History And Physical Examination
Patients with heart failure can have decreased exercise tolerance with dyspnea, fatigue, generalized weakness, and fluid retention, with peripheral or abdominal swelling and possibly orthopnea.3 Patient history and physical examination are useful to evaluate for alternative or reversible causes .3,4,8 Nearly all patients with heart failure have dyspnea on exertion. However, heart failure accounts for only 30 percent of the causes of dyspnea in the primary care setting.24 The absence of dyspnea on exertion only slightly decreases the probability of systolic heart failure, and the presence of orthopnea or paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea has a small effect in increasing the probability of heart failure .21,23
The presence of a third heart sound is an indication of increased left ventricular end-diastolic pressure and a decreased LVEF. Despite being relatively uncommon findings, a third heart sound and displaced cardiac apex are good predictors of left ventricular dysfunction and effectively rule in the diagnosis of systolic heart failure .21,23
Heart Failure With A Reduced Ejection Fraction
A central tenet of heart failure is that an abnormality of myocardial function is responsible for the failure of the heart to pump blood at a rate commensurate with the requirements of the metabolizing tissues or that it can do so only in the setting of elevated cardiac filling pressures. The pathobiology of the failing heart results in maladaptive regulation of multiple neurohormonal pathways that reduce intrinsic cardiac contractility and cause prototypical ventricular remodeling . Alterations in cardiac extracellular matrix and replacement fibrosis increase the connective tissue content and further impair systolic and diastolic function . Several neurohormonal pathways regulate myocardial fibrosis including aldosterone, matrix metalloproteinases, tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases , TNF-alpha, and ST2.
Natriuretic peptides counterbalance the vasoconstricting and sodium-retaining properties of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and sympathetic nervous systems by causing both arterial and venous vasodilation,natriuresis, and diuresis. The extent of natriuretic pathway activation is a marker of the severity of heart failure and is associated with adverse outcomes, including the risk for hospitalization and death.6
Shahrokh Javaheri, in, 2011
Iv Management With Co
-
Concurrent anemia: Treatment may improve heart failure symptoms.
-
Concurrent arrhythmias: Consider the role that uncontrolled arrhythmias may have on heart failure exacerbation. Improved control of atrial fibrillation or premature ventricular contractions may improve symptoms. Many antiarrhythmics are contraindicated in severe heart failure.
-
Concurrent cancer: Consider whether antineoplastics may be contributing to heart failure
-
Concurrent chronic kidney disease: Continue ACEI/ARB if possible, but if necessary to discontinue, replace with isosorbide/hydralazine combination. May contribute to anemia. Aldosterone antagonists have a substantially increased risk of hyperkalemia.
-
Concurrent diabetes: Avoid thiazolidinediones in all heart failure patients and metformin if there is significant renal dysfunction.
-
Concurrent gout: It is likely that diuretic dosing will need to be increased if a gout flareup is treated with steroids.
-
Concurrent liver disease: Liver congestion is common and may result in the need to alter dose of medications metabolized by the liver.
-
Concurrent osteoarthritis: Avoid nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs
-
Concurrent pulmonary disease: Does not typically contraindicate beta-blocker usage
-
Concurrent prostatic hypertrophy: Alpha blockers should be avoided, as they have been shown to increase mortality in heart failure patients.
-
Concurrent sleep apnea: Should be treated aggressively to minimize neurohormonal activation.
Also Check: What Should My Heart Rate Be During Exercise
Special Situations Congestive Heart Failure
Heart Failure Exacerbations
When a patient becomes volume-overloaded and presents with an acute episode of symptomatic heart failure, the term heart failure exacerbation is used.
Determining the etiology of heart failure exacerbation is crucial in order to direct medical therapy appropriately not only to improve the current HF symptoms, but to prevent recurrence.
Every patient with heart failure presenting to the ED or hospital ward should be evaluated for the following:
Heart Transplantation
Heart transplantation is considered a last resort therapy for end-stage heart failure when the above-mentioned therapies fail. Refractory heart failure patients should be referred to a HF program capable of heart transplantation especially if cardiopulmonary stress testing shows the maximal oxygen consumption, or VO2 max, is less than 10 mL/kg.
Heart transplantation can improve survival in carefully selected individuals. The surgical process itself has an approximate 5% mortality rate. Afterwards, immunosuppressant drugs including prednisone, cyclosporine and tacrolimus must be utilized in order to prevent rejection.
Heart transplantation is contraindicated in patients with severe fixed pulmonary hypertension, malignancy, any significant illness with limited survival and any illness that would be highly likely to occur in the transplanted heart. It is only a relative contraindication to be older than 70 years.
A ranking system is used to determine eligibility for transplantation:
What Medications Are Used For Hypertensive Heart Disease
Any medicine can have side effects, but its important to keep taking your medicines. If youre worried about a side effect from your medication, your provider may be able to switch you to a different one. Medicines to treat high blood pressure include:
- Diuretics that make your body clear excess fluid out.
- Calcium channel blockers that make your blood vessels more open.
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors that help loosen your blood vessels.
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers that help relax your blood vessels.
- Vasodilators that help blood vessels get wider.
- Renin inhibitors that help loosen up your blood vessels.
- Beta blockers that slow down your heart rate and make your hearts job easier.
Recommended Reading: How Are Hypertension Heart Disease And Stroke Related
Prevention Of Congestive Heart Failure
The best way to prevent heart failure is to control your risk factors. The good news is that you can reduce or eliminate many of the risk factors that lead to heart disease, such as high blood pressure. Lifestyle changes and adhering to any medication your doctor prescribes can go a long way in preventing heart failure.
Prognosis Of Systolic Heart Failure
In general, a diagnosis of heart failure is serious, since it can cause life-threatening arrhythmias and organ failure.
Taking medications as prescribed, monitoring fluid status, and close follow-up with a healthcare provider can help people with heart failure stay out of the hospital and improve quality of life.
Advanced treatments and heart transplant are also options for those with very severe heart failure.
Recommended Reading: How To Measure Max Heart Rate
Pulmonary Hypertension Caused By Systolic Heart Failure
Every time a healthy heart pumps oxygen-rich blood from the lungs into the rest of the body, it goes through two phases a contracting or pumping phase and a relaxing phase .
When a weakened heart can’t pump efficiently, that’s known as systolic dysfunction. Just like a kink in a garden hose, blood begins to back up into the lungs and causes pulmonary hypertension .
Exercise Response In Heart Failure
In systolic heart failure, left ventricular filling pressure is elevated and the heart is operating at the relatively flat portion of the Frank-Starling curve. Without stroke volume reserve, an increase in heart rate during exercise is the primary means to increase cardiac output.3 In a study of 22 patients with poor LV function and implanted rate-adaptive pacemakers, the benefit of rate response for improving exercise capacity was greatest in those patients with the poorest LV function.4 However, the benefits of an increased pacing rate may be counteracted by a detrimental effect on LV function because of a higher percentage of right ventricular apical pacing. On the other hand, in patients with left bundle branch block who received cardiac resynchronization therapy , rate response can be beneficial. In these patients chronotropic incompetence is quite common. In one study,5 using the criterion of failure to reach at least 70% of the age-predicted maximum heart rate, CI was found in 70% of patients with heart failure. In this CI group, rate-adaptive CRT pacing improved maximal oxygen consumption and work capacity compared with CRT pacing without rate response. This improvement was independent of AV interval adaptation during exercise. These data suggest that rate response also plays a critical role in patients with impaired LV function and chronotropic incompetence, provided that the detrimental effects of RV apical pacing can be addressed.
You May Like: What Happens When Your Heart Rate Is Too High
How To Treat Systolic Heart Failure
Unfortunately, theres no permanent cure for this condition, but there are certain systolic heart failure treatment options that can help alleviate and manage some of the symptoms.
Your doctor might recommend making lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, working to maintain a healthy weight for your body type , exercising to the best of your ability, and following a strict heart-healthy diet.
Certain medications may also be prescribed to help manage some of the symptoms that are associated with systolic heart dysfunction. These include the following:
- Digoxin
- Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists
- Beta-blockers
In more severe cases, your doctor might recommend undergoing a surgical procedure to implant certain medical devices like a defibrillator or a left ventricular assist device in your heart to help it pump blood more efficiently and function as normally as possible. A heart transplant could also be necessary depending on the gravity of the situation.
What Causes Heart Failure
Heart failure is most often related to another condition. The most common cause of heart failure is coronary artery disease , a disorder that causes narrowing of the arteries that supply blood and oxygen to the heart. Other conditions that may increase your risk of developing heart failure include:
- cardiomyopathy, a disorder of the heart muscle that causes the heart to become weak
- congenital heart disease
Heart failure can occur in either the left or right side of your heart. Its also possible for both sides of your heart to fail at the same time.
Heart failure is also classified as either diastolic or systolic.
Don’t Miss: How To Lower Your Heart Rate Fast
A History Part I: Pattern Recognition
Exertional dyspnea and fatigue are virtually universal. Volume overload is usually found, but in the modern era of powerful loop diuretics, some patients do not manifest fluid overload.
Nocturnal symptoms such as orthopnea and/or paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea are also highly suggestive of heart failure. Abdominal discomfort or fullness is also a frequently reported symptom. Patients with well-compensated heart failure may have minimal symptoms and no evidence of volume overload. Characteristics of end-stage heart failure may include cachexia and Cheyne-Stokes respirations.
What Is The Life Expectancy Of Someone With Systolic Or Diastolic Heart Failure
The prognosis of systolic and diastolic heart failure depends on many factors including:
- Age
- How your body responds to medical treatments
- Exercise intolerance
Survival rates in patients with heart failure are 75.9% at one year, 45.5% at five years, and 24.5% at 10 years, compared to 97%, 85%, and 75% in the general population, respectively.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Definition Of Congestive Heart Failure
Types Of Heart Failure
The chambers where your blood is pumped out of the heart are called ventricles. These may stiffen so that they no longer fill properly. Or, if your heart muscle becomes weak, the ventricles can fail to pump hard enough.
Heart failure can begin on either the left or right side of your heart. Sometimes, both sides may fail at the same time. The different types of heart failure correspond to where the heart is failing:
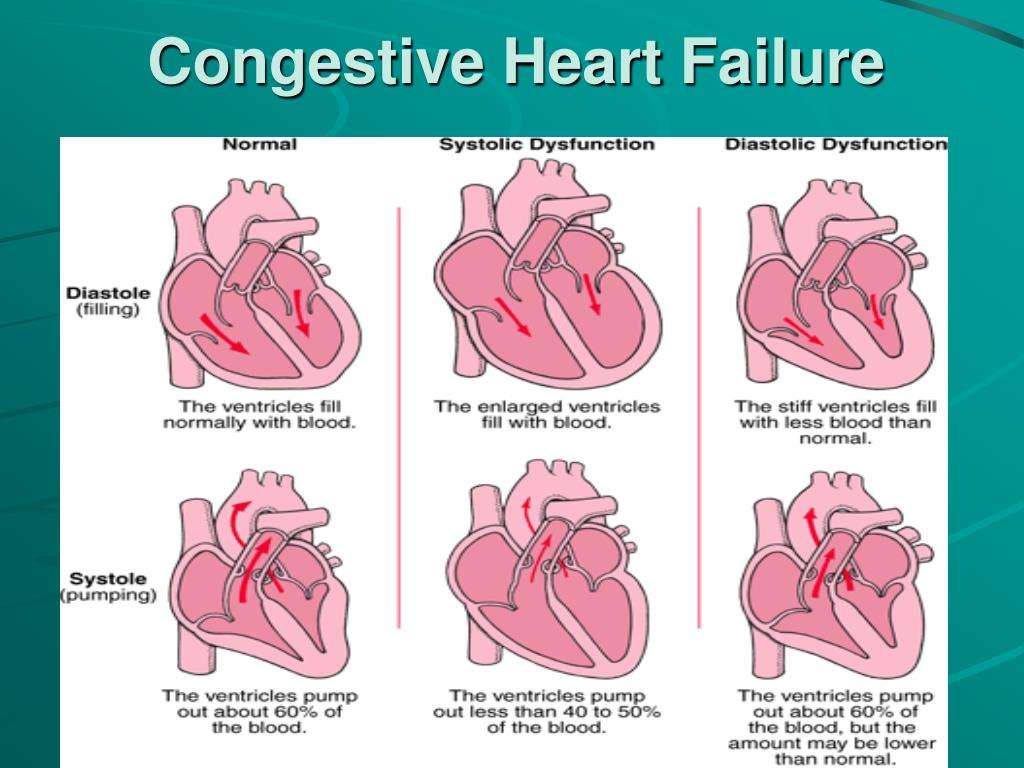
Systolic And Diastolic Heart Failure Defined
Both sides of the heart are prone to dysfunction, but heart failure on the left side is more common.
- Systolic heart failure occurs when the left side of the heart becomes too weak to squeeze normal amounts of blood out of the heart when it pumps.
- Diastolic heart failure occurs when the left side of the heart is too stiff to relax and fill normally with blood.
The most common culprits of left-sided heart failure are:
Also Check: How To Slow Heart Rate After Coke
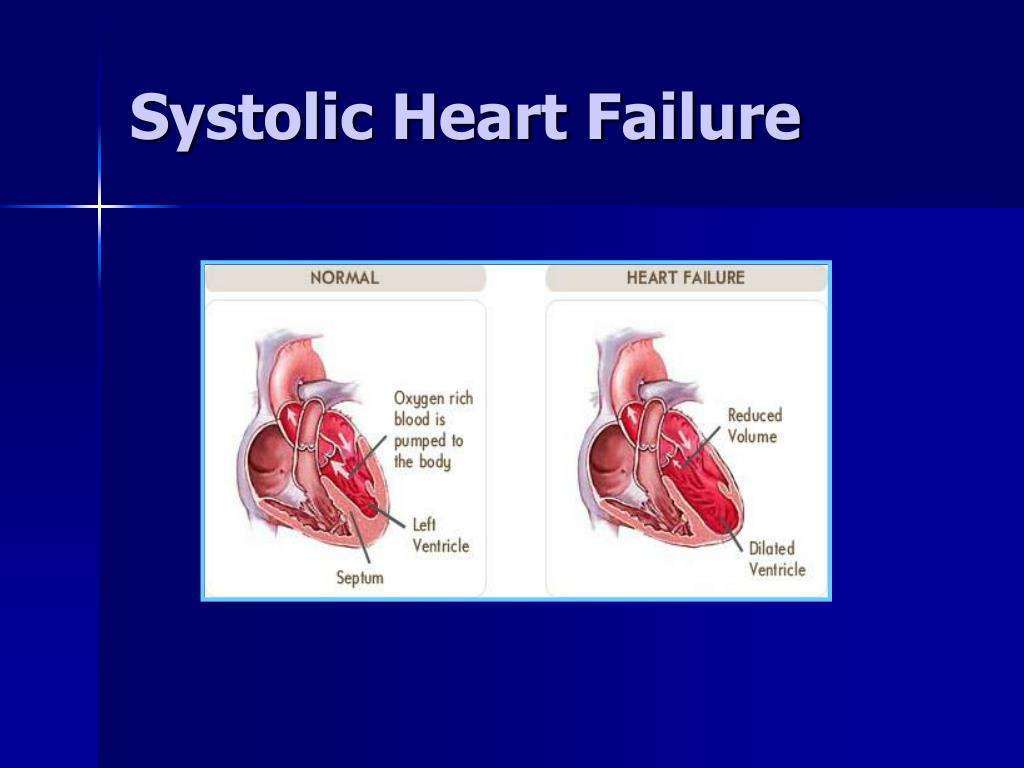
Systolic Heart Failure Overview
You already know by now what systolic heart failure is in simple words. It occurs when your heart starts beating too weakly. When the heart beats weekly it is understood that its not able to meet its requirements and circulate blood throughout the body as it should. The heart cannot function efficiently and cant exert force to pump the blood. As a result of this, the person starts struggling to get enough oxygen and starts feeling difficulty in breathing.
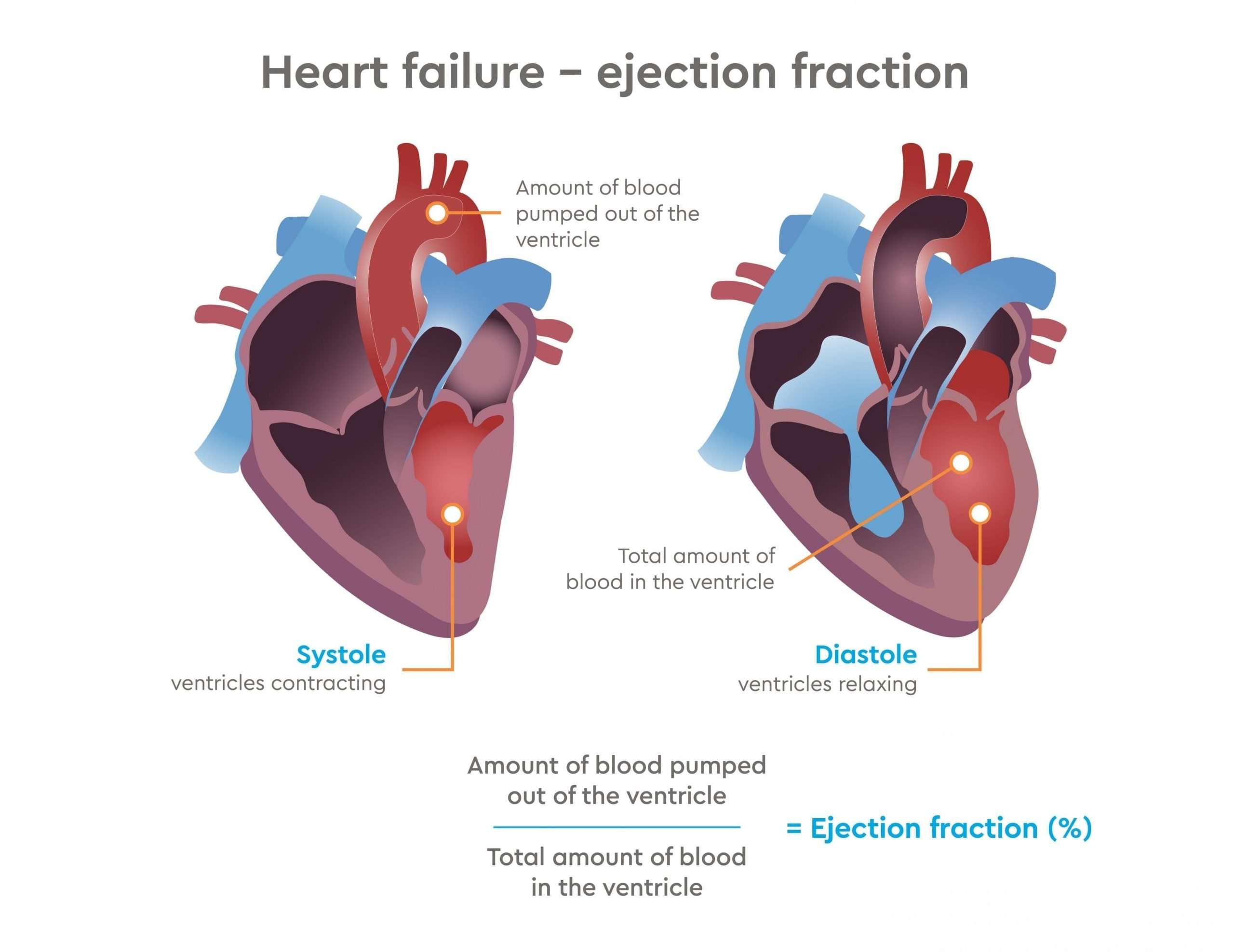
Systolic heart failure is also known as heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
For those of you who are not familiar with ejection fraction, it measures how well the left portion of your heart is pumping the blood out. It is a fraction of the blood present inside the heart which the heart has to eject. The normal and healthy heart usually pumps blood as an ejection fraction of 55 to 70%. When the fraction becomes lower, it refers to the failure of your left ventricle.
Another type of heart failure which was associated with left ventricular heart failure was diastolic heart failure. Lets see how it differs from systolic heart failure.
When To Get Medical Advice
See a GP if you experience persistent or gradually worsening symptoms of heart failure.
Call 999 for an ambulance or go to your nearest A& E department as soon as possible if you have sudden or very severe symptoms.
A number of tests can be used to help check how well your heart is working, including blood tests, an ECG and an echocardiogram.
Also Check: What Is Heart Bypass Surgery
How Can You Prevent Heart Failure
Some lifestyle measures can help treat heart failure and prevent the condition from developing. Maintaining a moderate weight and exercising regularly can significantly decrease your risk of heart failure. Reducing the amount of salt in your diet can also lower your risk.
Other habits that may prevent heart failure include:
- limiting alcohol intake
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
- What is my personal risk of hypertensive heart disease?
- Is there anything else I can do to reduce my risk of hypertensive heart disease?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
High blood pressure is a very common condition, but some people dont even know they have it. If you have been told you have high blood pressure, its very important to take the medicines your provider ordered for you. Keeping your blood pressure under control is a key factor in preventing hypertensive heart disease. You have the power to make healthy changes in your life for a healthy heart.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 09/21/2021.
References
You May Like: What Should Your Heart Rate Be When Running
B What’s The Evidence For Specific Management And Treatment Recommendations
2009 Focused update incorporated into the ACC/AHA 2005 guidelines for the diagnosis and management of heart failure in adults: A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association task force on practice guidelines. Developed in collaboration with the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation.
Causes Of Congestive Heart Failure
The cause of congestive heart failure is usually related to damage to the heart muscle. The possibility of pre-existing impairments in the heart or other conditions that directly affect the pumping action of the heart pose as risk factors for CHF. While in adults the symptoms are most commonly a result of hypertension and coronary artery disease, in children, CHF is caused majorly by cardiomyopathy and congenital heart disease. Below is a list of all general causes and potential risk factors of congestive heart failure adults.
Also Check: Does Ativan Lower Heart Rate
Signs And Symptoms Of Congestive Heart Failure
During heart failure, the body tries to compensate for reduced blood flow in other ways, including:
- Enlarging the Heart Chamber This is the bodys attempt to get the heart to contract more strongly, in order to pump more blood. Initially, it may help the heart function more efficiently, but ultimately it causes the heart to not pump as effectively and causes fluid retention, leading to congestion in the lungs.
- Developing More Heart Muscle Mass The contracting cells in the heart get bigger, which initially lets the heart pump more strongly.
- Increasing Heart Rate This causes the heart to pump faster and increase its output.
- Increasing Fluid and Salt Retention and Tightening Some Blood Vessels This helps maintain the hearts normal output.
These compensations may mask heart failure temporarily, but eventually heart failure gets worse, and people start to experience symptoms.
- F: Fatigue
Symptoms Congestive Heart Failure
The general symptoms of congestive heart failure are the same regardless of the etiology and attributed to either fluid retention related to the activated RAAS or low cardiac output. They can also be categorized as from left heart failure vs. right heart failure.
Left HF will result in low cardiac output symptoms and transmission of the increased left-sided cardiac pressures into the lungs, causing pulmonary edema and a sense of dyspnea. With physical exertion, the heart demands increased cardiac output that is unable to be satisfied in states of HF, significantly increasing left heart pressures and causing this transient pulmonary edema.
As those increased pressures from the left heart affect the right ventricle, right heart failure can ensue. The most common cause of right HF is left HF.
Right heart failure symptoms include lower extremity dependent edema. When the legs are elevated at night, the fluid redistributes centrally, causing pulmonary edema that results in orthopnea or paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, or PND. Hepatic congestion can occur, causing right upper quadrant abdominal pain.
Symptoms related to low cardiac output include fatigue, weakness and, in extreme cases, cardiac cachexia.
The New York Heart Association functional classification system helps to categorize patients based on their symptoms of heart failure.
Also Check: What Causes Low Blood Pressure And High Heart Rate
Other Causes Of Heart Failure
Pulmonary hypertension and heart failure
Heart failure can be caused by pulmonary hypertension . This condition can damage the right side of your heart, leading to heart failure. In some cases, the pulmonary hypertension itself is caused by an existing heart condition.
- Find out more about pulmonary hypertension on NHS Choices and PHA UK.
Amyloidosis
Amyloidosis happens when abnormal proteins, called amyloid, build up in organs and tissues. This affects how your organs work. If amyloidosis affects the heart it’s called cardiac amyloidosis or stiff heart syndrome and can lead to heart failure.
- Read more about amyloidosis treatment.
