Characteristics Of Patients With Hf Who Developed Hypotension
In the HF cohort , 2565 patients developed 1episode of hypotension over a mean ±standard deviation follow-up period of 3.31±3.97 years . Most of the cases were male , and 69.6% were aged 70 years at the index date . Also, 1041 of the cases had recurrent hypotension during follow-up , and 288 had symptomatic hypotension. The most common symptoms were dizziness related .
Factors significantly associated with the development of hypotension in patients newly diagnosed with heart failure
Of the examined cardiovascular comorbidities , hypotension antecedents, ischaemic heart disease, valvular cardiac disease and hyperlipidaemia were associated with an increased risk of hypotension. As expected, hypertension was associated with a markedly decreased risk of hypotension. Renal failure was an independent predictor of hypotension, with the risk of hypotension increasing with decreasing eGFR. Other non-cardiovascular comorbidities including infections , hypothyroidism, anaemia, liver disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, depression, and dementia were associated with an increased risk of hypotension, and diabetes was associated with a decreased risk .
Read Also: How To Lower Blood Pressure In The Morning
Strengths And Limitations Of This Study
-
We have analysed hypotension incidence and risk factors in a large real-world cohort of patients with incident heart failure in UK primary care.
-
Data are from The Health Improvement Network database, which has been extensively validated for use in pharmacoepidemiology.
-
Since blood pressure is not systematically tested in routine clinical practice, we cannot rule out some detection bias.
-
Due to the nature of data collection during routine clinical practice, we were unable to identify reliably the subgroup of cases with orthostatic hypotension, it was unclear if diagnoses of heart failure were made according to guidelines, and data on heart failure severity and ejection fraction were not complete for all patients.
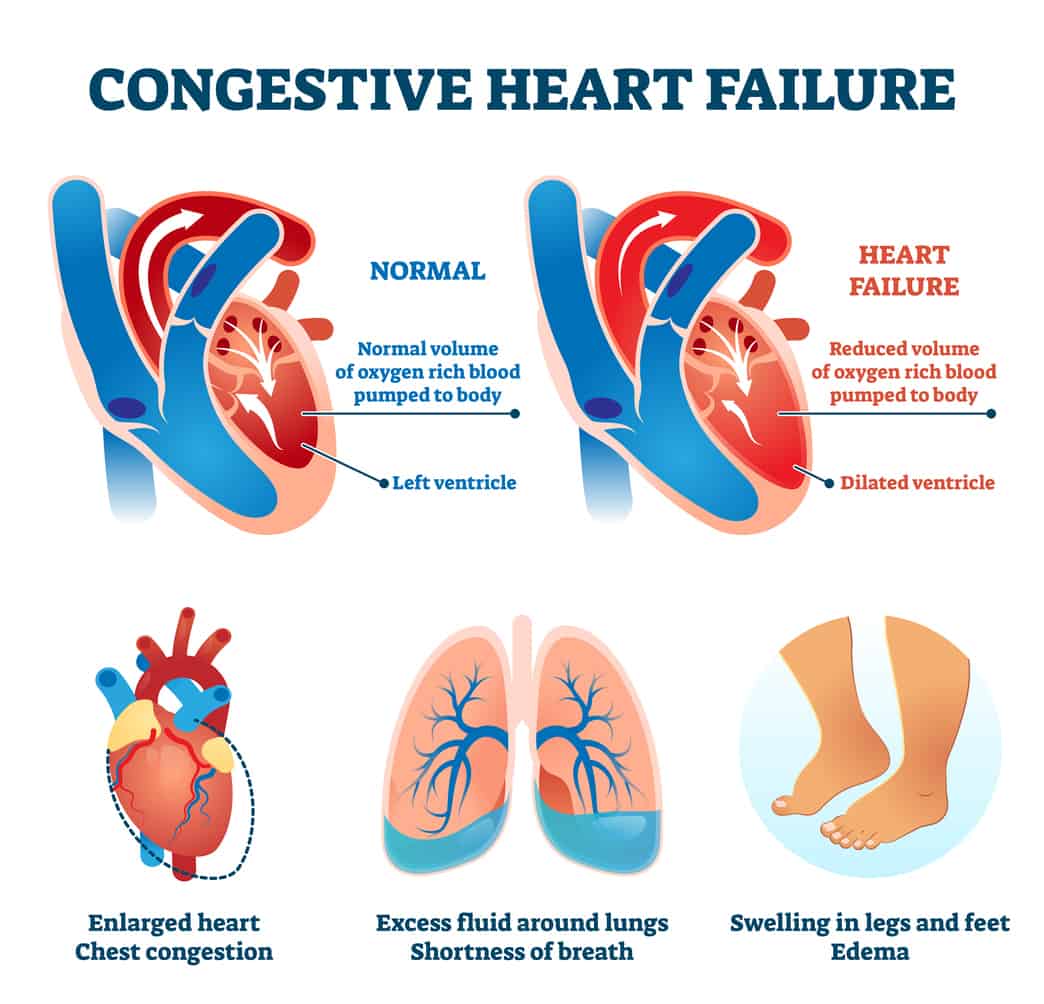
About Congestive Heart Failure
Heart failure, sometimes called congestive cardiac failure , is a condition in which the heart muscle is weakened and cant pump as well as it usually does. The main pumping chambers of the heart can change size and thickness, and either cant contract or cant relax as well as they should. This triggers fluid retention, particularly in the lungs, legs and abdomen.
The major causes of heart failure include coronary heart disease and heart attack, high blood pressure, damage to the heart muscle , heart valve problems and abnormal heart rhythms. Of these, coronary heart disease and heart attack are the most common causes.
The major factors that contribute to coronary heart disease include:
- reduced emotional and social wellbeing
- physical inactivity.
Heart failure is more common in elderly people. The survival rate for people with this disorder depends on the severity of their condition.
Most common treatments for heart failure are medications and self-managed lifestyle changes. Some less-common treatments may require insertion of implantable cardiac devices or valve replacement.
You May Like: How To Treat Heart Palpitations
When To Call The Doctor
- You are tired or weak.
- You feel short of breath when you are active or when you are at rest.
- You feel short of breath when you lie down, or an hour or two after falling asleep.
- You are wheezing and having trouble breathing.
- You have a cough that does not go away. It may be dry and hacking, or it may sound wet and bring up pink, foamy spit.
- You have swelling in your feet, ankles, or legs.
- You have to urinate a lot, particularly at night.
- You have gained or lost weight.
- You have pain and tenderness in your belly.
- You have symptoms that you think might be from your medicines.
- Your pulse, or heartbeat, gets very slow or very fast, or it is not steady.
History And Physical Exam
A clinician listens to your heart and lungs and measures your blood pressure and weight. They will also ask about your:
- Familys medical history, especially previous cardiac problems
- Medications, including prescriptions, over-the-counter drugs and supplements
- Personal medical history
Blood tests can measure several things related to heart failure:
- Sodium and potassium levels
- Creatinine, which helps measure how well your kidneys are working
- B-type natriuretic peptide , a hormone released from the ventricles in response to increased wall tension that occurs with heart failure
You May Like: How To Get Blood Pressure Down Immediately
Also Check: What Should My Heart Rate Be For Cardio
Your Heart Ejection Fraction
The treatment of heart failure aims to improve symptoms and exercise tolerance, to prevent worsening of symptoms, and to increase your survival. Your treatment will depend on how much blood your heart is able to pump out with each beat.
The amount of blood that is pumped out of your left ventricle when your heart contracts is your ejection fraction. Some blood always remains inside the chamber of the heart when it beats, even in the fittest person in the best of health, and an ejection fraction of 55% or above is considered normal.
Your ejection fraction is usually measured via an echocardiogram which is essentially an ultrasound of the heart.
For example, if your left ventricle has a total blood volume of 100 ml, and pumps out 60 ml during each heartbeat, then you have an ejection fraction of 60%, which is great.
If your left ventricle is enlarged and has a total blood volume of 140 ml and pumps out 60 ml with each heartbeat, you have an ejection fraction of just under 43%, which is reduced.
- A left ventricular ejection fraction of 55% to 70% is normal.
- A left ventricular ejection fraction of 40% to 54% is slightly below normal and you may not have symptoms of heart failure.
- An ejection fraction between 35% and 39% is moderately below normal and you may have mild to moderate heart failure symptoms.
- An ejection fraction between of less than 35% is severely below normal and you will have moderate to severe heart failure symptoms.
Factors That Can Worsen Symptoms Of Heart Failure
The symptoms of heart failure can be worsened by a number of factors, including:
- too much salt, fluid, or alcohol in the diet
- some viral and bacterial infections
- kidney diseases
Treatment for heart failure may include:
- medicines, such as
- diuretics to remove excess fluid and improve symptoms of heart failure
- mineralcortiocoid receptor antagonists are also recommended and used in most patients with heart failure to reduce mortality and hospitalisation
- ACE inhibitors to open up blood vessels, reduce blood pressure and reduce sodium retention and water retention
- certain beta-blockers to slow the heart rate and reduce its work
- aldosterone blockers to reduce blood pressure and reduce the effects of damage to the heart muscle
- ACE inhibitors, beta blockers and aldosterone blockers can increase survival and reduce the likelihood of hospitalisation.
Read Also: Congestive Heart Failure Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy
How Is The Heart Supposed To Function
Before we get into the details of congestive heart failure, lets briefly review how your heart works:
-
The hearts right atrium receives blood that has already passed through your body.
-
From there, it moves into the right ventricle, where it gets pumped over to the lungs to pick up more oxygen.
-
Then it returns to the left atrium and down into the left ventricle, to get pushed out to the body. This is why your left ventricle is the strongest chamber in the heart. It has the heaviest lift.
-
A series of valves between the hearts chambers help ensure the blood keeps flowing in the right direction. And your heartbeat? That steady rhythm helps ensure each part of the heart does its job at precisely the right time.
New Moms And Heart Failure Risk
The research supports the notion that at-risk women need closer observation during that time period.
The researchers also say that because many women are discharged from hospital care just a couple of days after giving birth and arent given a follow-up appointment until about six weeks later, the way doctors regard women who might be at risk of heart failure needs to change.
They call for comprehensive postpartum discharge health education, with emphasis on signs and symptoms to look for and when or where to seek immediate care.
Read Also: Clinical Manifestations Of Left Sided Heart Failure
Proposed Fivestep Algorithm For The Management Of Hypotension In Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction Patients
The prerequisite is to identify settings in which hypotension is related to cardiogenic shock and reflect a drop in stroke volume. In this case, although patients may have signs or symptoms of hypotension, they will also show significant congestion and/or signs of hypoperfusion . As specified in Figure1,1, in such circumstances, an urgent admission should be considered and if cardiogenic shock is confirmed, inotropes and/or mechanical support should be used. In the next steps, we will solely focus on stable HFrEF patients.
Causes Of Low Blood Pressure
Low blood pressure typically results from one or more of the following:
-
Dilation of small arteries
Dilation of arterioles can be caused by
-
Spinal cord injuries, in which the nerves that cause the arterioles to constrict are impaired
Low blood pressure also occurs when the nerves that conduct signals between the brain and the heart and blood vessels are impaired by neurologic disorders called autonomic neuropathies Autonomic Neuropathies Autonomic neuropathies are disorders affecting the peripheral nerves that automatically regulate body processes . Causes include diabetes, amyloidosis⦠read more .
When a person quickly moves from a sitting position to a standing position, blood pressure in the blood vessels to the brain decreases, resulting in a temporary sensation of light-headedness or faintness. This is called orthostatic hypotension Dizziness or Light-Headedness When Standing Up In some people, particularly older people, blood pressure drops excessively when they sit or stand up . Symptoms of faintness, light-headedness⦠read more . It can be more pronounced in people who are dehydrated or warm , have certain illnesses, or have been lying down or sitting for prolonged periods of time. Orthostatic hypotension can even cause people to faint. In most people, the body quickly acts to increase blood pressure and prevent the person from fainting.
You May Like: Heart Attack Signs In Females
Recommended Reading: How To Measure Your Heart Rate
Heart Failure: Pumping And Filling Problems
|
Normally, the heart stretches as it fills with blood , then contracts to pump out the blood . The main pumping chambers in the heart are the ventricles. Heart failure due to systolic dysfunction usually develops because the heart cannot contract normally. It may fill with blood, but the heart cannot pump out as much of the blood it contains because the muscle is weaker or because a heart valve malfunctions. As a result, the amount of blood pumped to the body and to the lungs is reduced, and the ventricle usually enlarges. Heart failure due to diastolic dysfunction develops because the heart muscle stiffens and may thicken so that the heart cannot fill normally with blood. Consequently, blood backs up in the left atrium and lung blood vessels and causes congestion. Nonetheless, the heart may be able to pump out a normal percentage of the blood it receives . The heart chambers always contain some blood, but different amounts of blood may enter or leave the chambers with each heartbeat as indicated by the thickness of the arrows. |
Signs And Symptoms Of Congestive Heart Failure
During heart failure, the body tries to compensate for reduced blood flow in other ways, including:
- Enlarging the Heart Chamber This is the bodys attempt to get the heart to contract more strongly, in order to pump more blood. Initially, it may help the heart function more efficiently, but ultimately it causes the heart to not pump as effectively and causes fluid retention, leading to congestion in the lungs.
- Developing More Heart Muscle Mass The contracting cells in the heart get bigger, which initially lets the heart pump more strongly.
- Increasing Heart Rate This causes the heart to pump faster and increase its output.
- Increasing Fluid and Salt Retention and Tightening Some Blood Vessels This helps maintain the hearts normal output.
These compensations may mask heart failure temporarily, but eventually heart failure gets worse, and people start to experience symptoms.
Also Check: Symptoms Of Heart Failure In Dogs
What Is Congestive Heart Failure Anyway
Just like you learned in biology class, your heart is a smallbut powerfulpump that constantly circulates oxygen- and nutrient-rich blood to every nook and cranny of the body. Once the good stuff is delivered and the toxins are filtered out by the kidneys and liver, the heart brings the blood back around to receive a fresh load of oxygen, and the process begins again.
However, when something interferes with your hearts ability to pump efficiently, it causes a systemwide slowdown. Blood and other fluids start to back up and collect in your veins and lungsthis is the congestive partmaking it even harder for your heart to do its job. You may feel shortness of breath, or notice swelling in your legs or arms, when this starts to happen.
This type of heart failure affects 6.5 million Americans, according the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Its a chronic and progressive condition, but there are plenty of treatment options that can ease symptoms and help your heart work with less strain. And while theres no skirting around the seriousness of this condition, don’t give up hope for a better tomorrow.
Chronic Heart Failure Prognosis
Effective treatment of chronic heart failure is usually successful in relieving symptoms and improving quality of life. Effective treatment can also significantly prolong your life but it is important to keep taking your medicines as prescribed.
The average age at first diagnosis of chronic heart failure is 76 years, although some people are significantly younger and others older, depending on the underlying cause. Treatments are improving all the time, and at least two in three people survive their first year after diagnosis, with around 50% of people surviving for over five years. While this may seem frightening, remember that the average age of diagnosis is 76 years, so a 5 year survival will take you into your 80s, which doesnt sound quite so bad.
The main reason why some people go downhill with chronic heart failure is because they do not take their medicines regularly as prescribed. Some medicines have to be taken twice a day, and even in clinical trials one in three people do not take their heart failure treatments properly. If you have problems remembering to take your medicines, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. For example, other treatment options that are only needed once a day may be available. Your pharmacist can also suggest different ways of reminding yourself to take your drugs every day.
Image credits: pixabay shutterstock
Recommended Reading: How To Know If You Had A Heart Attack
Prevalence Of Hypertension Among Heart Failure Patients
The prevalence of HTN as an HF etiology varies geographically and temporally . The findings from the Korean Heart Failure study, which recruited 3200 patients with HF from 2004 to 2009, showed that 36.7% of the patients had hypertensive HF . More recently, the findings from the Korean Acute Heart Failure study, which enrolled 5625 patients from 2011 to 2014, showed that only 4% of the patients had HF caused by HTN . Up to 30% of the patients in the Acute Decompensated Heart Failure National Registry had a hypertensive etiology, and this was more prevalent among the patients with normal EFs . The results from studies of other large dedicated HF registries have shown that HTN was the primary cause of HF in 1123% of the patients .
Table 1 Comparison of dedicated heart failure registries
Treatment And Medication Options For Congestive Heart Failure
Heart failure is a chronic condition, and there is no cure. However, once youve been diagnosed, there are several things you can do to treat the condition and manage it so that it does not progress. Chief among them are lifestyle changes. That includes exercising and maintaining a heart-healthy diet thats low in saturated fat, trans fats, and cholesterol.
You May Like: Can 30 Year Olds Have Heart Attacks
How Is Heart Failure Diagnosed
Your doctor will typically begin by assessing your symptoms, asking about your family history and performing a physical examination.
There are several tests that help to confirm a diagnosis of heart failure and identify which type it is:
- echocardiogram : high-frequency sound waves are used to examine the shape and function of your heart
- electrocardiogram : electrical leads are placed on your chest, arms and legs to record the electrical signals travelling through your heart muscle
- angiogram : fluid is inserted through a small tube to show whether your coronary arteries are narrowed or blocked
How Do I Take Care Of Myself
If you have hypotension with symptoms, the best thing you can do is follow your healthcare providerâs guidance on managing this condition. Their recommendations may include any of the following:
- Manage your diet. Following diet recommendations, especially how much salt you should have in your diet, can help avoid symptoms of hypotension.
- Take your medication. These can help you avoid the disruptive symptoms and effects of this condition.
- Dress up. Compression socks, which put light pressure on your legs and feet, can push blood upward and raise your blood pressure.
- Take it slow. Avoid standing up too quickly, especially with orthostatic hypotension. That can help you avoid the dizziness and fainting effects of hypotension.
- Have a seat. If you notice yourself feeling dizzy or lightheaded, sit down. Falling from standing height can put you at risk for severe or even catastrophic injuries from a fall, such as a broken hip, concussion, skull fracture or broken ribs.
Donât Miss: What Kind Of Jaw Pain Is Associated With Heart Attack
Don’t Miss: What Are Some Heart Disease
