Pain In Other Areas Of The Body
Heart attack pain can occur in places other than the chest, like the back, shoulders, arms, neck or jaw. According to Cleveland Clinic, when there’s a problem in the heart, such as a blocked artery, it can trigger the nerves in your heart to give a signal that something is wrong, and you’ll feel pain. Considering the vagus nerve is connected to not only the heart, but also the brain, chest, abdomen, and neck, you may feel those pain signals in other areas of the body aside from the heart region.
What Are The Early Signs Of A Heart Attack
There are heart attack symptoms in women that are different from heart attack symptoms in men. But the common signs and symptoms they usually share are as follows:
- Chest pain or discomfort: The discomfort usually lasts for more than a few minutes or it may go away and come back. The discomfort may feel like pressure, squeezing, fullness or pain at the center of the chest.
- Discomfort in other areas of the upper body: This may include pain or discomfort in the back, jaw, stomach or in one or both arms.
- Shortness of breath: This may occur with, before or without chest pain or discomfort.
- Breaking out in a cold sweat
- Nausea or light-headedness
Meanwhile, heart attack symptoms in women sometimes go unnoticed. These include the following:
- Pressure, fullness, squeezing pain in the center of the chest, spreading to the neck, shoulder or jaw
- Unusual fatigue
- Treating or managing conditions that can be a risk factors of heart attack such as diabetes
What You Can Do Now To Prevent An Early Heart Attack
Although some risk factors are beyond your control, there are many thingsyou can do to protect your heart health. It’s estimated that 80% of heartdisease, including heart attacks and strokes, can be prevented throughlifestyle changes, such as:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese increases your heart disease risk. Get tips on how to watch your weight.
- Eating a heart-healthy diet: Avoid processed foods and excess sugar. Eat a diet rich in whole, nutritious foods .
- Exercising regularly: A consistent workout routine can boost your heart health. Aim for at least 150 minutes per week. Learn the kinds of exercise that can boost heart health.
You May Like: What Are The Stages Of Heart Failure
Here Are The Most Common Types Of Medications:
Medicines to prevent blood clots
- After your heart attack, the stent or bypass procedure that you received increases your chances of having a blood clotwhich could lead to a stroke.
- Blood clots are clumps of blood cells, known as platelets.
- Anti-platelets help keep your blood cells from sticking together.
- Examples of anti-platelets include Plavix® , Effient® , Brilinta® , and Aspirin.
Medicines to lower blood pressure
- After a heart attack, its important to protect your blood vessels.
- High blood pressure can damage the walls of your blood vessels and lead to serious health problems. Anti-hypertensive medications work to keep your blood vessels relaxed and open.
- There are many medications that can lower blood pressure in different ways: diuretics, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and more!
Medicines to lower bad cholesterol
- Bad cholesterol that has built up overtime likely played a role in your heart attack by clogging at least one of the arteries in your heart.
- Statins help to lower your levels of bad cholesterol and reduce the risk of another heart attack. They work by slowing the production of cholesterol in your liver.
- Examples of statins are Lipitor® , Pravachol® , Crestor® , and Zocor® .
- There are some prescription medications that can be used in addition to statins to lower bad cholesterol and also reduce your risk of another heart attack.
Learn more about one of these medications by clicking below.
Learn more
Do Hormones Affect Your Risk Of A Heart Attack

Many women use prescription hormone drugs for birth control or for reducingsymptoms of menopause . Could thesedrugs jeopardize your heart health?
“Birth control pills can increase your risk of having a blood clot, eitherin the heart or in the legs, and they can also raise your blood pressure.So, if you have a history of high blood pressure or clotting problems,other types of contraception might be a better fit for you,” says Colliver.”But for most young women, it’s safe to take birth control medication.”
Colliver notes that women over the age of 50 are at an increased risk forheart disease and should completely avoid estrogen and progesterone drugs,if possible. “If your overall risk of heart attack is extremely low and youdesperately need relief from hot flashes and other postmenopausal symptoms,then hormone replacement therapy may be fine for you,” says Colliver. “Butafter the age of 65, we really try to avoid using them at all because theydo increase the risk of heart disease and potentially breast cancer.”
You May Like: Can Allergy Cause Heart Attack
What Are The Risk Factors For Heart Attack
Several health conditions, your lifestyle, and your age and family history can increase your risk for heart disease and heart attack. These are called risk factors. About half of all Americans have at least one of the three key risk factors for heart disease: high blood pressure, high blood cholesterol, and smoking.2
Some risk factors cannot be controlled, such as your age or family history. But you can take steps to lower your risk by changing the factors you can control.
Learn more about risk factors for heart disease and heart attack.
What Can I Expect If I Have A Silent Heart Attack
Everyones experience is a bit different based on how much their heart attack hurt their heart, but most people can get back to doing regular things little by little and have active lives.
Some people can get abnormal heart rhythms or heart failure, which can be serious. People who wait too long to get help for a heart attack run the risk of severe damage to their hearts and may not survive if they dont get help soon enough.
Read Also: How Do You Get Congestive Heart Failure
Heart Attacks In Older Adults
Elderly people have a higher risk of suffering from a silent heart attack. As mentioned, damaged vessels can be supported through the development of collateral circulation, which can help maintain blood flow to the heart. For this reasons, heart attack symptoms may start off as mild and persist for many days. The most commonly-seen symptoms in older adults are sweats, breathlessness, paleness, changes in heart rate, and chest discomfort.
Every case is different, however, and symptoms in older adults can vary. Chest pain can range from mild to intense, or the crushing sensation may be light or heavy. Pain may occur in the upper abdomen, which may be confused with gastritis or heartburn.
Older adults have a greater risk of developing heart disease overtime due to changes in circulation, changes in the natural pacemaker, or due to changes in the heart’s overall functioning. The risk for heart disease can, however, decrease with a healthy lifestyle that includes physical activity and a diet rich in vegetables and low in carbohydrates and fat,
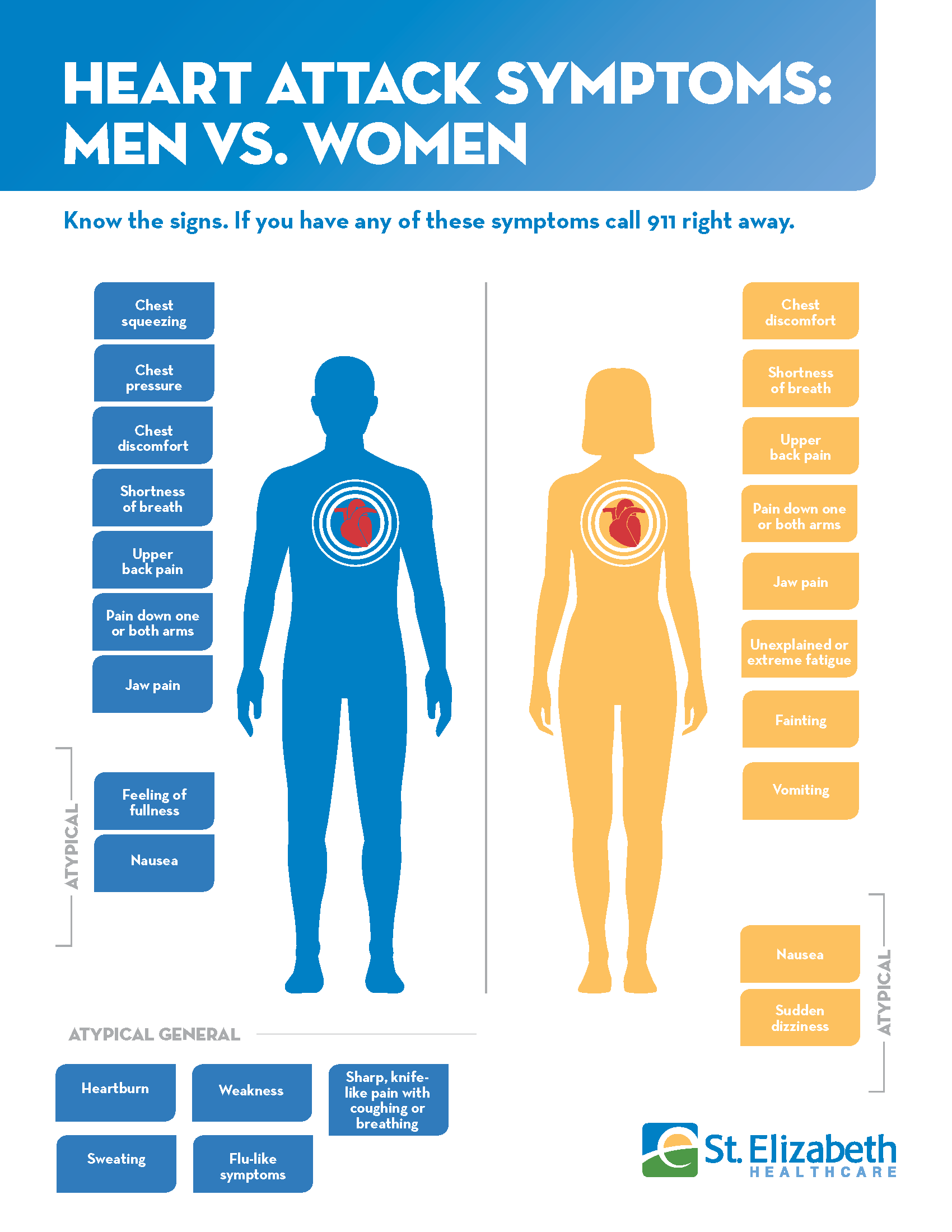
Heart Attack Signs And Symptoms
Early Heart Attack Care *
Remember: When in doubt, call 9-1-1! In this time of COVID-19, many hospitals are experiencing a decrease in the number of patients with symptoms of heart attack or stroke in emergency departments. Experts worry that patients who need critical care are delaying their treatment because of concerns about the pandemic. We encourage patients in our community to pay close attention to heart attack or stroke symptoms, particularly if they have a pre-existing heart condition, and call 911 immediately if they believe they’re having a heart attack or stroke.
DID YOU KNOW HEART ATTACKS HAVE BEGINNINGS?
Like other diseases, heart attacks have early sign and symptoms. These beginnings occur in over 50 percent of patients. However, if recognized in time, these beginnings can be treated before the heart is damaged. 85 percent of heart damage occurs within the first two hours of a heart attack. EHAC is knowing the subtle danger signs of a heart attack and acting upon them immediatelyBEFORE HEART DAMAGE OCCURS.
LEARN THE EARLY SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
- Chest pressure, squeezing, aching or burning
- Shortness of breath
- Pain that travels down one or both arms
- Feeling of fullness
WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE ?
WHAT ARE ATYPICAL PRESENTATIONS?
In an atypical presentation, the signs and symptoms are different. How? The patient may not complain about pain or pressure in the chest.
Be alert for the following:
WHAT ARE THE RISK FACTORS?
HOW CAN YOU PREVENT A HEART ATTACK?
Don’t Miss: Can Congestive Heart Failure Be Reversed
How Is A Heart Attack Diagnosed
Doctors typically diagnose a heart attack after they perform a physical exam and review your medical history. Your doctor will likely conduct an electrocardiogram to check your hearts electrical activity.
An echocardiogram, which uses sound waves to create an image of the hearts chambers and valves, can reveal how blood is flowing through the heart and what parts of the heart, if any, have been damaged.
Your doctor may also order a cardiac catheterization. This is a probe inserted into the blood vessels through a flexible tube called a catheter. It allows your doctor to view areas in and around your heart where plaque may have built up. They can also inject dye into your arteries, order an X-ray to see how the blood flows, and view any blockages.
Your healthcare team will likely also take a sample of your blood or perform other tests to see if theres evidence of heart muscle damage.
A commonly used blood test checks for levels of troponin T, a protein found in the heart muscle. Elevated levels of troponin T in the bloodstream is associated with a heart attack.
If youve had a heart attack, your doctor may recommend a procedure . These procedures can relieve pain and help prevent another heart attack from occurring.
Common procedures include:
Your doctor may also prescribe medications to treat your heart attack, including:
- blood pressure medication
- beta-blockers
Take The Ehac Oath With Us
We encourage you to start taking care of your heart health today. We can kick this commitment off by taking the EHAC oath together.
I understand that heart attacks have beginnings and on occasion, signs of an impending heart attack may include chest discomfort, shortness of breath, shoulder and/or arm pain and weakness. These may occur hours or weeks before the actual heart attack. I solemnly swear that if happens to me or anyone I know I will call 9-1-1 or activate Emergency Medical Services.
You May Like: How To Reverse Heart Disease
What Is A Heart Attack
Heart attack signs and symptoms in men and women: Chest pain or discomfort Shortness of breath Pain or discomfort in the jaw, neck, back, arm, or shoulder Feeling nauseous, light-headed, or unusually tired.
A heart attack, also called a myocardial infarction, happens when a part of the heart muscle doesnt get enough blood.
The more time that passes without treatment to restore blood flow, the greater the damage to the heart muscle.
Coronary artery disease is the main cause of heart attack. A less common cause is a severe spasm, or sudden contraction, of a coronary artery that can stop blood flow to the heart muscle.
Shoulder Pain From Heart Attack
Although heart attack is most commonly associated with chest pain, it can also cause pain or discomfort in other parts of the body, including the shoulder.
Both women and men may experience shoulder pain during a heart attack. Some research suggests shoulder pain during a heart attack may be more common in women than men.
A 2018 study looked at 532 people who had an ST-elevation myocardial infarction , a type of heart attack that affects the whole heart muscle wall. Shoulder pain was twice as common in women than men. Throat and back pain were also more common in women.
Heart attack in men usually causes chest pain or discomfort, which may feel like pain, heaviness, pressure, fullness, squeezing, or heartburn. It typically lasts for more than a few minutes or goes away but returns again.
Also Check: How To Lower Your Resting Heart Rate
Genetics Or Underlying Health Conditions
Genetics, while not an ultimate determinant for the likelihood to get a heart attack, to a certain degree can determine whether individuals are predisposed to heart disease. Additionally, having prior medical conditions, like suffering a stroke, obesity, or diabetes can increase ones risk of getting a heart attack.
By taking a DNA test such as the one from CircleDNA, you can find out your genetic risk factors.
About Half Of All Heart Attacks Are Mistaken For Less Serious Problems And Can Increase Your Risk Of Dying From Coronary Artery Disease
Image: goir/Getty Images
You can have a heart attack and not even know it. A silent heart attack, known as a silent myocardial infarction , account for 45% of heart attacks and strike men more than women.
They are described as “silent” because when they occur, their symptoms lack the intensity of a classic heart attack, such as extreme chest pain and pressure stabbing pain in the arm, neck, or jaw sudden shortness of breath sweating, and dizziness.
“SMI symptoms can feel so mild, and be so brief, they often get confused for regular discomfort or another less serious problem, and thus men ignore them,” says Dr. Jorge Plutzky, director of the vascular disease prevention program at Harvard-affiliated Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
For instance, men may feel fatigue or physical discomfort and chalk it up to overwork, poor sleep, or some general age-related ache or pain. Other typical symptoms like mild pain in the throat or chest can be confused with gastric reflux, indigestion, and heartburn.
Also, the location of pain is sometimes misunderstood. With SMI, you may feel discomfort in the center of the chest and not a sharp pain on the left side of the chest, which many people associate with a heart attack. “People can even feel completely normal during an SMI and afterward, too, which further adds to the chance of missing the warning signs,” says Dr. Plutzky.
Also Check: How Does Atropine Increase Heart Rate
Catch The Signs Early
Dont wait to get help if you experience any of these heart attack warning signs. Some heart attacks are sudden and intense. But most start slowly, with mild pain or discomfort. Pay attention to your body and call 911 if you experience:
- Chest discomfort. Most heart attacks involve discomfort in the center of the chest that lasts more than a few minutes or it may go away and then return. It can feel like uncomfortable pressure, squeezing, fullness or pain.
- Discomfort in other areas of the upper body. Symptoms can include pain or discomfort in one or both arms, the back, neck, jaw or stomach.
- Shortness of breath. This can occur with or without chest discomfort.
- Other signs. Other possible signs include breaking out in a cold sweat, nausea or lightheadedness.
Download the common heart attack warning signs infographic |
What Do These Early Symptoms Typically Look Like
Dr. Xu says the majority of patients experience somewhat typical symptoms, such as radiating chest pain, heaviness or discomfort, heart palpitations, cold sweats, and shortness of breath. Others — women more so than men — will experience some atypical symptoms as well, which may include fatigue, a general sense of unease, vague discomfort, back or abdominal pain and declining stamina. Both types of symptoms can be experienced months before an actual heart attack occurs.
You May Like: Congestive Heart Failure Swelling Abdomen
Signs And Symptoms Of A Heart Attack
Symptoms are not the same for all heart attack patients. Below are just some of the symptoms of a heart attack:
- Sudden upset stomach, indigestion with a heartburn-like choking feeling, nausea, and vomiting
- Dizziness and lightheadedness
- Unusual bouts of anxiety, fatigue, severe weakness, or shortness of breath
- Discomfort in the jaw, back, arm, shoulders, or throat
- Uneven or too fast a heartbeat with excessive sweating
- Discomfort or pain in the jaw, neck, back, arm, or shoulders
- Pain, squeezing, pressure, or a sense of fullness in the chest
Note that you may not experience all these symptoms. Suffering from at least a few signs or feeling like there are noticeable changes in the way your body feels is sufficient reason to contact a medical professional.
Heart Failure Signs And Symptoms
By themselves, any one sign of heart failure may not be cause for alarm. But if you have more than one of these symptoms, even if you haven’t been diagnosed with any heart problems, report them to a healthcare professional and ask for an evaluation of your heart. Congestive heart failure is a type of heart failure which requires seeking timely medical attention, although sometimes the two terms are used interchangeably.
This table lists the most common signs and symptoms, explains why they occur and describes how to recognize them.
You May Like: What Side Of The Heart Has Oxygenated Blood
What Are Heart Failure Symptoms
If you have heart failure, you may not have any symptoms, or the symptoms may range from mild to severe. Symptoms can be constant or can come and go. Heart failure symptoms are related to the changes that occur to your heart and body, and the severity depends on how weak your heart is. The symptoms can include:
- Congested lungs. A weak heart causes fluid to back up in the lungs. This can cause shortness of breath with exercise or difficulty breathing at rest or when lying flat in bed. Lung congestion can also cause a dry, hacking cough or wheezing.
- Fluid and water retention. A weak heart pumps less blood to your kidneys and causes fluid and water retention, resulting in swollen ankles, legs, and abdomen and weight gain. This can also cause an increased need to urinate during the night as your body attempts to get rid of this excess fluid. Bloating in your stomach may cause a loss of appetite or nausea.
- Dizziness, fatigue, andweakness. Less blood to your major organs and muscles makes you feel tired and weak. Less blood to the brain can cause dizziness or confusion.
- Rapid or irregular heartbeats. The heart beats faster to pump enough blood to the body. This can cause a fast or irregular heartbeat. Irregular heartbeats also can become more common as the heart weakens.
