of adding salt
- drink mainly water
What Should I Do If I Have Symptoms Of Heart Attack
If you think you may be having a heart attack, get treatment right away. Follow these steps:
- Dial 911 Do not have someone else drive you to the hospital. Do not try to drive yourself. EMTs will give you life-saving treatment in the ambulance on the way to the hospital.
- After calling for help, take 1 uncoated adult aspirin or 4 uncoated baby aspirins . Dont take this if youre allergic to aspirin.
- If you are alone and are able, unlock your door to let emergency personnel enter your home.
- Sit in a comfortable chair and wait for help.
- Keep a phone near you.
Recommended Reading: Laparoscopic Bypass Surgery Heart
Heart Attack In Winter: The Cold Weather Increases The Risk Of Heart Attacks In People Who Already Have Cardiovascular Issues
| Edited by Tanya Garg
Heart Attack in Winters: The drop in temperature can have unanticipated effects on your health, particularly your heart. The most frequent health risk you face during the winter is the cold, but many people associate this risk with severe conditions like hypothermia or frostbite and even a heart stroke. Heart attack is a risk at any and every age! Given the increased risk during the winter and the existing high levels of pollution, it is even more crucial to adopt the proper strategy, maintain a healthy lifestyle, and prevent cardiac illnesses.
Is A Cardiac Arrest The Same Thing As A Heart Attack
A cardiac arrest and a heart attack are both medical emergencies. However, they are not the same thing, and sometimes a heart attack can progress into a cardiac arrest.
During a cardiac arrest, the electrical system that controls your heart rate and rhythm stops working, and the heart stops beating.
When someone has a cardiac arrest, they experience different symptoms and receive different treatments to someone who has a heart attack.
Someone having a cardiac arrest will collapse and have no pulse. They may not breathe properly, or maybe not at all, and they will lose consciousness.
If someone has a cardiac arrest, they need help immediately. Call 000 for an ambulance. While waiting for the ambulance to arrive, begin chest compressions , or use a device called a defibrillator, if available. Once the person gets to hospital, a medical team will treat them.
Recommended Reading: Symptoms Of Heart Attack Man
Q Any Dietary Things Happen To Slow Down Heart Attack Symptoms
Diagnosis Of A Heart Attack
Tests to help diagnose a heart attack include:
- a blood test to measure levels of enzymes released into the blood when the heart muscle is damaged
- cardiac catheterisation a tube, or catheter, is threaded into the coronary arteries via a blood vessel in the groin. A special dye is then injected into the coronary artery. This outlines the artery while movie x-rays are taken. Narrowings and blockages within the artery are outlined by the dye
- electrocardiogram a reading of the hearts electrical impulses.
Also Check: Back Pain And Heart Attack
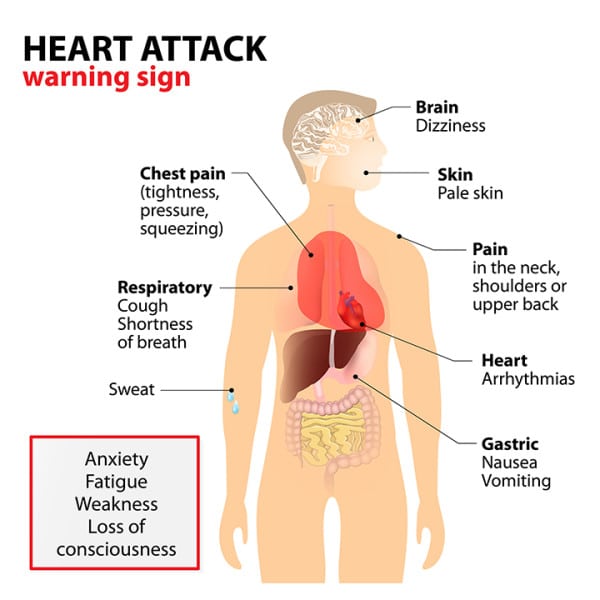
The Most Common Signs Of A Heart Attack For Both Men And Women Include:
- Chest pain or discomfort – Most heart attacks cause pain or discomfort in the center or left side of the chest. This feeling can be mild or severe. The discomfort typically lasts longer than a few minutes and can go away and return. It may feel like pressure, fullness, pain, or squeezing in the chest.
- Upper body discomfort – Heart attacks may cause pain or discomfort in one or both arms, shoulders, back, neck, jaw, or upper stomach.
- Shortness of breath – Shortness of breath may be the only symptom of a heart attack or may occur before or with chest pain. It can occur while resting or doing physical activity.
Causes Of Heart Disease In Women
Heart disease encompasses different heart and blood vessel conditions, such as coronary artery disease, vascular disease, high blood pressure, and heart failure. The most common cause of heart disease is atherosclerosis. It is caused by plaque buildup, a collection of cholesterol and fatty deposits, on the walls of the arteries. Over time, atherosclerosis restricts blood flow to the heart.
As blood flow becomes more restricted, the heart lacks oxygen and nutrient-rich blood. This condition is called ischemia, and the heart becomes less effective. Ischemia causes some of the symptoms of heart disease, such as chest pain, or angina.
You May Like: Pathophysiology For Congestive Heart Failure
Symptoms Of Heart Disease
Women typically have symptoms of heart disease about 10 years later than men. For men, chest pain is a common symptom. In women, symptoms of a heart attack are more subtle and can include:
- Pain or aching in the chest and upper arms or back
- Unusually fast heartbeat
Dont Miss: Does Benadryl Lower Heart Rate
Q Does Your Body Warn You Before A Heart Attack
- Uncomfortable pressure, squeezing, fullness, pain or discomfort in the chest.
- Discomfort or pain in one or both arms, the back, neck, jaw or stomach.
- Shortness of breath.
- Cold sweat or lightheadedness.
Also Check: Low Heart Rate When Sleeping
Ibuprofen Can Triple Stroke Risk Painkillers Can Double Heart Attack Chances
Many of us commonly use painkillers to squelch the common headache or relieve back pains. However it has been found that even over the counter ibuprofen can increase stroke risk by three times and drugs such as rofecoxib and lumiracoxib can double the risk of heart attack. NSAIDs are commonly prescribed for the inflammation of arthritis and other body tissues, such as in tendinitis and bursitis.
Pain, fever, and inflammation are promoted by the release in the body of chemicals called prostaglandins. Ibuprofen, for example, blocks the enzyme that makes prostaglandins , resulting in lower levels of prostaglandins. As a consequence, inflammation, pain and fever are reduced.
A study published today by the British Medical Journal online examined the effect of include traditional non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs as well as new generation anti-inflammatory drugs, known as COX-2 inhibitors and risk associated with heart attack and stroke.
Doctors and patients need to be aware that prescription of any anti-inflammatory drug needs to take cardiovascular and stoke risks into serious consideration.
The Swiss authors of the study state:
Our study provides the best available evidence on the safety of this class of drugs. Although uncertainty remains, little evidence exists to suggest that any of the investigated drugs are safe in cardiovascular terms. Cardiovascular risk needs to be taken into account when prescribing any non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug.
Q Are There Any Female
Read Also: High Blood Pressure And Heart Attack
Covid And Heart Attacks
Two-thirds of Australians, or around 16.5 million people, have been infected with COVID since the beginning of the pandemic.
Heart disease is the leading killer of Australians, with more than 50,000 people having heart attacks each year. More than 10% of these are fatal.
So the fact that someone who had a heart attack may have previously been infected with COVID is not that surprising.
However, this does not discount the fact that SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID, may affect your risk of having a heart attack.
We already accept that COVID infection has more immediate effects on the heart. Emerging evidence also suggests theres an increased frequency of future cardiovascular disease such as heart attack, stroke and heart failure after COVID infection. While this early evidence needs to be interpreted with some caution, these findings are clearly concerning.
Read more:Even mild COVID raises the chance of heart attack and stroke. What to know about the risks ahead
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
- Is there a test I can take to see if my arteries or blocked so I know if Im at risk of a having a heart attack?
- What is the likely cause of my heart attack?
- How serious was my heart attack?
- What course of treatment do you recommend? Do I need medicine? Surgery?
- Do I need to participate in a cardiac rehabilitation program?
- When can I return to normal physical and sexual activity?
- What is my risk of having another heart attack?
- Are my family members at an increased risk of heart attack?
- Do I need to take medicine to prevent another heart attack?
- Will the medicine interact with any of the medicine I already take?
- What lifestyle changes should I make at home to prevent another heart attack?
- Can sexual activity cause a heart attack?
You May Like: How Accurate Is The Apple Watch Heart Rate
Avoiding The Post Hoc Fallacy
Its important that we resist the urge to assume that one event causes another just because an event occurred before another.
Its also important to understand that those seeking to mislead you will use a number of tactics to induce you to make this and other errors of reasoning.
In recognising logic fallacies the hope is that you will be less susceptible to being manipulated by those spreading false information.
Cv Risks Of Nsaids In Patients After Hospitalization For Serious Coronary Heart Disease

The question of CV safety is of particular importance for patients with existing serious coronary heart disease, as their baseline risk of CV events is increased., This retrospective cohort study examined 5 individual NSAIDs in 48,556 patients recently hospitalized for myocardial infarction , revascularization or unstable angina pectoris. The follow-up began 45 days postadmission, so results cannot be generalized to the early postdischarge period. The primary end point was serious coronary heart disease . Secondary end points were a composite of serious CV disease and death from any cause. For naproxen, the incidence rate ratio relative to nonusers of any NSAID was 0.88 for the primary end point and 0.91 for the secondary end points, which were both lower than the rates of the other NSAIDs studied. When duration of use was taken into account, an increased risk of serious coronary heart disease was associated with short-term use of ibuprofen , diclofenac , rofecoxib and celecoxib , unlike naproxen . Longer duration of use, however, did not result in a significant increase in CV risk. The most commonly prescribed dose of naproxen was 1000 mg/d or greater, and there was no evidence of increased CV risk at these higher doses.
Dont Miss: What Heart Chamber Pushes Blood Through The Aortic Semilunar Valve
Recommended Reading: Restrictions After Open Heart Surgery
