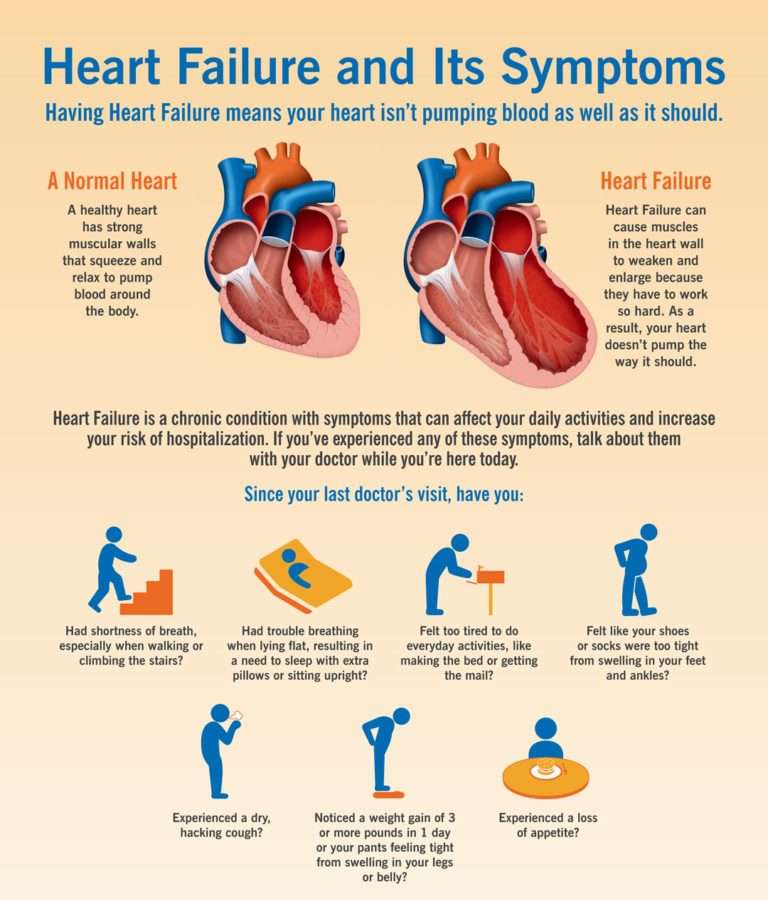
Signs Of Heart Failure And Congestive Heart Failure
Most cases of heart failure and CHF are chronic and develop over time. Symptoms to watch for are:
- Chest pain, especially while you are exerting yourself
- New or increased dyspnea or shortness of breath
- Dizziness, light-headedness, or feeling like you may faint
- Sudden weight gain
- New or increased swelling of the legs, ankles, or feet
- Sudden fatigue or weakness especially while doing normal physical activities
How Heart Failure Is Diagnosed
A diagnosis of heart failure or CHF is made by a doctor who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of heart-related conditions, called a cardiologist. Your cardiologist will take a complete medical history, conduct a physical exam, and may order a variety of tests, including blood work and imaging tests.
The following tests and scans may be performed to help diagnose heart failure:
- Natriuretic peptide tests: Measures levels of B-type natriuretic peptide or N-terminal prohormone of B-type natriuretic peptide , which are released into the blood by the heart
- Echocardiogram: Determines the percent of blood that is pumped out of the heart with each heartbeat and evaluates the structure and function of the heart
- Electrocardiogram : Provides a tracing of the hearts electrical activity
- Stress test: Measures how the heart responds to exercise or chemically induced stress in a controlled environment
- Cardiac catheterization:Shows the interior of the arteries in your heart to see if they are blocked and allows for measurement of right and left heart pressures
- Other imaging tests such as cardiac computed tomography scan, cardiac magnetic resonance imaging , or nuclear heart scan can be used to show how well the heart is working.
Center For Advanced Heart Failure/cardiomyopathy At Brigham And Womens Hospital
The Center for Advanced Heart Failure/Cardiomyopathy, an integral part of the Heart & Vascular Center at Brigham and Womens Hospital , brings together heart failure experts, including cardiologists, interventional cardiologists, cardiac surgeons, cardiovascular imaging specialists, congenital heart disease specialists, and many others, to care for patients as one team. Together, the team tailors therapies to each patients needs, offering the latest medical, interventional, and surgical approaches to congestive heart failure treatment.
You May Like: What’s The Lowest Heart Rate
Heart Failure Treatment Is A Team Effort
Heart failure management is a team effort, and you are the key player on the team. Your heart doctor will prescribe your medications and manage other medical problems. Other team members — including nurses, dietitians, pharmacists, exercise specialists, and social workers — will help you achieve success. But it is up to YOU to take your medications, make dietary changes, live a healthy lifestyle, keep your follow-up appointments, and be an active member of the team.
If you notice anything unusual, don’t wait until your next appointment to discuss it with your doctor. Call them right away if you have:
- Unexplained weight gain
- Swelling in your ankles, feet, legs, or belly that gets worse
- Shortness of breath that gets worse or happens more often, especially if you wake up feeling that way
- Bloating with a loss of appetite or nausea
- Extreme fatigue or more trouble finishing your daily activities
- A lung infection or a cough that gets worse
- Fast heart rate
- New irregular heartbeat
Types Of Heart Attacks
A heart attack, also known clinically as myocardial infarction, is a form of acute coronary syndrome . It occurs when a significant blockage in the coronary arteries restricts blood flow to the heart.
The main types of heart attacks include:
- Non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction
- ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
Don’t Miss: Can Low Vitamin D Cause Heart Palpitations
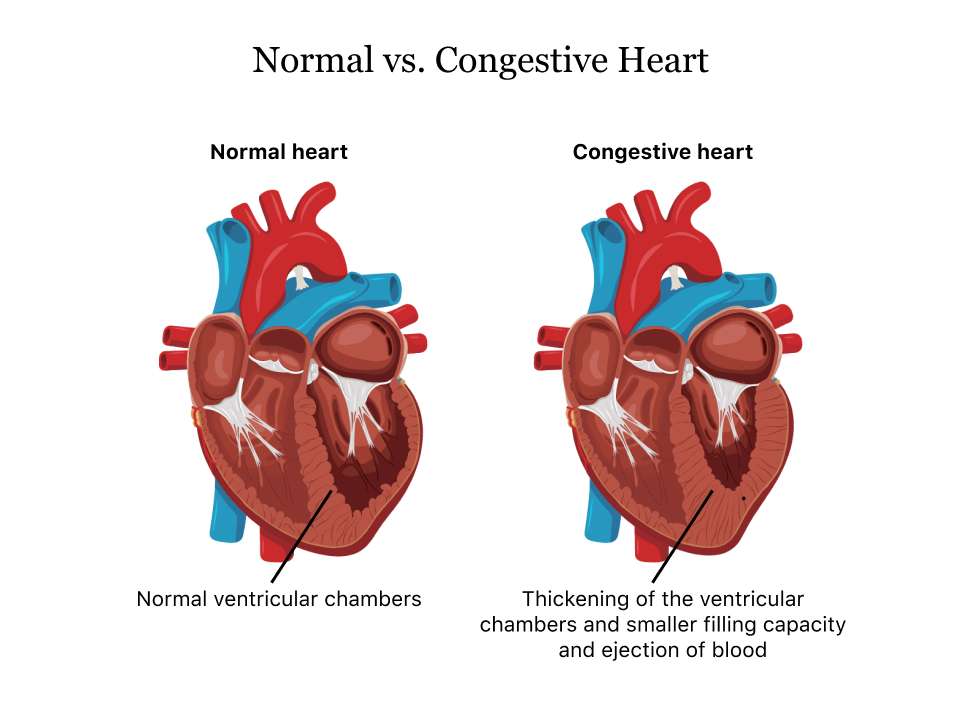
What Are The Symptoms Of Congestive Heart Failure
CHF symptoms develop due to a lack of adequate blood delivery to tissues and organs of the body due to inefficient heart pumping. Symptoms can vary among individuals and differ depending on the severity of the condition and the side of the heart affected.
It is possible to have some symptoms of both left sided and right sided CHF. Early symptoms may develop slowly, and in some cases, you may not have any noticeable symptoms until CHF has progressed and become severe.
Symptoms of CHF can include:
- swelling, which may include swelling of the:
How Does Chf Cause Congestion
This helps to keep the blood moving, but the heart muscle walls may eventually weaken and become unable to pump as efficiently. The kidneys may respond by causing the body to retain fluid and salt. If fluid builds up in the arms, legs, ankles, feet, lungs, or other organs, the body becomes congested.
What does pulmonary vascular congestion indicate?
lung congestion, distention of blood vessels in the lungs and filling of the alveoli with blood as a result of an infection, high blood pressure, or cardiac insufficiencies .
Also Check: Last Stage Congestive Heart Failure
Video Result For Recipes For Congestive Heart Failure
Dr. Using plant based diet to heal congestive heart
Congestive Heart Failure | Quick Medical
Low Sodium Diet for Congestive Heart Failure and Heart
Congestive Heart Failure for Nursing & NCLEX
Congestive Heart Failure Your Diet
How to eat with heart failure | Ohio State Medical
5 Tips for Living with Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive Heart Failure and the Healthy Heart
Natural Cures For Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive Heart Failure
Caring for a Dog with Congestive Heart Failure- Part 2
Food for people with heart failure
Heart Healthy Recipe from Food Network Host, Ellie
Plant Based Diet reverses Congestive Heart Failure in
Congestive Heart Failure CHF diagnostic Lab Values &
How to help your dog with congestive heart failure
How to simplify Congestive Heart Failure CHF
Caring for a Dog With Congestive Heart Failure- Part 1
Conjestive Heart Failure Training with Dr. Pruett
Living With Congestive Heart Failure
Dog Food for Congestive Heart Failure
Diets for Medical Conditions : Diet for Congestive
Congestive Heart Failure & Enlarged Heart in Dogs
Congestive Heart Failure: Left-sided vs Right-sided,
Potassium Rich Foods | CHF | Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive Heart Failure Tampa VA Patient Education
Congestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology,
Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive heart failure in pets
Congestive Heart Failure Life Expectancy â
Reduces the Risk of Heart Disease | Greek
forfor
Congestive Heart Failure Drugs
There are several medications that can be used to treat CHF, including ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and more.
ACE inhibitors
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors open up narrowed blood vessels to improve blood flow. Vasodilators are another option if you cant tolerate ACE inhibitors.
You may be prescribed one of the following:
voluntary recall of 5 lots of the drug Accupril due to the presence of nitrosamine. Nitrosamine, a known carcinogen with the potential to cause cancer, was found to exist in the drug at levels greater than the Acceptable Daily Intake as determined by the FDA. This recall is specific only to a handful of lot numbers and does not affect all Accupril tablets made by Pfizer. If you take Accupril tablets, talk with your pharmacist or doctor and they will help you determine if your medication has been impacted by the recall.
ACE inhibitors shouldnt be taken with the following medications without consulting a doctor, because they may cause an adverse reaction:
- Potassium-sparing diuretics and potassium supplements. These diuretics can cause potassium buildup in the blood, which may lead to abnormal heart rhythms. Examples include: riamterene , eplerenone , and spironolactone .
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs .NSAIDs such as ibuprofen, aspirin, and naproxen, can cause sodium and water retention. This may reduce the ACE inhibitors effect on your blood pressure.
Beta-blockers
This may be achieved with:
Diuretics
Your doctor may recommend:
Recommended Reading: Is It Gerd Or Heart Attack
What Are The Symptoms Of Heart Failure
You may not have any symptoms of heart failure, or the symptoms may be mild to severe. Symptoms can be constant or can come and go. The symptoms can include:
- Congested lungs. Fluid backup in the lungs can cause shortness of breath with exercise or difficulty breathing at rest or when lying flat in bed. Lung congestion can also cause a dry, hacking cough or wheezing.
- Fluid and water retention. Less blood to your kidneys causes fluid and water retention, resulting in swollen ankles, legs, abdomen , and weight gain. Symptoms may cause an increased need to urinate during the night. Bloating in your stomach may cause a loss of appetite or nausea.
- Dizziness, fatigue, and weakness. Less blood to your major organs and muscles makes you feel tired and weak. Less blood to the brain can cause dizziness or confusion.
- Rapid or irregular heartbeats. The heart beats faster to pump enough blood to the body. This can cause a rapid or irregular heartbeat.
If you have heart failure, you may have one or all of these symptoms or you may have none of them. They may or may not indicate a weakened heart.
When Should I Get Emergency Care
Go to the ER or call 911 if you have:
- New, unexplained, and severe chest pain that comes with shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, or weakness
- Fast heart rate , especially if you are short of breath
- Shortness of breath that doesn’t get better if you rest
- Sudden weakness, or you can’t move your arms or legs
- Sudden, severe headache
- Fainting spells
Also Check: Does Dopamine Increase Heart Rate
Clinical Course Of Congestive Signs And Symptoms
It is notable that moderate-to-severe signs and symptoms of congestion were present at baseline assessment, which occurred up to 48 h after admission, well after the timeframe traditionally ascribed to the very acute phase. Previous research has demonstrated that with early initiation of standard therapy dyspnoea measured in a seated and upright position improved substantially within 6 h of initial presentation. This finding suggests that initial therapy may have been delayed in the EVEREST trial due to diagnostic uncertainty, or, alternatively, dyspnoea may resolve more rapidly and improvement in other congestive signs and symptoms may lag behind temporally. In contrast, by discharge close to 85% of patients enrolled in the EVEREST trial were found to have minimal or no signs or symptoms of congestion. Traditionally, relieving dyspnoea has been the primary endpoint for short-term efficacy in pivotal clinical trials in HF. The observation that standard therapy rapidly and dramatically improved clinical congestion suggests that it may be difficult for novel therapies to beat placebo.
A more unexpected outcome is the finding that pulmonary rales were the least prevalent among patients with the highest CCS. This seemingly paradoxical finding may be at least partially explained by a bias towards right-sided HF signs in defining CCS and the fact that the prevalence of pulmonary rales may not accurately reflect the severity.
Diuretic Response And Resistance In Heart Failure
In achieving euvolaemia, the degree of volume overload and diuretic response will determine the success of therapy. The capacity of inducing natriuresis or diuresis following diuretic administration is defined as diuretic response. Diuretic resistance is defined as an impaired sensitivity to diuretics resulting in reduced natriuresis and diuresis limiting the possibility to achieve euvolaemia. Diuretic response should always be interpreted in light of the dose and type of the diuretic agent administered and the degree of volume overload, body composition and kidney function. As loop diuretics form the mainstay of diuretic therapy in heart failure, the terms diuretic resistance and loop diuretic resistance are often used interchangeably., – To assess the response to an initiated diuretic regimen, physicians need an indicator of the diuretic response. Currently, net fluid output and changes in body weight are frequently used. While assessment of weight might appear to be a simple measurement, it is technically challenging and fluctuations in weight might not represent changes in volume redistribution. Furthermore, there is a poor correlation between weight loss and fluid output.
Read Also: What Is The Pathway Of Blood Through The Heart
What Is The Outlook With Heart Failure
With the right care, congestive heart failure wont stop you from doing the things you enjoy. Your prognosis, or outlook for the future, will depend on:
- How well your heart muscle is working.
- Your symptoms.
- How well you respond to your treatment plan.
- How well you follow your treatment plan.
One study says that people with heart failure have a life span 10 years shorter than those who dont have heart failure. Another study showed that the survival rates of people with chronic heart failure were 80% to 90% for one year, but that dropped to 50% to 60% for year five and down to 30% for 10 years.
A different study found that people who had heart failure and were discharged from the hospital had expected life spans ranging from three to 20 years, depending on various factors like age and gender. Its important to look at your specific situation when considering your prognosis.
How Do You Get Diagnosed With Congestive Heart Failure
If youre experiencing any symptoms of heart failure, you should schedule an appointment with a cardiologist or a primary care doctor . Your doctor should ask about your medical history to identify potential heart failure risk factors, such as diabetes or high blood pressure. You can expect to have a physical exam where your doctor listens to your heart and breathing and examines your neck vein, which can help your doctor identify congestion, according to Stanford Medicine.
Additionally, your doctor may recommend imaging, such as X-rays, to look for warning signs like areas of fluid buildup. If you have signs of congestion, like a swollen leg, shortness of breath, or bloated abdomen, you may be tested for a hormone called B-type natriuretic peptide, or BNP, according to the Cleveland Clinic.
Your BNP levels increase as your heart becomes stretched by fluid overload, Dr. Haythe says. BNP levels tend to rise as heart failure becomes worse and are lower when the condition is more stable. So, high BNP levels could be a sign of fluid retention resulting from heart failure.
You May Like: Aha Heart Failure Classification
Mental And Behavioral Home Health Services
A congestive heart failure diagnosis comes with a high emotional cost. Its life-changing, and its never easy. Living with congestive heart failure takes a toll on your physical health and your mental health. Centric Healthcare offers compassionate professional services to help as you learn to cope with your new normal. Its important to remember as you live with your disease that you dont need to do it alone. We can help.
To schedule a free consultation and learn more about these and other services offered by Centric Healthcare, call us at 224-5535 in the Twin Cities, or call us at 205-7322 in Rochester.
Heart Failure Signs And Symptoms
By themselves, any one sign of heart failure may not be cause for alarm. But if you have more than one of these symptoms, even if you haven’t been diagnosed with any heart problems, report them to a healthcare professional and ask for an evaluation of your heart. Congestive heart failure is a type of heart failure which requires seeking timely medical attention, although sometimes the two terms are used interchangeably.
This table lists the most common signs and symptoms, explains why they occur and describes how to recognize them.
Recommended Reading: What Is My Target Heart Rate Zone
Congestive Heart Failure Treatments
Currently, there is no cure for congestive heart failure. Treatments are designed to reduce symptoms and slow the progression of the disease. However, early diagnosis and treatment can help you lead a long and active life. The good news is that more congestive heart failure treatment options exist today than ever before. The specific treatment plan prescribed for you will depend largely upon the type of heart failure you have and on its underlying causes. All treatment options will have the same four basic goals:
1. Treat the underlying diseases and conditions causing your heart failure.
2. Reduce the symptoms of heart failure.
3. Stop your heart failure from getting worse.
4. Maximize the quality and length of your life after diagnosis.
Treatment options for congestive heart failure will fall under one of four categories:
What Causes Chf And Pulmonary Edema In Heart Failure
A variety of cardiac diseases cause CHF and pulmonary edema and initial evaluation questions should reflect these processes.The most common cause of heart failure is coronary artery disease, which is secondary to loss of left ventricular muscle, on-going ischemia, or decreased diastolic ventricular compliance.
You May Like: What Bnp Level Is Heart Failure
Distinguishing Between Responders And Non
A number of clinically interesting findings emerged when patients were subdivided into responders and non-responders, or perhaps more accurately partial responders , at discharge. First, in interpreting these data it should be reiterated that the majority of patients enrolled in the EVEREST trial responded rapidly and dramatically in response to standard therapy alone and only 15% of patients were discharged with a CCS 3. However, it is notable that although responders and non-responders had clinically, although not numerically, comparable signs and symptoms of congestion at baseline there were substantial between-group differences in neurohormonal markers of haemodynamic congestion and more subtle discrepancies in renal function parameters .
In contrast, at discharge, by definition, responders exhibited minimal or no signs and symptoms of HF while non-responders manifested signs and symptoms similar in severity to responders at baseline. Baseline renal impairment and worsening renal function during hospitalization are markers of more severe HF requiring high-dose diuretic therapy to maintain fluid homoeostasis, perhaps at least partially explaining the disparity in congestion relief observed in the present analysis., However, it is difficult to hypothesize whether diuresis was impeded or intentionally limited in non-responders by renal dysfunction.
Heart Failure Vs Congestive Heart Failure: What’s The Difference
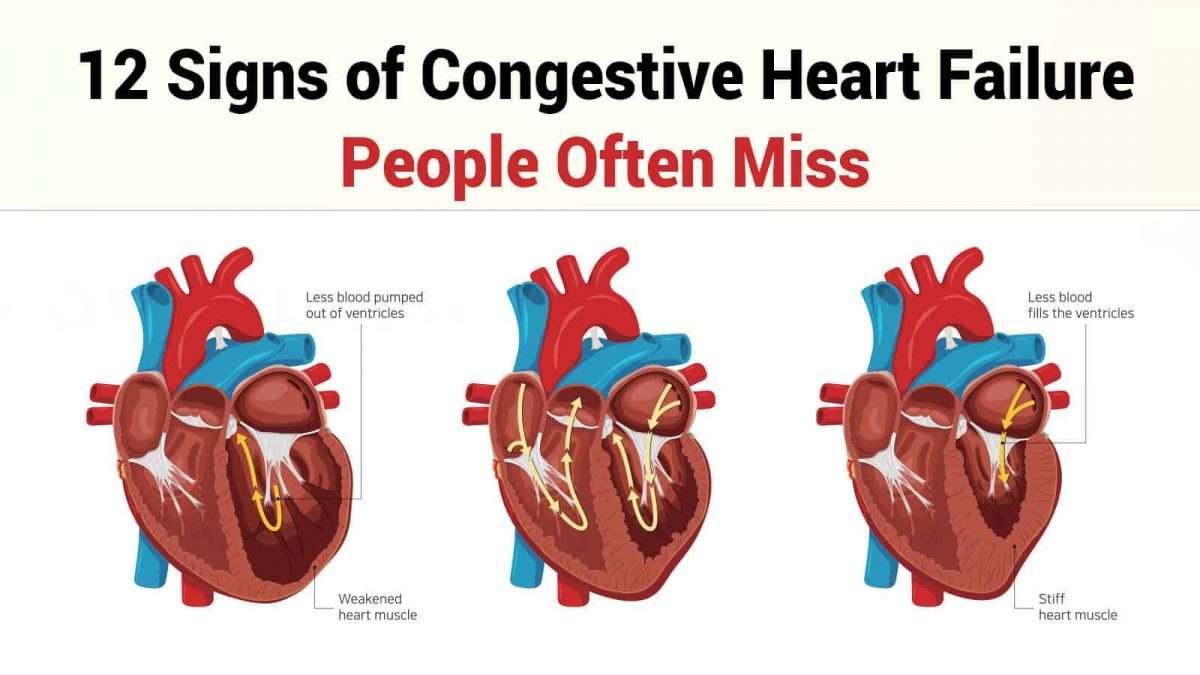
Heart failure affects people of all ages, from children and young adults to the middle-aged and older adults. About 6.2 million adults in the United States are currently living with heart failure, and over 64 million people are dealing with some form of heart failure worldwide.
Approximately 550,000 new cases are diagnosed in the United States each year, but many more remain undiagnosed as the initial symptoms of heart failure can be subtle and mimic similar symptoms seen in other conditions.
Congestive heart failure refers to the inadequate functioning of the heart muscle such that fluid builds up in the lungs, abdomen, feet, and arms . The condition can either be acute or chronic .
Untreated heart disease can be aggressive and fatal. The five-year survival rate is about 50% for all stages. In 2018, heart failure led to nearly 400,000 deaths, according to death certificate data, with the highest prevalence of disease primarily in the South and Midwest.
You May Like: What Does Increased Heart Rate Mean
