Abnormal Fetal Heart Rate Treatments
If your babyâs heart rate isn’t what it should be, the doctor may try:
- Changing your positions to move the baby
- Giving you fluids through an IV
- Having you breathe extra oxygen
- Relaxing your uterus with medicine to slow contractions
- Giving you other drugs
If these steps donât return your babyâs heart rate to normal, you may need to deliver them right away. If your cervix is completely open, the doctor may use a tool called forceps or a special vacuum to help you push the baby out. Otherwise, youâll have the baby by emergency cesarean section.
Show Sources
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists: âFetal heart rate monitoring during labor,â âSpecial tests for monitoring fetal health.â
Johns Hopkins Medicine: âFetal heart monitoring.â
American Academy of Family Physicians: âMonitoring babyâs heart rate during labor.â
American Family Physician: âInterpretation of the electronic fetal heart rate during labor.â
What Causes Fetal Arrhythmia
Fetal arrhythmia has been linked to a number of possible causes. In some cases, healthcare providers may not be able to pinpoint the source, especially if the abnormal rhythm is transient.
It is possible that high levels of caffeine consumption may cause heartbeat irregularities, but currently, only case studies have been performed. It is suggested that pregnant women limit their caffeine intake to 200mL of caffeine a dayroughly the amount found in one cup of coffee.
Also, arrhythmia may, at some point in development, be normal. During the second trimester, the babys heart may begin to beat irregularly as the electrical pathways of the heart mature. This is natural, and not a cause for alarm unless the irregularity lasts for a considerable period of time.
Some arrhythmias may indicate a structural abnormality of the heart, in which case your healthcare provider will run further tests and take any appropriate action necessary. If the babys heart rate is consistently high, your doctor may prescribe you medication that is passed through the placenta to the baby to help regulate the heartbeat.
What Happens If My Baby Is Distressed During Labour And Birth
- Increasing your fluid levels by offering you a drink or via a drip.
- Offering you paracetamol if you have a raised temperature.
- Lying you down on your left-hand side to reduce the pressure of your womb on a major vein in your body . This prevents reduced blood flow to the placenta and your baby.
- Temporarily stopping any medications you’ve been given, to increase your contractions .
Recommended Reading: How Do I Find My Heart Rate
What Are The Risks Of Fetal Heart Monitoring
Radiation is not used for this test. The transducer usually causes nodiscomfort.
You may find the elastic belts that hold the transducers in place slightlyuncomfortable. These can be readjusted as needed.
You must lie still during some types of fetal heart rate monitoring. Youmay need to stay in bed during labor.
With internal monitoring, you may have some slight discomfort when theelectrode is put in your uterus.
Risks of internal monitoring include infection and bruising of your babysscalp or other body part.
Note:You should not have internal fetal heart rate monitoringif you are HIV positive. This is because you may pass the infection on toyour baby.
You may have other risks depending on your specific health condition. Besure to talk with your provider about any concerns you have before theprocedure.
Certain things may make the results of fetal heart rate monitoring lessaccurate. These include:
- Obesity of the mother
- Position of the baby or mother
- Too much amniotic fluid
- Cervix is not dilated or the amniotic sac is not broken. Both of these need to happen to do internal monitoring
What Are The Signs That My Baby Is Distressed During Labour
- Intermittently , also called intermittent auscultation.
- Continuously, also called continuous electronic fetal monitoring and sometimes shortened to cardiotocography .
Intermittent monitoringContinuous electronic fetal monitoring
- a lack of change in your baby’s heartbeat
- a drop in the heartbeat following a contraction
- your baby taking time to recover from each contraction .
You May Like: How To Check Your Resting Heart Rate
Is A Fetal Heart Rate Of 175 Normal
There is no consensus about the normal fetal heart rate. Current international guidelines recommend for the normal fetal heart rate baseline different ranges of 110 to 150 beats per minutebeats per minuteBusiness process management is the discipline in which people use various methods to discover, model, analyze, measure, improve, optimize, and automate business processes. Any combination of methods used to manage a company’s business processes is BPM.https://en.wikipedia.org wiki Business_process_managementBusiness process management – Wikipedia or 110 to 160 bpm.
Nonstress Test And Cardiotocography
Fetal heart rate characteristics are normally controlled through parasympathetic innervation, in which the vagus nerve innervates both the sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes. This tonic influence results in decreased rates of firing, thereby controlling the FHR. The vagus nerve also transmits impulses that result in FHR variability. When a fetus is exposed to prolonged periods of uteroplacental insufficiency, a noradrenergic response through the fetal adrenals occurs. This supersedes vagal influence, leading to both fetal tachycardia and decreased variability. If this continues, there is ultimately myocardial depression that manifests as late decelerations. Thus, in theory, instituting nonstress tests should identify fetuses at risk for adverse perinatal outcome. This is supported by observational studies demonstrating lower stillbirths in pregnancies with reactive NSTs than in those with nonreactive NSTs in addition to a lower stillbirth rate when NSTs are increased from once to twice per week.160,161
Andrew D. Hull, Thomas R. Moore, in, 2005
You May Like: What Can You Do For Congestive Heart Failure
What Happens After The Baby Is Born
After birth, babies usually do very well even though you took medication during pregnancy. After your baby is born, we recommend that they have an electrocardiogram to check their heart rhythm. The doctors looking after your baby will then talk to you about whether any further treatment or monitoring is needed. The causes of your babys tachycardia will be investigated and may require further treatment.
Your babys fast heart rate is likely to continue after birth, but in some cases the tachycardia can slow down to a normal rate by itself. In either situation, a period of monitoring will be required and in most cases medications are still used to control the fast heart rate.
Your baby will be referred to a paediatric cardiologist who will review your baby, ECG and ECHO results and will help to manage the medications your baby needs. Occasionally more than one medication is required.
What Is Considered Normal For My Babys Heartbeat
Indications that everything with the baby is fine include:
- Heartbeat between 110 and 160 beats per minute.
- Heart rate increases when baby moves.
- Heart rate increases during contractions.
- Heart rate returns to normal after baby moves or after a contraction.
- Your contractions are strong and regular during labor.
Recommended Reading: What Caused Elvis Presley’s Heart Attack
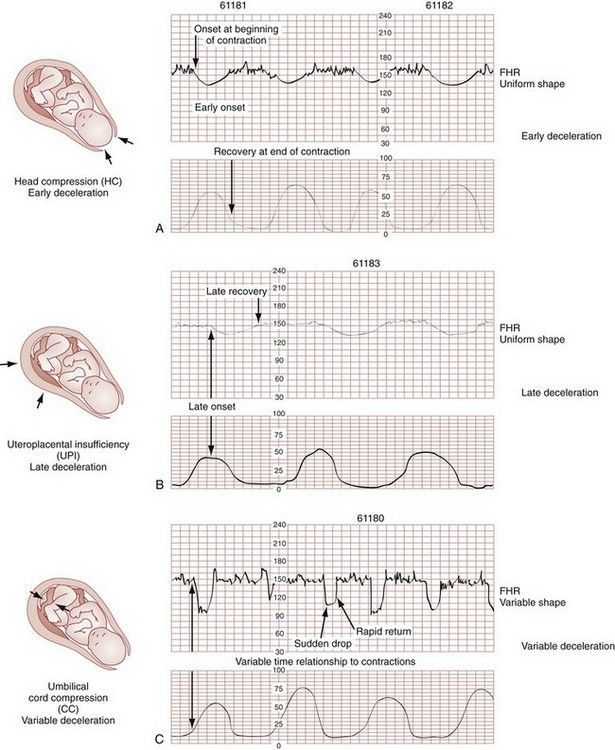
What Are The Most Important Facts To Know About Fetal Decelerations
Fetal decelerations refer to short-term but clear decreases of the fetal heart rate identified during monitoring. They are classified into three categories according to their shape and timing related to uterine contractions: early, late, and variable decelerations. The causes of fetal decelerations mainly depend on the category of deceleration. Signs and symptoms of fetal decelerations resemble those of fetal distress, such as a decrease in fetal movements and maternal cramping. When the diagnosis is confirmed by FHR monitoring, immediate measures are taken. Maternal repositioning, administration of and oxygen are always necessary. Additionally, if the decelerations are persistent, or emergency delivery may be necessary.
Listening To Your Baby’s Heartbeat
A major part of midwifery care during labour is listening to and recording your babys heartbeat to help identify if there are any problems.
Most babies come through labour without any problems, but there are a few babies who run into difficulties. The best way of finding out which babies are having trouble is to listen to every babys heartbeat regularly throughout labour.
Recommended Reading: How Long Do People Live With Congestive Heart Failure
Prenatal Ultrasound Showing Fetal Tachycardia
This information sheet from Great Ormond Street Hospital explains about fetal tachycardia detected during a prenatal ultrasound scan and what this might mean for your child. It will support the information discussed with you by your doctor and nurse at your appointment and it is important to remember that every case is slightly different.Tachycardia is an abnormally fast heart rate. The normal fetal heart rate is between 120 and 160 beats per minute. Typically, an abnormally fast heart rate is over 200 beats per minute.
The heart is made up of four chambers two at the top called atria and two at the bottom called ventricles. The ventricles are the pumping chambers of the heart. It is the top two chambers of the heart that set the pace of the heart, and normally the ventricles only respond to electrical impulses from the atria.
In some fetuses, the atria and ventricles are both beating fast but at the same rate . In others, the atria beat exceedingly fast , much faster than the ventricles . Other rhythm disturbances may occur but are much rarer.
Is 150 Heart Rate High For A Fetus
There is no consensus about the normal fetal heart rate. Current international guidelines recommend for the normal fetal heart rate baseline different ranges of 110 to 150 beats per minute or 110 to 160 bpm.
Fetal Heart Rate Patterns: Normal And Abnormal Findings, Veal Chop – Maternity Nursing – L& D
Don’t Miss: How To Reduce Heart Rate
Did Your Child Suffer A Birth Injury Due To Fetal Distress We Can Help
If your child suffered a birth injury due to improper monitoring of fetal distress, our Philadelphia birth injury attorneys at The Villari Firm, PLLC are here to help you seek justice. Our experienced attorneys work with leading experts, including doctors and other legal professionals, to investigate and prepare cases for our clients. We spare no expense to ensure we are armed with everything needed to help our clients receive the compensation they deserve.
Contact The Villari Firm, PLLC at 372-8889 to schedule a free consultation today.
What Kind Of Monitoring Do I Need
Auscultation is generally considered an acceptable form of monitoring if:
- Your pregnancy is low-risk.
- You havent had complications during labor.
You will need continuous monitoring if:
- You have a high-risk pregnancy.
- Complications develop during labor.
- You have an epidural for pain.
- You have to have medicine to induce or speed up labor.
Recommended Reading: How Do I Check My Heart Rate
What If My Doctor Detects A Problem
Changes in heart rate do not necessarily mean there is a problem. Some are natural, such as it increasing when your baby moves or during a contraction. These changes are considered signs of well-being in your baby. If your babys heart rate is very rapid or dips down, there are some simple changes your doctor may suggest:
- Changing your position.
- Giving you more fluids through an IV.
- Giving you supplemental oxygen.
Other things your doctor could do include:
- Stopping oxytocin if youve been receiving it.
- Giving you medicine to relax your uterus. This decreases your contractions.
- Infusing sterile fluid into your uterus if your water has broken.
If none of these interventions help, your doctor may consider speeding up delivery. To do this, you could have an assisted delivery. Your doctor uses forceps or a special vacuum to pull your baby out instead of waiting for the contractions to push him out. Or they may suggest you have a c-section.
Abnormal Fetal Heart Rate
Sometimes a fetal heart rate is outside the normal range simply because the fetus is moving around. Other times, it indicates a health concern for the baby. When the healthcare team detects a possible problem, their first step will be to try to find the cause.
Depending on the stage of pregnancy, different tests will be used to clarify the problem. Sometimes, a fetal heart rate is abnormal because of something happening in the mothers body. These are called maternal causes and may include:
Also Check: How To Tell If You’ve Had A Heart Attack
Increased Fetal Heart Rate During Labor And Delivery
by | Apr 15, 2021 | Birth Injuries, Blog, Cerebral Palsy, HIE , How Lawsuits Work, Obstetrical Malpractice |
In todays educational articles we are going to discuss increased fetal heart rate during labor and delivery. This post is the flipside of a post I did a few days ago in which we talk about decreased fetal heart rate during labor and delivery. Both conditions, when coupled with non-reassuring readings on the electronic fetal heart monitor can pose a danger to babies in some instances.
It is imperative for doctors and nurses to accurately diagnose and treat medical conditions as they arise during labor and delivery. Failure to do so can in some cases lead to disastrous results for not only mother, but for baby too.
Interactive Multiple Choice Questions
This Education in Heart article has an accompanying series of six EBAC accredited multiple choice questions .
To access the questions, click on BMJ Learning: Take this module on BMJ Learning from the content box at the top right and bottom left of the online article. For more information please go to: Please note: The MCQs are hosted on BMJ Learningthe best available learning website for medical professionals from the BMJ Group.
If prompted, subscribers must sign into Heart with their journal’s username and password. All users must also complete a onetime registration on BMJ Learning and subsequently log in on every visit.
Additional references appear on the Heart website
Don’t Miss: How Do You Count Your Heart Rate
Does The Heart Rate Vary For Boys And Girls
No. The heart rate is not different in boys and girls. You might have heard the old wives tale that a heart rate over 140 bpm predicts a girl, and one lower than 140 bpm indicates a boy. There is no scientific basis for this fact.
You will start to clearly hear your baby’s heartbeat at six weeks of pregnancy. Your baby hasn’t developed enough to look like the fetus pictures you might have seen online at this stage. They look like a tadpole, better known as the fetal pole, and you wont be able to know the gender yet.
The easiest way to find out the sex of your baby is via ultrasound. Your doctor will perform an ultrasound on you at 18 to 20 weeks. They will determine the sex of your baby by looking at the genitals on the babys image.
Data Extraction And Quality Assessment
Two authors selected relevant publications . They independently screened titles and abstracts, crosschecked reference lists for further relevant papers, and conducted full-text screening based on the eligibility criteria as described above. In case of disagreements, a third author was consulted to achieve consensus.
Figure 1. PRISMA flow diagram showing identified, included, and excluded studies.
Data were extracted from included studies by at least two authors . Two authors conducted the quality assessment. As no suitable quality assessment tool was found, we elaborated our own with the following main topics: risk of allocation, selection, information, detection and reporting bias including design, population, method of data acquisition, method of signal processing and R-wave detection, method of fetal movement detection and heart rate variability analyses.
Table 2. Methodological quality and risk of bias assessment of the included studies.
Read Also: How To Prevent A Stroke Or Heart Attack
Fetal Heart Rate Variability Is Affected By Fetal Movements: A Systematic Review
- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark
- 2Department of Health Science and Technology, Aalborg University, Aalborg, Denmark
- 3Department of Cardiology, Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark
Introduction: Fetal heart rate variability evaluates the fetal neurological state, which is poorly assessed by conventional prenatal surveillance including cardiotocography . Accurate FHRV on a beat-to-beat basis, assessed by time domain and spectral domain analyses, has shown promising results in the scope of fetal surveillance. However, accepted standards for these techniques are lacking, and the influence of fetal breathing movements and gross movements may be especially challenging. Thus, current standards for equivalent assessments in adults prescribe rest and controlled respiration. The aim of this review is to clarify the importance of fetal movements on FHRV.
Methods: A systematic review in accordance with the PRISMA guidelines based on publications in the EMBASE, the MEDLINE, and the Cochrane Library databases was performed. Studies describing the impact of fetal movements on time domain, spectral domain and entropy analyses in healthy human fetuses were reviewed. Only studies based on fetal electrocardiography or fetal magnetocardiography were included. PROSPERO registration number: CRD42018068806.
How To Monitor Fetal Heartbeat At Home:
There are quite a few ways you can monitor your baby’s heartbeat while at home. However, not all of them are as accurate as going to your doctor to get an ultrasound.
Here are some devices that you can use at home to listen to your babys heartbeat:
- Stethoscope: A stethoscope will detect your baby’s heartbeat at 18 to 20 weeks.
- Fetal doppler: This is a device that allows you to listen to your baby’s heartbeat by sending soundwaves through the mother’s belly to the baby. A fetal doppler can be used as early as nine weeks to listen to your baby’s heartbeat.
Also, note that you should not substitute at-home fetal monitoring with a real doctors appointment.
Don’t Miss: What Is A Healthy Resting Heart Rate By Age
Signs Of Fetal Distress
Some common signs and symptoms of fetal distress include:
- Abnormal Heart Rates
Each of these signs or symptoms may indicate fetal distress and should be monitored closely.
Abnormal Heart Rates
Babies who are progressing well in utero will have stable and robust heartbeats. Changes in heart rates and slower movement patterns or no movement at all can indicate a fetus may be in fetal distress. According to the National Center for Biotechnology Information , a healthy fetal heart rate should be between 110 and 160 beats per minute . The following are heart rate abnormalities that can be associated with fetal distress:
- Fetal tachycardia is an abnormally fast heart rate and is identified by a heart rate higher than 160 to 180 bpm.
- Fetal bradycardia is an abnormally slow heart rate and is identified by a heart rate of less than 110 bpm.
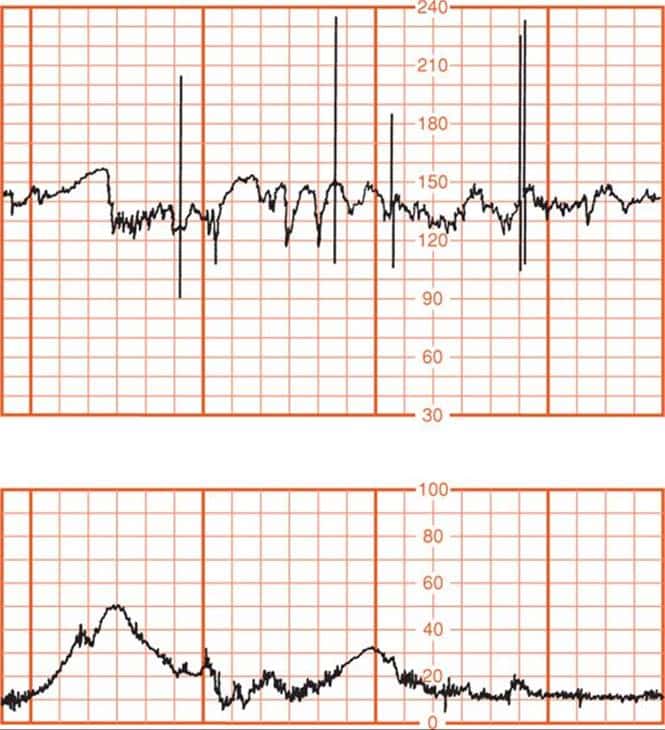
- Variable decelerations happen when there is a sudden decrease in the fetal heart rate, and the decline is greater than or equal to 15 beats per minute and lasts for longer than 15 seconds but less than 2 minutes from the onset to the return of the baseline rate.
- Late decelerations in a fetal heartbeat can happen through excessive uterine contractions or maternal hypotension, resulting in a decreased blood flow to the placenta. This is a cause for concern, and it can point to fetal acidemia. Fetal acidemia occurs when the blood becomes abnormally acidic.
Maternal Cramping
Maternal Weight Gain
Vaginal Bleeding
Meconium in the Amniotic Fluid
