Diagnostic Tests And Procedures
To diagnose narrowed arteries or an aortic aneurysm, your doctor may have you undergo some of the following tests and procedures:
- Chest magnetic resonance imaging to look for aneurysms in the aorta. This test works well for detecting aneurysms and pinpointing their size and exact location.
- Computer tomography angiography and magnetic resonance angiography to take pictures of your blood vessels. These tests may give your doctor more information about the flow of blood and whether arteries are narrowed or have aneurysms.
- Coronary angiography to see how blood flows through your coronary arteries. This type of test involves injecting dye into your blood so that your blood vessels can be seen by X-ray.
- Fractional flow reserve can help determine how narrow the artery is. This is an added test done during CTA or coronary angiography to check the blood pressure in a specific artery.
- Ultrasound to see whether plaque has narrowed or blocked your carotid or peripheral arteries or to see if you have an aneurysm and where it may be located. This painless test uses high-energy sound waves to create pictures of the insides of your blood vessels.
- Echocardiography to evaluate the structure and function of your heart. Echocardiography uses sound waves to create moving pictures of your heart.
- Nuclear imaging to see whether the blood is flowing normally to the heart. Your doctor will inject a tracer substance that will show whether the heart is receiving enough blood flow.
What Is A Cardiac Catheterization
Coronary artery disease is the narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries, as shown in the illustration below. After an interventional procedure, the coronary artery is opened, increasing blood flow to the heart.
Cardiac catheterization is an invasive imaging procedure that allows your doctor to evaluate your heart function. Cardiac catheterization is used to:
- Evaluate or confirm the presence of coronary artery disease, valve disease or disease of the aorta
- Evaluate heart muscle function
- Determine the need for further treatment
During a cardiac catheterization, a long, narrow tube called a catheter is inserted through a plastic introducer sheath . The catheter is guided through the blood vessel to the coronary arteries with the aid of a special x-ray machine. Learn more about cardiac catheterization.
With IVUS, a miniature sound-probe is positioned on the tip of a coronary catheter. The catheter is threaded through the coronary arteries and, using high-frequency sound waves, produces detailed images of the inside walls of the arteries. IVUS produces an accurate picture of the location and extent of plaque.
With FFR, a special wire is threaded through the artery and a vasodilator medication is given. This test is functionally performing a very high quality stress test for a short segment of the artery. What is an interventional procedure?
The Benefits Of Revascularization
For non-emergency treatment of CAD, both procedures can help significantly reduce symptoms. Often, though, they are not better than other kinds of therapy.
Generally speaking, non-emergency revascularization by either method doesn’t improve survival. It is also difficult to know if it helps reduce the rate of subsequent heart attacks.
However, both stenting and CABG can improve outcomes for patients who are experiencing acute coronary syndrome. This term describes an emergency heart condition like a heart attack. Both procedures can also improve outcomes for patients who have:
- Complex lesions in several coronary arteries
- Disease of the left main coronary artery
Revascularization can also be a good option if you have pain that doesn’t seem to be improving with medication.
You May Like: How To Lower High Heart Rate
What Is An Interventional Procedure
An interventional procedure is a non-surgical treatment used to open narrowed coronary arteries to improve blood flow to the heart. An interventional procedure can be performed during a diagnostic cardiac catheterization when a blockage is identified, or it may be scheduled after a catheterization has confirmed the presence of coronary artery disease.
An interventional procedure starts out the same way as a cardiac catheterization. Once the catheter is in place, one of these interventional procedures is performed to open the artery: balloon angioplasty, stent placement, rotablation or cutting balloon.
Balloon angioplasty: A procedure in which a small balloon at the tip of the catheter is inserted near the blocked or narrowed area of the coronary artery. The technical name for balloon angioplasty is percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty or percutaneous coronary intervention . When the balloon is inflated, the fatty plaque or blockage is compressed against the artery walls and the diameter of the blood vessel is widened to increase blood flow to the heart. This procedure is sometimes complicated by vessel recoil and restenosis.
Angioplasty with stenting is most commonly recommended for patients who have a blockage in one or two coronary arteries. If there are blockages in more than two coronary arteries, coronary artery bypass graft surgery may be recommended.
If you have concerns about drug-eluting stents, please talk with your physician.
Why Do I Required A Stent Surgery
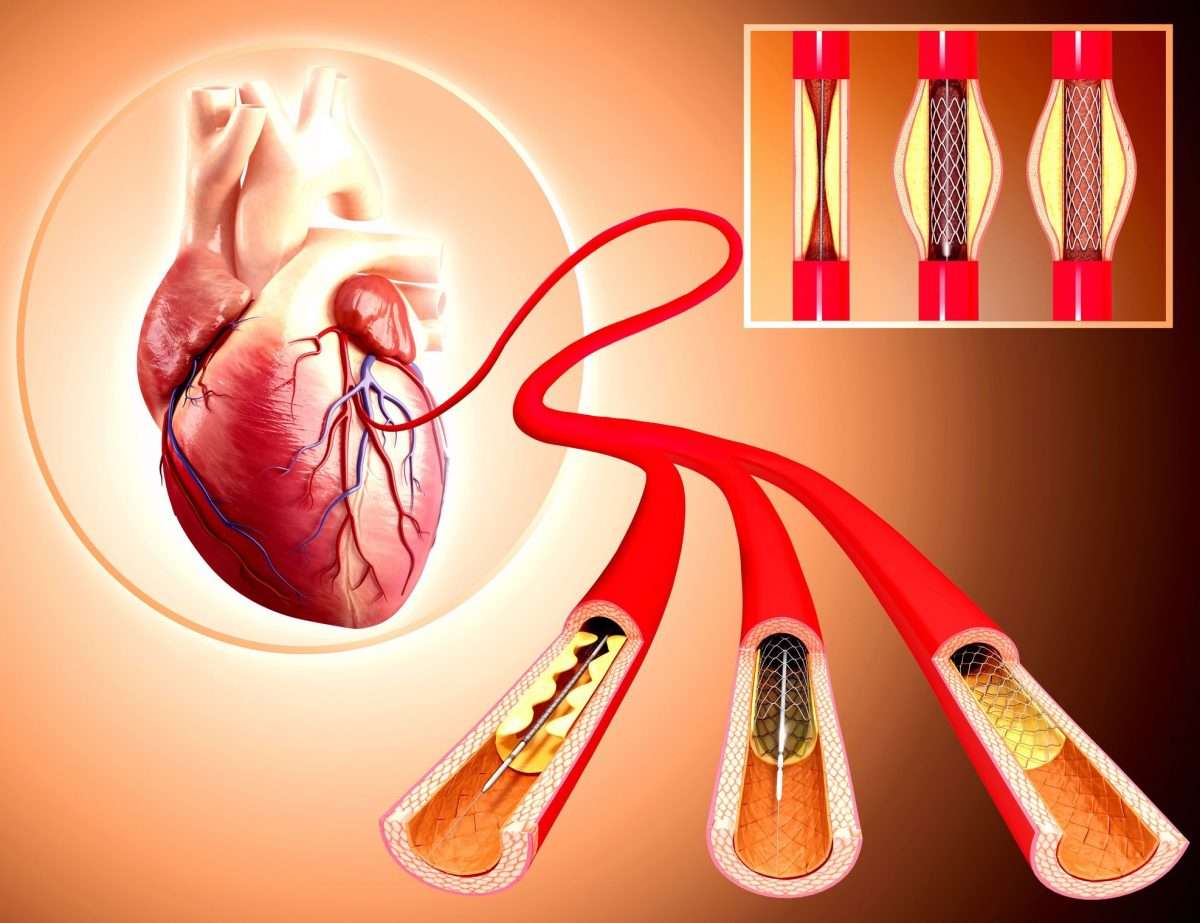
Stents are usually essential when plaque obstructs a blood vessel. Plaque is made of cholesterol and other substances that connect to the walls of a vessel.
You may need a stent during an emergency situation procedure. An emergency situation procedure is more common if an artery of the heart called a coronary artery is blocked. Your doctor will first place a catheter into the blocked coronary artery. This will permit them to do a balloon angioplasty to open the clog. Theyll then place a stent in the artery to keep the vessel open.
Stents can likewise be useful when theres an aneurysm in your brain.
Besides blood vessels, stents can open any of the following passageways:
- bile ducts, which are tubes that bring bile to and from digestive organs
- bronchi, which are little respiratory tracts in the lungs
- ureters, which are tubes that bring urine from the kidneys to the bladder
These tubes can become blocked or harmed much like blood vessels can.
Recommended Reading: What Is Target Heart Rate
When A Coronary Angioplasty Is Used
Like all organs in the body, the heart needs a constant supply of blood. This is supplied by the coronary arteries.
In older people, these arteries can become narrowed and hardened , which can cause coronary heart disease.
If the flow of blood to the heart becomes restricted, it can lead to chest pain known as angina, which is usually triggered by physical activity or stress.
While angina can often be treated with medication, a coronary angioplasty may be required to restore the blood supply to the heart in severe cases where medication is ineffective.
Coronary angioplasties are also often used as an emergency treatment after a heart attack.
Staying Healthy After Receiving A Heart Stent
Beyond following your discharge instructions, you can speed your recovery by adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle that includes:
-
Drinking plenty of water. Adequate hydration keeps your whole body happy and helps your medications work better.
-
Eating a healthy diet thats rich in vegetables, fruits, lean meats and whole grains.
-
Increasing your activity levels to achieve a goal of purposeful exercise at least three times a week. When your doctor releases you to normal activity, start by walking for half an hour every day.
You May Like: How Much Can Marijuana Increase A Person’s Heart Rate
How Safe Is A Coronary Angioplasty
A coronary angioplasty is 1 of the most common types of treatment for the heart.
Coronary angioplasties are most commonly performed in people aged 65 or older, as theyâre more likely to have heart disease.
As the procedure doesnât involve making major incisions in the body, itâs usually carried out safely in most people. Doctors refer to this as a minimally invasive form of treatment.
The risk of serious complications from a coronary angioplasty is generally small, but this depends on factors such as:
- your age
- whether youâve had a heart attack
Serious problems that can occur as a result of the procedure include:
- excessive bleeding
Read more about the possible complications of a coronary angioplasty.
Incision Site Care After A Stent Procedure
When you go home, you will have an incision in your groin or arm, depending on where your doctor inserted the heart catheter. This incision could potentially open and bleed or become infected, so its important you keep it clean and avoid straining it.
To care for your incision:
-
Wash the incision daily with mild soap and water. You can do this in the shower, if you like. Apply the soapy water using the palm of your hand and rub gentlydo not scrub the incision.
-
If instructed by your doctor, apply antibiotic ointment to the wound. Otherwise, avoid applying any kind of ointment, lotion or cream to the incision.
-
Apply a small adhesive bandage to the incision site each day after cleansing.
-
Avoid soaking in a bath or hot tub for at least a week after the procedure, as this can slow wound healing.
Your incision site may be swollen and bruised at first, but this should slowly improve over time. If your incision site progressively becomes more swollen, hot, red and angry-looking, or if you develop a fever over 101 degrees Fahrenheit, call your doctor. This could be a sign the wound is infected.
If your incision starts bleeding, lie down and apply firm, direct pressure to the wound for at least 30 minutes. If possible, have someone else apply the pressure. If the wound does not stop bleeding after 30 minutes, maintain pressure and call 911.
Read Also: What Is Ideal Resting Heart Rate
How Long Does A Heart Stent Last
There is no fixed life of a stent. A lot depends on how your body responds to its presence, your medical dosage, diet, medical history and your lifestyle. They have been known to last for up to 15 years after which one may require a heart stent replacement. Stents for heart operation come with their share of risks. So, post surgery, regular monitoring of heart condition by a physician is advisable.
Though there are associated risks, stent technology has helped millions reclaim their lives. Care for your heart through regular exercise and a healthy diet. That may go a long way in preventing such extreme measures like heart surgeries to be required in the first place. However, the incidence of heart ailment is even found in regularly exercising men and women. The best we can do is keep our body in shape and eat right.
Disclaimer: This article is meant for reference purposes only. It is not intended to supplant the advice of a certified medical practitioner.
Should You Have Stenting Or Bypass Surgery
Many factors go into your physicians recommendation.
When fatty plaques threaten to obstruct the coronary arteries, there are two options for restoring blood flow : open the blockages with a balloon , followed by the placement of a stent or bypass the blockages with coronary artery bypass grafting .
Balloon angioplasty can open a narrowed artery, and the stent can hold it open. Angioplasty and stenting is a minimally invasive, nonsurgical procedure with less postoperative pain, a shorter hospital stay, and faster recovery than CABG. So its no surprise that its popularity has soared. But despite these advantages, its not the best choice for everyone. Now that thousands of stents have been implanted, cardiologists better understand the long-term effects of the procedure and can make an informed decision about which treatment might be best for each individual.
To continue reading this article, you must log in.
- Research health conditions
- Prepare for a doctors visit or test
- Find the best treatments and procedures for you
- Explore options for better nutrition and exercise
Also Check: How Long Is Open Heart Surgery
How Is Coronary Angioplasty Done
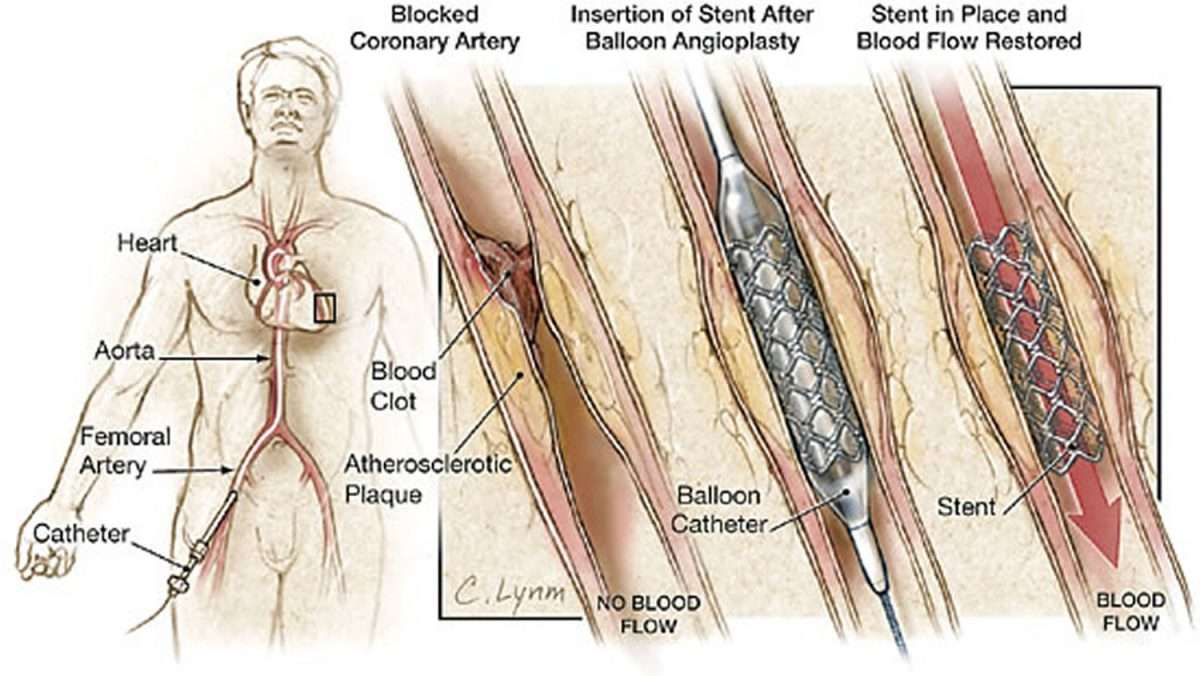
Before coronary angioplasty is done, your doctor will need to know whether your coronary arteries are blocked. If one or more of your arteries are blocked, your doctor will need to know where and how severe the blockages are.
To find out, your doctor will do an angiogram and take an x-ray picture of your arteries. During an angiogram, a small tube called a catheter with a balloon at the end is put into a large blood vessel in the groin or arm. The catheter is then threaded to the coronary arteries. A small amount of dye is injected into the coronary arteries and an x-ray picture is taken.
This picture will show any blockages, how many, and where they’re located. Once your doctor has this information, the angioplasty can proceed. Your doctor will blow up the balloon in the blockage and push the plaque outward against the artery wall. This opens the artery more and improves blood flow.
The illustration shows a cross-section of a coronary artery with plaque buildup. The coronary artery is located on the surface of the heart. Figure A shows the deflated balloon catheter inserted into the narrowed coronary artery. In figure B, the balloon is inflated, compressing the plaque and restoring the size of the artery. Figure C shows the widened artery.
A small mesh tube called a stent is usually placed in the newly widened part of the artery. The stent holds up the artery and lowers the risk of the artery re-narrowing. Stents are made of metal mesh and look like small springs.
Difference Between Open Heart Surgery And Angioplasty
Key Difference: Open heart surgery deals with the structures inside the heart. In an open-heart surgery, a large incision in the chest is made to open the rib cage. A heart-lung machine is required in an open heart surgery. An angioplasty is a procedure in which coronary arteries are unblocked. An angioplasty procedure does not require an open heart surgery.
Open heart surgery is traditionally associated with the types of surgery that involves cracking the walls of the chest. However, the other types of open heart surgery includes less invasive surgeries in which small incisions are made between ribs. In broad context, it refers to a type of surgery that involves repairing or fixing structures that are located inside the heart. In this type of surgery, the chest wall is surgically opened and the heart is exposed. Open refers to the chest not the heart. However in few cases, surgeon may also open the heart. This surgery is performed on the muscles, valves, or arteries of the heart. The function of the heart during this surgery is conducted by a heart-lung machine. During this surgery, heart beats are temporarily stopped and the demand of oxygen is fulfilled by a heart-lung machine. Special tubes called cannular are placed in the veins as well as in the arteries of the heart. A variant of open heart surgery is known as the beating heart surgery. In this type of surgery, the heart is not stopped from beating.
Comparison between Open Heart Surgery and Angioplasty:
Recommended Reading: What Happens To Heart Rate During Heart Attack
Normal Heart Rate After Stent Placement
|
After having a planned coronary angioplasty, you’ll normally be able to leave hospital the same day or following day. Arrange for someone to take you home. Table of Contents Before you leave hospital, you should be given advice on:
You may also be given a date for a follow-up appointment to check on your progress. You may have a bruise under the skin where the catheter was inserted. This isn’t serious, but it may be sore for a few days. Occasionally, the wound can become infected. Keep an eye on it to check it’s healing properly. Your chest may also feel tender after the procedure, but this is normal and usually passes in a few days. If necessary, you can take paracetamol to relieve any pain. |
Your hospital team can usually advise you about how long it will take to recover and if there are any activities you need to avoid in the meantime.
In most cases, you’ll be advised to avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activities for about a week, or until the wound has healed.
Heart Blockage Moderate Coronary Artery Disease
A moderate amount of heart blockage is typically that in the 40-70% range, as seen in the diagram above where there is a 50% blockage at the beginning of the right coronary artery. Usually, heart blockage in the moderate range does not cause significant limitation to blood flow and so does not cause symptoms. Moderate coronary artery disease is treated much in the same way as mild disease, basically attention to risk factors, medications, and healthy lifestyle modification. Occasionally, heart blockage at the higher end of the moderate range may require additional testing to see if it is significant or not and may be responsible for symptoms.
Don’t Miss: What Should Your Resting Heart Beat Be
How Does Your Doctor Put In A Stent
To put a stent in, your doctor makes a small cut in a blood vessel in your groin, arm, or neck. They then thread a thin tube called a catheter through the blood vessel to the blocked artery.
The tube has a tiny balloon at the end of it. Your doctor inflates the balloon inside your blocked artery. This widens your artery so blood can flow through it again.
They then place the stent inside your artery. They’ll remove the catheter and balloon, but the stent stays inside to keep the artery open.
The procedure takes about an hour, but you’ll probably stay in the hospital overnight.
Who Needs Coronary Angioplasty
Coronary angioplasty is used to restore blood flow to the heart when the coronary arteries have become narrowed or blocked due to coronary artery disease .When medicines and lifestyle changes, such as following a healthy diet, quitting smoking and getting more physical activity, don’t improve your CAD symptoms, your doctor will talk to you about other treatment options. These options include angioplasty and coronary artery bypass grafting , a type of open-heart surgery.Your doctor will take into account a number of factors when recommending the best procedure for you. These factors include how severe your blockages are, where they’re located, and other diseases you may have.
Angioplasty is often used when there is less severe narrowing or blockage in your arteries and when the blockage can be reached during the procedure.CABG might be chosen if you have severe heart disease, multiple arteries that are blocked, or if you have diabetes or heart failure.
Compared with CABG, some advantages of angioplasty are that it:
- Has fewer risks than CABG
- Isn’t surgery, so it won’t require a large cut
- Is done with medicines that numb you and help you relax. Unlike CABG, you won’t be put to sleep for a short time
- Has a shorter recovery time
Quickly opening a blockage lessens the damage to the heart during a heart attack and restores blood flow to the heart muscle. Angioplasty can quickly open the artery and is the best approach during a heart attack.
Read Also: Acute Diastolic Heart Failure
