Women Have Heart Attacks Too
Women and men usually experience the same heart attack symptoms. But research shows women tend to not recognise the symptoms as a sign of a heart attack as quickly.
If you’re experiencing symptoms of a heart attack, you should call 999 immediately.In the UK, an average of three women die of coronary heart disease every hour, many of them due to a heart attack.You dramatically reduce your chance of survival if you don’t call 999 straight away.
Most heart attacks are caused by coronary heart disease .
CHD causes your coronary arteries to become narrowed by a gradual build-up of fatty deposits called atheroma.
If a piece of atheroma breaks off, a blood clot forms around this to try and repair the damage to the artery wall.
This clot can block your coronary artery either a partial blockage or total blockage . This causes your heart muscle to be starved of blood and oxygen.
Other less common causes of a heart attack include:
High Blood Pressure Is A Major Risk Factor For Heart Disease
High blood pressure occurs when the pressure of the blood in your arteries and other blood vessels is too high and can cause the arteries to stiffen.
You can lower your blood pressure with lifestyle changes like reducing sodium intake or taking medication to reduce your risk for heart disease and heart attack.
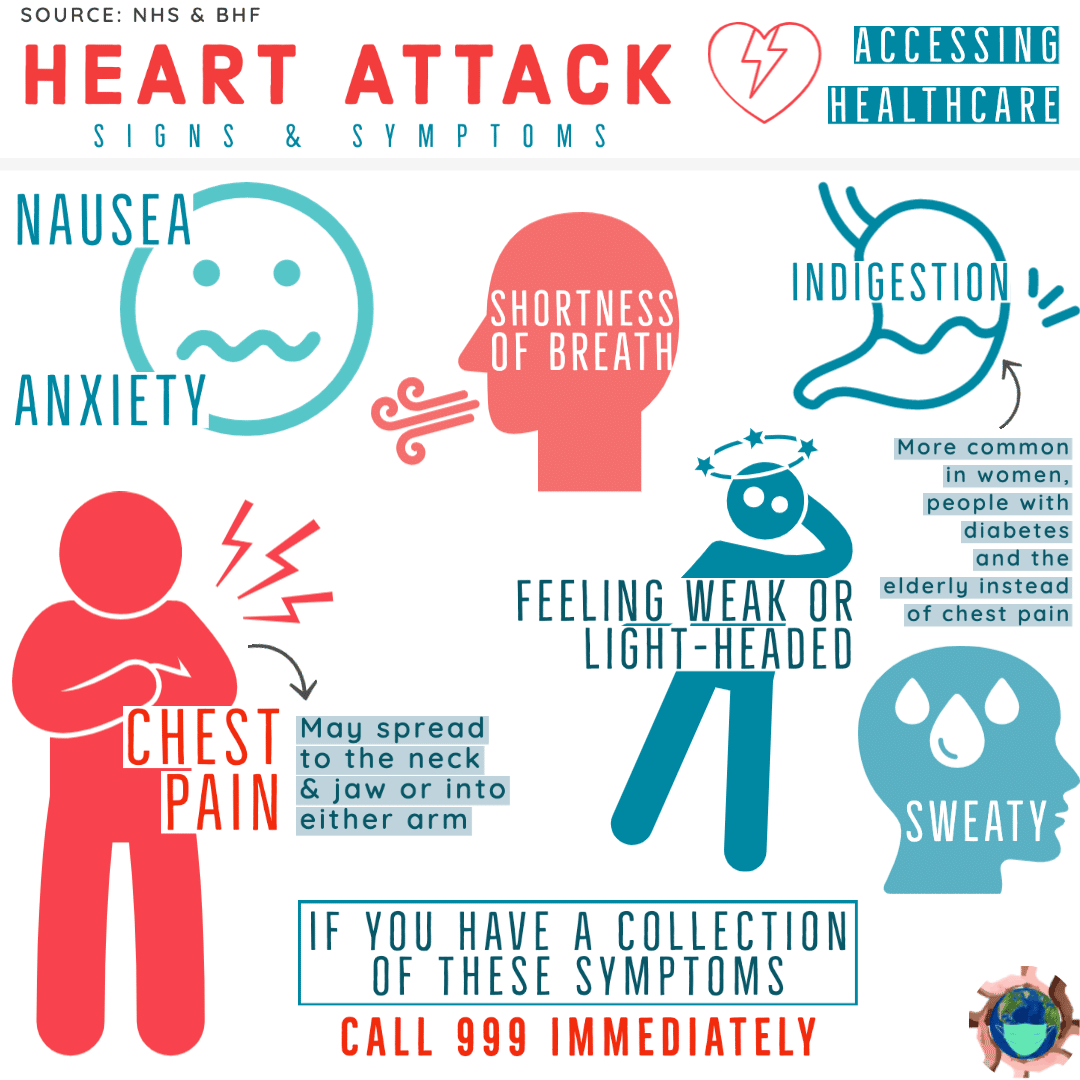
What Are Common Symptoms Of A Heart Attack
The classic image of a person having a heart attack is one of a person clutching their chest, complaining of crushing chest pain or an elephant sitting on their chest. However, in real life, the symptoms can be more subtle. Thats why you should go to the hospital as quickly as possible if you suspect you are having a heart attack, even if youre not experiencing the stereotypical symptoms.
The most common symptoms of a heart attack include:
- Chest pain: Most heart attacks involve some sort of pain in the center or left side of the chest. This pain can either be severe or mild. Some people, especially women, experience discomfort rather than pain during a heart attack. This discomfort can feel like pressure, squeezing or even indigestion.
- Upper body discomfort: Chest pain can sometimes radiate to the left arm or to the jaw. These symptoms can also occur in isolation, without chest pain.
- Shortness of breath: This symptom may accompany chest pain or discomfort, or it may be the only symptom of the heart attack.
Here are some other symptoms that might accompany the ones above:
- Breaking out in cold sweat
Don’t Miss: What Is Congested Heart Failure
Preventing A Heart Attack
There are 5 main steps you can take to reduce your risk of having a heart attack :
- smokers should quit smoking
- lose weight if you’re overweight or obese
- do regular exercise adults should do at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity each week, unless advised otherwise by the doctor in charge of your care
- eat a low-fat, high-fibre diet, including wholegrains and at least 5 portions of fruit and vegetables a day
- moderate your alcohol consumption
Catriona Found A Listening Ear

Mum of two Catriona had a heart attack just as lockdown was beginning, and she felt anxious and on edge because the usual support wasnt available.
I was given booklets about diet and exercise when I was discharged home and I was told someone would be in touch, but I didnt know when. I did feel quite isolated and I wasnt confident about what to do next, so thats why I phoned Chest Heart & Stroke Scotland.
Catriona began talking to Wendy from our Advice Line and got the invaluable practical and emotional support she really needed.
I feel like I can ask Wendy anything even if its a daft question. And I know I could call her at any time if I feel worried. It is so reassuring to know she is there for me.
You May Like: Does Magnesium Lower Heart Rate
What Can I Do To Recover After A Heart Attack
Take our quiz to see how much you know about cardiac rehabilitation.
If youve had a heart attack, your heart may be damaged. This could affect your hearts rhythm and its ability to pump blood to the rest of the body. You may also be at risk for another heart attack or conditions such as stroke, kidney disorders, and peripheral arterial disease .
You can lower your chances of having future health problems following a heart attack with these steps:
- Physical activityTalk with your health care team about the things you do each day in your life and work. Your doctor may want you to limit work, travel, or sexual activity for some time after a heart attack.
- Lifestyle changesEating a healthier diet, increasing physical activity, quitting smoking, and managing stressin addition to taking prescribed medicinescan help improve your heart health and quality of life. Ask your health care team about attending a program called cardiac rehabilitation to help you make these lifestyle changes.
- Cardiac rehabilitationCardiac rehabilitation is an important program for anyone recovering from a heart attack, heart failure, or other heart problem that required surgery or medical care. Cardiac rehab is a supervised program that includes
- Physical activity
- Education about healthy living, including healthy eating, taking medicine as prescribed, and ways to help you quit smoking
- Counseling to find ways to relieve stress and improve mental health
How Is A Heart Attack Diagnosed
The ambulance team will do an electrocardiogram to detect whether you’re having a heart attack. If the ECG shows youre having a heart attack, youre likely to have emergency treatment as soon as you arrive in hospital. If the ECG doesnt confirm a heart attack you might need further tests to investigate if you are having a heart attack, including:
- an assessment of your symptoms and medical history
- physical examinations, including measuring your blood pressure and monitoring your heart rhythm and heart rate
- blood tests including a troponin test to detect if theres been any damage to your heart muscle
- an echocardiogram.
You might hear a heart attack being called acute coronary syndrome, myocardial infarction or coronary thrombosis while you’re at hospital.
Read Also: What Can Cause Low Heart Rate
Myth: Chest Pain Is The Only Symptom Of A Heart Attack
The American Heart Association and other organizations that conduct public health campaigns have done a great job of educating the public that tightening in the chest and chest pain are warning signs of a heart attack. However, chest pain isnt the only symptom. Heart attack symptoms can differ from person to person, and a womans symptoms may differ from a mans.
Typically, chest pain is the most common symptom during a heart attack for both men and women. However, women more so than men experience symptoms such as shortness of breath, nausea, or back or jaw pain.
Keep in mind that just because you experience one or one of these symptoms doesnt mean youre having a heart attack. Nevertheless, its always best to get it checked out and not to wait to see whether the symptoms pass.
Who Is Most At Risk For A Heart Attack
Several key factors affect your risk of having a heart attack. Unfortunately, some of these risk factors aren’t things you can control.
- If you have certain health conditions or diseases.
Age and sex
Your risk of heart attack increases as you get older, and your sex also influences when your risk of a heart attack starts to increase:
- Men: The risk of heart attack increases greatly at age 45.
- Women: The risk of heart attack increases greatly at age 50 or after menopause.
Family history
If you have a parent or sibling with a history of heart disease or heart attack especially at a younger age your risk is even greater. That risk increases with the following:
- Your father or a brother who was diagnosed with heart disease at age 55 or younger.
- Your mother or a sister who was diagnosed with heart disease at age 65 or younger.
Lifestyle
The lifestyle choices you make can also affect your risk of having a heart attack. The following lifestyle factors increase your risk of heart attack:
- Lack of physical activity.
- Eating disorders .
Don’t Miss: How Many Heart Attacks Can You Have And Live
What Tests Will Be Done To Diagnose This Condition
Anyone with heart attack symptoms should undergo a physical examination, including checking pulse, blood oxygen levels, blood pressure, and listening to heart and lung sounds.
Other tests used to diagnose heart attack include:
- Electrocardiogram : This is one of the first tests done when someone comes to an ER with heart attack symptoms. This test uses sensors called electrodes that attach to the skin of your chest. The electrodes pick up electrical activity in the heart and show it as a wave on a display or printout. By looking at the wave, providers can see the strength and timing of the electrical signal as it travels through your heart. When the signal doesnt travel like it should, the shape of the wave changes, which can indicate a heart attack or similar problems. EKG for a heart attack is usually continuous to monitor for changes in heart activity.
STEMI and non-STEMI heart attacks
The wave of your heart’s electrical signal is divided into sections using letters of the alphabet starting at P and ending at U. One particular section of the wave, the ST segment, shows activity in the heart’s lower two chambers. Those chambers are the left ventricle and right ventricle.
- Blood tests. During a heart attack, the damage to heart muscle cells almost always causes a chemical marker to appear in your bloodstream. Blood tests that look for that marker are among the most reliable methods to diagnose a heart attack.
Managing Heart Attack Risk Factors
Here are ways to manage your risks for a heart attack:
- Look at which risk factors apply to you, then take steps to eliminate or reduce them.
- Learn about high blood pressure and high cholesterol levels. These may be “silent killers.”
- Change risk factors that aren’t inherited by making lifestyle changes. Talk with your healthcare provider to find out how to do so.
- Talk with your healthcare provider to find out if you have risk factors that can’t be changed. These can be managed with medicine and lifestyle changes.
Recommended Reading: How Bad Does A Heart Attack Hurt
Should I Still Call 999 Or Go To Hospital If I’m Worried About My Health
Whether or not you have coronavirus symptoms, it’s essential to dial 999 if you have symptoms that could be a heart attack, or if your heart symptoms get worse.
We are hearing that fewer people are being seen in hospital with heart attacks in recent weeks, which suggests that people are not seeking help when they should do. If you have any of the symptoms described above, you should call 999.
Don’t delay because you think hospitals are too busy – the NHS still has systems in place to treat people for heart attacks. If you delay, you are more likely to suffer serious heart damage and more likely to need intensive care and to spend longer in hospital.
Myth: Heart Attacks Are Purely Hereditary
The idea that just because a condition runs in your family means you have it, too, and you cant do anything about it is pure fiction. Heart attacks may not be completely preventable, but you can keep many of the risk factors at bay by committing to a healthy lifestyle.
Its true that genetics is a part of the picture and may put you at a higher risk of having a heart attack. However, lifestyle choices in diet, exercise, and whether you smoke play a greater role.
Recommended Reading: Acute Systolic Congestive Heart Failure
Is My Heart Permanently Damaged
When a heart attack occurs, the heart muscle that has lost blood supply begins to suffer injury. The amount of damage to the heart muscle depends on the size of the area supplied by the blocked artery and the time between injury and treatment.
Heart muscle damaged by a heart attack heals by forming scar tissue. It usually takes several weeks for your heart muscle to heal. The length of time depends on the extent of your injury and your own rate of healing.
The heart is a very tough organ. Even though a part of it may have been severely injured, the rest of the heart keeps working. But, because of the damage, your heart may be weakened, and unable to pump as much blood as usual.
With proper treatment and lifestyle changes after a heart attack, further damage can be limited or prevented.
Learn more about heart damage detection.
What Do I Do If I Have A Heart Attack
After a heart attack, you need quick treatment to open the blocked artery and lessen the damage. At the first signs of a heart attack, call 911. The best time to treat a heart attack is within 1 or 2 hours after symptoms begin. Waiting longer means more damage to your heart and a lower chance of survival.
If youâve called emergency services and are waiting for them to arrive, chew an aspirin . Aspirin is a potent inhibitor of blood clots and can lower the risk of death from a heart attack by 25%.
Don’t Miss: How To Get Resting Heart Rate Down
What Does Depression Have To Do With A Heart Attack
Depression is common after a heart attack. As many as 1 out of every 3 people who have had a heart attack report feelings of depression. People with a higher risk of depression after a heart attack include:
- People who have had depression before
- People who feel alone and without social or emotional support
Many people who have depression dont recognize it. They dont seek help or get treatment. Being depressed can make it harder for you to recover physically. Depression can be treated.
Some people have anxiety after a heart attack, fearing it will happen again. Talk to your doctor about your feelings so that you can manage or reduce your anxiety.
What Are The Risk Factors For Heart Attack
Several health conditions, your lifestyle, and your age and family history can increase your risk for heart disease and heart attack. These are called risk factors. About half of all Americans have at least one of the three key risk factors for heart disease: high blood pressure, high blood cholesterol, and smoking.2
Some risk factors cannot be controlled, such as your age or family history. But you can take steps to lower your risk by changing the factors you can control.
Learn more about risk factors for heart disease and heart attack.
Read Also: Living With Heart Failure
Why Didnt I Have Any Warning
The process of atherosclerosis has no symptoms. When a coronary artery narrows and constricts blood flow, other nearby blood vessels that serve the heart sometimes expand to compensate, which may explain why there are no warning signs.
Such a network of expanded nearby blood vessels is called collateral circulation, and it helps protect some people from heart attacks by delivering needed blood to the heart. Collateral circulation can also develop after a heart attack to help the heart muscle recover.
Cardiac Arrest Or Heart Attack
A heart attack is not the same as a cardiac arrest. They are two different types of cardiac event.
A heart attack occurs when a coronary artery becomes blocked, preventing blood flow to part of the heart muscle. During a heart attack a person remains conscious and keeps breathing.
A cardiac arrest occurs when the heart stops pumping blood around the body. Normal breathing stops and consciousness is lost.
Sometimes a heart attack can cause a cardiac arrest. This is because a person who is having a heart attack may develop a dangerous heart rhythm, which causes a cardiac arrest. A heart attack and a cardiac arrest are both emergency situations. Call 111 straight away.
Recommended Reading: How To Find My Heart Rate
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
- Is there a test I can take to see if my arteries or blocked so I know if Im at risk of a having a heart attack?
- What is the likely cause of my heart attack?
- How serious was my heart attack?
- What course of treatment do you recommend? Do I need medicine? Surgery?
- Do I need to participate in a cardiac rehabilitation program?
- When can I return to normal physical and sexual activity?
- What is my risk of having another heart attack?
- Are my family members at an increased risk of heart attack?
- Do I need to take medicine to prevent another heart attack?
- Will the medicine interact with any of the medicine I already take?
- What lifestyle changes should I make at home to prevent another heart attack?
- Can sexual activity cause a heart attack?
Heart Disease In The United States
- Heart disease is the leading cause of death for men, women, and people of most racial and ethnic groups in the United States.1
- One person dies every 34 seconds in the United States from cardiovascular disease.1
- About 697,000 people in the United States died from heart disease in 2020thats 1 in every 5 deaths.1,2
- Heart disease cost the United States about $229 billion each year from 2017 to 2018.3 This includes the cost of health care services, medicines, and lost productivity due to death.
Coronary Artery Disease
- Coronary heart disease is the most common type of heart disease, killing 382,820 people in 2020.2
- About 20.1 million adults age 20 and older have CAD .2
- In 2020, about 2 in 10 deaths from CAD happen in adults less than 65 years old.2
Early Action Is Important for Heart Attack
- In the United States, someone has a heart attack every 40 seconds.2
- Every year, about 805,000 people in the United States have a heart attack.2 Of these,
- 605,000 are a first heart attack2
- 200,000 happen to people who have already had a heart attack2
- About 1 in 5 heart attacks are silentthe damage is done, but the person is not aware of it.2
You May Like: Clinical Manifestations Of Heart Failure
