Congestive Heart Failure Lab Work Up
Definition of the congestive heart failure
Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive heart failure
Clinical presentation of heart failure
Is Catheterization Indicated/useful
Most of the times the non-invasive studies above should provide you sufficient information to manage the patient. In some cases the state of coronary artery disease may be needed. In such cases an LV catheterization maybe done.
Patients not responding to standard therapy may need right heart catheterization to choose and to monitor therapy.
Management will be the next topic.
Point Of Maximal Impulse
The point of maximal impulse of the left ventricle is usually located in the midclavicular line at the fifth intercostal space. With the patient in a sitting position, the physician uses fingertips to identify this point. Cardiomegaly usually displaces the cardiac impulse laterally and downward.
At times, the point of maximal impulse may be difficult to locate and therefore loses sensitivity . Yet the location of this point remains a specific indicator for evaluating the size of the heart.14
Don’t Miss: What Is My Target Heart Rate To Burn Fat
Three Of The Most Important Labs
There are a lot of tests everyone with heart failure will have drawn and should know about, but these are three of what I would consider the most important. It is good to understand lab values so you know when and why you could be out of the normal range, but it is never good to try to correct them without your doctor being involved in the method of how you do it. Hopefully, this helps you understand these lab values better and motivates you to research other lab values on your own.
What Causes Heart Failure

Although the risk of heart failure doesnt change as you get older, youre more likely to have heart failure when youre older.
Many medical conditions that damage the heart muscle can cause heart failure. Common conditions include:
- Tobacco and recreational drug use.
- Medications. Some drugs used to fight cancer can lead to heart failure.
Also Check: What Is A Good Heart Rate For Exercise
Coronary Catheterization And Angiogram
In coronary catheterization and angiogram, your doctor uses X-ray images taken in real time to create cross-sectional images of the heart. This enables the doctor to determine how well the heart is pumping blood to the rest of the body and to view any blockages in the blood vessels.
After you are given local anesthesia and a sedative, your doctor guides a small, hollow tube called a catheter into a puncture in a vein in the arm or groin. He or she advances it through the aorta, the bodys largest artery, to the heart.
An X-ray instrument called a fluoroscope is inserted into the catheter and led to the heart to provide live X-rays of the hearts chambers. Your doctor also injects a contrast agent into the catheter to highlight any blockages.
Diagnostic Tests And Procedures
This animation discusses some of the tests used to diagnose heart failure. These tests may include an electrocardiogram to look at your hearts electrical activity, an echocardiogram to measure how well your heart is working and look at the structure, and a chest X-ray to see if your heart is enlarged or there is fluid in your lungs. Other tests may include blood tests and an exercise, or stress test. .
Don’t Miss: Can Heart Failure Get Better
Assessment Of Functional Capacity
Cardiopulmonary stress testing can help in the assessment of a patients chance of survival within the next year, as well as determine the need for referral for either cardiac transplantation or implantation of mechanical circulatory support. A 6-minute walk test evaluates the distance walked, dyspnea index on a Borg scale from 0 to 10, oxygen saturation, and heart rate response to exercise. A normal value is walking more than 1500 feet. Patients who walk less than 600 feet have severe cardiac dysfunction and a worse short- and long-term prognosis.
References
Ho KK, Pinsky JL, Kannel WB, Levy D. The epidemiology of heart failure: the Framingham Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1993 Oct. 22:6A-13A. . .
American Heart Association. Classes of heart failure. Available at . Updated: May 8, 2017 Accessed: June 18, 2017.
Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, et al, American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. Circulation. 2013 Oct 15. 128:e240-327. . .
Pina IL. Key points from the new heart failure guidelines . TheHeart.org. Available at . May 4, 2022 Accessed: May 6, 2022.
How Is Congestive Heart Failure Treated
Advanced treatment approaches are extending and improving quality-of-life for patients with congestive heart failure. Congestive heart failure is treated and managed through a combination of lifestyle modifications and a wide range of therapies, including medication and interventions, which help the heart to work more effectively and alleviate heart failure symptoms. Pacemakers and ventricular assist devices can make it easier for heart the heart to pump blood and remain in rhythm. For some patients with advanced heart failure, a heart transplant may be an option.
Don’t Miss: Chest Pain Low Heart Rate
What Makes Yale Medicines Approach To Treating Congestive Heart Failure Unique
Yale Medicines team comprises heart failure cardiologists and cardiac surgeons, dedicated advanced-practice, registered nurses and nurse coordinators, dietitians, exercise physiologists, financial counselors, immunologists specializing in transplants, psychologists, and specialists in palliative care.
With a multidisciplinary approach, Yale Medicine physicians include the patients desires as well as input from the family to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that’s right for them.
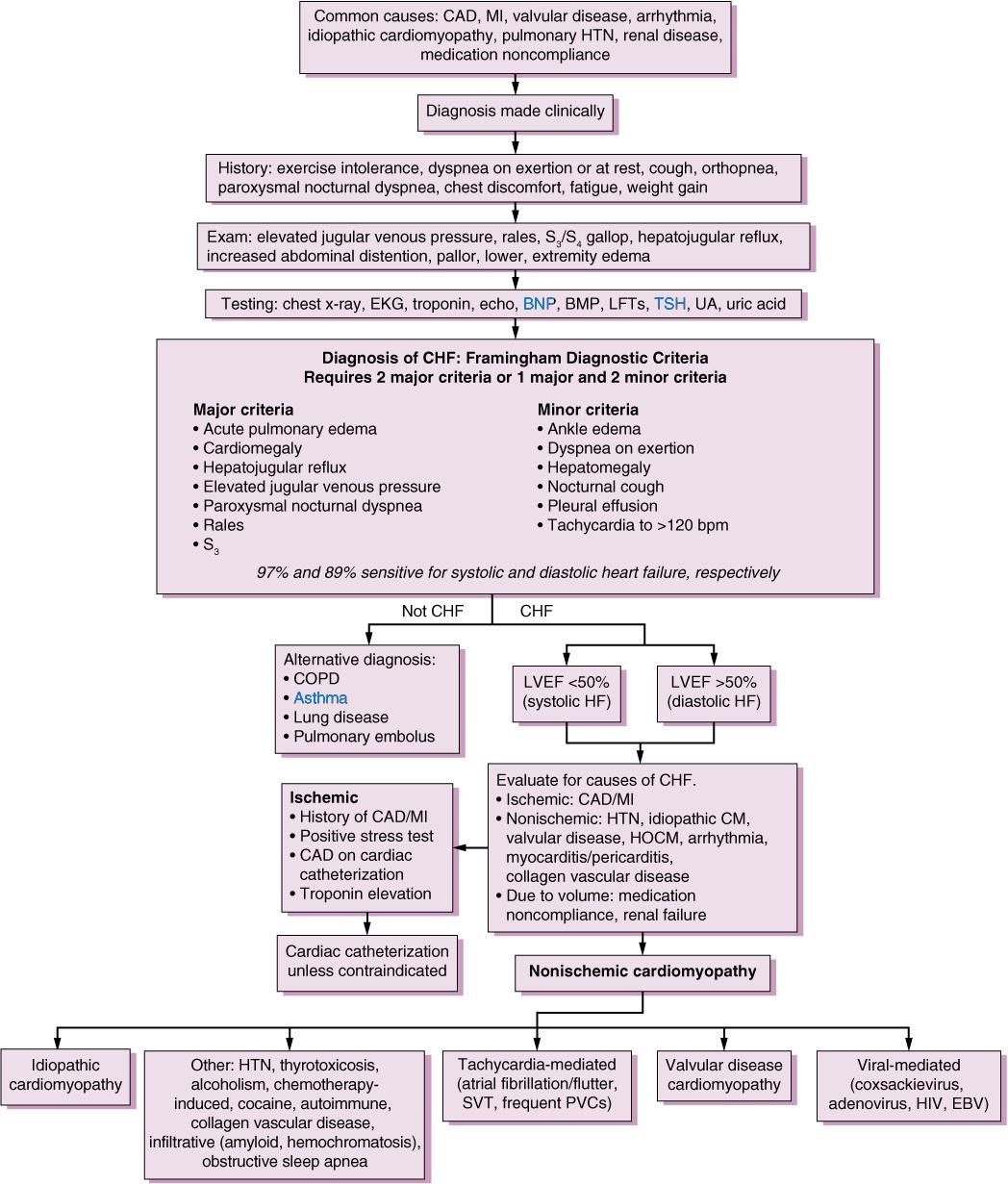
History And Physical Examination
Patients with heart failure can have decreased exercise tolerance with dyspnea, fatigue, generalized weakness, and fluid retention, with peripheral or abdominal swelling and possibly orthopnea.3 Patient history and physical examination are useful to evaluate for alternative or reversible causes .3,4,8 Nearly all patients with heart failure have dyspnea on exertion. However, heart failure accounts for only 30 percent of the causes of dyspnea in the primary care setting.24 The absence of dyspnea on exertion only slightly decreases the probability of systolic heart failure, and the presence of orthopnea or paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea has a small effect in increasing the probability of heart failure .21,23
The presence of a third heart sound is an indication of increased left ventricular end-diastolic pressure and a decreased LVEF. Despite being relatively uncommon findings, a third heart sound and displaced cardiac apex are good predictors of left ventricular dysfunction and effectively rule in the diagnosis of systolic heart failure .21,23
Read Also: Does Prednisone Cause Heart Palpitations
Tests To Measure Your Ejection Fraction
Your provider may order an echocardiography or other imaging tests to measure your ejection fraction. Your ejection fraction is the percent of the blood in the lower left chamber of your heart that is pumped out of your heart with each heartbeat. Ejection fraction measures how well your heart pumps. This helps diagnose the type of heart failure you have and guides your treatment.
- If 40% or less of the blood in your left ventricle is pumped out in one beat, you have heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
- If 50% or more of the blood in your left ventricle is pumped out in one beat, you have heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.
- If your ejection fraction is somewhere in between 41% to 49%, you may be diagnosed with heart failure with borderline ejection fraction.
Congestive Heart Failure: Prevention Treatment And Research
Congestive heart failure is a serious condition in which the heart doesnt pump blood as efficiently as it should. Despite its name, heart failure doesnt mean that the heart has literally failed or is about to stop working. Rather, it means that the heart muscle has become less able to contract over time or has a mechanical problem that limits its ability to fill with blood. As a result, it cant keep up with the bodys demand, and blood returns to the heart faster than it can be pumped outit becomes congested, or backed up. This pumping problem means that not enough oxygen-rich blood can get to the bodys other organs.
The body tries to compensate in different ways. The heart beats faster to take less time for refilling after it contractsbut over the long run, less blood circulates, and the extra effort can cause heart palpitations. The heart also enlarges a bit to make room for the blood. The lungs fill with fluid, causing shortness of breath. The kidneys, when they dont receive enough blood, begin to retain water and sodium, which can lead to kidney failure. With or without treatment, heart failure is often and typically progressive, meaning it gradually gets worse.
More than 5 million people in the United States have congestive heart failure. Its the most common diagnosis in hospitalized patients over age 65. One in nine deaths has heart failure as a contributing cause.
Also Check: What Is The Difference Between Heart Rate And Blood Pressure
What Are The Complications Of Heart Failure
Some of the complications from heart failure include:
- Irregular heartbeat.
- History of taking drugs that can damage your heart muscle, such as some cancer drugs.
Stage B
Stage B is considered pre-heart failure. It means your healthcare provider has given you a diagnosis of systolic left ventricular dysfunction but youve never had symptoms of heart failure. Most people with Stage B heart failure have an echocardiogram that shows an ejection fraction of 40% or less. This category includes people who have heart failure and reduced EF due to any cause.
Stage C
People with Stage C heart failure have a heart failure diagnosis and currently have or previously had signs and symptoms of the condition.
There are many possible symptoms of heart failure. The most common are:
- Shortness of breath.
- Need to urinate while resting at night.
- Rapid or irregular heartbeats .
- A dry, hacking cough.
- A full or hard stomach, loss of appetite or upset stomach .
There may be times that your symptoms are mild or you may not have any symptoms at all. This doesn’t mean you no longer have heart failure. Symptoms of heart failure can range from mild to severe and may come and go.
Unfortunately, heart failure usually gets worse over time. As it worsens, you may have more or different signs or symptoms.Its important to let your doctor know if you have new symptoms or if your symptoms get worse.
What Is A Cardiac Risk Assessment
This is a group of tests and health factors that have been proven to indicate your chance of having a cardiovascular event such as a heart attack or stroke. They have been refined to indicate the degree of risk: borderline, intermediate, or high risk.
Perhaps the most important indicators for cardiac risk are your personal health history. These include:
- Pre-existing heart disease, or already having had a heart attack
There are some imaging tests that may be used in cardiac risk assessment. Non-invasive tests may include, for example, an electrocardiogram or a stress test, also called ECG stress test or metabolic stress test. Invasive tests may also be used to evaluate for the presence of cardiovascular disease , but they are usually used for diagnostic purposes in people with signs and symptoms and not for risk assessment. Examples include an angiography/arteriography and cardiac catheterization.
The lipid panel is the most important blood test for cardiac risk assessment.
Don’t Miss: Target Heart Rate For Cardio
What Are The Most Common Symptoms Of Congestive Heart Failure
Swelling is the most common symptom of congestive heart failure. Often, swelling is most apparent in the extremities, especially in the legs and ankles, but it can occur in other parts of the body as well. Fluid collection in and around the lungs can cause shortness of breath , especially during physical activity or when lying down. Other common symptoms of heart failure include fatigue, loss of appetite, and weight gain.
How Are Blood Tests Performed
Blood tests may be performed in a lab or providers office.1-2 They are a typical part of a routine exam. Sometimes blood tests are done before you eat for the day, after an 8-12 hour fast. Samples of blood are drawn by a needle from a vein in the arm into test tubes which are then analyzed by a lab for the levels of specific components.2
Also Check: Is 105 Heart Rate High
Biomarkers Indications For Use
Abbreviations:ACC: American College of Cardiology, AHA: American Heart Association, ADHF: acute decompensatedheart failure, BNP: B-type natriuretic peptide, COR: Class of Recommendation, ED: emergency department, HF: heart failure, NT-proBNP: N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide, NYHA: New York Heart Association, pts: patients
Other biomarkers of injury or fibrosis include soluble ST2 receptor, galectin-3, and high-sensitivity troponin.
Stages Of Heart Failure
When you’re diagnosed with heart failure, your doctor will usually be able to tell you what stage it is.
The stage describes how severe your heart failure is.
It’s usually given as a class from 1 to 4, with 1 being the least severe and 4 being the most severe:
- class 1 you don’t have any symptoms during normal physical activity
- class 2 you’re comfortable at rest, but normal physical activity triggers symptoms
- class 3 you’re comfortable at rest, but minor physical activity triggers symptoms
- class 4 you’re unable to carry out any physical activity without discomfort and may have symptoms even when resting
Knowing the stage of your heart failure will help your doctors decide which treatments they think are best for you.
Page last reviewed: 19 May 2022 Next review due: 19 May 2025
Don’t Miss: How To Lower Your Heart Rate Fast
What Is The Importance Of Ejection Fraction
Your ejection fraction is one way to measure the severity of your condition. If its below normal, it can mean that you have heart failure. Your ejection fraction tells your healthcare provider how good of a job your left or right ventricle is doing at pumping blood. Usually, your EF number is talking about how much blood your left ventricle is pumping out because its your heart’s main pumping chamber.
Several non-invasive tests can measure your EF. With this information, your healthcare provider can decide how to treat you or find out if a treatment is working as it should.
A normal left ventricular ejection fraction is 53% to 70%. An LVEF of 65%, for example, means that 65% of the total amount of blood in your left ventricle is pumped out with each heartbeat. Your EF can go up and down, based on your heart condition and how well your treatment works.
How Is Chf Diagnosed
After reporting your symptoms to your doctor, they may refer you to a heart specialist, or cardiologist.
The cardiologist will perform a physical exam, which will involve listening to your heart with a stethoscope to detect abnormal heart rhythms.
To confirm an initial diagnosis, a cardiologist might order certain diagnostic tests to examine your hearts valves, blood vessels, and chambers.
There are a variety of tests used to diagnose heart conditions. Because these tests measure different things, your doctor may recommend a few to get a full picture of your current condition.
Recommended Reading: Repair Heart Valve Surgery
Natriuretic Peptides: Bnp Or Nt
- Plasma concentrations of NPs are recommended as initial diagnostic tests in patients with symptoms suggestive of HF to rule out the diagnosis.
- Elevated concentrations support a diagnosis of HF.
- Other causes of an elevated NP include atrial fibrillation, increasing age, and acute or chronic kidney disease.
- NP concentrations may be low in obesepatients.
- The upper limits of normal in the non-acute setting are 35 pg/mL for BNP, and 125 pg/mL for NT-proBNP.
The CoDE-HF decision support tool may help diagnose heart failure. The CoDE-HF interprets the N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide in various settings including obesity.
| Causes of elevated concentrations of natriuretic peptides |
- BNP or its amino-terminal cleavage equivalent is generated by cardiomyocytes in the context of numerous triggers, most notably myocardial stretch.
- BNP levels may be useful in the initial establishment of the diagnosis of heart failure in the patient with dyspnea of unclear etiology. In a meta-analysis, BNP was superior N-terminal pro-BNP and was associated with a sensitivity of 85% and specificity of 84% in the diagnosis of heart failure in the primary care setting.
- These biomarkers have been studied for the detection of elevated cardiac pressures., low ejection fraction, or both.
- Clinical practice guidelines suggest their measurement is helpful for diagnosis or ruling out heart failure especially in the acute settings.
