Congestive Heart Failure Nursing Diagnosis
Congestive heart failure is a condition in which the heart is unable to pump blood effectively. This can lead to shortness of breath, fluid accumulation in the lungs, and edema of the legs or other parts of the body. The nurses role in caring for patients with CHF is to monitor for signs and symptoms related to congestive heart failure and provide interventions aimed at preventing complications from developing.
What Is Congestive Heart Failure
Heart failure is a chronic, progressive condition. It occurs when the heart is unable to pump effectively and produce enough cardiac output to successfully perfuse the rest of the bodys tissues and organs. An individual can have right-sided or left-sided heart failure as well as systolic or diastolic heart failure.
Left-sided heart failure is also known as Congestive Heart Failure . In CHF, the heart is either unable to contract completely or fill completely during relaxation. It can lead to an inadequate amount of blood pumping out of the heart. Thereby, backing up into the right side and then ultimately to the lungs and throughout the body causing congestion.
Systolic heart failure means the heart is not able to contract completely and affects its ability to pump blood out of the heart.
Diastolic heart failure means the heart is unable to relax fully between heartbeats and allows the appropriate amount of blood into the ventricle.
In this post, well formulate a sample nursing care plan for a patient with Congestive Heart Failure based on a hypothetical case scenario.
Nursing Diagnosis For Complete Heart Block
Cardiovascular system: K14.2,K40.7
Nursing Diagnosis Code: Nursing diagnosis code: 10338: NANDA-I code: K14.2, K40.7
Pain: CHF is usually diagnosed based on observed signs and symptoms of the disease/condition and diagnostic tests such as blood tests, EKGs to evaluate the electrical activity in the heart, and cardiac catheterization to assess blockages affecting blood flow from the heart. Patients with CHF often experience pain throughout their bodies due to poor circulation. However, this is not always a defining characteristic of CHF.
Signs & Symptoms: This may include the potential for long-term changes in mental status, anxiety, and depression.
Trauma: CHF is usually diagnosed based on observed signs and symptoms of the disease/condition and diagnostic tests such as blood tests, EKGs to evaluate the electrical activity in the heart, and cardiac catheterization to assess blockages affecting blood flow from the heart. Patients with CHF often experience pain throughout their bodies due to poor circulation. However, this is not always a defining characteristic of CHF.
Get the following premium features for free after ordering a custom nursing essay from us:
Also Check: Can Low Potassium Cause Heart Palpitations
How To Prevent Complications Of Coronary Artery Disease
If you have confirmed that you have CAD, your doctor may recommend medicines to help treat or prevent the disease from getting worse.
The blood-thinning medicine aspirin prevents clotting in your arteries. It helps reduce the chance of a heart attack or stroke because it keeps atheromatous plaque from sticking to the lining of your arteries.
If you have diabetes and CAD, the possibility of a heart attack or death is much greater. Fortunately, with careful control of blood glucose, it may be possible to reduce these risks.
People who have cardiovascular disease should avoid certain medicines that can cause bleeding in the blood vessels of the brain or gastrointestinal tract. These medicines include aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen unless your doctor says its OK to take them.
Smokers should stop smoking because it can lead to heart disease. If you have CAD and smoke, quitting will reduce your risk of death by 50% or more in the first 20 years after giving up cigarettes.
A healthy lifestyle can also help you prevent the complications of CAD. These include:
-Eating fruits, vegetables, and a low-fat diet
-Exercising for 30 minutes daily
-Not drinking excessive amounts of alcohol
-Controlling your weight
Complications Of Heart Failure
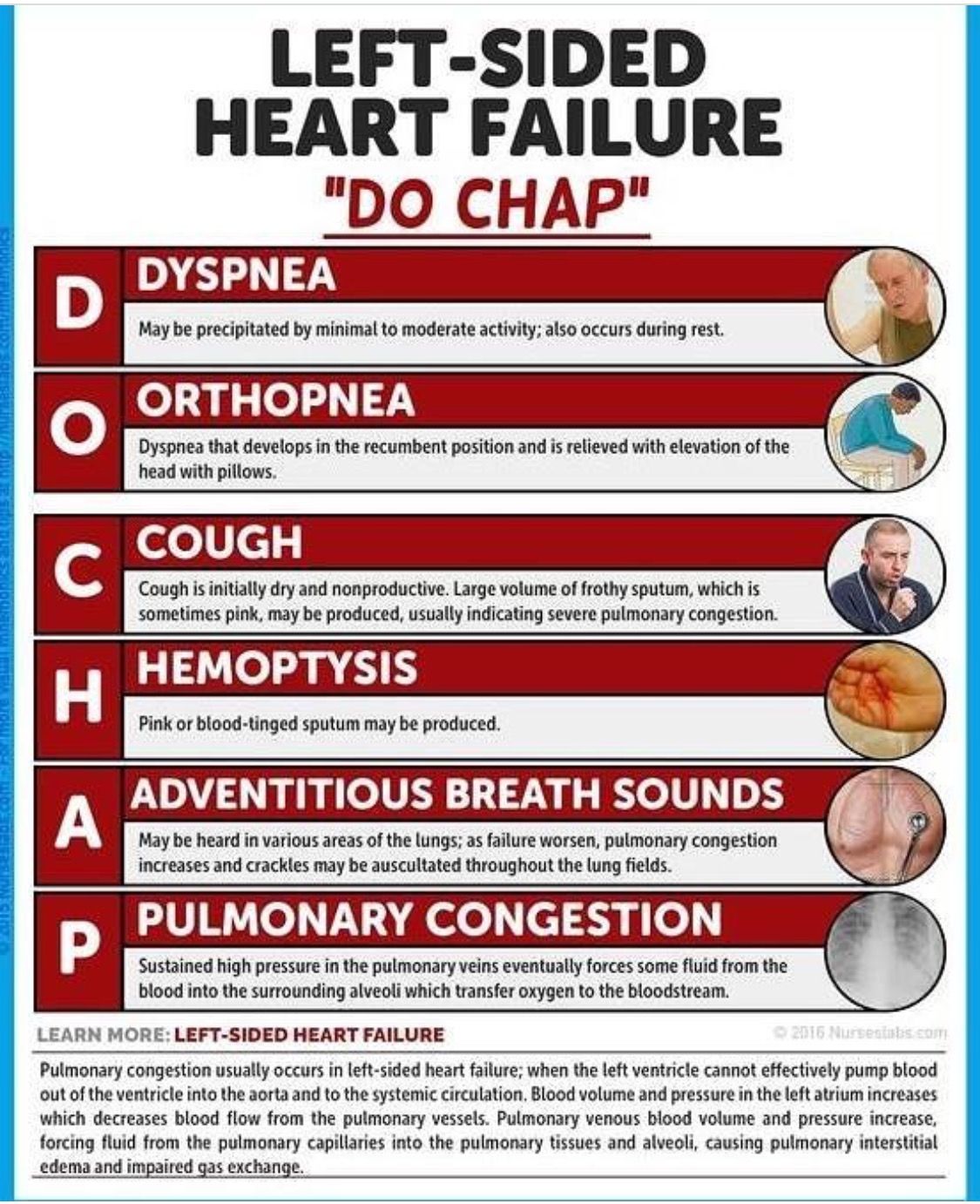
Also Check: Congestive Heart Failure And Kidney Failure
Examples Of Medicines That Are Used In Treating Cad
ACE inhibitors help relax blood vessels, so more blood flows to your heart. There are several types of ACE inhibitors.
Some examples are:
Calcium channel blockers help control blood pressure by relaxing blood vessels and lowering heart rate. Examples include:
Diuretics remove excess water, salt, and minerals from your body, helping it to lower blood pressure and giving you more energy. Examples include:
- Hydrochlorothiazide Chlorothiazide
- Spironolactone Amiloride HCl
Beta-blocker + Diuretic medicines effectively treat high blood pressure and help prevent a second heart attack. This combination is also effective in treating chest pain and improving exercise tolerance.
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors + Beta-blockers are very effective treatments for CAD patients who have had a heart attack or have congestive heart failure and high blood pressure.
Coronary artery bypass graft surgery is used to treat severe coronary heart disease. This procedure involves moving a healthy vein from your leg or chest wall and using it to bypass the narrowed section of an artery in the heart muscle, restoring blood flow around the blockage.
Nursing Assessment For Deficient Knowledge
| Assessment | Rationale |
| Assess the patients knowledge regarding causes, treatment, and follow up care to heart failure. | This information provides data regarding knowledge of the patient about heart failure. It helps to plan educational sessions for the patient and family members. |
| Discuss with the patient and relatives about the disease and find out the existing misconceptions regarding treatment and care. | Finding out misconceptions and Clearing them out from the mind also guide future interventions. |
You May Like: How Fatal Are Heart Attacks
How To Conduct Electrocardiogram To Diagnose Heart Failure
Step 1: The patient will lie down or sit down if theyre too weak to stand.
Step 2: The doctor will place electrodes on the patients chest to check for electrical activity in the heart. These electrodes are placed over each of the hearts four chambers, and one electrode is also placed on their back .
Step 3: The doctor will apply a small amount of gel to each electrode and also put the back electrode in place.
Step 4: The doctor will turn on the EKG machine and read its printout for irregularities that may indicate heart failure. Depending on what is found, they may refer you to a specialist who can do further tests.
Epidemiology Of Heart Failure
Heart failure is mostly found in elderly patients . About 2% to 3% of the United States Of America population are affected by Heart failure, of which 10% are male and 8% are female. According to a CDC report, around 6.3 million heart failure patients were there in 2018. USA government-issued 379,800 death certificates mentioning death cause as heart failure.
Read Also: What Is A Mini Heart Attack
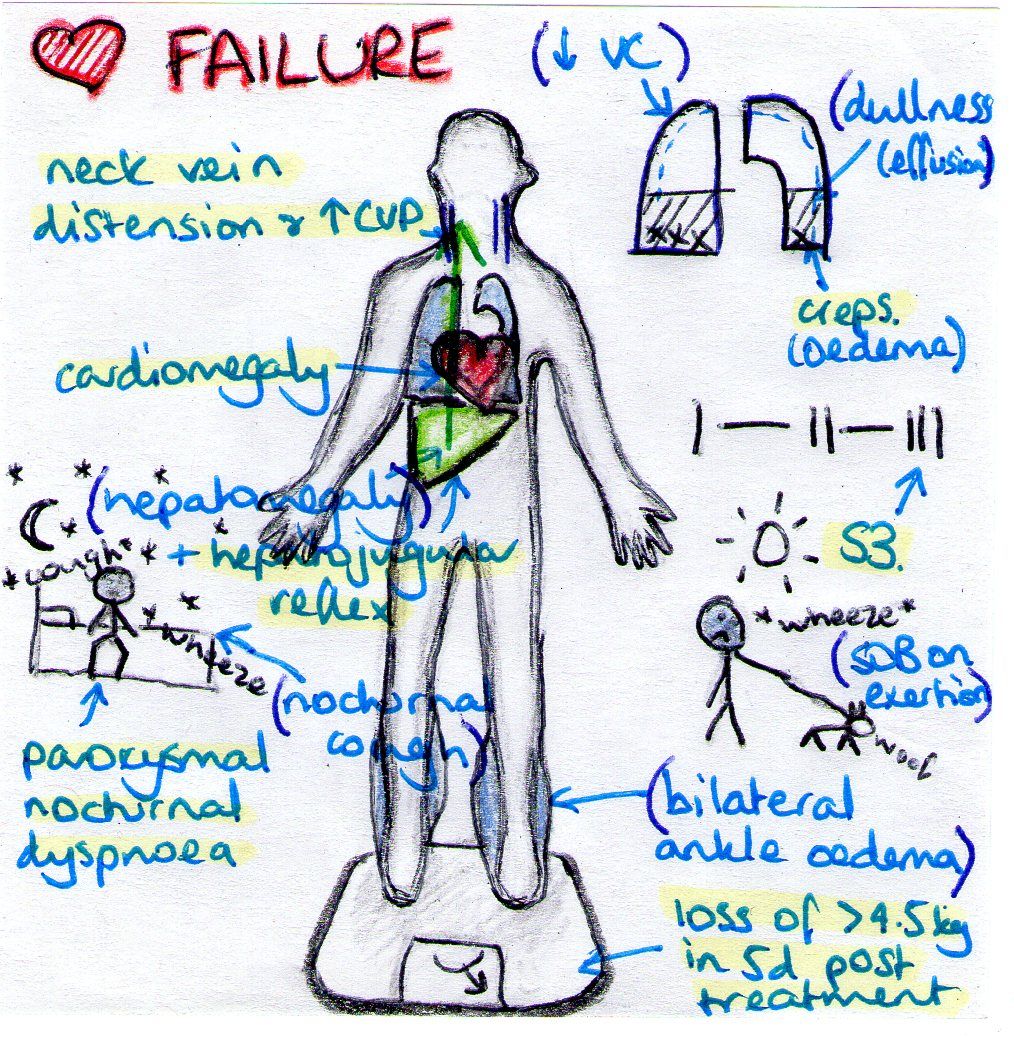
Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion
May be related to:tissue ischemia, reduction or interruption of blood flow, vasoconstriction, hypovolemia, shunting, depressed ventricular function, dysrhythmias, conduction defects.
As evidenced by:abnormal hemodynamic readings, dysrhythmias, decreased peripheral pulses, cyanosis, decreased blood pressure, shortness of breath, dyspnea, cold and clammy skin, decreased mental alertness, changes in mental status, oliguria, anuria, sluggish capillary refill, abnormal electrolyte, hypoxia, ABG changes, chest pain, ventilation perfusion imbalances, changes in peripheral resistance, impaired oxygenation of myocardium, ECG changes in S-T segment, T wave, U wave, palpitations.
Types Of Heart Failure
There are two types of heart failure depending on the type of underlying disease that has caused it.
1. Congestive Heart Failure results from an inability of the left ventricle to fill with blood upon relaxation and a diminished stroke volume . This produces increased pressure in the left ventricle and pulmonary vascular bed.
2. Restrictive Cardiomyopathy is caused by the loss of heart muscle, usually because of a disease or an injury.
The pathophysiology of cardiomyopathy is different from that of congestive heart failure in that it does not involve the left ventricle. Also, with cardiomyopathy, there is a decreased ventricular compliance, and the stiffness of the heart muscle increases.
Also Check: How To Find My Heart Rate
Risk For Ineffective Cardiac Tissue Perfusion Related To Decreased Perfusion Of Oxygen And Nutrients To Body Tissues
Ineffective Cardiac Tissue Perfusion Related to Decreased Perfusion of Oxygen and Nutrients to Body Tissues
Risk for ineffective cardiac tissue perfusion related to decreased perfusion of oxygen and nutrients to body tissues. Ineffective cardiac tissue perfusion may be a result of several factors: acute or chronic changes in heart function, autonomic nervous system dysfunction or failure, decreased systemic blood pressure, reduced venous return from the extremities , low cardiac output states , sustained tachycardia or bradycardia, respiratory acidosis and alkalosis. The patient with this condition is at increased risk for the development of other health problems such as pulmonary edema if compensatory mechanisms are not functioning well enough.
Nursing Intervention In Semi
- The patients family should be educated regarding the target goal, the underlying cause of the heart failure, and signs of toxicity with medications. It is also important to teach them about medications and their activities and the signs of toxicity, as this will lead to more effective medication management.
- Teaching about medications and their activities: It is important to teach the patient, and family members/ loved ones about heart disease, especially congestive heart failure, as this will lead to a proper understanding of their pharmacological needs. It is also important to teach them about medications and their activities and the signs of toxicity, as this will lead to more effective medication management.
The patients family should be educated regarding the target goal, underlying cause for procedures such as pericardiocentesis, and complications. It is also important to teach them about medications and their activities and the signs of toxicity, as this will lead to more effective medication management.
Recommended Reading: Is 190 Heart Rate Bad
How To Improve Symptoms Of Cad
Although CAD has no cure, proper treatment can cause the disease to remain stable or even improve over time.
Treatment may include medicines, lifestyle changes, and surgery to repair a damaged heart valve or replace an artery narrowed or blocked by atheromatous plaque.
Treatment begins with diagnostic tests that determine which arteries and veins are affected by CAD and its severity.
These tests help your doctor identify which medicines may be right for you and allow your doctor to choose the best treatment option.
Examples of tests include Blood tests to check the amounts of fats and blood sugar in your bloodstream
Angiogram, a procedure that uses X-rays and dye injected into an artery in the groin or arm to produce an image of the arteries
Echocardiogram, an ultrasound that uses sound waves to create images of the heart and blood vessels.
Once these diagnostic tests have been done, your doctor will be able to determine the best treatment for you.
Chf Nursing Care Plan 3
Nursing Diagnosis: Deficient Knowledge related to new diagnosis of Congestive Heart Failure as evidenced by patients verbalization of I want to know more about my new diagnosis and care
Desired Outcome: At the end of the health teaching session, the patient will be able to demonstrate sufficient knowledge of congestive heart failure and its management.
Also Check: How Does A Pulse Oximeter Measure Heart Rate
Nursing Intervention Of Heart Failure Patients In Emergency Department
- Elicit Cardiac History and Physical Assessment
- Auscultation of all four cardiac sounds for rate, rhythm, and quality. . Then auscultate for murmur grade 1 to 6 .
- Palpation for LV hypertrophy by feeling the sternum and observing for sharp, deep systolic murmur in apex beat.
- Check pulse oximetry heard 100% on room air .
- Teaching: It is important to teach the heart failure patient and family members/ loved ones about the disorder, its prognosis, and the cause of disease projections in addition to reassurance for available treatment modalities. It is also important to teach them about medications and their activities and the signs of toxicity, as this will lead to more effective medication management.
Risk For Fluid Volume Excess
May be related to: increased sodium and water retention, decreased organ perfusion.
As evidenced by: edema, weight gain, intake greater than output, increased blood pressure, increased heart rate, shortness of breath, dyspnea, orthopnea, crackles , oliguria, jugular vein distention, pleural effusion, specific gravity changes, altered electrolyte levels.
You May Like: What Are The Final Stages Of Congestive Heart Failure
Health Teaching And Health Promotion
Nursing care plans for patients with HF must include patient education to improve clinical outcomes and reduce hospital readmissions. Patients need education and guidance on self-monitoring of symptoms at home, medication compliance, daily weight monitoring, dietary sodium restriction to 2 to 3 g/day, and daily fluid restriction to 2 L/day. In addition, patients with HF need aggressive treatment for underlying risk factors and the potential triggers for HF exacerbations. Modifiable risk factors include diabetes mellitus, hypertension, obesity, nicotine use, alcohol use disorder, and recreational drug use, especially cocaine. Patients with sleep apnea and HF should be encouraged to use continuous positive airway pressure therapy as uncontrolled sleep apnea can also increase HF-associated morbidity and mortality.
What Are The Reducing Risk Factors For Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease is the buildup of fatty deposits, also known as plaque, on the walls of your hearts arteries. The accumulation of plaque narrows or blocks blood vessels that supply blood to the heart muscle and reduces blood flow.
One of the reasons for this behavior is that CAD involves a type of cholesterol called low-density lipoprotein . LDL, also known as bad cholesterol, is often referred to by doctors as the silent killer because it can build up in the walls of arteries and slowly narrow or block the arteries.
Don’t Miss: Why Does My Resting Heart Rate Fluctuate
Nursing Diagnosis: Acute Cardiac Failure Cardiogenic Shock
Nanda-I Diagnosis Code: Nursing diagnosis code: 10213: NANDA-I code: K33.208
Signs & Symptoms: CHF is a condition where the heart fails to pump blood sufficiently throughout the body leading to vascular congestion and fluid accumulation in the lungs . This can lead to difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, fatigue, and ultimately death if not aggressively treated. Common signs of CHF include shortness of breath , fatigue, swelling, and weight gain in the abdominal region due to fluid retention. Cardiogenic shock signs and symptoms are similar to CHF, but they tend to be more severe, leading to a significantly increased risk for death within days or weeks if left untreated.
Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To An Accumulation Of Secretions
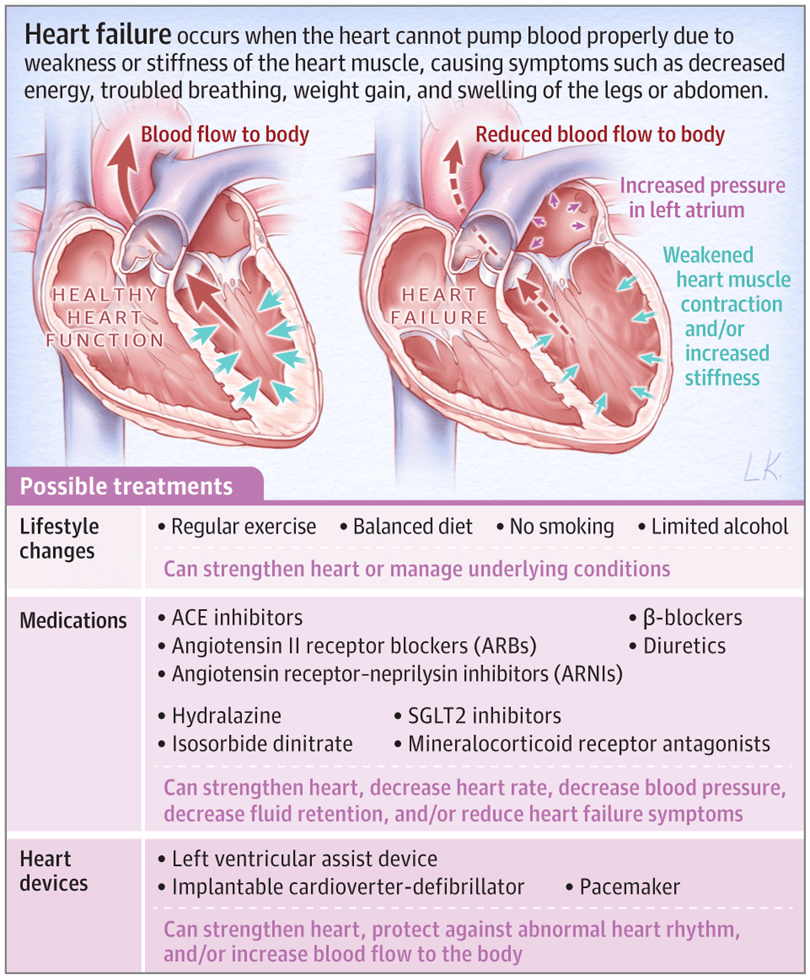
Patients with CHF may have difficulty breathing and shortness of breath. They may experience chest congestion, wheezing, dyspnea and/or feeling of impending suffocation. Ineffective airway clearance related to an accumulation of secretions can lead to a buildup of mucus in the lungs that make it difficult for oxygen to enter the bloodstream.
When a patients blood flow is decreased due to heart failure, this causes less blood flow through the lungs and reduces their ability to breathe properly by clearing out excess fluid from the respiratory tract . This results in increased amounts of secretions such as sputum or phlegm which can be difficult or impossible for patients who have weakened respiratory muscles due to chronic injury caused by fluid accumulation within their lungs or bronchi .
You May Like: What Is A Good Resting Heart Rate By Age
What Are The Nanda Ii Nursing Diagnoses Involving Cardiac Function
Acute cardiac failure: Cardiogenic shock. Circulatory overload: Due to fluid accumulation in the lungs , this can lead to shortness of breath, fatigue, and ultimately death if not aggressively treated. Cardiomyopathy: Defined as a disease/condition involving the muscular wall of the heart causing dysfunctions in pumping and circulating blood. CHF is one type of cardiomyopathy.
Study Population And Sample
The population consisted of hospitalized patients with heart failure over a period of 12 months , considering a simple random sampling selection and overall margin of error resulting in a maximum of n = 5%. Total sample size corrected by the size of the N population was calculated using the following formula: n=/1+1111 Callegari-Jacques SSM. Bioestatística: princípios e aplicações Porto Alegre: Artmed 2003.. The sample selected for this study respecting the inclusion and exclusion criteria included 70 patients. Therefore, the estimated ratios in this study are subject to maximum error of 8.75% and a 95% confidence level.
The sample selection was non-probabilistic with an initial composition of 84 patients, but with four losses due to hospital discharge before the end of data collection, six losses due to death and two losses due to discontinuity by transfers. The final sample consisted of 72 patients followed for three weeks of hospitalization from the time of hospital admission.
Also Check: How Do You Calculate Maximum Heart Rate
Causes Of Heart Failure
