Is There A Treatment For Heart Failure
There are more treatment options available for heart failure than ever before. Tight control over your medications and lifestyle, coupled with careful monitoring, are the first steps. As the condition progresses, doctors specializing in the treatment of heart failure can offer more advanced treatment options.
The goals of treating heart failure are to try to keep it from getting worse , to ease symptoms, and to improve quality of life.
Some common types of medicines used to treat it are:
- ACE inhibitors
- Aldosterone antagonists
- ARBs
- ARNIs
- Selective sinus node inhibitors
- Soluble guanylate cyclase stimulator
Your doctor may also recommend a program called cardiac rehabilitation to help you exercise safely and keep up a heart-healthy lifestyle. It usually includes workouts that are designed just for you, education, and tips to lower your chance of heart trouble, like quitting smoking or changing your diet.
Cardiac rehab also offers emotional support. You can meet people like you who can help you stay on track.
Precipitating Causes Of Heart Failure
A previously stable, compensated patient may develop heart failure that is clinically apparent for the first time when the intrinsic process has advanced to a critical point, such as with further narrowing of a stenotic aortic valve or mitral valve. Alternatively, decompensation may occur as a result of the failure or exhaustion of the compensatory mechanisms but without any change in the load on the heart in patients with persistent, severe pressure or volume overload. In particular, consider whether the patient has underlying coronary artery disease or valvular heart disease.
The most common cause of decompensation in a previously compensated patient with heart failure is inappropriate reduction in the intensity of treatment, such as dietary sodium restriction, physical activity reduction, or drug regimen reduction. Uncontrolled hypertension is the second most common cause of decompensation, followed closely by cardiac arrhythmias . Arrhythmias, particularly ventricular arrhythmias, can be life threatening. Also, patients with one form of underlying heart disease that may be well compensated can develop heart failure when a second form of heart disease ensues. For example, a patient with chronic hypertension and asymptomatic LV hypertrophy may be asymptomatic until an MI develops and precipitates heart failure.
- Profound anemia
- Pregnancy
- Nutritional deficiencies
Systolic And Diastolic Failure
Systolic and diastolic heart failure each result in a decrease in stroke volume. This leads to activation of peripheral and central baroreflexes and chemoreflexes that are capable of eliciting marked increases in sympathetic nerve traffic.
Although there are commonalities in the neurohormonal responses to decreased stroke volume, the neurohormone-mediated events that follow have been most clearly elucidated for individuals with systolic heart failure. The ensuing elevation in plasma norepinephrine directly correlates with the degree of cardiac dysfunction and has significant prognostic implications. Norepinephrine, while directly toxic to cardiac myocytes, is also responsible for a variety of signal-transduction abnormalities, such as downregulation of beta1-adrenergic receptors, uncoupling of beta2-adrenergic receptors, and increased activity of inhibitory G-protein. Changes in beta1-adrenergic receptors result in overexpression and promote myocardial hypertrophy.
You May Like: What Takes Blood Away From The Heart
What Is The Prognosis For Children With Congenital Heart Defects
The prognosis depends on the defect. In many cases, children with congenital heart defects go on to live normal lives. In most cases, people with heart defects are at greater risk for developing infection of the heart and valves. They may need to take antibiotics when having certain dental or surgical procedures in order to prevent endocarditis, an infection of the hearts lining.
Our Favorite Online Support Groups
Sponsored by the American Association of Heart Failure Nurses, this online support community for anyone who has been affected by heart failure allows you to connect with others and to hear from real medical experts. There is also a resource section that has information on things like low-salt cookbooks and patient tips for getting through the holidays.
This network has tracks for various heart conditions, where you can post questions, share your story, and learn more about your condition. Once you sign up to become a part of the community, you will receive personalized content based on your condition and concerns.
Also Check: Home Is Where The Heart Attack Is
Treatment And Medication Options For Congestive Heart Failure
Heart failure is a chronic condition, and there is no cure. However, once youve been diagnosed, there are several things you can do to treat the condition and manage it so that it does not progress. Chief among them are lifestyle changes. That includes exercising and maintaining a heart-healthy diet thats low in saturated fat, trans fats, and cholesterol.
What Can Be Done To Prevent Pediatric Congenital Heart Defects
In most cases, there is no way to prevent heart defects. However, certain precautions can be taken:
- A pregnant woman should not drink alcohol or take drugs that have not been prescribed to her.
- Women with certain chronic conditions should ask their doctors for advice on medications or special diets before they become pregnant.
- A woman who is able to become pregnant should get 400 micrograms of folate or folic acid per day to prevent birth defects.
Recommended Reading: Does Diltiazem Lower Heart Rate
Improving Quality Of Life
Currently, CHF has no cure. People living with the disease have to commit to heart-healthy lifestyles and take medication regularly.
To stay healthy, here are some tips to follow.
Tips for Living Better with CHF
- Monitor symptoms and check for sudden weight gain and swelling in legs and feet.
- Monitor blood pressure and weight and get lab work done regularly to be aware of your heart health and disease progression.
- Stay positive and find ways to alleviate stress including finding relaxing hobbies, talking to a therapist, finding a support group or talking to loved ones and friends.
- Ask questions about the stage of your disease and guidelines for how active you should be. This includes work, sex and exercise. Depending on the stage of disease, your doctor will have different recommendations about how active you should be, including work, sexm and exercise.
- Keep all appointments with your doctors.
- Make all the lifestyle changes your doctor recommends. If you need help with your diet, ask to see a nutritionist or dietician.
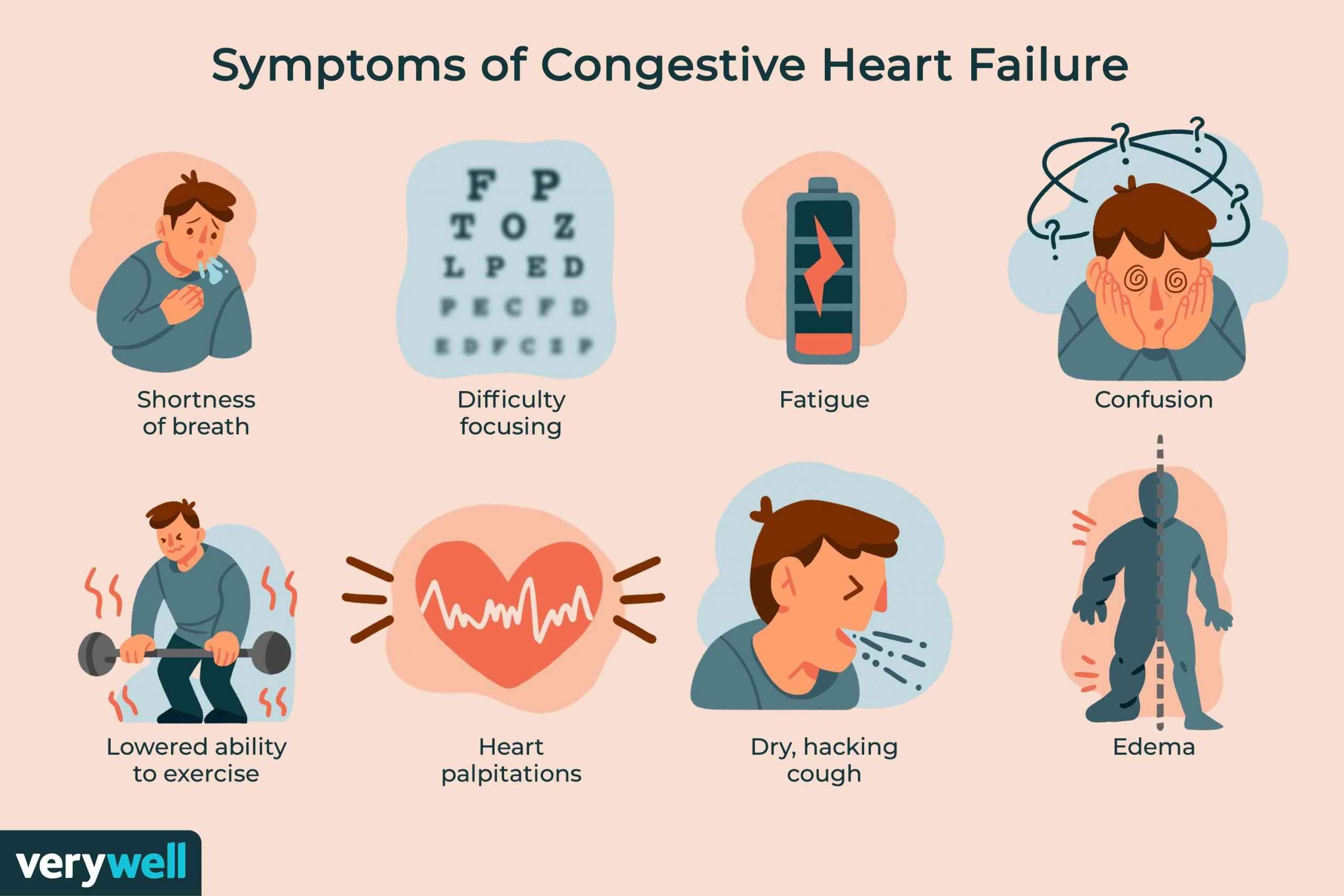
What Are The Symptoms Of Heart Failure
You may not have any symptoms of heart failure, or the symptoms may be mild to severe. Symptoms can be constant or can come and go. The symptoms can include:
- Congested lungs. Fluid backup in the lungs can cause shortness of breath with exercise or difficulty breathing at rest or when lying flat in bed. Lung congestion can also cause a dry, hacking cough or wheezing.
- Fluid and water retention. Less blood to your kidneys causes fluid and water retention, resulting in swollen ankles, legs, abdomen , and weight gain. Symptoms may cause an increased need to urinate during the night. Bloating in your stomach may cause a loss of appetite or nausea.
- Dizziness, fatigue, and weakness. Less blood to your major organs and muscles makes you feel tired and weak. Less blood to the brain can cause dizziness or confusion.
- Rapid or irregular heartbeats. The heart beats faster to pump enough blood to the body. This can cause a rapid or irregular heartbeat.
If you have heart failure, you may have one or all of these symptoms or you may have none of them. They may or may not indicate a weakened heart.
Read Also: What Should Resting Heart Rate Be For A Woman
Diagnosis Of Congestive Heart Failure
If you have symptoms of CHF, your healthcare provider will consider your diagnosis based on a review of your symptoms, a physical examination, blood tests, imaging tests, and other diagnostics designed to measure heart function.
If you have CHF, it will be classified to direct the appropriate course of treatment.
How Is Congestive Heart Failure Treated
Doctors will assess the current health status of the patient to establish a baseline, and develop a long-term health plan with the goal of improving the patients health. This may involve the optimization of medicines and therapies, adding new medication, or possibly enrollment in a clinical trial.
Stabilizing and/or reversing a patients condition often involves long-term, collaborative follow-up with a referring cardiologist or physician.
In serious situations, advanced therapies, which include mechanical solutions, a heart transplant, or hospice, may be offered.
Also Check: What Age Can You Have A Heart Attack
Outlook For Heart Failure
Heart failure is a serious long-term condition that will usually continue to get slowly worse over time.
It can severely limit the activities you’re able to do and is often eventually fatal.
But it’s very difficult to tell how the condition will progress on an individual basis.
It’s very unpredictable. Lots of people remain stable for many years, while in some cases it may get worse quickly.
Center For Advanced Heart Failure/cardiomyopathy At Brigham And Womens Hospital
The Center for Advanced Heart Failure/Cardiomyopathy, an integral part of the Heart & Vascular Center at Brigham and Womens Hospital , brings together heart failure experts, including cardiologists, interventional cardiologists, cardiac surgeons, cardiovascular imaging specialists, congenital heart disease specialists, and many others, to care for patients as one team. Together, the team tailors therapies to each patients needs, offering the latest medical, interventional, and surgical approaches to congestive heart failure treatment.
Also Check: What Are Signs Of A Heart Attack
Why Is This Treatment Done/used
A heart transplant is a last-resort treatment when you have end-stage heart failure. That means your heart has permanent damage or weakness that keeps it from pumping enough blood to your body.
This kind of heart failure can happen for a wide variety of reasons, ranging from infections that damage your heart muscle to abnormal heart rhythms that may cause a reversible weakening of the heart.
Diagnoses most likely to result in heart transplant
The following conditions make up the majority of reasons for heart transplant:
- Cardiomyopathy. This refers to any disease that damages your heart muscle . Diseases that cause this kind of damage include infections, genetic diseases and damage from medical treatments .
- Coronary artery disease. This is a condition that affects the arteries that supply your heart. Its a common cause of heart attack.
- Congenital heart disease. This is any heart disease you have when youre born.
- Valvular heart disease. These are conditions that involve damage to your heart valves.
- Retransplants. These are instances where a person needs a second transplant to replace the first. This can happen because the donor’s body rejects the first transplanted heart or for other reasons.
What Is Congestive Heart Failure
CHF usually develops over a long period of time. The course and symptoms of heart failure depend on which regions of the heart are affected.
CHF can lead to severe complications, and the condition requires ongoing medical treatment.
Types of CHF include:
- Right-sided heart failure: The heart does not sufficiently accommodate blood returning from the rest of the body.
- Left-sided heart failure: The heart cannot efficiently pump oxygenated blood throughout the body,
CHF can also be caused by heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Heart failure on one side of the heart predisposes to heart failure on the other side, so it is common to have both types.
Don’t Miss: What Does It Mean When Your Heart Rate Is High
New Moms And Heart Failure Risk
The research supports the notion that at-risk women need closer observation during that time period.
The researchers also say that because many women are discharged from hospital care just a couple of days after giving birth and arent given a follow-up appointment until about six weeks later, the way doctors regard women who might be at risk of heart failure needs to change.
They call for comprehensive postpartum discharge health education, with emphasis on signs and symptoms to look for and when or where to seek immediate care.
What Happens Before This Procedure
Because there are far more people who need hearts than donors, there’s a strict selection process that you have to undergo to receive a heart transplant. The goal of this process is to select recipients who have the best chance of long-term survival based on their overall health.
After a healthcare provider refers you to a transplant program, youll undergo the following.
Medical evaluation
To ensure that donor hearts go to people with the best chance of survival, healthcare providers will evaluate your overall health by running several different tests. Some, but not all, of the possible tests are listed below.
Lab tests will include tests on your blood, urine and other screenings. These tests will look for the following:
- Blood composition. This analyzes your bloods levels of red blood cells, platelets, and more. These tests will also analyze your blood chemistry, looking for signs of other conditions that might affect your ability to undergo a heart transplant.
- Immune system analysis. These tests help providers anticipate how well your immune system can tolerate a donor organ.
- Kidney function. These tests analyze your urine to see how well your kidneys are working.
- Tests for alcohol, tobacco and drugs. These are often important tests if you have a history of using recreational drugs or drinking too much alcohol. Most transplant centers require that youre sober and avoid using tobacco products and recreational drugs for an extended time before your transplant.
Recommended Reading: Can Lisinopril Cause Heart Palpitations
Universal Definition And Classification Of Heart Failure: A Step In The Right Direction From Failure To Function
- A
Quick Takes
- The proposed universal definition describes HF as a clinical syndrome with symptoms and/or signs caused by a structural and/or functional cardiac abnormality and corroborated by elevated natriuretic peptide levels and/or objective evidence of pulmonary or systemic congestion.
- HF stages have been revised to emphasize symptomatic nature of HF as a clinical syndrome: At risk for HF , PreHF , Symptomatic HF and Advanced HF .
- Classification of HF according to LVEF now includes:
- HFrEF: symptomatic HF with LVEF 40%
- HFmrEF: symptomatic HF with LVEF 41-49%
- HFpEF: symptomatic HF with LVEF 50%
- HFimpEF: symptomatic HF with a baseline LVEF 40%, a 10-point increase from baseline LVEF, and a second measurement of LVEF > 40%
A revised classification of HF by left ventricular ejection fraction was also proposed and is as follows:
Figure 1. Courtesy of Gibson GT, Blumer V, Mentz RJ, Lala A.
Figure 1
The new Universal Definition and Classification of HF represents a landmark advancement in our field. The standardization of the definition of HF is valuable for several reasons:
References
What Are The Advantages And Disadvantages Of This Procedure
The biggest advantage of heart transplantation is that its a life-saving option when other options didnt work, were too risky to use, or were unlikely to help.
The biggest disadvantages of heart transplant are:
- More people need a heart transplant than there are available donor hearts.
- Its an extremely complicated surgery, limiting it to only the most well-equipped and best-staffed hospitals.
- Some people may be too ill to survive the procedure.
- The procedure has several potential risks and complications .
What are the risks or complications of this procedure?
The most common risks and complications of heart transplant include the following:
- Organ rejection.
- Infections .
- Graft failure .
Read Also: Which Heart Chamber Sends Deoxygenated Blood To The Lungs
How Does Heart Failure Affect The Quality Of Life And Lifestyle
With the right care and treatment plan, many adults still enjoy life even though heart failure limits their activities. How well you feel depends on:
- How well your heart muscle is working.
- Your symptoms.
- How well you respond to your treatment plan.
- How well you follow your treatment plan.
This includes caring for yourself by:
- Taking your medications.
- Tracking and reporting new or worsening symptoms to your provider.
- Keeping regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider.
Because heart failure is a chronic, long-term illness, talk to your doctor and your family about your preferences for medical care. You can complete an advance directive or living will to let everyone involved in your care know what you want. A living will details the treatments you do or dont want to prolong your life. Its a good idea to prepare a living will while you are well in case you arent able to make these decisions at a later time.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
If you have heart failure, you can take steps to improve your heart health. Take your medications as instructed, follow a low-sodium diet, stay active or become physically active, take notice of sudden changes in your weight, live a healthy lifestyle, keep your follow-up appointments and track your symptoms. Talk to your healthcare provider about questions or concerns you have about your medications, lifestyle changes or any other part of your treatment plan.
References
What Are The Different Types Of Chf
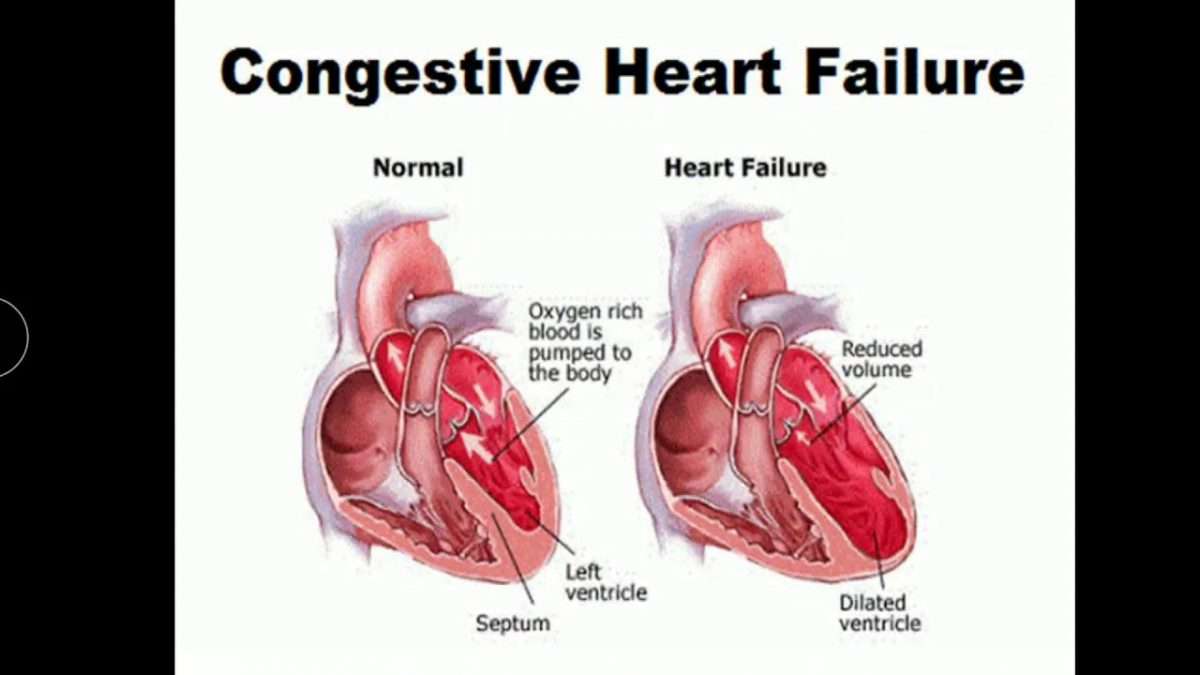
Heart failure can occur on the left side of the heart, the right side, or both. Most commonly, it begins in the heart’s primary pumping chamber – the left ventricle. Each specific type of CHF is accompanied by its own distinct characteristics:
- Right-sided CHF – Right-sided CHF develops when the right ventricle struggles to deliver blood to the lungs. As blood backs up into the blood vessels, the body begins to retain fluid in the abdomen and lower body.
- Left-sided CHF – Left-sided CHF is the most common form of CHF and begins when the left ventricle cannot effectively deliver blood throughout the body. Eventually, this can lead to fluid retention throughout the body, particularly around the lungs.
Cases of left-sided CHF can be further classified into one of two sub-types, characterized by the manner in which the ventricle is affected:
- Systolic CHF – Systolic CHF occurs when the left ventricle is unable to contract with enough force to circulate blood properly.
- Diastolic CHF – Diastolic CHF occurs when the heart muscle becomes stiff. Because the chamber must relax in order to fill with blood between contractions, this stiffness means that an inadequate amount of blood is available to pump out to the rest of the body.
You May Like: Congestive Heart Failure Edema
