Surgery And Percutaneous Procedures
Surgery may be appropriate when certain underlying disorders are present. Surgery in patients with advanced HF should be done in a specialized center.
Surgical closure of congenital or acquired intracardiac shunts can be curative.
If HF is primarily due to a valvular disorder Overview of Cardiac Valvular Disorders Any heart valve can become stenotic or insufficient , causing hemodynamic changes long before symptoms. Most often, valvular stenosis or insufficiency read more , valve repair or replacement should be considered. Patients with primary mitral regurgitation are more likely to benefit than patients with mitral regurgitation secondary to LV dilation, in whom poor myocardial function is likely to continue postoperatively. Surgery is preferably done before myocardial dilation and damage become irreversible. More recently, percutaneous mitral valve repair procedure, in which a clip is applied to approximate the anterior and posterior mitral leaflets, has been shown to reduce death and HF hospitalization in carefully selected patients with symptomatic HF despite optimal medical management and moderate to severe or severe mitral regurgitation with preserved LV size is a syndrome of ventricular dysfunction. Left ventricular failure causes shortness of breath and fatigue, and right ventricular failure causes peripheral and abdominal fluid read more ).
How Is Chf Diagnosed
After reporting your symptoms to your doctor, they may refer you to a heart specialist, or cardiologist.
The cardiologist will perform a physical exam, which will involve listening to your heart with a stethoscope to detect abnormal heart rhythms.
To confirm an initial diagnosis, a cardiologist might order certain diagnostic tests to examine your hearts valves, blood vessels, and chambers.
There are a variety of tests used to diagnose heart conditions. Because these tests measure different things, your doctor may recommend a few to get a full picture of your current condition.
Treatment Of Congestive Heart Failure:
Treatment of Congestive Cardiac Failure is focused on improving the symptoms and preventing the progression of the disease.
The major and often neglected form of treatment is lifestyle improvement, which includes:
1. Regulation of the salt and fluid intake: As the entire body suffers from congestion due to fluid accumulation and also that sodium leads to increased fluid accumulation in the body tissues, it is often recommended to restrict the sodium and fluid intake during the cardiac failure.
2. Exercise: It is recommended to do any activity which one can sustain for more than just a few minutes while your heart,lungs and muscles work overtime. Such an exercise is known as aerobic exercise.Regular exercise, according to the patients tolerance level, appears to provide significant benefits and should be used only when the patient is compensated and stable.
Also Check: What Heart Rate Should I Exercise At
Causes Of Heart Failure
The heart is a double pump made up of four chambers. Deoxygenated blood from the veins enters the right upper chamber , is passed to the right lower chamber , and then pumped to the lungs.
Oxygenated blood from the lungs enters the left upper chamber and then enters the left lower chamber . The blood is then pumped around the body, under pressure, via arteries.
In a person with heart failure, one or both ventricles dont empty properly. This leads to increased pressure in the atria and the nearby veins. This backlog of blood can affect the kidneys and lungs interfering with their function and leading to a build-up of fluid in the lungs, abdominal organs and legs.
In some people with heart failure, rather than failed pumping of the blood from the ventricle, there is failed relaxation of the ventricle.
If the heart is not pumping and becomes stiff and unable to relax, it can cause the blood to pool in the hearts ventricles. This can cause pressure build up and can put strain on the heart.
Heart failure can be caused by several conditions, including:
Overproduction Of Reactive Oxygen Species
Activated oxidative stress has been demonstrated in animal studies as well as in human studies to cause heart failure also lowered antioxidant activity in failing human hearts promotes oxidative stress . Furthermore, some risk factors for the development of heart failure also show increased oxidative stress i.e., hypertension, diabetes, obesity. Also in myocardial hypertrophy parameters of the redox-sensitive signaling pathways and transcription factors are activated . However, the complete mechanism is not understood yet . There are several factors activated via ROS which may influence contractility: proinflammatory mediators, periods of ischemia, auto-oxidation of catecholamines.
You May Like: What Cause Low Blood Pressure And High Heart Rate
Dyssynchrony And Resynchronization Therapy
Disease prevalence
In a Swedish registry, LBBB and IVCD were found in 25 and 15% of patients with HFrEF, respectively. The presence of both LBBB and IVCD increased the risk of all-cause mortality by 30%. In transcutaneous aortic valve implantation procedure, new-onset LBBB may even increase the risk of mortality by 50%. The pathophysiology paragraph describes the serious consequences of ventricular dyssynchrony. Therefore, ventricular dyssynchrony is an important therapeutic target in patients with HFrEF. It has been estimated that at least 400 patients per million of the population would be eligible for CRT, but in practice, only Germany and Italy at least approach such implantation numbers in Europe.
Cardiac resynchronization therapy
According to current guidelines, good candidates for CRT are those with HFrEF and an abnormal QRS complex . Likewise, because activation sequence in RV pacing mimicks that of LBBB, CRT is indicated for patients who are RV paced for a significant portion and have LVEF < 35% and patients with LVEF < 40% with high-degree AV block who have an indication for ventricular pacing.
Patient selection
Atrial fibrillation patients do not derive the same benefit from CRT, which may be due to several factors such as insufficient amount of biventricular stimulation , fusion or pseudofusion beats without proper biventricular stimulation, and lack of atrial contribution to ventricular filling.
Therapy delivery
Device optimization
What Are The Symptoms Of Heart Failure
You may not have any symptoms of heart failure, or the symptoms may be mild to severe. Symptoms can be constant or can come and go. The symptoms can include:
- Congested lungs. Fluid backup in the lungs can cause shortness of breath with exercise or difficulty breathing at rest or when lying flat in bed. Lung congestion can also cause a dry, hacking cough or wheezing.
- Fluid and water retention. Less blood to your kidneys causes fluid and water retention, resulting in swollen ankles, legs, abdomen , and weight gain. Symptoms may cause an increased need to urinate during the night. Bloating in your stomach may cause a loss of appetite or nausea.
- Dizziness, fatigue, and weakness. Less blood to your major organs and muscles makes you feel tired and weak. Less blood to the brain can cause dizziness or confusion.
- Rapid or irregular heartbeats. The heart beats faster to pump enough blood to the body. This can cause a rapid or irregular heartbeat.
If you have heart failure, you may have one or all of these symptoms or you may have none of them. They may or may not indicate a weakened heart.
You May Like: Can Benadryl Cause Heart Palpitations
Systolic And Diastolic Failure
Systolic and diastolic heart failure each result in a decrease in stroke volume. This leads to activation of peripheral and central baroreflexes and chemoreflexes that are capable of eliciting marked increases in sympathetic nerve traffic.
Although there are commonalities in the neurohormonal responses to decreased stroke volume, the neurohormone-mediated events that follow have been most clearly elucidated for individuals with systolic heart failure. The ensuing elevation in plasma norepinephrine directly correlates with the degree of cardiac dysfunction and has significant prognostic implications. Norepinephrine, while directly toxic to cardiac myocytes, is also responsible for a variety of signal-transduction abnormalities, such as downregulation of beta1-adrenergic receptors, uncoupling of beta2-adrenergic receptors, and increased activity of inhibitory G-protein. Changes in beta1-adrenergic receptors result in overexpression and promote myocardial hypertrophy.
Dont Miss: What Is A Normal Heart Rate For A Woman In Her 50s
What Causes Congestive Heart Failure
Several factors can cause congestive heart failure. They include:
- Presence of other diseases like diabetes and high blood pressure
- Addictions like smoking and alcohol
Although heart failure is a serious condition, it does not mean that the heart stops functioning altogether. With proper management, persons who have congestive heart failure can lead nearly normal lives, depending on its severity. Besides the required medical and surgical interventions, it is important to eat healthy, stay active as possible, and refrain from alcohol, smoking, and drug abuse. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , almost half of the patients with congestive heart failure live beyond five years.
Don’t Miss: How Much Can Marijuana Increase A Person’s Heart Rate
What Is Ejection Fraction
The ejection fraction is a measurement your doctor will use to determine the type of heart failure and to assess the stage of heart disease.
The ejection fraction represents the percentage of blood pumped out of the left ventricle when the heart contracts. When blood leaves the left ventricle, it moves into the aorta to deliver blood loaded with oxygen to the rest of the body.
In a healthy heart, the ejection fraction ranges from around 52%74%. When the ejection fraction drops below 52%, its considered low. Your healthcare professional may use your ejection fraction to determine the severity of heart failure.
What Is The Incidence Of Heart Failure And Its Prognosis
It is estimated that there are more than 15 million new cases of heart failure each year worldwide. There are more than 600,000 new cases of heart failure diagnosed each year in the USA, and ten times that number of Americans currently in heart failure. The numbers are rapidly increasing because of the aging population. Heart failure is the leading cause of hospitalization of patients over 65 years in age.
Despite many new advances in drug therapy and cardiac assist devices, the prognosis for chronic heart failure remains very poor. One year mortality figures are 50-60% for patients diagnosed with severe failure, 15-30% in mild to moderate failure, and about 10% in mild or asymptomatic failure.
Heart failure is a clinical syndrome caused by disease or other abnormal conditions in the body. Heart failure can be caused by factors originating from within the heart or from external factors that place excessive demands upon the heart. Intrinsic disease includes conditions such as . External factors that can lead to heart failure include long-term, uncontrolled , increased stroke volume , and hormonal disorders .
Chronic heart failure is a long-term condition that is associated with the heart undergoing adaptive responses to a precipitating cause. These adaptive responses, however, can be deleterious in the long-term and lead to a worsening condition.
Revised 06/30/2015
Read Also: How Long Does Heart Attack Chest Pain Last
Congestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology
Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction
In diastolic heart failure , the same pathophysiologic processes occur that lead to decreased cardiac output in systolic heart failure, but they do so in response to a different set of hemodynamic and circulatory environmental factors that depress cardiac output.
In HFpEF, altered relaxation and increased stiffness of the ventricle occur in response to an increase in ventricular afterload . The impaired relaxation of the ventricle then leads to impaired diastolic filling of the left ventricle .
Morris et al found that right venticular subendocardial systolic dysfunction and diastolic dysfunction, as detected by echocardiographic strain rate imaging, are common in patients with HFpEF. This dysfunction is potentially associated with the same fibrotic processes that affect the subendocardial layer of the LV and, to a lesser extent, with RV pressure overload. It may play a role in the symptomatology of patients with HFpEF.
Recommended Reading: How To Avoid Heart Disease
Myocytes And Myocardial Remodeling
In the failing heart, increased myocardial volume is characterized by larger myocytes approaching the end of their life cycle. As more myocytes drop out, an increased load is placed on the remaining myocardium, and this unfavorable environment is transmitted to the progenitor cells responsible for replacing lost myocytes.
Progenitor cells become progressively less effective as the underlying pathologic process worsens and myocardial failure accelerates. These featuresnamely, the increased myocardial volume and mass, along with a net loss of myocytesare the hallmark of myocardial remodeling. This remodeling process leads to early adaptive mechanisms, such as augmentation of stroke volume and decreased wall stress and, later, to maladaptive mechanisms such as increased myocardial oxygen demand, myocardial ischemia, impaired contractility, and arrhythmogenesis.
As heart failure advances, there is a relative decline in the counterregulatory effects of endogenous vasodilators, including nitric oxide , prostaglandins , bradykinin , atrial natriuretic peptide , and B-type natriuretic peptide . This decline occurs simultaneously with the increase in vasoconstrictor substances from the RAAS and the adrenergic system, which fosters further increases in vasoconstriction and thus preload and afterload. This results in cellular proliferation, adverse myocardial remodeling, and antinatriuresis, with total body fluid excess and worsening of heart failure symptoms.
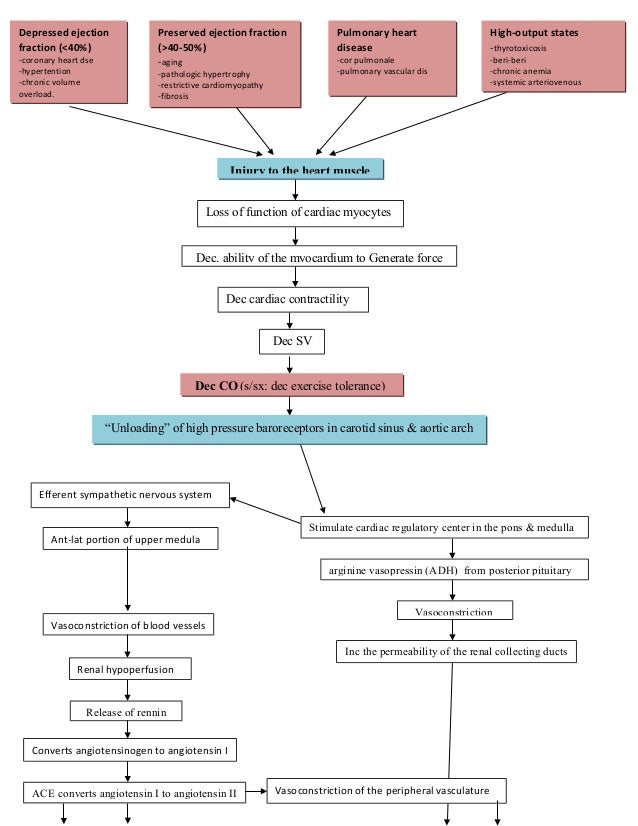
Congestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology And Schematic Diagram
Congestive heart failure otherwise known as cardiac failure refers as the inability of the heart to pump sufficient blood to meet needs of tissues for oxygenation and nutrition. This disease can affect the hearts ability to respond to circulation demands of the body. CHF is a slowly developing condition where cardiac output is lower-than-normal.
You May Like: How Do You Say Heart Attack In Spanish
Precipitating Causes Of Heart Failure
A previously stable, compensated patient may develop heart failure that is clinically apparent for the first time when the intrinsic process has advanced to a critical point, such as with further narrowing of a stenotic aortic valve or mitral valve. Alternatively, decompensation may occur as a result of the failure or exhaustion of the compensatory mechanisms but without any change in the load on the heart in patients with persistent, severe pressure or volume overload. In particular, consider whether the patient has underlying coronary artery disease or valvular heart disease.
The most common cause of decompensation in a previously compensated patient with heart failure is inappropriate reduction in the intensity of treatment, such as dietary sodium restriction, physical activity reduction, or drug regimen reduction. Uncontrolled hypertension is the second most common cause of decompensation, followed closely by cardiac arrhythmias . Arrhythmias, particularly ventricular arrhythmias, can be life threatening. Also, patients with one form of underlying heart disease that may be well compensated can develop heart failure when a second form of heart disease ensues. For example, a patient with chronic hypertension and asymptomatic LV hypertrophy may be asymptomatic until an MI develops and precipitates heart failure.
- Profound anemia
- Nutritional deficiencies
Pathophysiology Of Congestive Heart Failure
- William W. ParmleyCorrespondenceAddress for reprints: William W. Parmley, MD, Room 1186, Moffitt Hospital, University of California, 505 Parnassus Avenue, San Francisco, California 94143.AffiliationsFrom the University of California and the Cardiovascular Division, H. C. Moffitt Hospital, San Francisco, California, USA
Also Check: How Do You Find Your Resting Heart Rate
When Should I Get Emergency Care
Go to the ER or call 911 if you have:
- New, unexplained, and severe chest pain that comes with shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, or weakness
- Fast heart rate , especially if you are short of breath
- Shortness of breath that doesnt get better if you rest
- Sudden weakness, or you cant move your arms or legs
- Sudden, severe headache
- Fainting spells
What Is Congestive Heart Failure
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is unable to pump blood to body tissues efficiently. Congestive heart failure is a chronic disease that progresses with time if left untreated. Heart failure can occur due to diseases of the heart, the blood vessels supplying oxygen and nutrients to the heart, or sometimes from factors outside the heart . A healthy lifestyle plays a role in the treatment and prevention of congestive heart failure.
Recommended Reading: How To Decrease Resting Heart Rate
What Medications Should I Avoid If I Have Heart Failure
There are several different types of medications that are best avoided in those with heart failure including:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications such as Motrin or Aleve. For relief of aches, pains, or fever take Tylenol instead.
- Some nutritional supplements, such as salt substitutes, and growth hormone therapies
- Antacids that contain sodium
If youâre taking any of these drugs, discuss them with your doctor.
Itâs important to know the names of your medications, what theyâre used for, and how often and at what times you take them. Keep a list of your medications and bring them with you to each of your doctor visits. Never stop taking your medications without discussing it with your doctor. Even if you have no symptoms, your medications decrease the work of your heart so that it can pump more effectively.
Also Check: What Does Having A Heart Attack Feel Like
