When To Seek Hospice Care
Even physicians have difficulty determining life expectancy for people with end-stage heart-failure. The condition can be unpredictable, and symptoms can change. However, certain signs can indicate that hospice care would be beneficial, including:
- frequent chest pain
- significant fatigue or shortness of breath
- substantial decline in ability to do daily activities, such as self-care
- The patient has already received the best possible treatment, which are no longer working well, and the patient is not a candidate for other interventions.
- The patient has received the best possible treatment and has decided to decline further specialized interventions.
People can be reluctant to start hospice, as they may worry it means theyre giving up or that it will hasten death. But such concerns are unfounded. In fact, patients and families often wish they had started hospice sooner, because it makes such a positive difference in their lives. And research shows that early admission to hospice results in greater satisfaction with care among patients and family caregivers.
How Heart Failure Is Diagnosed
Symptoms of heart failure can mimic those of other health issues. It’s important to bring such concerns to your healthcare provider’s attention, so they can determine whether heart failure or another condition is the cause.
A heart failure diagnosis is usually made based on your medical history, a physical examination, and heart function tests, primarily electrocardiogram and echocardiogram . Brain natriuretic peptide measurement has gained attention because it can be done using a blood test. It can be used with an EKG and an echo to piece together a diagnosis of heart failure.
Verywell
Can The Progression Of The Congestive Heart Failure Be Stopped
Congestive heart failure and its progression cannot really be stopped. However, if proper lifestyle changes and proper medical guidance is followed, the progression of the disease can slow down. Some of the changes in lifestyle include-
Exercise: Getting routine exercise can help patients lead an active life that prevents the progression of the disease. It may happen so that some patient may need modified version of the already existing regime. The patient should consult the doctor if need be.
Losing Weight- It is important to maintain a healthy weight. Being obese can make patient more prone to getting tired and feeling fatigued. It is recommended that the patient checks his weight from time to time to ensure proper body weight.
Relaxing- Stress can act as a precipitating factor lead to the rapid progression of the disease. Stress management techniques like therapy or meditation can help patient relieve from stress and keep the mind calm.
Healthy Diet: It is important to concentrate on a healthy diet which is particularly low in sodium and trans fat. Sodium increases the risk of water retention which in turn can lead to increased body weight.
Regular Vaccination: A patient must get his regular vaccines especially pneumococcal pneumonia. Exposures to infections like this may lead to rapid progression of congestive heart failure.
You May Like: Icd 10 Congestive Heart Failure
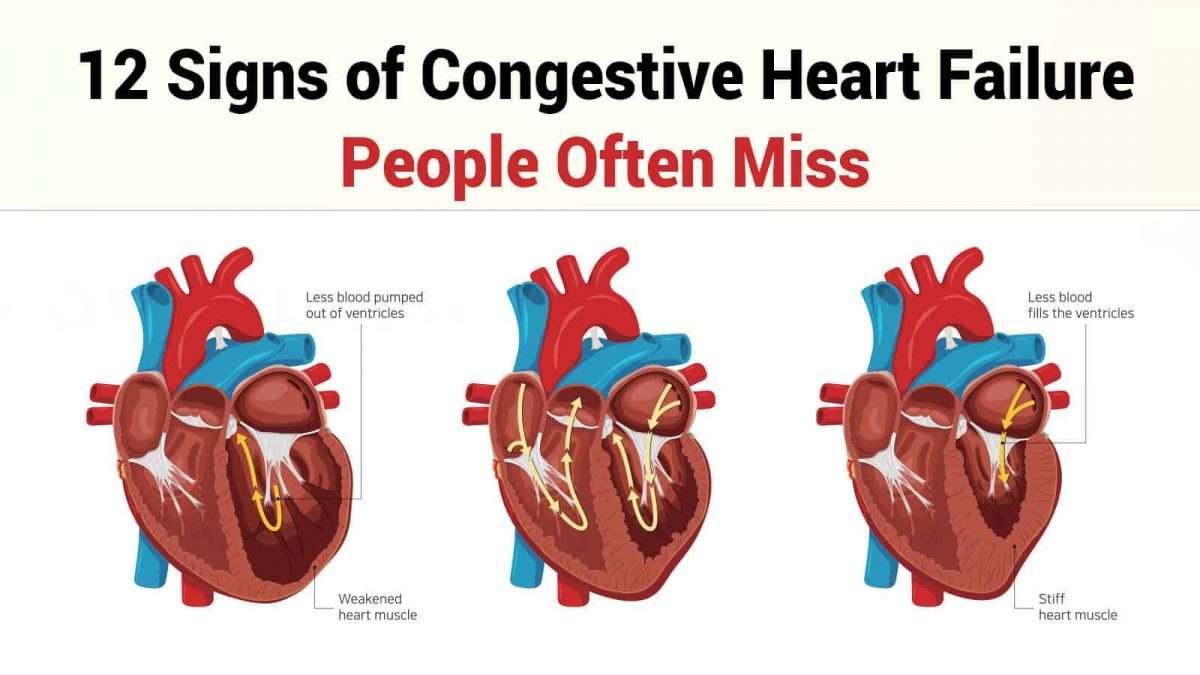
Signs Of Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive heart failure symptoms vary based on the type and stage of the disease youre experiencing. Some people may not have any physical signs of heart failure, while others notice mild to severe symptoms that come and go or remain constant. Here are some of the most common signs:
- Shortness of breath, wheezing or coughing
- Dizziness, fatigue and weakness
- Swelling, especially in the ankles
- Rapid or irregular heart rate
Always tell your doctor or health care provider about new and worsening symptoms. Seek emergency medical treatment for sudden or unexplained symptoms like chest pain, which may be a sign of a severe heart condition.
Diagnosing Heart Failure Before It Shows
If you have no symptoms or signs of heart failure, how can you be diagnosed with heart failure? Some people are at a much higher risk of developing heart failure than others. By diagnosing you with stage A heart failure, your doctor will monitor your heart health closely, and suggest treatments that may ward off heart failure signs for as long as possible. A few examples of people who are at risk of developing heart failure include those who have:
-
A family history of heart failure
-
Chronic medical conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, or coronary heart disease
-
A history of alcohol abuse
-
Taken medications, like chemotherapy, that could damage heart tissue
Recommended Reading: Stroke After Open Heart Surgery
Systolic And Diastolic Failure
Systolic and diastolic heart failure each result in a decrease in stroke volume. This leads to activation of peripheral and central baroreflexes and chemoreflexes that are capable of eliciting marked increases in sympathetic nerve traffic.
Although there are commonalities in the neurohormonal responses to decreased stroke volume, the neurohormone-mediated events that follow have been most clearly elucidated for individuals with systolic heart failure. The ensuing elevation in plasma norepinephrine directly correlates with the degree of cardiac dysfunction and has significant prognostic implications. Norepinephrine, while directly toxic to cardiac myocytes, is also responsible for a variety of signal-transduction abnormalities, such as downregulation of beta1-adrenergic receptors, uncoupling of beta2-adrenergic receptors, and increased activity of inhibitory G-protein. Changes in beta1-adrenergic receptors result in overexpression and promote myocardial hypertrophy.
Heart Failure Expectations Unrealistic
In the study, researchers surveyed 122 people with moderate to advanced congestive heart failure about their perception of their life expectancy.
They found the heart failure patients tended to overestimate their life expectancy by about three years. The average patient survival estimate was 13 years compared with a validated medical model estimate of 10 years.
Overall, 63% of people with heart failure overestimated their remaining life expectancy by an average of 40% compared with medical model predictions. Those who were younger and with more advanced disease were most likely to overestimate how long they had left to live.
During the three-year follow-up period, 29% of the people involved in the survey died. Researchers found no relationship between longer life expectancy perceptions and survival.
You May Like: How To Tell If Heart Attack Is Coming
What Is Heart Failure
Heart failure, or congestive heart failure, is a long-term condition that gets worse over time. Although the name sounds like your heart has stopped working, heart failure means your heart isnt able to pump blood as well as it should. When your heart has less pumping power, that can damage your organs and fluid can collect in your lungs.
In All Heart Failure Patients
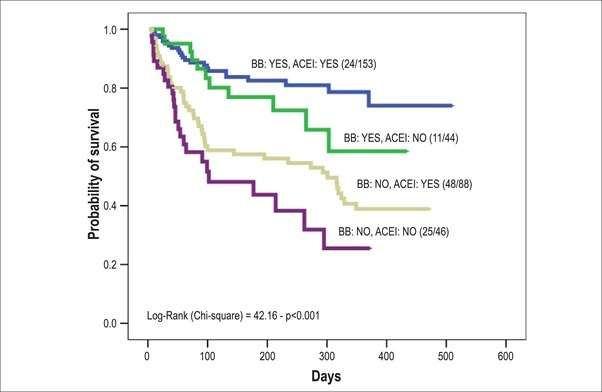
The 2016 ESC guidelines recognize the importance of ECG in the diagnosis and prognosis of HF patients. The guidelines recommend ECG to all HF patients at presentation to assess potential etiology, inform appropriate therapy, and predict cardiac events . The guidelines also indicate that normal ECG findings are unlikely in HF patients . In support of these recommendations, current data on some ECG parameters including QRS duration, T wave, ST-segment elevation, and/or depression at presentation strongly support their ability in predicting cardiac events and clinical outcomes in HF patients .
Other significant ECG parameters on admission that can predict cardiac events in HF patients include QTc duration, changes in ST segment, low voltage, and Q waves. Admission ECG done on 246 consecutive HF patients demonstrate that QTc peak duration is a significant multivariate predictor of a composite endpoint of cardiac events, rehospitalization, or death . The prognostic value of the presence of atrial fibrillation in HF patients has been known for decades in a cohort of patients admitted with acute HF and were followed for 30 days with regard to cardiac events, those patients with an event had a significantly higher incidence of atrial fibrillation on admission ECG as compared to those without .
Kyung U. Hong, Roberto Bolli, in, 2016
K. Ono, in, 2017
Recommended Reading: What Is Heart Valve Disease
Outlook For Heart Failure
Heart failure is a serious long-term condition that will usually continue to get slowly worse over time.
It can severely limit the activities you’re able to do and is often eventually fatal.
But it’s very difficult to tell how the condition will progress on an individual basis.
It’s very unpredictable. Lots of people remain stable for many years, while in some cases it may get worse quickly.
Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction
In heart failure with preserved ejection fraction , formerly known as diastolic heart failure, the left side of the heart retains its ability to pump but the stiffening of the heart muscle does not allow it to relax during beats.
Losing the ability to relax during beats means that the left ventricle chamber loses its capacity to adequately fill with blood, so when it pumps, less blood is pushed out.
You May Like: How To Fix Congestive Heart Failure
Troponin And Chronic Heart Failure
The role of myocyte injury in prognosis of stable outpatients with heart failure was evaluated by Hudson and colleagues.141 The authors assessed the association of elevated cardiac troponin T levels with the severity, cause, and prognosis of heart failure in 136 stable, ambulatory patients. Patients with elevated cTnT levels had an increased risk of death from or hospitalization for heart failure and of death alone at 14 months.141 In a larger outpatient data set from the Val-HeFT study, Latini and associates142 measured levels of cTnT and high-sensitive troponin T in 4053 patients with chronic stable heart failure. Levels of cTnT were detectable in 10.4% of the population with the cTnT assay , in comparison with levels of htTNT in 92.0% with the new hsTnT assay . Patients in whom cTnT level was elevated or in whom hsTnT level was above the median had more severe heart failure and worse prognoses.142 Increased concentration of cTnT was associated with an increased risk of death and increased risk of first hospitalization for heart failure in multivariable models. For each 0.01-ng/mL increase in hsTnT level, risk of death increased 5% .142
Blase A. Carabello, in, 2011
What Is Ejection Fraction
The ejection fraction is a measurement your doctor will use to determine the type of heart failure and to assess the stage of heart disease.
The ejection fraction represents the percentage of blood pumped out of the left ventricle when the heart contracts. When blood leaves the left ventricle, it moves into the aorta to deliver blood loaded with oxygen to the rest of the body.
In a healthy heart, the ejection fraction ranges from around 52%74%. When the ejection fraction drops below 52%, its considered low. Your healthcare professional may use your ejection fraction to determine the severity of heart failure.
Also Check: Does Arousal Increase Heart Rate
Causes Of Heart Failure
Heart failure is often the result of a number of problems affecting the heart at the same time.
Conditions that can lead to heart failure include:
- coronary heart disease where the arteries that supply blood to the heart become clogged up with fatty substances , which may cause angina or a heart attack
- high blood pressure this can put extra strain on the heart, which over time can lead to heart failure
- conditions affecting the heart muscle
- heart rhythm problems , such as atrial fibrillation
- damage or other problems with the heart valves
- congenital heart disease birth defects that affect the normal workings of the heart
Sometimes obesity, anaemia, drinking too much alcohol, an overactive thyroid or high pressure in the lungs can also lead to heart failure.
Stage A Treatment Options
Treatment options in stage A mainly focus on promoting your overall health and disease prevention. If you meet the stage A criteria, your doctor will recommend lifestyle changes to slow or stop disease progression.
Heart Failure Doctor Discussion Guide
Also Check: What Is Heart Palpitations Symptoms
Prognosis Of Congestive Heart Failure In Elderly Patients With Normal Versus Abnormal Left Ventricular Systolic Function Associated With Coronary Artery Disease
- AffiliationsFrom the Hebrew Hospital for Chronic Sick, 2200 Givan Avenue, Bronx, New York 10475, USAFrom the Department of Epidemiology and Social Medicine, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, New York, USAFrom the Department of Medicine, New York University School of Medicine, New York, New York, USA
- AffiliationsFrom the Hebrew Hospital for Chronic Sick, 2200 Givan Avenue, Bronx, New York 10475, USAFrom the Department of Epidemiology and Social Medicine, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, New York, USAFrom the Department of Medicine, New York University School of Medicine, New York, New York, USA
- AffiliationsFrom the Hebrew Hospital for Chronic Sick, 2200 Givan Avenue, Bronx, New York 10475, USAFrom the Department of Epidemiology and Social Medicine, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, New York, USAFrom the Department of Medicine, New York University School of Medicine, New York, New York, USA
What Are The Complications Of Heart Failure
Some of the complications from heart failure include:
- Irregular heartbeat.
- History of taking drugs that can damage your heart muscle, such as some cancer drugs.
Stage B
Stage B is considered pre-heart failure. It means your healthcare provider has given you a diagnosis of systolic left ventricular dysfunction but youve never had symptoms of heart failure. Most people with Stage B heart failure have an echocardiogram that shows an ejection fraction of 40% or less. This category includes people who have heart failure and reduced EF due to any cause.
Stage C
People with Stage C heart failure have a heart failure diagnosis and currently have or previously had signs and symptoms of the condition.
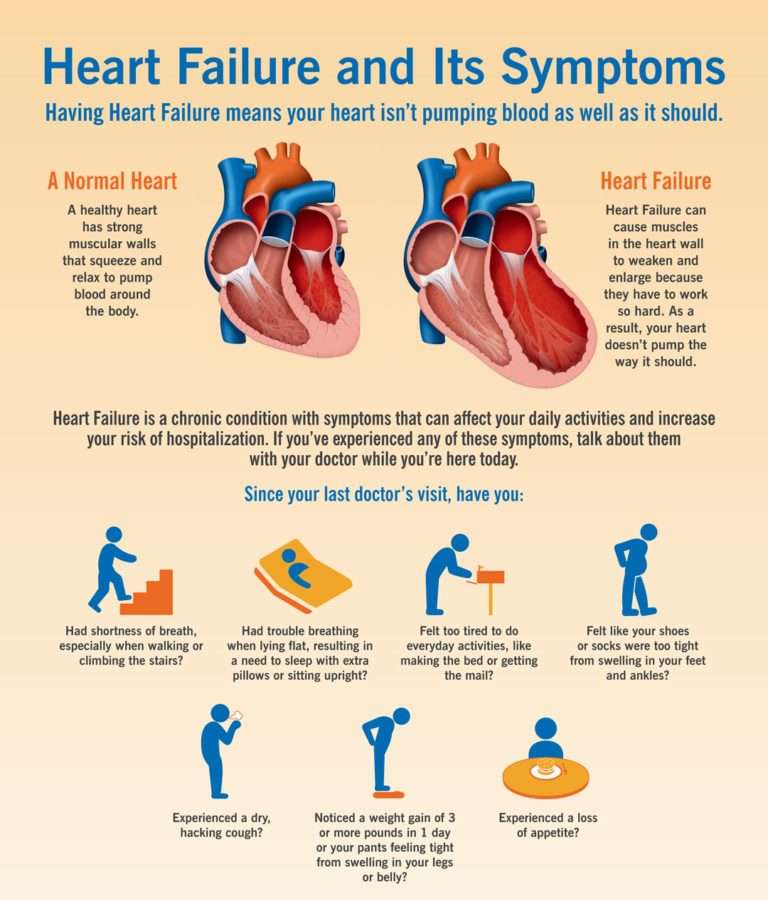
There are many possible symptoms of heart failure. The most common are:
- Shortness of breath.
- Need to urinate while resting at night.
- Rapid or irregular heartbeats .
- A dry, hacking cough.
- A full or hard stomach, loss of appetite or upset stomach .
There may be times that your symptoms are mild or you may not have any symptoms at all. This doesn’t mean you no longer have heart failure. Symptoms of heart failure can range from mild to severe and may come and go.
Unfortunately, heart failure usually gets worse over time. As it worsens, you may have more or different signs or symptoms.Its important to let your doctor know if you have new symptoms or if your symptoms get worse.
Recommended Reading: What Causes Fast Heart Rate
Other Negative Prognostic Indicators
Increasing age is the factor most strongly associated with poor prognosis.5,6,15 Other independently associated factors related to poor prognosis reflect haemodynamic or electrolyte instability and vascular risk factors. They include: low systolic blood pressure on admission tachycardia high naturietic peptides hyponatreamia anaemia acute kidney injury chronic kidney disease prior stroke smoking male sex previous myocardial infarction chronic obstructive pulmonary disease peripheral vascular disease or significantly high or low body mass index. Symptoms are also important signs of deterioration. The New York Heart Association classification is used to quantify the degree of breathlessness in patients with HF as shown in Box 2.
Congestive Heart Failure: Symptoms Treatment And Prognosis
Sharing is caring!
Congestive heart failure is a condition that may develop when the heart cant pump enough blood through to the body.
Heart failure does not imply that the heart has ceased beating Rather, it signifies that coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, or infections have weakened or harmed the heart.
Heart failure can gradually develop and worsen over time, or come about very quickly, depending on the cause.
Most of those living with CHF control their condition, with a healthy heart patient diet and regular exercise.
Recommended Reading: How Many Heart Rate Zones Are There
What Are The Symptoms Of End
Heart Failure: Quick Facts
1. More than 6 million U.S. adults have heart failure.
2. About half of people who develop heart failure die within 5 years of diagnosis.
3. Most people with end-stage heart failure have a life expectancy of less than 1 year.
4. The leading causes of heart failure are diseases that damage the heart, such as heart disease, high blood pressure, and diabetes.
Heart failure worsens over time, so symptoms are most severe during the final stages. It causes fluid to build up in the body, which produces many of these symptoms:
- Shortness of breath . In the final stages of heart failure, people feel breathless both during activity and at rest.
- Persistent coughing or wheezing. This may produce white or pink mucus. The cough may be worse at night or when lying down.
- Weight gain or swelling of the feet, ankles, legs, abdomen, or neck veins.
- Tiredness, weakness.
In addition, people in the final stages of heart failure may suffer from:
- depression, fear, insomnia, and isolation
- anxiety about their future
- trouble navigating the health care system
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Congestive Heart Failure
Shortness of breath
The hallmark and most common symptom of left heart failure is shortness of breath and may occur:
Chest Pain
Right heart failure, left heart failure, or both
Don’t Miss: Does Amlodipine Lower Heart Rate
