Balance Between Preventing Decompensation And Preferences
This core-concept means that patients with HF try to maintain their agelong preferences to give their life a purpose, such as by maintaining long-term friendships and continuing to engage in interests. Instead of limiting all their activities, they stop engaging in activities that they learn would be bad for their heart and choose to continue those activities not be harmful.
They seek medical guidance to determine which activities were considered good for the heart or feasible within the scope of their limited lifestyle. They begin to reassemble their life into ones that do not put a strain on the heart while making up for lost parts of their life as a result of HF. They describe taking walks, singing a song, and engaging in new physical activities or hobbies within their realm of possibility. They determine which activities caused symptoms to appear and how far they could push themselves even if these were vacation activities or when invited by acquaintances. They make an effort to exercise at their own pace and master how to regulate their amount of exercise so as to avoid placing strain on the heart and causing symptoms.
In summary, nurses need to recognize and value patients views and experiences to support their self-care management.
Assessment of experience and knowledge about HF.
Congestive Heart Failure: Nursing Diagnosis & Care Plan
The nursing intervention plan is to be started from the patients education within the scope of CHF. The daily intake of fluid should be appropriate and include all liquids consumed per day, including tea, juice, soup, fruits, and vegetables. When dry mouth and thirst appear, one needs to rinse mouth, add lemon or a piece of ice to the water, take a small sip of water. The intake of table salt is limited, the daily rate of sodium chloride is a teaspoon, and it should not be forgotten that salt is added to food, so one does not have to add salt to ready-made meals and does not eat salty foods . Refusal to use all types of alcoholic beverages and smoking cessation are recommended.
Control of body weight is prescribed daily in the morning on an empty stomach in the same clothes as self-control diary. Among the indicators for home, self-control is also blood pressure measurement two times a day in the morning and evening and pulse control. These indicators must be recorded in the patients diary which can be monitored by a nurse in order to show them to the attending physician at the next visit . The optimal types of exercise for patients are walking, swimming, cycling. It is easier to start physical training with activities that do not require the support of their own weight. For a nurse, there is also a necessity to assess vital signs at least every 4 hours.
Heart Failure Nursing Diagnosis
Several nursing diagnoses could be used when caring for patients with heart failure. Some of the more common ones include
Anxiety occurs because those who suffer from heart failure may have symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and palpitations, resulting in constant worry about their health. Excessive anxiety may lead to depression and may affect the ability of the individual to carry out daily activities.
Diarrhea because heart failure commonly causes hypoproteinemia, a deficiency of protein in the blood, it can cause an inability to control bowel movements or trouble with defecation. This may prove to be embarrassing for the patient and have a negative impact on their well-being.
like congestive heart failure , restrictive cardiomyopathy is caused by decreased cardiac output due to impaired ventricular function, resulting in insufficient blood flow through the body. Because of this, heart failure patients may develop clinical signs such as peripheral edema and shortness of breath.
Chronic Pain heart failure can be associated with chronic pain due to the stress on the body from the reduced cardiac output and fluid overload .
Activity intolerance those who suffer from heart failure are often limited in the amount of physical activity they can participate in, which may severely impact their quality of life.
Fluid Overload heart failure is commonly related to fluid overload, which can be dangerous and lead to complications such as pulmonary edema.
Read Also: How To Differentiate Between Anxiety And Heart Attack
Chf Nursing Care Plan 6
Nursing Diagnosis:Acute Pain related to decreased myocardial blood flow as evidenced by pain score of 10 out of 10, verbalization of pressure-like/ squeezing chest pain , guarding sign on the chest, blood pressure level of 180/90, respiratory rate of 29 cpm, and restlessness
Desired Outcome: The patient will demonstrate relief of pain as evidenced by a pain score of 0 out of 10, stable vital signs, and absence of restlessness.
Nursing Care Plan Diagnosis Interventions Risk For Aspiration Impaired Swallowing Ineffective Swallowing Difficulty Swallowing Dysphagia Peg Tube Feeding And Difficulty Chewing
This nursing care plan and diagnosis with nursing interventions is for the following condition: Risk For Aspiration, Impaired Swallowing, Ineffective Swallowing, Difficulty Swallowing, Dysphagia, Peg Tube Feeding, and Difficulty Chewing. What are nursing care plans? How do you develop a nursing care plan? What nursing care plan book do you recommend helping you develop a nursing
Recommended Reading: How To Reduce Risk Of Heart Attack
What Is Congestive Heart Failure
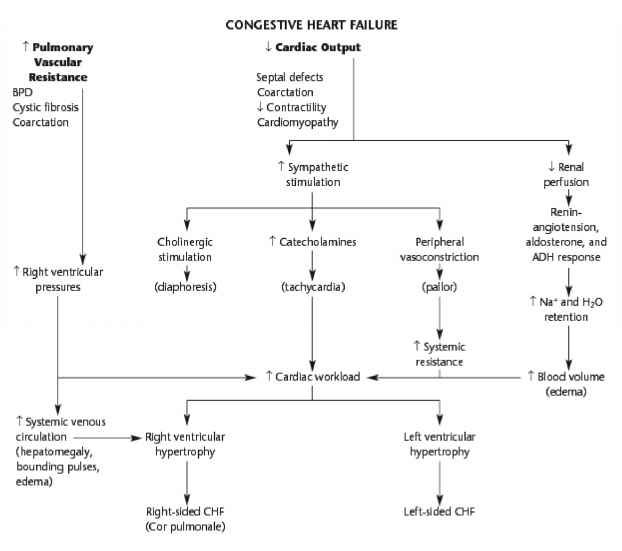
Heart failure is a chronic, progressive condition. It occurs when the heart is unable to pump effectively and produce enough cardiac output to successfully perfuse the rest of the bodys tissues and organs. An individual can have right-sided or left-sided heart failure as well as systolic or diastolic heart failure.
Left-sided heart failure is also known as Congestive Heart Failure . In CHF, the heart is either unable to contract completely or fill completely during relaxation. It can lead to an inadequate amount of blood pumping out of the heart. Thereby, backing up into the right side and then ultimately to the lungs and throughout the body causing congestion.
Systolic heart failure means the heart is not able to contract completely and affects its ability to pump blood out of the heart.
Diastolic heart failure means the heart is unable to relax fully between heartbeats and allows the appropriate amount of blood into the ventricle.
In this post, well formulate a sample nursing care plan for a patient with Congestive Heart Failure based on a hypothetical case scenario.
Nursing Care Plan Diagnosis Interventions For Anxiety Nervousness Inability To Cope And Ineffective Individual Coping
This free nursing care plan is for the following conditions: Anxiety, Nervousness, Inability to Cope, and Ineffective Individual Coping What are nursing care plans? How do you develop a nursing care plan? What nursing care plan book do you recommend helping you develop a nursing care plan? This care plan is listed to give an
You May Like: How To Stop Hormonal Heart Palpitations
Nursing Care Plan For Hypertension
These nanda nursing care plans include a diagnosis, and many nursing interventions for the following conditions: Hypertension What are nursing care plans ? How do you develop a nursing care plan? What nursing care plan book do you recommend helping you develop a nursing care plan? This care plan is listed to give an example of how a
Read Also: Does Vitamin B12 Increase Heart Rate
Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To A Decreased Respiratory Rate
Respiratory rate is the number of breaths a person takes in one minute. Its measured by counting how many times your patient breathes in one minute, and you can do this with a watch or by counting out loud. A normal respiratory rate is 12-20 breaths per minute . In patients with CHF, respiratory rate may be decreased due to difficulty breathing through the narrowed airways caused by edema or other interstitial lung disease. To monitor this condition, check your patients respiratory status every shiftespecially if they have symptoms such as shortness of breath or fatigueand keep track of what changes when you note an increase/decrease in their respiratory status over time
Also Check: How Does Fitbit Measure Heart Rate
Types Of Heart Failures:
Left & Right Side Heart Failure
Left-Sided Heart failure: the left side of the heart cannot pump blood out of the heart efficiently so blood starts to back-up in the lungs.
- Most common type of heart failure.
- Left-sided heart failure is likely to lead to right-sided heart failure.
The left ventricle becomes too weak and doesnt squeeze blood out properly.the heart failure can be either SYSTOLIC OR DIASTOLIC.
- Systolic: Left ventricular systolic dysfunction remember systolic is the contraction or squeezing phase of the heart. In systolic dysfunction, there is an issue with the left ventricle being able to eject blood properly out of the ventricle and the organs cant get all that rich-oxygenated blood it just received from the lungs. Patients will have a low ejection fraction.
- What is ejection fraction? Ejection fraction is a calculation used to determine the severity of heart failure on the left side. A normal EF is 50% or greater meaning that more than half of the blood that fills inside the ventricles is being pumped out. An EF can be measured with an echocardiogram, heart cath, nuclear stress test. An EF of 40% or less is a diagnosis for heart failure.
- Diastolic: left ventricular diastolic dysfunction remember diastole is the filling or resting phase of the heart. In diastolic dysfunction, the ventricle is too stiff to allow for normal filling of blood. Since there isnt an issue with contraction but filling the ejection fraction is usually normal.
Nursing Intervention In Semi
- The patients family should be educated regarding the target goal, the underlying cause of the heart failure, and signs of toxicity with medications. It is also important to teach them about medications and their activities and the signs of toxicity, as this will lead to more effective medication management.
- Teaching about medications and their activities: It is important to teach the patient, and family members/ loved ones about heart disease, especially congestive heart failure, as this will lead to a proper understanding of their pharmacological needs. It is also important to teach them about medications and their activities and the signs of toxicity, as this will lead to more effective medication management.
The patients family should be educated regarding the target goal, underlying cause for procedures such as pericardiocentesis, and complications. It is also important to teach them about medications and their activities and the signs of toxicity, as this will lead to more effective medication management.
Read Also: How To Watch When Calls The Heart
Also Check: How Are Hypertension Heart Disease And Stroke Related
Causes Of Heart Failure:
Mainly due to the heart muscle becoming damaged or too stiff.
Remember the mnemonic: Failure
Faulty heart valves: AV and SL valve problems that causes blood to back flow or stenosis . This causes the heart to work harder and become weak over time.
Arrhythmias: atrial fibrillation or tachycardia
Infarction coronary artery disease: part of the heart muscle dies due to a blockage in the coronary arteriesmuscle become ischemic and can die
Lineage family history
Uncontrolled Hypertension: overtime this can lead to stiffening of the heart walls because with untreated HTN the heart has to work harder and this causes the ventricles to become stiff.
Recreational Drug Use or alcohol abuse
Envaders : viruses or infections that attack the heart muscle
Donât Miss: Which Is A Potassium-sparing Diuretic Used In The Treatment Of Heart Failure
Nurses Can Care For Patients With Heart Failure By Preventing Further Damage To The Heart Through Several Interventions
Nurses can care for patients with heart failure by preventing further damage to the heart through several interventions. Nurses may include:
- Preventing further damage to the heart
- Halting disease progression
- Improving symptoms
- Optimizing effectiveness of medical therapy
Nurses may also improve quality of life by focusing on preventive strategies such as smoking cessation and weight management programs, along with exercise regimens.
Also Check: Medicines For Congestive Heart Failure
You May Like: How To Help Heart Palpitations
Heart Failure Treatment Management Nursing Interventions & Drugs
Heart failure happens when the heart is too weak to pump efficiently. This restricts it from providing proper cardiac output to maintain the bodys metabolic needs.
Complex clinical syndrome that results from any structural or functional impairment of ventricular filling or ejection of blood
2013 ACC/AHA
Systolic Heart Failure is attributed to a pumping problem experienced by the heart where it is unable to contract enough to pump blood to supply to the body, thus resulting in contraction and ejection fraction problems. In this case the patient presents with left ventricular failure with reduced ejection fraction of < 40% and marked cardiomegaly .
Diastolic Heart Failure is attributed to a filling problem experienced by the heart where it is unable to relax the left ventricle, leading to a build-up in the lungs, resulting in relaxation and blood filling problems. In this scenario the patient presents with pulmonary congestion and at times with slightly enlarged ventricles, both due to an increased resistance to filling due to increased ejection fraction of > 50%.
The ejection fraction is a comparison between the amount of blood in the heart and the amount of blood pumped out of the heart.
Cardiac output is the amount of blood pumped out of each ventricle per minute. Factors affecting cardiac output include the heart rate, blood volume, contractility and venous return.
Stroke volume is the volume of blood pumped out of each ventricle with every beat.
Causes of HF include:
Clinical Symptoms Of Heart Failure
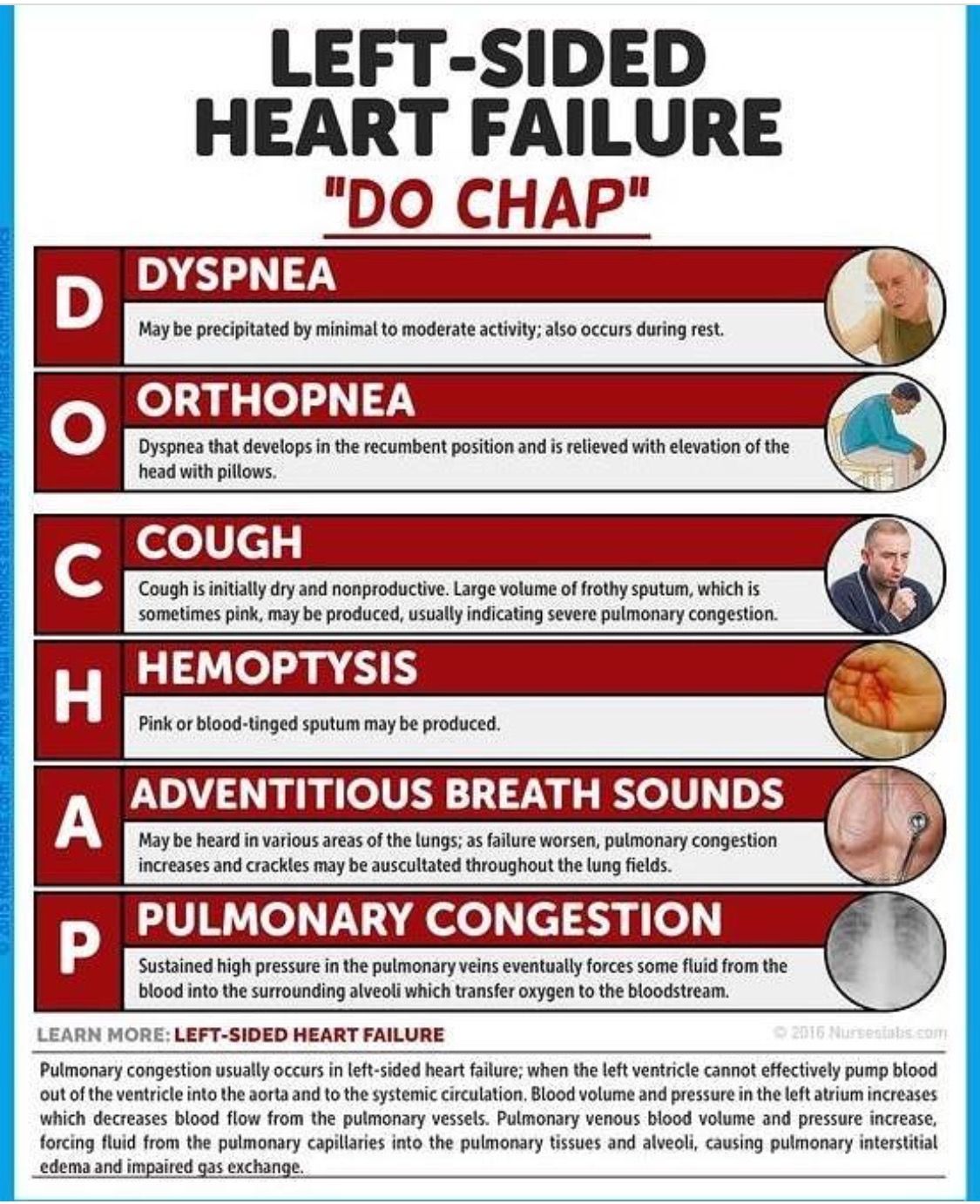
Heart failures early signs and symptoms are breathlessness or dyspnea, orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, lethargy/fatigue/weakness, oedema, abdominal distension, and right hypochondrial pain. The late stages of heart failure have signs and symptoms like tachycardia, pedal oedema, jugular vein distension, crackle sound of the lungs and S3 gallop sound.
Other symptoms of congestive heart failure are microvascular dysfunction which leads to an inadequate supply of oxygen. In some cases, hepatojugular reflux and ascites are found.
Read Also: Congestive Heart Symptoms
Nursing Care Plan For Chf Crf
Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Ventilation/perfusion Imbalance As Evidenced By Breath Sounds Crackling Sounds Coughing Up Mucus And/or Blood Use Of Accessory Muscles Dyspnea
Breathing problems may be a sign of heart failure. As the heart gets weaker, it cant pump blood well enough to support your lungs and other organs. The amount and quality of blood flowing through your lungs may be reduced or cut off entirely because the heart has lost its ability to pump blood effectively.
- Crackling sound : This happens when fluid builds up in the lungs and gets pushed out with each breath you take. The fluid in your lungs produces raspy sounds as it passes through them when you breathe out.
- Coughing up mucus: Mucus buildup in the throat causes coughing as it tries to clear itself out when you swallow or move around too much during sleep this is known as dyspnea .
Recommended Reading: What Can Be Done For Heart Failure
Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Breathing Pattern: Diagnosis And Interventions Dyspnea Respiratory Distress Syndrome Hyoxia Acute Respiratory Failure Hypoxemia And Respiratory Illness
Ineffective breathing pattern care plan: This nursing care plan and diagnosis is for the following condition: Ineffective Breathing Pattern, Dyspnea, Respiratory Distress Syndrome, Hypoxia, Acute Respiratory Failure, Hypoxemia, and Respiratory Illness What are nursing care plans? How do you develop a nursing care plan? What nursing care plan book do you recommend helping you develop
You May Like: Can Tens Unit Cause Heart Attack
Health Teaching And Health Promotion
Nursing care plans for patients with HF must include patient education to improve clinical outcomes and reduce hospital readmissions. Patients need education and guidance on self-monitoring of symptoms at home, medication compliance, daily weight monitoring, dietary sodium restriction to 2 to 3 g/day, and daily fluid restriction to 2 L/day. In addition, patients with HF need aggressive treatment for underlying risk factors and the potential triggers for HF exacerbations. Modifiable risk factors include diabetes mellitus, hypertension, obesity, nicotine use, alcohol use disorder, and recreational drug use, especially cocaine. Patients with sleep apnea and HF should be encouraged to use continuous positive airway pressure therapy as uncontrolled sleep apnea can also increase HF-associated morbidity and mortality.
Read Also: Recovery From Valve Replacement Heart Surgery
Diagnostic Tests For Heart Failure
