Fight Dehydration With Dripdrop Ors
When youre dehydrated, you may feel symptoms such as heart palpitations, increased heart rate, and lightheadedness. Staying hydrated can help to support a healthy heart. Thats because dehydration causes a decrease in blood flow and blood volume, which can decrease your risk of blood clots, high blood pressure, and heart attacks.
If you recognize the symptoms of dehydration, the best way to tackle the condition is to use an oral rehydration solution like DripDrop ORS. Medical-grade DripDrop ORS allows you to alleviate mild to moderate dehydration outside of a hospital setting, without the need for costly and painful IV therapy.
DripDrop ORS was developed by a doctor on a mission to defeat life-threatening dehydration. The patented formula provides medically relevant electrolyte levels, improving on the World Health Organizations Oral Rehydration Solution standards because of its delicious taste, giving you a medically viable ORS that also tastes great. By comparison, sports drinks contain about one-third the electrolytes of DripDrop ORS.
For cases of mild to moderate dehydration, DripDrop ORS is a fast, effective, and great tasting remedy. The convenient packaging allows you to have DripDrop ORS when you need it, where you need it.
Get started with a trial or our most popular multi-flavor pouch for dehydration relief fast. Or, if youre ready to make a purchase, and youre a first-time buyer, enjoy 15% off your order with code: FIRST15.
What Is The Pulse Rate
The pulse rate is a measurement of the heart rate, or the number of times the heart beats per minute. As the heart pushes blood through the arteries, the arteries expand and contract with the flow of the blood. Taking a pulse not only measures the heart rate, but also can indicate the following:
- Heart rhythm
- Strength of the pulse
The normal pulse for healthy adults ranges from 60 to 100 beats per minute. The pulse rate may fluctuate and increase with exercise, illness, injury, and emotions. Females ages 12 and older, in general, tend to have faster heart rates than do males. Athletes, such as runners, who do a lot of cardiovascular conditioning, may have heart rates near 40 beats per minute and experience no problems.
Top Questions Asked On This Page
Q: Why is pacing contraindicated in hypothermia?
A: Bradycardia may be physiologic in the hypothermic patient. This type of bradycardia is an appropriate response to the decreased metabolic rate that normally occurs with hypothermia.
Also the hypothermic ventricle is more prone to fibrillation with any sort of irritation. Thus the irritation of TCP could induce VF. Once the hypothermic ventricle begins to fibrillate, it is more resistant to defibrillation. Warm the patient and then treat any remaining arrhythmias.
Q: What is TCP?
A: TCP means transcutaneous pacing.
Q: What is chemical pacing?
A: Chemical pacing is when IV medications are used to increase the heart rate rather than the transcutaneous pacing which uses electricity to increase the heart rate.
You May Like: How Much Blood Does The Heart Pump
Correlation With Cardiovascular Mortality Risk
| This section needs more medical references for verification or relies too heavily on primary sources. Please review the contents of the section and add the appropriate references if you can. Unsourced or poorly sourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources:;“Heart rate”;;news;·newspapers;·books;·scholar;·JSTOR |
A number of investigations indicate that faster resting heart rate has emerged as a new risk factor for mortality in homeothermic mammals, particularly cardiovascular mortality in human beings. Faster heart rate may accompany increased production of inflammation molecules and increased production of reactive oxygen species in cardiovascular system, in addition to increased mechanical stress to the heart. There is a correlation between increased resting rate and cardiovascular risk. This is not seen to be “using an allotment of heart beats” but rather an increased risk to the system from the increased rate.
Given these data, heart rate should be considered in the assessment of cardiovascular risk, even in apparently healthy individuals. Heart rate has many advantages as a clinical parameter: It is inexpensive and quick to measure and is easily understandable. Although the accepted limits of heart rate are between 60 and 100 beats per minute, this was based for convenience on the scale of the squares on electrocardiogram paper; a better definition of normal sinus heart rate may be between 50 and 90 beats per minute.
What Is A Good Resting Heart Rate By Age

A healthy resting heart rate is about 60 beats per minute, but this number varies with age. The normal range for a resting heart rate is between 60 bpm and 100 bpm. Well-conditioned athletes, however, could have a resting heart rate of around 40 bpm.
If having a low resting heart is key for health and longevity, how can you lower your resting heart rate naturally?;
You May Like: Does Tylenol Increase Heart Rate
How Can You Care For Yourself
Bradycardia is often the result of another heart condition, so taking steps to live a heart-healthy lifestyle will usually improve your overall health. The steps include:
- Having a heart-healthy eating plan that includes vegetables, fruits, nuts, beans, lean meat, fish, and whole grains. Limit alcohol, sodium, and sugar.
- Being active on most, if not all, days of the week. Your doctor can tell you what level of exercise is safe for you.
- Losing weight if you need to, and staying at a healthy weight.
- Not smoking.
- Managing other health problems, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes.
How To Enable Irregular Rhythm Notifications
Don’t Miss: How To Calculate Target Heart Rate Zone
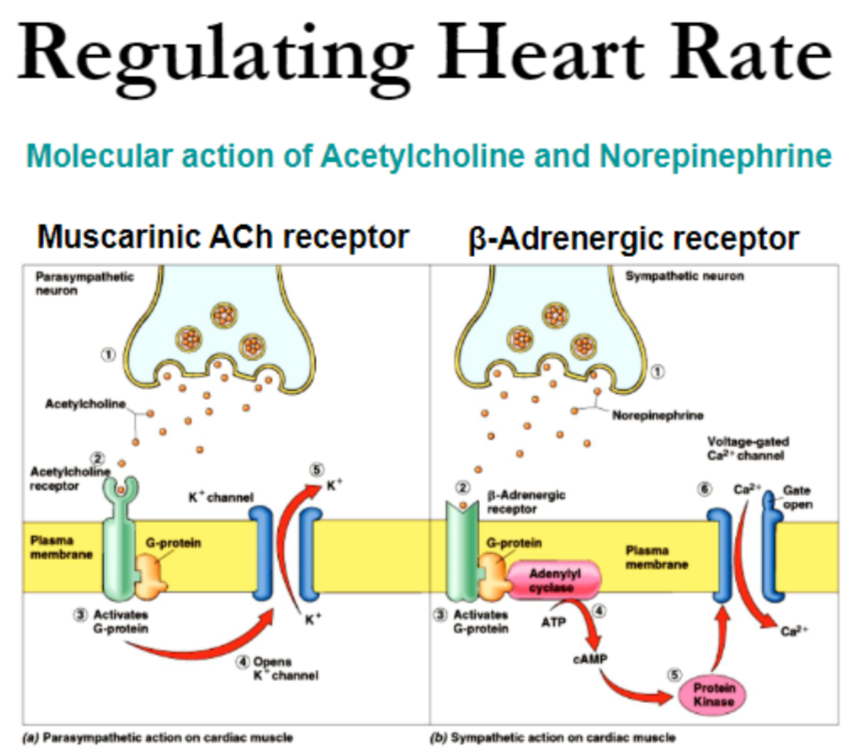
What Controls Heart Rate
Heart rate is controlled by the two branches of the autonomic nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system . The sympathetic nervous system releases the hormones to accelerate the heart rate. The parasympathetic nervous system releases the hormone acetylcholine to slow the heart rate. Such factors as stress, caffeine, and excitement may temporarily accelerate your heart rate, while meditating or taking slow, deep breaths may help to slow your heart rate.;; Exercising for any duration will increase your heart rate and will remain elevated for as long as the exercise is continued. At the beginning of exercise, your body removes the parasympathetic stimulation, which enables the heart rate to gradually increase. As you exercise more strenuously, the sympathetic system kicks in to accelerate your heart rate even more. Regular participation in cardiovascular exercise over an extended period of time can decrease your resting heart rate by increasing the hearts size, the contractile strength and the length of time the heart fills with blood. The reduced heart rate results from an increase in activity of the parasympathetic nervous system, and perhaps from a decrease in activity of the sympathetic nervous system.
What Is A Healthy Heart Rate What Is Optimal
An optimal heart rate about one beat per second; at rest, or . Consequently, for every 10 beats per minute increase, theres a 10 to 20% increased risk of premature death.
Theres strong evidence showing that everyone with a high heart rate is at risk , even otherwise healthy individuals. But there are ways that you can slow your heart rate naturally.
First, check your resting heart rate before you make any changes using the method in section 2. This reading will be your baseline number to track your progress and test which programs work for you. Secondly, record your heart rate after any changes you make.
Recommended Reading: Can Flonase Cause Heart Palpitations
Cardiac Sympathetic Nervous System
The sympathetic nervous system is the component of the ANS that is responsible for controlling the human bodys reaction to situations of stress or emergency , while the parasympathetic nervous system is generally responsible for basal organ system function.
Cardiac sympathetic preganglionic nerves emerge from the upper thoracic segments of the spinal cord . After traveling a short distance, preganglionic fibers leave the spinal nerves through branches called white rami and enter sympathetic ganglia. The cardiac sympathetic neurons form the sympathetic chain ganglia located along the side of the viscera column . These ganglia comprise the sympatheric trunks with their connecting fibers. The postganglionic fibers, extend to the viscera, such as the heart. In general, sympathetic preganglionic neurons are shorter than sympathetic postganglionic neurons .
Sympathetic receptors: There are two types of adrenergic receptors: and . In the cardiovascular system there are 1, 2, 1, and 2 adrenergic receptors .
Covid Vaccines Ama Recap
Emily also answered WHOOP member questions on the subject via an AMA in our app. Here are some of the highlights not covered in the podcast:
Hi Emily! Curious if you have looked at any data on members who logged testing positive for COVID-19 in close proximity to getting vaccinated, and the impact on vaccine symptoms/response? Thank you! Megan M
Hi Megan! We havent actually looked at that yet there are so many interesting questions we havent had time to answer yet! Because vaccine centers arent COVID testing the recipients, we know that a lot of people are unknowingly getting vaccinated with asymptomatic and pre-symptomatic COVID and it doesnt seem to be dangerous, but it is unclear right now how their symptoms would change.
I am interested in the difference in severity of the side effects as well as HRV, RHR, and recovery between men and women after dose 2? Also, do you plan to examine the data on where women are in their menstrual cycles when receiving the vaccine and how that might affect recovery? It looks like there may be a link between higher levels of estrogen and a more robust immune response. Lindsay D
What is something interesting that you all learned that isnt too commonly known from the study? Ray T
Have you seen people who previously had COVID show negative recovery stats after the 1st or 2nd dose of the vaccine or both? Chris V
Also Check: Acid Reflux Heart Fluttering
Causes Of Low Heart Rate
Firstly we will discuss things directly affecting the heart tissue and the conduction system called intrinsic disease. Aging is a common cause of slow heart rate, which results from degeneration of the conduction system of the heart. Heart attacks may damage areas of the conduction system also. Conditions that affect many organs of the body such as sarcoid, lupus and others can also affect the conduction system of the heart. Undergoing heart valve surgery such as the TAVR procedure for aortic stenosis, the mitraclip procedure for mitral regurgitation, mitral valve replacement or mitral valve repair, aortic valve replacement, or other complex heart surgeries may also cause trauma to the conduction system of the heart. Sometimes infection of the heart valves can extend in to the conduction system of the heart also.
Next we will discuss outside influences on the heart and conduction system known as extrinsic causes. Certain situations such as coughing, vomiting and others can lead to slow heart rate through the nerve system. Drugs that directly slow the heart rate include beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers and others. Metabolic disorders such as hypothyroidism can lead to a slow heart rate. Levels of electrolytes such as potassium derangement can lead to a slow heart rate.
Assessing The Pulses: What To Look For
A normal adult pulse will beat regularly between 60 and 100 times each minute at rest; in babies and children they are much faster. Pulses are usually easily palpable; patients with a weak or unstable pulse should be assessed further; weak pulses indicate reduced cardiac output and can progress to deterioration, for example fainting, or perhaps a more serious problem.
The rhythm of the pulses should be regular and consistent; unstable or irregular pulses indicate irregular contractions of the heart and should be referred to a senior clinician. A strong, bounding pulse indicates high blood pressure.
It is important that any deviations from the norm can be easily explained. As mentioned, pain, stress or exertion will increase the pulse rate, but it should return to normal when the underlying trigger is abated. A slower-than-normal pulse can result from some medications, for example digoxin and beta-blockers, and may also be present in people who are accustomed to strenuous activity. In the case of very fit people, a slower pulse results from their heart capacity being enlarged, and therefore needing to beat fewer times to circulate the blood adequately. Required competencies and documentation are listed in Box 1.
Box 1. Required competencies and documentation
- Posterior tibial;
- Dorsal pedal.
Carotid pulse
Brachial pulse
Radial pulse
Femoral pulse
Posterior tibial pulse
Dorsal pedal pulse
Read Also: How Do You Calculate Max Heart Rate
Before You Measure Your Blood Pressure:
- Rest for three to five minutes without talking before taking a measurement.
- Sit in a comfortable chair, with your back supported and your legs and ankles uncrossed.
- Sit still and place your arm, raised level with your heart, on a table or hard surface.
- Wrap the cuff smoothly and snugly around the upper part of your arm. The cuff should be sized to fit smoothly, while still allowing enough room for one fingertip to slip under it.
- Be sure the bottom edge of the cuff is at least one inch above the crease in your elbow.
It is also important, when taking blood pressure readings, that you record the date and time of day you are taking the reading, as well as the systolic and diastolic measurements. This will be important information for your doctor to have. Ask your doctor or another health care professional to teach you how to use your blood pressure monitor correctly. Have the monitor routinely checked for accuracy by taking it with you to your doctor’s office. It is also important to make sure the tubing is not twisted when you store it and keep it away from heat to prevent cracks and leaks.
Proper use of your blood pressure monitor will help you and your doctor in monitoring your blood pressure.
About The Digital Monitor
The digital monitor is automatic, with the measurements appearing on a small screen. Because the recordings are easy to read, this is the most popular blood pressure measuring device. It is also easier to use than the aneroid unit, and since there is no need to listen to heartbeats through the stethoscope, this is a good device for hearing-impaired patients. One disadvantage is that body movements or an irregular heart rate can change the accuracy. These units are also more expensive than the aneroid monitors.
Don’t Miss: Does Tylenol Increase Heart Rate
Foods That Lower Resting Heart Rate
People in the Blue Zones, areas where people live longer than average, eat plenty of beans. One reason beans are so healthy is that they can help lower your pulse.
In one study, participants were given a cup a day of beans, chickpeas, or lentils. Participants lowered their resting heart rate from an average of 74.1 to 70.7, a 3.4 point drop. The change was similar to those in the other study who exercised for 250 hours!
You might consider eating beans regularly to keep your resting heart rate in a healthy range. Beans are also an excellent source of vegan protein.
How Are Arrhythmias Treated
Many arrhythmias dont need treatment. For those that do,;these options might be used:
- Medicines. Many types of prescription anti-arrhythmic medicines are available to treat arrhythmia. Sometimes, these can increase symptoms and cause side effects, so the patient will be closely watched by the doctor.
- Pacemakers. A pacemaker is a small battery-operated device implanted into the body through a surgical procedure. Connected to the heart by a wire, a pacemaker can detect if the heart rate is too slow and send electrical signals to speed up the heartbeat.
- Defibrillators. A small battery-operated implantable cardioverter defibrillator is surgically placed near the left collarbone. Wires run from the defibrillator to the heart. The ICD senses if the heart has a dangerously fast or irregular rhythm and sends an electrical signal to restore a normal heartbeat.
- Catheter ablation.;A catheter is guided through a vein in the leg to the heart. Arrhythmias often are caused by microscopic defects in the heart muscle. Once the problem area of the heart is pinpointed, the catheter heats or freezes the defective muscle cells and destroys them.
- Surgery. Surgery is usually the treatment recommended only if all other options have failed. In this case, a person is put under anesthesia and a surgeon removes the tissue causing the arrhythmia.
You May Like: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
Read Also: How Much Can Marijuana Increase A Person’s Heart Rate
Correlation Between Heart Rates And Cardiac Output
Initially, physiological conditions that cause HR to increase also trigger an increase in SV. During exercise, the rate of blood returning to the heart increases. However as the HR rises, there is less time spent in diastole and consequently less time for the ventricles to fill with blood. Even though there is less filling time, SV will initially remain high. However, as HR continues to increase, SV gradually decreases due to decreased filling time. CO will initially stabilize as the increasing HR compensates for the decreasing SV, but at very high rates, CO will eventually decrease as increasing rates are no longer able to compensate for the decreasing SV. Consider this phenomenon in a healthy young individual. Initially, as HR increases from resting to approximately 120 bpm, CO will rise. As HR increases from 120 to 160 bpm, CO remains stable, since the increase in rate is offset by decreasing ventricular filling time and, consequently, SV. As HR continues to rise above 160 bpm, CO actually decreases as SV falls faster than HR increases. So although aerobic exercises are critical to maintain the health of the heart, individuals are cautioned to monitor their HR to ensure they stay within the target heart rate range of between 120 and 160 bpm, so CO is maintained. The target HR is loosely defined as the range in which both the heart and lungs receive the maximum benefit from the aerobic workout and is dependent upon age.
