Chf Nursing Care Plan 4
Nursing Diagnosis: Activity intolerance related to imbalance between oxygen supply and demand as evidenced by fatigue, overwhelming lack of energy, verbalization of tiredness, generalized weakness, and shortness of breath upon exertion
Desired Outcome: The patient will demonstration active participation in necessary and desired activities and demonstrate increase in activity levels.
| CHF Nursing Interventions | Rationales |
| Assess the patients activities of daily living, as well as actual and perceived limitations to physical activity. Ask for any form of exercise that he/she used to do or wants to try. | To create a baseline of activity levels and mental status related to fatigue and activity intolerance. |
| Encourage progressive activity through self-care and exercise as tolerated. Explain the need to reduce sedentary activities such as watching television and using social media in long periods. Alternate periods of physical activity with rest and sleep. | To gradually increase the patients tolerance to physical activity. |
| Teach deep breathing exercises and relaxation techniques. Provide adequate ventilation in the room. | To allow the patient to relax while at rest and to facilitate effective stress management. To allow enough oxygenation in the room. |
| Refer the patient to physiotherapy / occupational therapy team as required. | To provide a more specialized care for the patient in terms of helping him/her build confidence in increasing daily physical activity. |
Living With Congestive Heart Failure
Tags: Heart Failure ,
If you have been told by your doctor that you have “heart failure,” that doesn’t mean that your heart has, well, failed. It does mean, however, that the heart muscle does not pump effectively. It may have stretched out of its normal size and shape. It may have stiffened over time and has to work harder to keep blood flowing through the heart valves and chambers.
In congestive heart failure, the hearts pumping chambers, called ventricles, are unable to either contract or relax fully. The ventricle can become stretched, and the heart’s ability to pump blood to the rest of the body is impaired.
The word “failure” may be frightening, but it doesn’t mean that your heart has stopped working or is about to break down. With treatment and careful attention, many people living with congestive heart failure can manage their condition and still be active and energetic.
Causes Of Heart Failure And Congestive Heart Failure
Heart failure and CHF are typically caused by other conditions that damage the heart. Some of these conditions are:
When the heart is weakened, it has difficulty pumping blood forward, so blood and fluid back up into the lungs. Fluid in the lungs can cause shortness of breath, a common symptom of congestive heart failure.
If the heart is having serious difficulty with pumping, then you might experience edemaa buildup of blood fluid in the feet, ankles, and legs.
Also Check: What Is Good Heart Rate
What Are Congestive Heart Failure Symptoms
If your heart is only slightly weaker than it should be, you may not notice any symptoms at all. Some people can live with congestive heart failure for years without even suspecting that they have a problem. But if the heart loses enough strength, heart failure becomes impossible to ignore. The main symptoms of heart failure are shortness of breath, fatigue, and fluid retention . Even a short trip up the stairs can leave you gasping. You also may have a cough that gets worse at night. And at bedtime, you may notice that it’s hard to breathe when you lie down flat.
- Rapid weight gain
- Shortness of breath, especially when lying down
- Swelling in the hands, feet, legs or stomach
- Dizziness and confusion
- Fatigue
Certainly, the term heart failure itself engenders a lot of concern among people because they think that my heart is failing, said Vijay U. Rao, MD, PhD, a Franciscan Physician Network cardiologist in Indianapolis whose practice focuses on advanced heart failure.The outcomes with folks with heart failure are getting better with new treatments and therapies. But it’s definitely something that needs to be taken seriously.”
What Are The 4 Stages Of Heart Failure
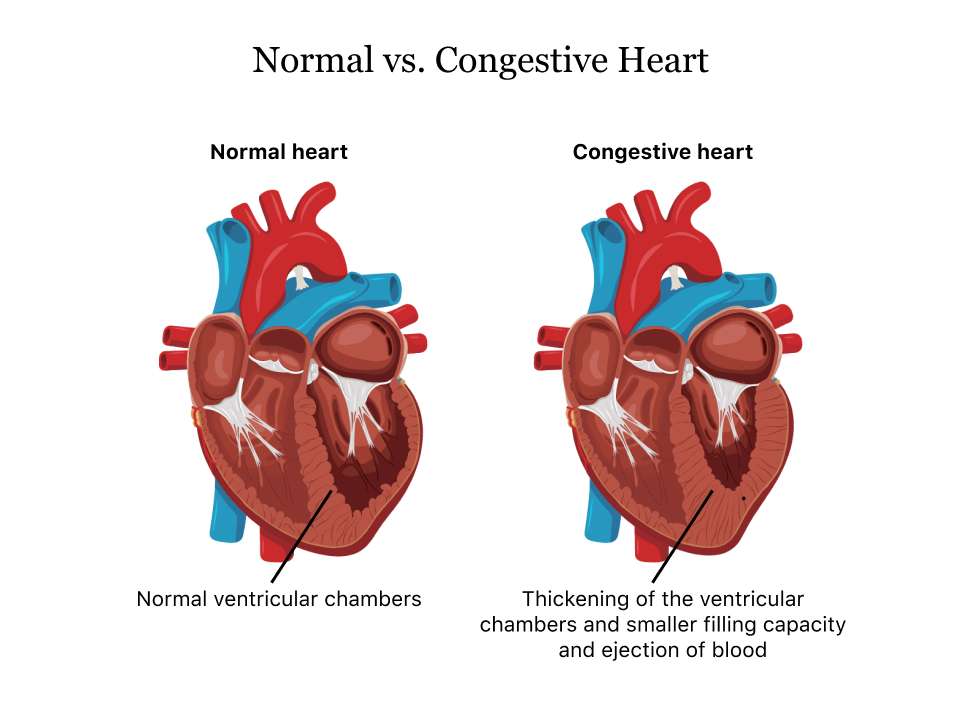
There are four stages of heart failure stage A, B, C and D which range from high risk of developing heart failure to advanced heart failure.
The four stages of heart failure are different to the four classes of heart failure symptoms also described in New York Heart Association , which illustrates the severity of symptoms, ranging from class one to the most severe, which is class four .
You May Like: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
Also Check: What Happens After A Mild Heart Attack
What Is The Prognosis And Life Expectancy For Congestive Heart Failure
- The degree to which other organ systems are involved and the severity of other accompanying conditions
- The persons symptoms and degree of impairment
- Other factors that remain poorly understood
With the availability of newer drugs to potentially favorably affect the progression of the disease, the prognosis in congestive heart failure is generally more favorable than that observed just 10 years ago. In some cases, especially when the heart muscle dysfunction has recently developed, a significant spontaneous improvement is not uncommonly observed, even to the point where heart function becomes normal.
Heart failure is often graded on a scale of I to IV based on the patients ability to function.
The prognosis of heart failure patients is very closely associated with the functional class.
An important issue in congestive heart failure is the risk of heart rhythm disturbances . Of those deaths that occur in individuals with congestive heart failure, approximately 50% are related to progressive heart failure. Importantly, the other half are thought to be related to serious arrhythmias.
What Are The Types Of Heart Failure
There are many causes of heart failure, but the condition is generally broken down into these types:
Left-sided heart failure
Heart failure with reduced left ventricular function The lower left chamber of your heart gets bigger and cannot squeeze hard enough to pump the right amount of oxygen-rich blood to the rest of your body.
Heart failure with preserved left ventricular function Your heart contracts and pumps normally, but the bottom chambers of your heart are thicker and stiffer than normal. Because of this, your ventricles can’t relax properly and fill up all the way. Because there’s less blood in your ventricles, your heart pumps out less blood to the rest of your body when it contracts.
Right-sided heart failure
Heart failure can also affect the right side of your heart. Left-sided heart failure is the most common cause of this. Other causes include certain lung problems and issues in other organs.
You May Like: Why Is My Heart Rate Higher On Keto Diet
What Happens With Heart Failure
The term Heart Failure suggests that the heart has stopped working or has failed. This is not the case. What it actually means is that the heart is not working as well as it should, and cannot pump enough blood to meet the bodys needs.
This happens because the heart is weakened by conditions or diseases that damage the heart muscle. Most of these conditions weaken the heart little by little, over a period of time.
Also Check: Why Do Av Nodal Cells Not Determine The Heart Rate
Symptoms Of Heart Failure
Symptoms of heart failure include:
- new or worsening shortness of breath
- difficulty lying flat at night
- fainting or passing out
- weight gain
- muscular fatigue, tiredness
- swelling of ankles or legs
- swelling of abdomen
- heart palpitations
- chest pain or discomfort in parts of the upper body
- unexplained coughing and wheezing
- constipation.
Recommended Reading: Latest Study On Aspirin And Heart Attacks
What Is The Long
Yes, heart failure can be fatal when its not treated. Healthline explains that about 50-percent of patients with CHF live beyond 5-years following diagnosis, and points to a study that estimates around 20-years for those diagnosed under age 50 with lower risk factors.
The source also notes age and gender can affect these outcomes. Women with CHF tend to live a bit longer than men with this condition but may experience more symptoms.
Read Also: How Much Can Marijuana Increase A Persons Heart Rate
What Is The Outlook With Heart Failure
With the right care, congestive heart failure wont stop you from doing the things you enjoy. Your prognosis, or outlook for the future, will depend on:
- How well your heart muscle is working.
- Your symptoms.
- How well you respond to your treatment plan.
- How well you follow your treatment plan.
One study says that people with heart failure have a life span 10 years shorter than those who dont have heart failure. Another study showed that the survival rates of people with chronic heart failure were 80% to 90% for one year, but that dropped to 50% to 60% for year five and down to 30% for 10 years.
A different study found that people who had heart failure and were discharged from the hospital had expected life spans ranging from three to 20 years, depending on various factors like age and gender. Its important to look at your specific situation when considering your prognosis.
Recommended Reading: Can Ibs Cause Heart Palpitations
When Should I Get Emergency Care
Go to the ER or call 911 if you have:
- New, unexplained, and severe chest pain that comes with shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, or weakness
- Fast heart rate , especially if you are short of breath
- Shortness of breath that doesn’t get better if you rest
- Sudden weakness, or you can’t move your arms or legs
- Sudden, severe headache
- Fainting spells
What Are The Stages Of Congestive Heart Failure
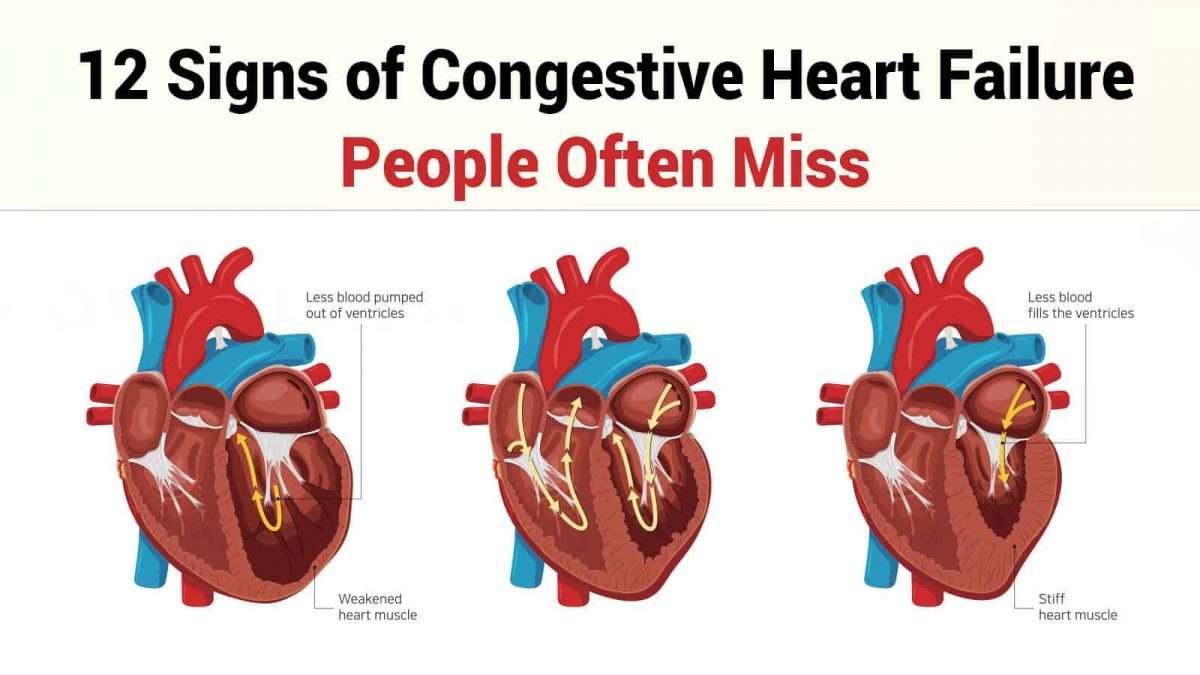
The New York Heart Association has developed a scale that commonly is used to determine the functional capabilities of heart failure.
New York Heart Association Functional Classification of Heart Failure
Read Also: Can Zinc Cause Heart Palpitations
Can You Reverse The Effects Of Congestive Heart Failure
Making simple changes to the lifestyle as well as in the diet can help put brakes on congestive heart failure. Additional changes include bringing down the weight and how well you can manage stress. Apart from slowing the process, it is now possible to reverse the effects of congestive heart failure. You can only do a few of the symptoms, but not all. You can just feel the lasting effects only when you make changes to the lifestyle and adhere to the same.
Signs Of Heart Failure And Congestive Heart Failure
Most cases of heart failure and CHF are chronic and develop over time. Symptoms to watch for are:
- Chest pain, especially while you are exerting yourself
- New or increased dyspnea or shortness of breath
- Dizziness, light-headedness, or feeling like you may faint
- Sudden weight gain
- New or increased swelling of the legs, ankles, or feet
- Sudden fatigue or weakness especially while doing normal physical activities
Don’t Miss: When Is Heart Rate Too Low
Diagnostic Tests For Heart Failure
Articles On Heart Failure Types & Stages
Congestive heart failure doesn’t mean your heart has stopped. It means it’s not pumping blood the way it should. When that happens, blood and fluid can back up in your body and make it harder for your kidneys to flush out sodium and water. That can make you hold on to too much fluid, which causes swelling.
There’s no cure. But your doctor may give you medication to do things like lower your blood pressure, relax your blood vessels, make your heart beat stronger, or ease swelling. And diet and lifestyle changes — like not smoking — can help, too.
Also Check: What Does Heart Rate Mean
How Heart Failure Is Diagnosed
A diagnosis of heart failure or CHF is made by a doctor who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of heart-related conditions, called a cardiologist. Your cardiologist will take a complete medical history, conduct a physical exam, and may order a variety of tests, including blood work and imaging tests.
The following tests and scans may be performed to help diagnose heart failure:
- Natriuretic peptide tests: Measures levels of B-type natriuretic peptide or N-terminal prohormone of B-type natriuretic peptide , which are released into the blood by the heart
- Echocardiogram: Determines the percent of blood that is pumped out of the heart with each heartbeat and evaluates the structure and function of the heart
- Electrocardiogram : Provides a tracing of the hearts electrical activity
- Stress test: Measures how the heart responds to exercise or chemically induced stress in a controlled environment
- Cardiac catheterization:Shows the interior of the arteries in your heart to see if they are blocked and allows for measurement of right and left heart pressures
- Other imaging tests such as cardiac computed tomography scan, cardiac magnetic resonance imaging , or nuclear heart scan can be used to show how well the heart is working.
Classes Of Congestive Heart Failure
There are several ways that CHF has been classified. healthcare providers usually identify each stage of heart failure according to the severity of symptoms.
The New York Heart Association Functional Classification defines class I through IV based on limitations in physical functioning.
The categories are outlined below.
| Classes of Heart Failure | |
|---|---|
| Class I | No limitation of physical activity. Ordinary physical activity does not cause undue fatigue, palpitation, dyspnea . |
| Class II | Slight limitation of physical activity. Comfortable at rest. Ordinary physical activity results in fatigue, palpitation, dyspnea . |
| Class III | |
| Class IV | Unable to carry on any physical activity without discomfort. Symptoms of heart failure at rest. If any physical activity is undertaken, discomfort increases. |
Heart failure generally worsens, and it is not possible to reverse it or go to a less advanced stage. Treatment can help prevent progression.
Read Also: Does Fever Increase Heart Rate
What Causes Heart Failure
Although the risk of heart failure doesnt change as you get older, youre more likely to have heart failure when youre older.
Many medical conditions that damage the heart muscle can cause heart failure. Common conditions include:
- Tobacco and recreational drug use.
- Medications. Some drugs used to fight cancer can lead to heart failure.
What Is Heart Failure
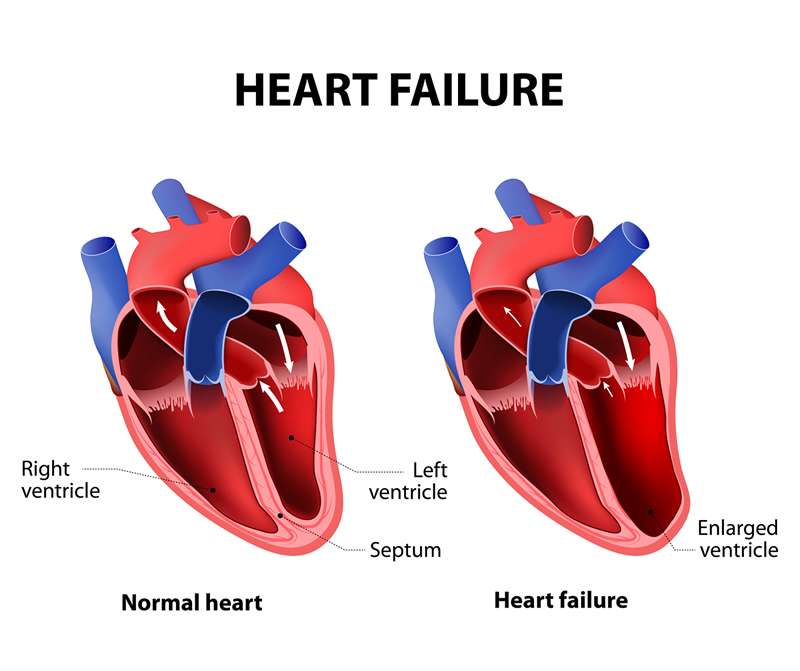
Heart failure, or congestive heart failure, is a long-term condition that gets worse over time. Although the name sounds like your heart has stopped working, heart failure means your heart isnt able to pump blood as well as it should. When your heart has less pumping power, that can damage your organs and fluid can collect in your lungs.
Don’t Miss: Can Congestive Heart Failure Be Reversed
What Is It Used For
A BNP test detects a rise in BNP, which indicates heart failure. Your doctor may recommend this test if you have symptoms of heart failure, such as shortness of breath.
Early diagnosis of heart failure can ensure that you get quick and effective treatment to prevent further complications.
Your doctor may order a BNP blood test if you have symptoms of heart failure, including:
- abnormally high or irregular heart rate
- coughing a lot, and producing white or pink phlegm
- nausea or having no appetite
A BNP test can also help rule out heart failure. Other conditions can cause elevated BNP levels, including lung or kidney conditions and obesity.
Stage 2 Of Congestive Heart Failure
Stage two of congestive heart failure will produce symptoms such as fatigue, shortness of breath, or heart palpitations after you participate in physical activity. As with stage one, lifestyle changes and certain medication can help improve your quality of life. Your doctor will discuss treatment with you and help you on your healthcare journey while living with CHF.
Also Check: How To Lower Heart Rate And Blood Pressure
Is There A Treatment For Heart Failure
There are more treatment options available for heart failure than ever before. Tight control over your medications and lifestyle, coupled with careful monitoring, are the first steps. As the condition progresses, doctors specializing in the treatment of heart failure can offer more advanced treatment options.
The goals of treating heart failure are to try to keep it from getting worse , to ease symptoms, and to improve quality of life.
Some common types of medicines used to treat it are:
- ACE inhibitors
- Aldosterone antagonists
- ARBs
- ARNIs
- Selective sinus node inhibitors
- Soluble guanylate cyclase stimulator
Your doctor may also recommend a program called cardiac rehabilitation to help you exercise safely and keep up a heart-healthy lifestyle. It usually includes workouts that are designed just for you, education, and tips to lower your chance of heart trouble, like quitting smoking or changing your diet.
Cardiac rehab also offers emotional support. You can meet people like you who can help you stay on track.
