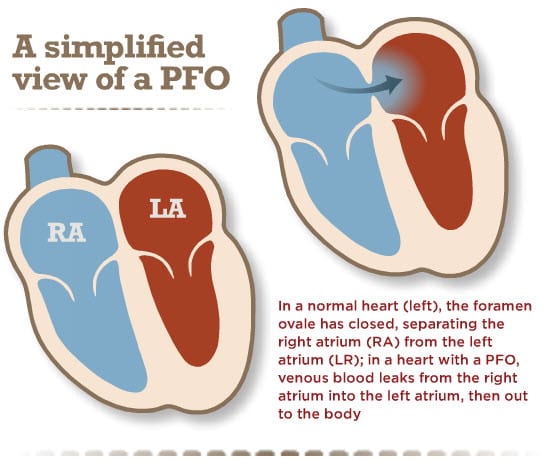
What Is Patent Foramen Ovale And How Is It Treated
This type of hole in the heart is something that occurs in infancy. As a baby in utero, there is a hole in the heart tissue that separates the left and right chambers, also known as the interatrial septum. This hole is called a foramen ovale and it exists to allow blood to bypass the fetal lungs since they dont work until exposed to air. However, once born, this hole naturally closes at birth and if it doesnt, the hole that continues to exist is known as a PFO.
This type of hole is often small in size, and, in most cases, the only effect of a PFO is blood leaking between the right and left chambers. Unless a PFO is detected during childhood, it may go undetected for years, until a person experiences conditions like migraine or stroke that require careful investigation and diagnosis.
Most PFOs require minimal treatment or none at all, they may be left open. In some cases, treatment may be recommended using structural heart intervention, where a closure device is deployed using minimally-invasive techniques.
How Do I Get Ready For Patent Foramen Ovale Transcatheter Repair
Ask your healthcare provider about how to get ready for this procedure. You should not eat or drink anything after midnight before the day of the procedure. You may also need to stop taking any medicine beforehand.
Your healthcare provider may want some extra tests before the procedure. These might include:
- Electrocardiogram to look at your heart rhythm
- Blood tests to check general health
- Echocardiogram to look at the heart anatomy and blood flow through the heart
- Transcranial and transmitral Doppler to see the blood moving through the heart
- Bubble study that is used with the 2 above tests to view the PFO
Hair from around the catheter insertion site may be removed before the procedure.
Vsd Repair Requires A Lengthy Recovery
For every day a patient is sedentary with illness, it takes approximately a week to regain lost strength. This could mean several months of recovery for the patient after they have been discharged from the hospital.
So, after the VSD closure, patients must diligently perform physical therapy to rebuild their muscles and improve their nutrition.
UT Southwestern offers a strong Cardiac Rehabilitation program to help patients recover after heart surgery or heart failure. The dietitians, physical therapists, and other specialists track the patient’s progress, helping them grow stronger and reduce their risk of future heart problems.
Percutaneous VSD closure is a complex, major procedure and a lengthy, strenuous experience that can be avoided. Please go to the emergency room at that first sign of heart attack. There is no reason to wait when your life is at stake.
Recommended Reading: Does Alcohol Raise Heart Rate
How Does An Asd Closure Work
There are several techniques for ASD closure. It may require open-heart surgery. Sometimes, it can be accomplished with a minimally invasive procedure called cardiac catheterization using a catheter threaded from a vein in your groin up to your heart.
The hole can be:
- Covered by a patch made of synthetic material or your own tissue, taken from another area of your heart.
- Plugged with a closure device.
- Sewn shut with sutures .
Your healthcare provider will recommend the appropriate technique for you, depending on:
- Any other heart conditions you may have.
- The size and location of the hole.
- Your overall health.
Some medical facilities even use robotic-assisted surgery to repair an ASD.
Potential Complications During And After
Some of the more common complications of heart surgery are routinely dealt with during the hours and days of recovery in the hospital. The patient is closely monitored for these complications by staff and through lab tests.
- Bleeding: May occur at the incision site or from the area of the heart where surgery is performed
- Abnormal Heart Rhythm: In rare cases, a temporary external, or permanent internal pacemaker may be necessary to correct this problem.
- Ischemic Heart Damage: Damage to heart tissue caused by a lack of blood flow to the heart
- Death: The risk of death is increased in surgeries where the heart is stopped for the procedure.
- Blood Clots: Clots may form in and around the heart or travel through the bloodstream.
- Stroke: Often caused by clots that form in the blood after surgery
- Blood Loss: In some cases, a transfusion may be necessary.
- Emergency Surgery: If a problem is discovered after surgery, emergency surgery may be necessary to repair any problems.
- Cardiac Tamponade : A life-threatening condition where the pericardium, the sac surrounding the heart, fills with blood. This makes it difficult, or impossible, for the heart to fully function.
- : Separation of the sternum may slow the healing process of the bone. Sternal precautions help prevent this as well as excessive pulling on the surgical incision.
Recommended Reading: How To Prevent A Heart Attack In 10 Seconds
Structural Heart Center At Georgia Heart Institute
When there are conditions affecting the structure of the heart, like PFO or ASD, its essential to receive highly-specialized care that starts with a precise diagnosis and innovative treatment options. Did you know that the Georgia Heart Institute of NGMC has a specialized program devoted to heart valve disease and congenital heart defects? Our team offers unparalleled expertise and unique care options for those who issues with the structure of their heart. Contact our Structural Heart Center at 770-219-5242 or learn more below!
How Do I Help My Child Get Ready For Ventricular Septal Defect Surgery
Ask your childs healthcare provider how to help your child get ready for VSD repair. Your child should not eat or drink anything after midnight before the day of the surgery. Your child may also need to stop taking any medicine beforehand.
Your childs healthcare provider may want some extra tests before the surgery. These might include:
- Electrocardiogram, to look at the heart rhythm
- Blood tests, to check general health
- Echocardiogram, to look at heart anatomy and blood flow through the heart
Don’t Miss: What Is The Correct Definition For Target Heart Rate Range
A Hole In The Heart Increases Post
by Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
New research published in the Journal of the American Medical Association indicates that a common anatomic anomaly – a hole between the upper chambers of the heart that fails to close after birth – doubles the risk of stroke within 30 days of non-cardiac surgery. The research suggests the hole itself, known as a patent foramen ovale , contributes to the risk for stroke in patients following surgery. Stroke is a common complication after surgery.
Normally, the heart pumps blood through the right atrium and ventricle to the lung to pick up oxygen. The freshly oxygenated blood returns to the heart’s left atrium and ventricle, from which it travels to the rest of the body. However, in one in five people , a PFO allows blood from the right side of the heart to mix with blood in the left – bypassing the lung – and ultimately travel to the brain. If a clot is present it too can reach the brain, causing stroke.
“We already knew that a PFO increases the risk of a second stroke in people who have previously had a stroke,” said Matthias Eikermann, MD, PhD, of the Department of Anesthesiology at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center , who lead the current study. “Our laboratory is looking for ways to reduce complications after non-cardiac surgery so we investigated whether the presence of PFO increases stroke risk after surgery.”
Explore further
How Do I Manage Post
A cardiac anesthesiologist is also a pain management specialist for conditions related to surgery. Your anesthesiologist will talk to you about your options for managing post-operative pain. Before your surgery, the anesthesiologist may ask about your pain tolerance to help gauge how best to manage your post-operative pain, guiding decisions such as the proper narcotics dosage, the feasibility of nonnarcotic pain medication options, and the need for nerve blocks.
Although most heart surgeries are major surgeries, they are typically not a source of long-term pain. Even in the short term, the pain may be less severe than with operations on other areas of the body. Opioids are used when necessary, but there are many other pain management options, including:
- Lidocaine infusion
Also Check: Why Does Left Arm Go Numb During Heart Attack
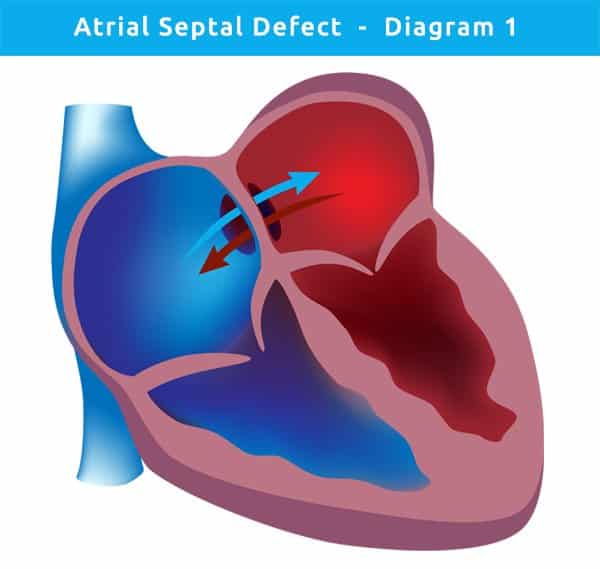
How Are Atrial Septal Defects Diagnosed
After hearing the heart murmur that suggests a hole in the atrial septum, a doctor may refer a child to a pediatric cardiologist, a doctor who specializes in diagnosing and treating heart disease in kids and teens.
The cardiologist might order one or more of these tests:
- chest X-ray: an image of the heart and surrounding organs
- electrocardiogram : a record of the heart’s electrical activity
- echocardiogram : a picture of the heart and the blood flow through its chambers. This is often the primary tool used to diagnose an ASD.
Why Might My Child Need Ventricular Septal Defect Surgery
The purpose of this surgery is to ease symptoms caused by the VSD and to prevent future symptoms. No one knows what causes most cases of this common heart defect.
Not everyone with a VSD needs to have the hole repaired. Very small holes in the ventricular septum may not let much blood pass between the ventricles. In these cases, the heart and lungs dont have to work harder and no repairs are needed. These smaller holes dont cause any symptoms. Sometimes these small holes will close up on their own naturally. Your childs healthcare provider might wait to see whether that happens before planning to do a repair, especially in a very young child.
If your child has a larger VSD, he or she may need some type of repair. Infants and children with larger VSDs often have symptoms like breathing faster and harder than normal. They may also fail to gain weight normally. A large, unrepaired VSD can eventually cause elevated pressure in the blood vessels in the lungs. The higher pressure can lead to decreased oxygen levels in the body.
Healthcare providers often recommend some type of repair for children who have a large VSD, even if they dont have symptoms yet. It can prevent long-term damage to the lungs. Healthcare providers often do the surgery in infants or children. Sometimes adults also need this type of repair if their VSD was not found during childhood.
You May Like: What Heart Rate Is Tachycardia
Asd Amplatzer Device Closure Method
This procedure is suitable for some patients with ASD. It involves the insertion of a long thin tube into the groin, through to the heart. The catheter carries a collapsed closure device into the heart, which, when deployed, opens like an umbrella to close the defect. The amplatzer device used in the closure remain permanently implanted, with tissue growing over it, so the device becomes part of the muscle wall. Patients tend to only need to be hospitalized for one day when having this an Amplatzer Device closure procedure, with minimal recovery time. However, Amplatzer Device closure using a catheter is not always possible if the hole on the hearts chamber is abnormally large or difficult to locate. The video below demonstrates the process of an Amplatzer Device closure.
What If The Defect Is Still Present Should It Be Repaired In Adulthood
If the opening is small, surgery or other treatments may not be needed.
Most large atrial septal defects now can be closed either with open-heart surgery or during a cardiac catheterization using a device inserted into the opening to plug it ). However, if the ASD is in an unusual position within the heart, or if there are other heart defects such as abnormal connections of the veins bringing blood from the lungs back to the heart , the ASD cannot be closed with the catheter technique. Then surgery is needed. Even when the defect is discovered in adulthood, patients benefit from closure of large defects.
Also Check: What I Felt Before My Heart Attack
What Happens During Transcatheter Asd Closure
If you have a smaller ASD and no other heart conditions that need correcting, you may be able to have transcatheter ASD closure. This method is less invasive and generally makes recovery easier and faster.
For transcatheter ASD closure, you may receive general anesthesia or medications that sedate you. Sedation makes you sleepy and relaxed, but youre still conscious .
To perform a transcatheter ASD closure, your interventional cardiologist:
What Activities Can My Child Do
Your child may not need any special precautions and may be able to participate in normal activities without increased risk. After surgery or catheter closure, your child’s pediatric cardiologist may advise some activity changes for a short time. But after successful healing from surgery or catheter closure, no restrictions are usually needed. Sometimes medicines to prevent blood clots and infection are used for a few months after ASD closure.
Don’t Miss: Which Is A Potassium-sparing Diuretic Used In The Treatment Of Heart Failure
What Is Patent Foramen Ovale Transcatheter Repair
A patent foramen ovale is a small hole between the two upper chambers of the heart, the right and the left atrium. Patent foramen transcatheter repair is a procedure to fix this hole in the heart.
Normally, the atrial septum separates the right and left atria. No blood flows between these 2 chambers. If a PFO exists, a little blood can flow between the atria. This flow of blood between the atria is not normal. This hole is normally present in the heart before birth. But in most people, it closes soon after birth.
During transcatheter repair, a healthcare provider inserts a device that can plug up the PFO. This device attaches to the end of a long, flexible tube called a catheter. The healthcare provider inserts the catheter through a blood vessel in the groin and guides it to the PFO. He or she uses the device to fix the hole and then removes the catheter from the body.
How Does The Asd Affect Me
Some patients with ASD have no symptoms. If the opening is small, it won’t cause symptoms because the additional work done by the heart and lungs is minimal. If the opening is large, it may cause mild shortness of breath, especially with exercise. The increased blood in the lung may increase a patient’s susceptibility to pneumonia and bronchitis. On physical examination, the only abnormal finding may be a murmur and other abnormal heart sounds. However, with progressive damage to the lung vessels, the pressures in the lung may rise, and the patient can become more severely limited, eventually developing Eisenmenger’s syndrome, described below.
Also Check: How To Slow Your Heart Rate
Left Ventricular Assist Device
A VAD – also known as an LVAD for Left Ventricular Assist Device – is a circulatory support device. It takes blood from the left ventricle and pumps it into the aorta , helping the heart in pumping blood round the body.
It was originally designed to support the work of the heart while someone was waiting for a heart transplant. However, its now also used as a long-term support therapy for people who are not candidates for transplant and have end-stage heart failure.
Learn more about left ventricular assist devices through the British Heart Foundation.
Why Might I Need Patent Foramen Ovale Transcatheter Repair
Most PFOs do not cause any symptoms and do not need any treatment. But sometimes PFOs can lead to complications. The most significant of these is stroke. Stroke can result from a traveling blood clot that blocks a blood vessel in the brain. PFOs do not cause most strokes, but having a PFO may slightly increase the risk for stroke in some people.
You usually do not need treatment if you have no risk factors for stroke or any history of traveling blood clots. Your healthcare provider may want to treat your PFO if you have had problems, such as strokes from these traveling blood clots.
Treatment for PFOs in these cases varies. In some cases, your healthcare provider may still choose not to treat the PFO. Another choice is treatment with antiplatelet medicines such as aspirin. Or you may take anticoagulant medicines such as warfarin. These can help prevent blood clots. Your healthcare provider may also the PFO by transcatheter repair or heart surgery.
A transcatheter repair is less invasive than a surgical repair. You usually recover more quickly. Your healthcare provider might be less likely to recommend this treatment if you need surgical repair for another heart problem in addition to the PFO. Ask your healthcare provider what treatment is best for you.
Read Also: What Are The Symptoms Of A Mild Heart Attack
After Heart Attack This Rare Procedure Can Save Patients From A Hole In The Heart
Heart attack symptoms should be considered an emergency under any circumstance you cant take chances with the hardest working muscle in your body.
In the ER, we can quickly assess the damage, potentially stop the heart attack, and save your life, whether you are experiencing unstable angina or having heart attack from a blocked artery.
Waiting to seek emergency care, however, can have a range of dire consequences. Among them is a complex condition called acquired ventricular septal defect a tear in the heart that is fatal for 25% of patients within 24 hours of when it forms.
The insidious hole, also known as a ventricular septal rupture , affects approximately 1 in 1,000 patients who dont seek care within a week of experiencing heart attack symptoms. Nearly all those patients die within a year if they don’t receive care for this condition.
But there is hope for lifesaving treatment. If a patient can get to an academic medical center quickly, or at least within two weeks after a heart attack, we can potentially repair the rupture with percutaneous VSD closure an advanced, catheter-based alternative to open heart surgery. William P. Clements Jr. University Hospital is one of fewer than 10 Texas hospitals that offer this advanced procedure.
