Causes Of Coronary Artery Disease
When you are young, your coronary arteries usually have smooth healthy walls. As you get older, the inner lining of your coronary arteries comes under attack from risk factors like toxins from cigarette smoke, mechanical injury from high blood pressure, high cholesterol or blood sugar from a diet high in saturated fats and sugars, and lack of exercise. These injuries start a chain of events that lead to the build-up of fatty streaks in your coronary arteries.
There are a number of factors that are known to increase your risk of coronary artery disease. Some risk factors you cant do anything about include age, ethnicity, gender, personal or family history of heart attack or stroke.
Other risk factors are within your power to change, such as smoking, high cholesterol, high blood sugar , high blood pressure, being overweight, physical inactivity, poor nutrition and poor mental health and wellbeing.
There are choices you can make today to better manage your coronary artery disease and help to lower your risk of having another heart attack.
Is My Heart Permanently Damaged
When a heart attack occurs, the heart muscle that has lost blood supply begins to suffer injury. The amount of damage to the heart muscle depends on the size of the area supplied by the blocked artery and the time between injury and treatment.
Heart muscle damaged by a heart attack heals by forming scar tissue. It usually takes several weeks for your heart muscle to heal. The length of time depends on the extent of your injury and your rate of healing.
The heart is a tough organ. Even though part of it may have been severely injured, the rest of the heart keeps working. But, because of the damage, your heart may be weakened, and unable to pump as much blood as usual.
With proper treatment and lifestyle changes after a heart attack, further damage can be limited or prevented.
Learn more about heart damage detection.
Why Didnt I Have Any Warning
The process of atherosclerosis may have no symptoms in its early stages. But when an artery is narrowed by over 70%, muscle pain or cramps may occur when tissue needs more oxygen than its able to receive.
When a coronary artery narrows and constricts blood flow, other nearby blood vessels that serve the heart sometimes expand to compensate, which may explain why there may be no warning signs.
Such a network of expanded nearby blood vessels is called collateral circulation, and it helps protect some people from heart attacks by delivering needed blood to the heart. Collateral circulation can also develop after a heart attack to help the heart muscle recover.
Read Also: Is Congestive Heart Failure Treatable
What Is A Heart Attack
A myocardial infarction is an extremely dangerous condition that happens because of a lack of blood flow to your heart muscle. The lack of blood flow can occur because of many different factors but is usually related to a blockage in one or more of your hearts arteries. Without blood flow, the affected heart muscle will begin to die. If blood flow isnt restored quickly, a heart attack can cause permanent heart damage and death.
A heart attack is a life-threatening emergency. If you suspect you or someone youre with is having a heart attack, call 911 . Time is critical in treating a heart attack, and a delay of even a few minutes can result in permanent heart damage or death.
What does a heart attack feel like?
When a heart attack happens, blood flow to a part of your heart stops or is far below normal, which causes injury or death to that part of your heart muscle. When a part of your heart cant pump because its dying from lack of blood flow, it can disrupt the pumping sequence for your entire heart. That reduces or even stops blood flow to the rest of your body, which can be deadly if it isnt corrected quickly.
What are the symptoms of a heart attack?
Heart attacks can have a number of symptoms, some of which are more common than others. Men and people assigned male at birth are likely to have different heart attack symptoms than women and people assigned female at birth .
Symptoms of a heart attack that people describe most often include:
How Is A Heart Attack Different From Cardiac Arrest
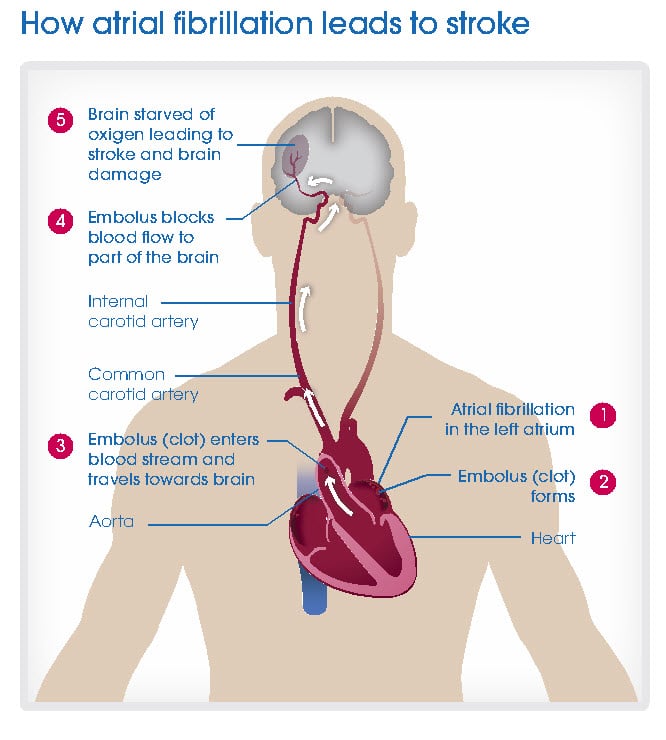
People often use these terms to mean the same thing, but they describe different events.
A heart attack is when blood flow to the heart is blocked. Its a circulation problem.
With sudden cardiac arrest , the heart malfunctions and suddenly stops beating. Sudden cardiac arrest is an electrical problem caused by irregular heart rhythms called arrhythmias. A common and potentially deadly arrhythmia is ventricular fibrillation. This happens when the hearts lower chambers suddenly start beating chaotically and dont pump blood.
A heart attack can cause ventricular fibrillation, which in turn can cause sudden cardiac arrest. Death can occur within minutes after the heart stops.
Cardiac arrest may be reversed if CPR is performed and a defibrillator is used within minutes to shock the heart and restore a normal heart rhythm.
You May Like: How To Reverse Congestive Heart Failure
Angina Vs Heart Attack
Chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart muscle is called angina. Its a common symptom of heart disease. There are two main types of angina:
- stable angina, the most common type of angina and one that is predictable often occurring with physical exertion or stress
- unstable angina, which is unpredictable and should be treated as a medical emergency
An angina attack can feel like a heart attack, and in many cases especially with unstable angina it can be hard to tell angina from an actual heart attack.
If you have stable angina thats brought on with exertion and eases with rest, you may assume a sudden but brief bout of chest pain is only an angina attack. If chest pain doesnt subside with rest or comes and goes for a period of 10 minutes or more, you may be having a heart attack.
Talking with your doctor about how to manage your angina will help you better understand the difference between angina and heart attack symptoms, and help prepare you if your chest pain is actually a symptom of a heart attack.
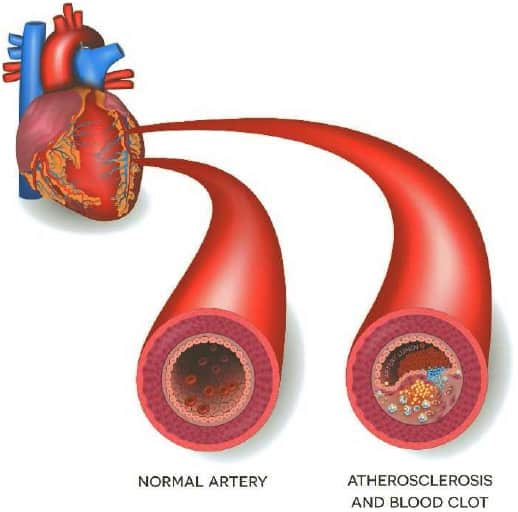
The leading cause of heart attacks is coronary heart disease. This is where plaque builds up in the arteries that supply blood to the heart. The general buildup of plaque in the arteries is also known as atherosclerosis.
There are two main types of heart attack.
In type II heart attacks the heart does not receive as much oxygen-rich blood as it needs, but there is not a complete blockage of an artery.
Other causes of heart attacks include:
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitors
Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors are important drugs for treating many people who have had a heart attack, particularly for people with and at risk for heart failure. ACE inhibitors should be given on the first day to such people with a heart attack, unless there are medical reasons for not taking them.
Almost all people admitted for ACS should receive ACE inhibitors if they have symptoms of heart failure or evidence of reduced left ventricular fraction on an echocardiogram. These drugs are also commonly used to treat high blood pressure and are recommended as first-line treatment for people with diabetes and kidney damage.
ACE inhibitors include captopril , ramipril , enalapril , quinapril , benazepril , perindopril , and lisinopril . All of these drugs are available in generic form.
Side Effects
Side effects of ACE inhibitors are uncommon but may include an irritating dry cough, excessive drops in blood pressure, and allergic reactions.
You May Like: When Does Heart Attack Happen
Honorhealth’s Commitment To Heart Attack Treatment
Surviving and recovering from a heart attack depends on two factors:
- The size of heart muscle affected by a blocked artery.
- How quickly the blockage is treated.
HonorHealth’s emergency cardiac care specialists live by the slogan “time is muscle.” The sooner we can provide emergency care that restores blood flow to your heart, the more likely youll survive without lasting heart damage.
One critical measure of emergency heart care is “door-to-balloon time” the time that elapses between your arrival in an emergency department and the moment a coronary artery is re-opened with a balloon catheter, if appropriate. HonorHealth has refined its processes to consistently perform far better than the national standard of 90 minutes.
Likewise, four HonorHealth medical centers are certified Cardiac Arrest Centers, meaning that we provide specialized cardiac care that increases survival rates. One example is reducing patients’ core temperature immediately following cardiac arrest, aiding chances of survival and full neurological recovery.
Duration Of A Heart Attack
If you experience symptoms that may indicate a heart attack for longer than five minutes, its important to seek emergency medical attention immediately.
Dont delay treatment by waiting to see if your symptoms go away. Even if your symptoms let up or change, there may be ongoing damage to your heart.
The sooner treatment is administered, the less likely a heart attack is to cause significant or long-lasting damage to your heart muscle.
You May Like: What Can Mimic Heart Attack Symptoms
Preparation For Open Heart Surgery
“Patients should openly inform the doctor about any drugs they are taking, even over-the-counter medications, vitamins, and herbs. Also inform the doctor If the patients have any illnesses like herpes outbreak, cold, flu, or fever. In the two weeks before the surgery, the patients are advised to quit smoking. Patients should also tell the doctor about alcohol consumption before preparation of the surgery. The day before the surgery Patients may be advised not to eat or drink anything after midnight,” says Dr Singh.
What About Hormone Therapy For Treating Heart Attack In Women
After menopause, the production of estrogen by the ovaries gradually diminishes over several years. Along with this reduction, there is an increase in LDL and a small decrease in HDL . These changes in lipid levels are believed to be one of the reasons for the increased risks of developing CAD after menopause. Women who have had their ovaries surgically removed or experience early menopause, also have an accelerated risk of CAD.
Since treatment with estrogen hormone results in higher HDL and lower LDL cholesterol levels, doctors thought for many years that estrogen would protect women against CAD . Many studies have found that postmenopausal women who take estrogen have lower CAD rates than women who do not.
Unfortunately, many of the studies were observational studies . Observational studies have serious shortcomings because they are subject to selection bias for example, women who choose to take estrogen hormones may be healthier and have a lower risk of heart attacks than those who do not. In other words, something else in the daily habits of women who take estrogen may make them less likely to develop heart attacks. Therefore, only a randomized trial can establish whether hormone therapy after menopause can prevent CAD.
HERS trial results
WHI trial results
An increase in breast cancer became apparent after three to five years, but the increase in heart disease and pulmonary emboli occurred early on, in the first year.
MedicineNet Medical Editors believe that:
Recommended Reading: What Is Heart Attack
Common Heart Attack Types And Treatments
The type of heart attack you experienced determines the treatments that your medical team will recommend. A heart attack occurs when a blockage in one or more coronary arteries reduces or stops blood flow to the heart, which starves part of the heart muscle of oxygen.
The blockage might be complete or partial:
- A complete blockage of a coronary artery means you suffered a STEMI heart attack or ST-elevation myocardial infarction.
- A partial blockage is an NSTEMI heart attack or a non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction
Treatments differ for a STEMI versus NSTEMI heart attack, although there can be some overlap.
Hospitals commonly use techniques to restore blood flow to part of the heart muscle damaged during a heart attack:
- You might receive clot-dissolving drugs , balloon angioplasty , surgery or a combination of treatments.
- About 36 percent of hospitals in the U.S. are equipped to use a procedure called percutaneous coronary intervention , a mechanical means of treating heart attack.
At a hospital equipped to administer PCI, you would likely be sent to a department that specializes in cardiac catheterization, sometimes called a cath lab. There, a diagnostic angiogram can examine blood flow to your heart and reveal how well your heart is pumping. Depending on the results of that procedure, you may be routed to one of three treatments: medical therapy only, PCI or coronary artery bypass grafting .
How Is Heart Attack In Women Treated
Thrombolytic therapy has been shown to reduce death from heart attacks similarly in men and women however, the complication of strokes from the thrombolytic therapy may be slightly higher in women than in men.
Emergency percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty or coronary stenting for acute heart attack is as effective in women as in men however, women may have a slightly higher rate of procedure-related complications in their blood vessels and death. This higher rate of complications has been attributed to women’s older age, smaller artery size, and greater severity of angina. The long-term outcome of angioplasty or stenting, however, is similar in men and women, and should not be withheld due to gender. This is still the preferred mode of therapy if it can be performed in a timely fashion.
The immediate mortality from coronary artery bypass graft surgery in women is higher than that for men. The higher immediate mortality rate has been attributed to women’s older age, smaller artery size, and greater severity of angina . Long-term survival, rate of recurrent heart attack, and/or need for reoperation, however, are similar in men and women after CABG.
You May Like: Heart Attack Survival Rate By Age
Medications For Heart Attacks
Less severe heart attacks may be treated with medication. Your doctor will prescribe you medications based on your condition, risk factors, and overall health. These drugs may include:
- clot busters to dissolve clots that are blocking arteries
- blood pressure medications to help reduce the hearts workload and control blood pressure
- blood thinners to prevent blood clots
- statins to help lower LDL cholesterol
What Can I Do To Recover After A Heart Attack
Take our quiz to see how much you know about cardiac rehabilitation.
If youve had a heart attack, your heart may be damaged. This could affect your hearts rhythm and its ability to pump blood to the rest of the body. You may also be at risk for another heart attack or conditions such as stroke, kidney disorders, and peripheral arterial disease .
You can lower your chances of having future health problems following a heart attack with these steps:
- Physical activityTalk with your health care team about the things you do each day in your life and work. Your doctor may want you to limit work, travel, or sexual activity for some time after a heart attack.
- Lifestyle changesEating a healthier diet, increasing physical activity, quitting smoking, and managing stressin addition to taking prescribed medicinescan help improve your heart health and quality of life. Ask your health care team about attending a program called cardiac rehabilitation to help you make these lifestyle changes.
- Cardiac rehabilitationCardiac rehabilitation is an important program for anyone recovering from a heart attack, heart failure, or other heart problem that required surgery or medical care. Cardiac rehab is a supervised program that includes
- Physical activity
- Education about healthy living, including healthy eating, taking medicine as prescribed, and ways to help you quit smoking
- Counseling to find ways to relieve stress and improve mental health
You May Like: Does Heart Attacks Run In Families
How Heart Attack Symptoms Vary Between Men And Women
We use women and men in this article to reflect the terms that have been historically used to gender people. But your gender identity may not align with how your body experiences symptoms of a heart attack. Your doctor can better help you understand how your specific circumstances will translate into symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment.
Many people experience a mix of heart attack symptoms regardless of sex or gender. However, there are sex-specific differences in the presentation, biology, and outcomes of heart attacks.
A women , the pain is often described as tightness, squeezing, or pressure in the chest, while men tend to describe it as a heavy weight on the chest.
According to the American Heart Association , women are somewhat more likely than men to experience the following heart attack symptoms:
- shortness of breath
- pain in the upper back or jaw
- dizziness or lightheadedness
- extreme fatigue
Higher levels of estrogen can reduce the risk of a heart attack. As a result, women have a greater risk of a heart attack after menopause than before menopause.
However, women who have a heart attack are more at risk of underdiagnosis and undertreatment.
For example, a 2018 Swiss study found that women tend to wait longer to contact emergency services after experiencing typical heart attack symptoms. Researchers also found that women tend to experience greater delays in receiving treatment in emergency settings.
Are There Other Causes Of Heart Attack Besides Blockage
Sometimes a coronary artery temporarily contracts or goes into spasm. When this happens, the artery narrows and blood flow to part of the heart muscle decreases or stops.
A spasm can occur in normal-appearing blood vessels as well as in vessels partly blocked by atherosclerosis. A severe spasm can cause a heart attack.
Another rare cause of heart attack is spontaneous coronary artery dissection , which is a spontaneous tearing of the coronary artery wall.
Don’t Miss: Do Heart Palpitations Make You Cough
