What Is Heart Rate Variability
As the term suggests,heart rate variability isVerified SourceHarvard HealthBlog run by Harvard Medical School offering in-depth guides to better health and articles on medical breakthroughs.View sourcea measurement of the variation in time between each heartbeat. In other words, it expresses how well the heart changes speeds throughout the day.
For example, you may measure your heart rate and find its about 90 beats per minute. However, that doesnt mean that every single heartbeat takes about of a second. The interval between each heartbeat varies. In this same example, you may have of a second between beats and later a full second between beats.
These increments between beats are called R-R intervals and are measured in milliseconds. The term R-R intervals comes from the heartbeats R-phase. These intervals are essentially the spikes you see on the results of anelectrocardiogram test.Verified SourceMedline PlusOnline resource offered by the National Library of Medicine and part of the National Institutes of Health.View source
During the R phase, most of the heart is activated resulting in the greatest wave shown by the ECG recording, according to a2016 review on heart rate variability in humans.Verified SourceNational Library of Medicine Worlds largest medical library, making biomedical data and information more accessible.View source
Heart Rate Variations During Sleep
During sleep, the pulse or heart rate is typically lower than while an individual is awake. Though, when a sleepy person goes through the distinct phases of sleep, the heart rate also varies. For example, in the early phases of light sleep, the heart rate starts to decrease.
The heart rate reaches its lowest levels during deep sleep. On the other hand, during rapid eye movement sleep, the pulse rate may increase to an analogous pace when a person is awake.
The majority of individuals experience a slower pulse rate during non-rapid eye movement sleep, which protects them from cardiac events . In contrast, REM sleep is frequently characterized by periods of increased activity.
Even though this is normal, researchers think that the increase in activity during REM sleep may help clarify why individuals who are already weak often have heart attacks and other bad things that happen in the morning when they spend more time in REM sleep than other stages of sleep.
It is important to mention here, sleep issues can have significant effects on your heart and cardiovascular health, contributing to a faster heart rate and increased blood pressure. Sleep disorders including periodic limb movements, sleep apnea, and shift work disorder have been associated with an increased risk of heart disease.
How Can You Measure Your Sleeping Heart Rate
To measure your sleeping heart rate at home, you can use a smart watch. Some companies are also starting to offer smart sensors that integrate into the bed. If your doctor suspects you may have a sleep disorder, they may order an in-lab or at-home sleep study with professional equipment that delivers a more accurate heart rate reading.
To calculate your resting heart rate during the day, lightly press the tips of your index and middle finger over the artery on your neck, your chest, or the inside of your wrist. Count your heartbeats for the next 30 seconds and multiply by two.
Also Check: How Do I Check My Heart Rate
Whats A Dangerous Heart Rate
A racing heart can be scary.
Heart attack? Panic attack? The symptoms can be similar.
A fast-beating heart may be concerning or it could just be anxiety, which can come and go. A normal pulse or heart rate is between 60 and 100 beats per minute taken when youre not exercising, known as your resting heart rate.
Anything that causes increased stimulation, whether physical or emotional, could increase your heart rate. That includes caffeine and other herbal and medicinal stimulants.
What Can Affect Sleeping Heart Rates

Sleep is a vital part of our lives, and disruptions can lead to health problems. Not only is a persons sleep quality compromised because of sleep apnea, but they also cause the heart to beat faster than usual. Sleeping heart rates are one measure of sleep quality, and they can be affected by a variety of factors. Obesity, age, and even the time of day can all have an impact on sleeping heart rates.
Read Also: What Causes Elevated Heart Rate
How Can You Manage Your Sleeping Heart Rate
While it may seem largely out of your control, there are actually several ways you can ensure your sleeping heart rate is in the normal range. With a focus on engaging in healthy lifestyle habits that improve overall cardiovascular health, these ideas from Jean include:
- Exercise regularly, aiming for at least 150 minutes a week of moderate-intensity fitness and two days a week of strength training. Being physically fit is associated with a lower resting heart rate, Jean says.
- Eat a healthy diet. Some examples include the Mediterranean diet, a plant-based diet, a flexitarian diet, and the DASH diet . You want to avoid processed foods and limit your intake of unhealthy fats, says Jean. A heart-healthy diet consists of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and lean sources of protein, such as fish and poultry over red meat.
- Avoid nicotine.
- Avoid caffeine before going to bed.
- Limit alcohol intake to the recommended amount . Alcohol in excess has been linked to poor sleep quality and insomnia, Jean says. You should avoid drinking alcohol before going to bed.
- Get the recommended seven to nine hours of sleep at night.
- Reduce stress and anxiety. Consider yoga, meditation, therapy, and deep breathing exercises.
- Get treatment for underlying conditions such as hypothyroidism and sleep apnea.
Normal sleeping heart rate depends on several factors, which is why its important to consult with your medical provider if you have any concerns or symptoms, Jean concludes.
Bradycardia: How Low Is Too Low
While a normal sleeping heart rate can dip below 60, the Cleveland Clinic explains that a sustained heart rate below 60 when you’re not sleeping or resting may be a medical condition called bradycardia.
Bradycardia is a condition that increases with age. It’s most common in men and women over age 65, Cleveland Clinic says. Although healthy and fit young people and trained athletes can have heart rates down into the 40s without any symptoms, bradycardia may cause symptoms for other people. These can include:
The most common cause of symptomatic bradycardia is a problem that develops with the heart’s natural pacemaker, called the sinus node, Cleveland Clinic notes. There may also be a block of electrical signals between the upper and lower chambers of the heart, called an AV block. Another common cause is a heart or blood pressure medication that slows down the heart, it says.
“Symptoms of bradycardia may only be felt during activity. You could have a heart rate of 50 at rest without any symptoms, but if you get up and active, even a heart rate of 60 or 65 could be too slow and cause symptoms. If you have symptomatic bradycardia, you may need treatment,” Dr. Santucci says.
Mayo Clinic recommends letting your doctor know if you’re not a trained athlete and your resting heart rate is under 60. This is even more important if you have symptoms of bradycardia.
Recommended Reading: Treatment Of Congestive Heart Failure
What Is Resting Heart Rate
Heart rate is defined as the number of contractions of the heart, expressed in beats per minute . Heart rate can be measured during activity , but is most often clinically assessed at rest in the absence of extraneous stress and other factors.
Resting heart rate is utilized to evaluate an individuals cardiovascular health and function. While most healthy adults have a resting heart rate between 60 and 80 bpm, factors such as fitness level, body composition, room temperature, body position, stress, and use of certain medications can affect heart rate.
Heart Rate Variability During Sleep
Whoop, a performance optimization device, captures your heart rate variability while awake and while asleep.
Your heart rate variability simply refers to the variation in the amount of time between heart beats.
If you’re in fight-or-flight mode and your heart is racing, there is little time between heart beats . On the other hand, when you’re relaxed, your heart beats slower and there’s more time between heart beats .
The higher your HRV, the better, especially during sleep. If you have a high HRV, it means your body is adaptable and at the ready. Your HRV is a direct indication of how much stress your body is under at a given time — which is why you want to see a high HRV during sleep.
If your sleep tracker data shows low HRV, your body is in overdrive during sleep for some reason. Studies show that low sleep HRVs may indicate sleep disorders, so if yours is consistently low, consider the factors that may affect it: stress levels, bedtime routine, sleep environment. If you suspect a medication or medical condition is the culprit, talk to your doctor.
The information contained in this article is for educational and informational purposes only and is not intended as health or medical advice. Always consult a physician or other qualified health provider regarding any questions you may have about a medical condition or health objectives.
Don’t Miss: Is 200 Heart Rate Bad
Your Heart Rate During Sleep And Sleep Apnea
Obstructive Sleep Apnea is one of the most prevalent sleep disorders in the US with greater than 25 million confirmed cases and research suggesting a high prevalence of undiagnosed patients. During an apneic event, individuals experience a partial or complete collapse of their airway depriving them of oxygen for several seconds. In addition to sleep disturbances, this can lead to an acute change in heart rate and oxygen saturation.
So what are some indications that you may have OSA? Kathleen Davis states that loud snoring, accompanied by restless sleep and daytime fatigue, could indicate the presence of sleep apnea.
According to Medline Plus, this sleep disorder can cause pauses in breathing that can last from a few seconds to several minutes, with a transition back to normal breathing marked by a gasp, snort or choke, which may startle the sleeper . These sleep disruptions have been credited for symptoms of daytime tiredness, even after a full nights sleep, in patients with sleep apnea.
Fatigue and frustration aside, sleep apnea also affects nocturnal heart rate. When you stop breathing while you sleep, your heart rate drops, and then your involuntary reflexes make you startle into a micro-arousal, which causes your heart rate to accelerate quickly, saysThe National Sleep Foundation. In addition to elevated blood pressure, this rapid decrease and increase in heart rate may lead to an irregular heart rhythm, or cardiac arrhythmia.
What Is A Normal Resting Heart Rate
A normal resting heart rate is between 60 and 100 beats per minute.
Having a heart rate in that sweet spot is important because it decreases the demand on your heart muscle. That means it doesnt have to work as hard as it would if it were out of that zone, explains Kate Traynor, M.S., R.N., director of Cardiovascular Disease Prevention Center at Massachusetts General Hospital.
Think of your heart as a car and your blood’s oxygen as the gas. The faster you drive, the more gas you use . More gas means more work for the heart, which can put it in constant overdrive, says Traynor.
You May Like: Can You Have High Blood Pressure And Low Heart Rate
What Are The Harmless Causes Of Low Heart Rate
It is normal for our heart rate to fluctuate throughout the day. It naturally changes in response to what our body needs and what we are doing. Some harmless causes of bradycardia include:
-
Sleep: Our heart rate is generally lower when we are asleep or in a relaxed state. This is also known as our resting heart rate. When we are lying down and resting, our heart doesn’t have to work as hard against gravity to get the blood everywhere it needs to go. When were sleeping, our bodies dont use as much energy, so our nervous system tells the heart to take a little bit of a break.
-
Physical fitness: Cardiovascular activity strengthens our heart muscle. And a stronger heart can pump blood more efficiently. When the heart beats more efficiently in someone who has been physically training over time, their heart rate tends to be lower.
-
Certain medications: Some medications lower the heart rate in order to decrease the amount of work the heart has to do. Some examples include blood pressure medications, like beta blockers or calcium channel blockers.
While these causes of bradycardia are expected, there are some concerning conditions that can also cause a low heart rate.
Calculating Active Heart Rate
According to scientists, your target heart rate during moderate physical activity should be between 64% and 76% of your maximum heart rate:
- Maximum heart rate. This is the maximum speed your heart should be beating. Its related to your age. Doctors use a simple formula to work this out:
220 = maximum heart rate
So, if you are 40, your maximum heart rate will be 180. It is worth checking in with a doctor if your heart rate regularly goes above this.
- Target heart rate. During moderate exercise, you should aim for 64% to 76% of 180, equal to 113.4 to 136.8 BPM.
Aim for 77% to 93% of your maximum heart rate during intense activity. For 40-year-olds, that means 138.6 to 167.4 BPM.
But what about when you are sleeping?
Recommended Reading: Treatments Of Congestive Heart Failure
Typical Heart Rates During Exercise
During exercise, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends aiming for a target heart rate between 64% and 76% of your maximum heart rate for moderate-intensity workouts, and 77% to 93% for high-intensity workouts.
You can estimate your maximum heart rate by subtracting your age from 220. For example, the maximum heart rate for a 50-year-old would be estimated to be 170 bpm, and 200 bpm for a 20-year-old. This means that the 20-year-old may want to aim for a heart rate between 128 and 152 bpm during a moderate-intensity workout, or between 154 and 186 bpm for a high-intensity workout.
However, there are additional factors to consider when calculating your target heart rate. It is important to consult with a medical professional to determine any potential risks prior to engaging in vigorous exercise.
Does Bradycardia Require Treatment
If your heart rate is slow, but you dont have symptoms, theres no reason to worry. However, its a good idea to know the signs of trouble because bradycardia in some cases does require treatment.
For example, if your heart rate drops into the 30s, you might not get enough oxygen to your brain, making fainting, lightheadedness, and shortness of breath possible. Blood can also pool in your heart chambers, causing congestive heart failure.
You May Like: What Is Congenital Heart Failure
Tips For Improved Sleep
When youre sound asleep, your body is wide awake. Welcome its feedback, listen closely to what it has to say, and take steps towards optimizing your sleep.
Use the following tips to help boost your sleep routine:
- Try to wake up at the same time seven days a week.
- Time your meals mindfully late meals may show up as the Downward Slope.
- If your sleep pattern is optimal , take notes. Think about what you did the previous day and continue to make similar choices.
Read More About What Your Sleeping Heart Rate Can Tell You:
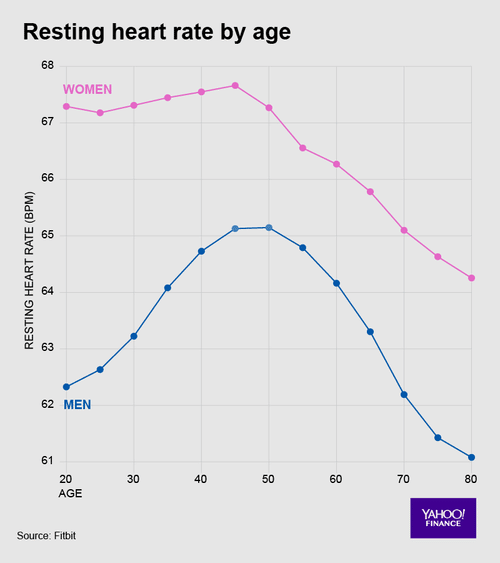
Typical Resting Heart Rates
For most adults, a normal resting heart rate is considered to be between 60 to 100 bpm, though this range can vary and depends on multiple factors. Adult males tend to have lower heart rates.
A heart rate outside of this range may still be considered healthy in certain situations. For example, athletes and physically fit individuals may have resting heart rates as low as 30 bpm. Your doctor can help you assess whether your resting heart rate is healthy for you.
Resting heart rate decreases with age. For example, one large study found that the upper limit of the average resting heart rate is 110 bpm for adults 18 to 45 years old, 100 bpm for those between 45 and 60 years old, and 95 bpm for those older than 60. These are the average resting heart rates for healthy adults, as reported by the same study:
| Age |
|---|
| 63-85 bpm |
Recommended Reading: Viral Attack On Heart
Irregular Heart Rhythms And Risks
While irregular heartbeats can be caused by a variety of factors, more studies are revealing the direct relationship between cardiac arrhythmias and sleep disorders such as OSA. One of the most common types of arrhythmia, atrial fibrillation is marked by irregular contractions of the upper heart chambers.
According to a clinical study conducted at the University of Ottawa, researchers found that OSA may increase the risk of atrial fibrillation with secondary symptoms including palpitations, lightheadedness, weakness, fatigue, shortness of breath, and chest pain. Atrial fibrillation is also associated with stroke, heart failure, and other cardiovascular conditions.
The Biostrap Buzz
Sign up to our email newsletter to receive curated content on the latest news in digital health and health optimization. Plus, special access to Biostrap offers and community updates.
What Is Your Sleeping Heart Rate
Your heart rate at rest or during sleep measures how fast your heart beats in this state. A good measure of this biomarker is how many heartbeats you record per minute at a relatively passive time, such as immediately you rise before you even get out of bed.
The resting heart rate is of cardinal significance to health. This figure indicates how much exertion your heart muscles have to undertake to maintain blood supply and keep a steady heartbeat.
Hence, with sleeping heart rate unlike with maximum heart rate lower scores are better.
A lower resting heart rate indicates that your heart, heart muscles, and other related circulatory mechanisms are in prime condition. Lower RHR means they dont have to overexert themselves to maintain proper cardiovascular function.
Consequently, the closeness of your resting heart rate to average can often be a valid predictor of your risk factor for heart disease, heart failure, and high blood pressure.
What then, is the perfect resting heart rate? Like with most physiological metrics, it depends.
According to the American Heart Association, barring any underlying medical conditions, the reasonable resting heart rate for most people should fall between 60-100 beats per minute, with healthier people often falling on the lower end of that range.
However, this broad range does not tell the whole story.
Don’t Miss: Increased Heart Rate After Eating
