Whats The Outlook For People With Right
For many people, the right combination of therapies and lifestyle changes can slow or stop the disease and improve symptoms. They can lead full, active lives.
About 1 in 10 American adults who live with heart failure have advanced heart failure. That means treatments arent working, and symptoms are getting worse. You may feel symptoms, such as shortness of breath, even when youre sitting. If you have advanced heart failure, talk with your care team about important care decisions and next steps.
Right Ventricular Myocardial Infarction
People who have a myocardial infarction caused by a blockage in the right coronary artery may suffer from damage to the right ventricular muscle, producing right-sided heart failure. Treating a right ventricular heart attack is similar to treating any myocardial infarction, including rapidly opening up the blocked blood vessel with clot-busting drugs or a stent.
However, because right-sided heart failure can limit the amount of blood that reaches the left side of the heart, drugs aimed mainly at treating left-sided ventricular weakness need to be used with great caution in people having right ventricular heart attacks.
Can Heart Failure Be Prevented
You may be able to prevent or delay heart failure if you:
- Work with your provider to manage any health conditions that increase your risk of developing heart failure
- Make healthy changes in your eating, exercise, and other daily habits to help prevent heart disease
NIH: National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute
Recommended Reading: How To Calculate Target Heart Rate Zone
Systolic And Diastolic Failure
Systolic and diastolic heart failure each result in a decrease in stroke volume. This leads to activation of peripheral and central baroreflexes and chemoreflexes that are capable of eliciting marked increases in sympathetic nerve traffic.
Although there are commonalities in the neurohormonal responses to decreased stroke volume, the neurohormone-mediated events that follow have been most clearly elucidated for individuals with systolic heart failure. The ensuing elevation in plasma norepinephrine directly correlates with the degree of cardiac dysfunction and has significant prognostic implications. Norepinephrine, while directly toxic to cardiac myocytes, is also responsible for a variety of signal-transduction abnormalities, such as downregulation of beta1-adrenergic receptors, uncoupling of beta2-adrenergic receptors, and increased activity of inhibitory G-protein. Changes in beta1-adrenergic receptors result in overexpression and promote myocardial hypertrophy.
Dont Miss: Increased Heart Rate When Standing Up
Treatment Of Heart Failure Congestive In Dogs
Dogs with moderate to severe problems may need to be hospitalized until the condition is stabilized. Taps will be inserted to remove fluid from the abdomen and around the heart . Strong diuretics, such as furosemide, may be injected to further encourage fluid elimination, and dogs may need additional oxygen.
Once the immediate attack is stabilized, long-term medications will be prescribed to help to control symptoms. Diuretics and ace inhibitors are the most common medications used to reduce fluid build-up and improve blood flow. Pimobendan can increase the force of the hearts contractions, and digoxin may be prescribed if your dogs heart rate is very fast. Beta-blockers and calcium blockers could also be suggested depending on your dogs condition. Most treatment plans will combine a number of different medications.
Other treatment will focus on eliminating the problem that is causing CHF. If your dog has heartworm, it can be treated with medication once your dogs symptoms are stabilized. Some conditions, like atrial septal defect, can be treated with surgery. Others cannot. Valve replacement is only done very rarely in dogs, so problems that affect the valves are often only untreatable symptomatically.
Worried about the cost of Heart Failure Congestive Right Sided treatment?
Pet Insurance covers the cost of many common pet health conditions. Prepare for the unexpected by getting a quote from top pet insurance providers.
Don’t Miss: Can This 10 Second Trick Prevent Your Heart Attack
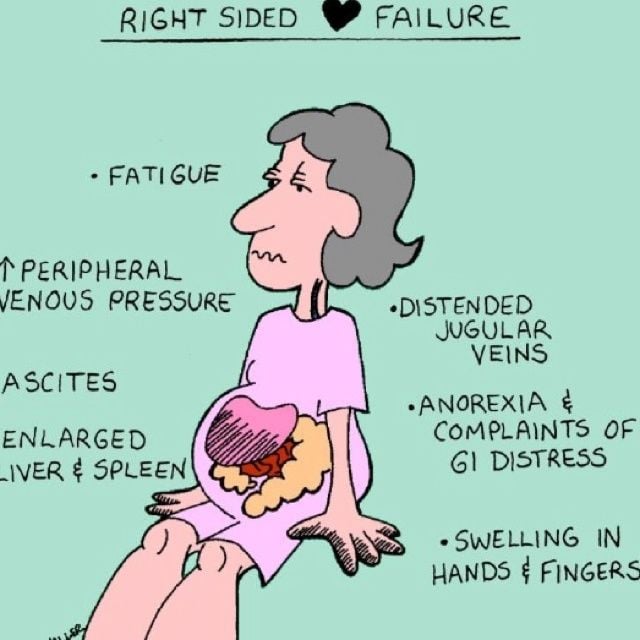
What Are The Symptoms Of Right
The main sign of right-sided heart failure is fluid buildup. This buildup leads to swelling in your:
- Feet, ankles and legs.
- Gastrointestinal tract and liver .
Other signs include:
Where you accumulate fluid depends on how much extra fluid and your position. If youre standing, fluid typically builds up in your legs and feet. If youre lying down, it may build up in your lower back. And if you have a lot of excess fluid, it may even build up in your belly.
Fluid build up in your liver or stomach may cause:
Once right-sided heart failure becomes advanced, you can also lose weight and muscle mass. Healthcare providers call these effects cardiac cachexia.
Clinical Characteristics And Evaluation
Clinical characteristics of right-sided HF are caused by increased pressure in the right atrium and reduced left ventricular filling as a result of the effect of ventricular interdependence. Elevated central venous pressure impedes lung lymphatic drainage, so in patients with pulmonary hypertension resulting from left-sided heart diseases, lung fluid clearance decreases and excessive pulmonary edema can lead to pleural effusion.
Don’t Miss: What Does Heart Failure Mean
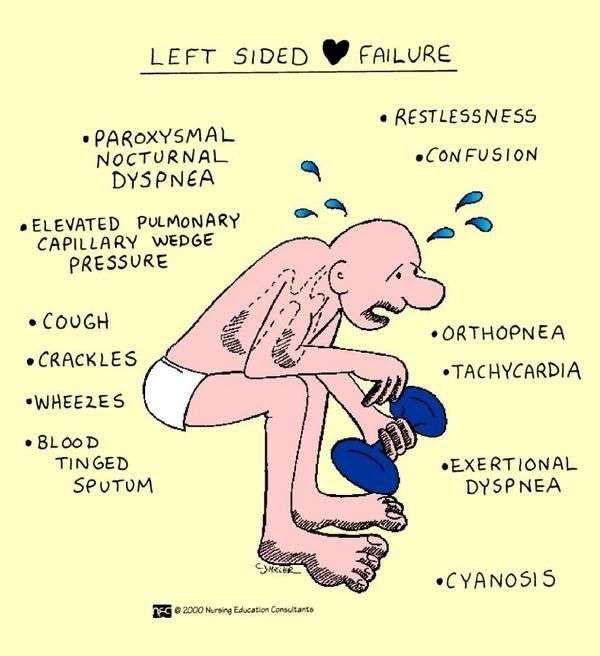
Left Sided Heart Failure
primary cause of right sided heart failure.
When the left ventricle is not working as effectively, fluid pressure increases and ends up moving back through the lungs. This can cause an overload to the heartâs right side.
Consequently, when the right side is unable to pump blood, fluid accumulates in the veins, resulting in swelling.
Treatments For Heart Failure
Treatment for heart failure usually aims to control the symptoms for as long as possible and slow down the progression of the condition.
How youâre treated will depend on what is causing your heart failure.
Common treatments include:
- lifestyle changes including eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly and stopping smoking
- medicine a range of medicines can help many people need to take 2 or 3 different types
- devices implanted in your chest these can help control your heart rhythm
- surgery such as a or a heart transplant
Treatment will usually be needed for life.
A cure may be possible when heart failure has a treatable cause. For example, if your heart valves are damaged, replacing or repairing them may cure the condition.
You May Like: Congestive Heart Failure Stage 4
Symptoms Of Heart Failure
The main symptoms of heart failure are:
- breathlessness after activity or at rest
- feeling tired most of the time and finding exercise exhausting
- feeling lightheaded or fainting
- swollen ankles and legs
Some people also experience other symptoms, such as a persistent cough, a fast heart rate and dizziness.
Symptoms can develop quickly or gradually over weeks or months .
How Does Right Sided Heart Failure Affect The Liver
They conclude that right-sided heart failure resulting in hepatic venous congestion, may predispose the liver to hepatic injury induced by a hypotensive event. The most presumed causes of car diac induced ALF are hepatic congestion from venous hypertension and decreased oxygen delivery from a decreased CI .
Read Also: How To Slow Down Heart Rate
Energetic Aspects In Heart Failure
The contractile machinery is dependent on a substrate utilization , oxidative phosphorylation , and high-energy phosphate metabolism . Each of these components or a combination of these may be affected in heart failure and lead to energy starvation and in consequence affect contractile function . Mitochondrial high-energy phosphate production is the predominant energy source for cardiomyocytes. Alterations in the mitochondrial energy support lead to myocyte dysfunction , promote apoptosis and thus may favor heart failure further . Thus, reduced energy levels inhibit Ca2+ influx via the sarcolemmal L-Type calcium channel and reduce sarcoplasmatic Ca2+-re-uptake via reduced phosphorylation of phospholamban. These mechanisms reduce contractility and slower relaxation and may also be the target for treatment options . In patients with heart failure treatments targeting substrate utilization and/or oxidative stress in mitochondria will be tested in addition to the well defined neuroendocrine inhibition .
Heart Failure During Covid
Your heart failure nurse might have been redeployed, making it hard to have in-person appointments or check-ups. âThe key thing is to look after yourself well, and always phone your GP or heart failure team if your symptoms change or worsen,â says BHF nurse Lucy Martin. âIn fact, call your GP or heart failure team if you have any concerns about your medication or care â they are there to help you.â
Your GP is qualified to answer any questions you might have. Dont worry about wasting their time this is exactly what theyre there for.
- Find out more about coronavirus and how it affects people with heart conditions at our coronavirus support hub.
You May Like: Why Is It Important To Know Your Target Heart Rate
Don’t Miss: Alternative To Open Heart Surgery
What Are The Symptoms Of Heart Failure
The main symptoms of heart failure are:
- Shortness of breath when youre active or resting, because youre not getting enough oxygen.
- Swollen feet, ankles, stomach and around the lower back area, caused by fluid build up.
- Feeling unusually tired or weak because theres not enough blood and oxygen getting to your muscles.
You should see your GP immediately if you begin to experience any of these symptoms.
Recommended Reading: How To Increase Heart Rate Immediately
What Is The Difference Between Left And Right
Heart failure can occur in the left side of the heart, the right side of the heart or on both sides. The major difference between left-sided heart failure and right-sided heart failure is in the side of the heart that is weakened. In left-sided heart failure, the left side of the heart is weakened and results in reduced ability for the heart to pump blood into the body. In right-sided heart failure, the right side of the heart is weakened and results in fluid in your veins, causing swelling in the legs, ankles, and liver.
To understand these conditions, it is important to know a little about how blood flows through the heart.
The heart is made up of four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria and the lower chambers are called ventricles. Each side of the heart has paired upper and lower chambers. Blood returns from the body and enters the right atrium. From there it moves to the right ventricle, which pumps it to the lungs where it is oxygenated. Blood moves from the lungs into the left atrium, down to the left ventricle and then out to the body to supply organs and tissues with oxygen and nutrients.
You May Like: How Accurate Is Ecg For Heart Attack
You May Like: Can Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
Frequent Urination At Night
One of the other symptoms of this condition is frequent urination at night, which is also known as nocturia. This is usually seen as an effect of the edema, wherein the fluid that gets accumulated on the ankle and legs returns into systemic circulation when the person is sleeping or is in supine position. This leads to excessive urine being produced, and hence excess urination.
Also Check: What Is My Resting Heart Rate
Heart Failuresigns And Symptoms
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart fails to function properly. The terms “heart failure” and “congestive heart failure ” don’t mean that the heart has actually “failed” or stopped but mean one or more chambers of the heart “fail” to keep up with the volume of blood flowing through them.
Heart failure is brought on by a variety of underlying diseases and health problems.
Your condition may involve the left side, the right side or both sides of the heart. Each side has two chambers:
- An atrium or upper chamber
- A ventricle or lower chamber
Any one of these four chambers may not be able to keep up with the volume of blood flowing through it.
Two types of heart dysfunction can lead to heart failure, including:
- Systolic Heart Failure This is the most common cause of heart failure and occurs when the heart is weak and enlarged. The muscle of the left ventricle loses some of its ability to contract or shorten. In turn, it may not have the muscle power to pump the amount of oxygenated and nutrient-filled blood the body needs.
- Diastolic Failure The muscle becomes stiff and loses some of its ability to relax. As a result, the affected chamber has trouble filling with blood during the rest period that occurs between each heartbeat. Often the walls of the heart thicken, and the size of the left chamber may be normal or reduced.
You May Like: Can High Cholesterol Cause Heart Palpitations
What Are The Treatments For Heart Failure
Your treatment will depend on the type of heart failure you have and how serious it is. There’s no cure for heart failure. But treatment can help you live longer with fewer symptoms.
Even with treatment, heart failure usually gets worse over time, so you’ll likely need treatment for the rest of your life.
Most treatment plans include:
You may need heart surgery if:
- You have a congenital heart defect or damage to your heart that can be fixed.
- The left side of your heart is getting weaker and putting a device in your chest could help. Devices include:
- A biventricular pacemaker .
- A mechanical heart pump or a total artificial heart).
As part of your treatment, you’ll need to pay close attention to your symptoms, because heart failure can worsen suddenly. Your provider may suggest a cardiac rehabilitation program to help you learn how to manage your condition.
Comorbidities: Anemia Iron Deficiency Kidney Failure Diabetes Frailty
Moderate anemia is often prevalent in patients with heart failure regardless of HFrEF or HFpEF . The incidence is higher in women, elderly and diabetic patients as well as in patients with renal failure. Increased blood loss in patients treated with oral anticoagulants , aspirin or both as well as decreased absorption of vitamin and/or iron may favor anemia. Similar as in other chronic illnesses iron deficiency is common in heart failure and may influence prognosis worse. Whether anemia and/or iron deficiency are markers of heart failure severity or whether they affect outcome of heart failure disease and thus should be treated is not entirely clear. In patients with heart failure with as well as without anemia intravenous ferric carboxymaltose has improved quality of life and NYHA class but not prognosis .
Heart failure and chronic kidney disease frequently coexist and share many risk factors also. CKD worsen prognosis in heart failure patients however, patients with severe CKD often have been excluded from randomized clinical trials and thus there is limited evidence-based therapy available.
Comorbidities and aging via influencing cognitive and self-care ability affect management of heart failure patients. Also, polypharmacy is present often. In addition, frailty is common in these patients. In consequence, a multidisciplinary team is needed to take care especially for older heart failure patients to reduce hospitalizations and improve outcome.
You May Like: Open Heart Surgery Start To Finish
Overproduction Of Reactive Oxygen Species
Activated oxidative stress has been demonstrated in animal studies as well as in human studies to cause heart failure also lowered antioxidant activity in failing human hearts promotes oxidative stress . Furthermore, some risk factors for the development of heart failure also show increased oxidative stress i.e., hypertension, diabetes, obesity. Also in myocardial hypertrophy parameters of the redox-sensitive signaling pathways and transcription factors are activated . However, the complete mechanism is not understood yet . There are several factors activated via ROS which may influence contractility: proinflammatory mediators, periods of ischemia, auto-oxidation of catecholamines.
What Is Congestive Heart Failure In Cats
Congestive heart failure is a term that refers to the heartâs inability to pump enough blood to the body. Due to this, blood starts to back up into the lungs and fluid accumulates in the chest, abdomen, or both. This lead to further constriction of the heart and lungs, and limits oxygen flow throughout the body. There are many causes of CHF in cats, but the two most common causes are:
- Mitral valve insufficiency , which refers to a leaky mitral valve, which is the valve between the left atrium and the left ventricle.
- Dilated cardiomyopathy , which is when the heart chambers enlarge and lose their ability to contract.
Clinical signs of CHF vary depending on whether the cat has left- or right-sided heart failure.
Right-sided congestive heart failure
This occurs when a heart contraction causes some blood to leak into the right atrium from the right ventricle rather than being pushed through the lungs and becoming oxygenated. As a result, the main circulation system becomes congested with blood, and fluid accumulates in the abdomen, interfering with adequate organ function. Excess fluid might also build up in the limbs and cause swelling known as peripheral edema.
Left-sided congestive heart failure
You May Like: Steps In Dying From Congestive Heart Failure
Don’t Miss: What Is Considered A Low Heart Rate
Causes Of Heart Failure
Heart failure is often the result of a number of problems affecting the heart at the same time.
Conditions that can lead to heart failure include:
- coronary heart disease where the arteries that supply blood to the heart become clogged up with fatty substances , which may cause angina or a heart attack
- high blood pressure this can put extra strain on the heart, which over time can lead to heart failure
- conditions affecting the heart muscle
- heart rhythm problems , such as atrial fibrillation
- damage or other problems with the heart valves
- congenital heart disease birth defects that affect the normal workings of the heart
Sometimes obesity, anaemia, drinking too much alcohol, an overactive thyroid or high pressure in the lungs can also lead to heart failure.
Precipitating Causes Of Heart Failure
A previously stable, compensated patient may develop heart failure that is clinically apparent for the first time when the intrinsic process has advanced to a critical point, such as with further narrowing of a stenotic aortic valve or mitral valve. Alternatively, decompensation may occur as a result of the failure or exhaustion of the compensatory mechanisms but without any change in the load on the heart in patients with persistent, severe pressure or volume overload. In particular, consider whether the patient has underlying coronary artery disease or valvular heart disease.
The most common cause of decompensation in a previously compensated patient with heart failure is inappropriate reduction in the intensity of treatment, such as dietary sodium restriction, physical activity reduction, or drug regimen reduction. Uncontrolled hypertension is the second most common cause of decompensation, followed closely by cardiac arrhythmias . Arrhythmias, particularly ventricular arrhythmias, can be life threatening. Also, patients with one form of underlying heart disease that may be well compensated can develop heart failure when a second form of heart disease ensues. For example, a patient with chronic hypertension and asymptomatic LV hypertrophy may be asymptomatic until an MI develops and precipitates heart failure.
- Profound anemia
Recommended Reading: What Does A Slow Heart Rate Mean
