The Diet Plan Should Include Restriction Of Sodium Potassium And Fluid Intake Adequate Calorie Intake And Lowfat Foods For Weight Control
The diet plan should include restriction of sodium , potassium, and fluid intake adequate calorie intake and low-fat foods for weight control. The diet plan should be individualized to meet the needs of each patient. It should also provide at least 1 g of protein per kilogram body weight daily, with an upper limit of 2 g/kg. In addition, patients should receive a minimum intake of vitamins A and C and iron according to their age group requirements.
Many drugs are used in treating heart failure in order to reduce symptoms such as shortness of breath or swelling when fluid builds up in your ankles or legs because your heart isnt pumping well enough on its own. These medications include diuretics that cause you urinate more often than usual which helps rid excess fluids from your body other medications expand blood vessels so that more oxygenated blood reaches your heart muscle resulting in improved pumping ability ACE inhibitors lower levels of certain hormones produced by your kidneys that cause constriction within smaller blood vessels throughout our bodies including those found inside our hearts causing them too work harder than usual thus increasing risk for damage over time without proper treatment intervention measures being taken immediately upon discovering signs/symptoms during routine checkups etcetera
To read more about medications used during treatment please visit this link: https://www
Imbalanced Nutrition: More Than Body Requirements
May be related to:poor dietary habits, lack of exercise, excessive eating compared to nutritional needs, eating in response to emotional cues or external stimuli, poor dietary habits, lack of knowledge about appropriate portion size and food preparation.
As evidenced by:increased BMI, undesirable eating patterns, and sedentary lifestyle.
Donât Miss: Increased Resting Heart Rate
Atrial Fibrillation Nursing Care Plan 4
Acute Pain
Nursing Diagnosis: Acute pain related to decreased myocardial blood flow and increased cardiac workload or oxygen consumption secondary to atrial fibrillation as evidenced by reports of pain with varying frequency, duration and intensity, narrowed focus, distraction behaviors , and autonomic responses
Desired Outcomes:
- For the patient to report anginal episodes that have decreased in frequency, duration, and severity.
- For the patient to demonstrate pain relief as evidenced by the absence of muscle tension and restlessness, and stable vital signs.
Recommended Reading: How Does Music Affect Your Heart Rate
Patients Should Be Instructed In The Appropriate Use Of Daily Weights To Identify Fluid Retention
The patient should be instructed in the appropriate use of daily weights to identify fluid retention. If a significant increase in weight is noted, diuretics should be increased and dietary modifications made. Diuretics should be started early in the day and taken with meals to minimize side effects such as hypotension and gastrointestinal disturbances.
Prevention Of Atrial Fibrillation
Preventing atrial fibrillation involves the following lifestyle modifications:
- Eating healthy foods, specifically a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Exercising regularly and increasing physical activity
- Quitting tobacco smoking
Recommended Reading: How Long To Recover From Heart Attack
Read Also: Preventing Strokes And Heart Attacks
Types Of Heart Failure
There are two types of heart failure depending on the type of underlying disease that has caused it.
1. Congestive Heart Failure results from an inability of the left ventricle to fill with blood upon relaxation and a diminished stroke volume . This produces increased pressure in the left ventricle and pulmonary vascular bed.
2. Restrictive Cardiomyopathy is caused by the loss of heart muscle, usually because of a disease or an injury.
The pathophysiology of cardiomyopathy is different from that of congestive heart failure in that it does not involve the left ventricle. Also, with cardiomyopathy, there is a decreased ventricular compliance, and the stiffness of the heart muscle increases.
Nurses Can Care For Patients With Heart Failure By Preventing Further Damage To The Heart Through Several Interventions
Nurses can care for patients with heart failure by preventing further damage to the heart through several interventions. Nurses may include:
- Preventing further damage to the heart
- Halting disease progression
- Improving symptoms
- Optimizing effectiveness of medical therapy
Nurses may also improve quality of life by focusing on preventive strategies such as smoking cessation and weight management programs, along with exercise regimens.
Also Check: Medicines For Congestive Heart Failure
Chf Nursing Care Plan 3
Nursing Diagnosis: Deficient Knowledge related to new diagnosis of Congestive Heart Failure as evidenced by patients verbalization of I want to know more about my new diagnosis and care
Desired Outcome: At the end of the health teaching session, the patient will be able to demonstrate sufficient knowledge of congestive heart failure and its management.
Nursing Intervention In Cardiac Catheterization Lab
The patient will be prepared in the dressing room and will be placed on a stretcher. He will then be brought to the cath lab by staff members and placed on the table prepped with sterile drapes and sheets specific for cardiac catheterizations. An EKG monitor will be attached to the patient. The nurse or physicians assistant will connect a medication line and secure an arterial line for blood pressure monitoring if needed. An intravenous access site for IV medications and fluids will also be established on one of the arms for drug therapy and fluid administration.
After the intervention has been performed, the patient will be taken back to the dressing room, where he will be discharged from the Cath Lab. The nurse must ensure that no air bubbles are present in any line attached to the patient before discharging him from the Cath Lab. The nurse should place a warm blanket around the patient, and he will be accompanied to his room by staff members. The nurse will then continue monitoring vital signs, EKG and oxygen saturation, and respiratory changes using the AVPU scale . The nurse will re-assess the patients pain level using a verbal rating scale of 0 to 10. A post-procedure chest x-ray may be taken. The cath lab nurse must remain in constant contact with the nursing staff in the ICU and cardiac floor to ensure no untoward reactions or complications.
- Monitor complete blood count with differential, urinalysis, BMP, and creatinine/urinary output hourly.
You May Like: What Can Cause Increased Heart Rate
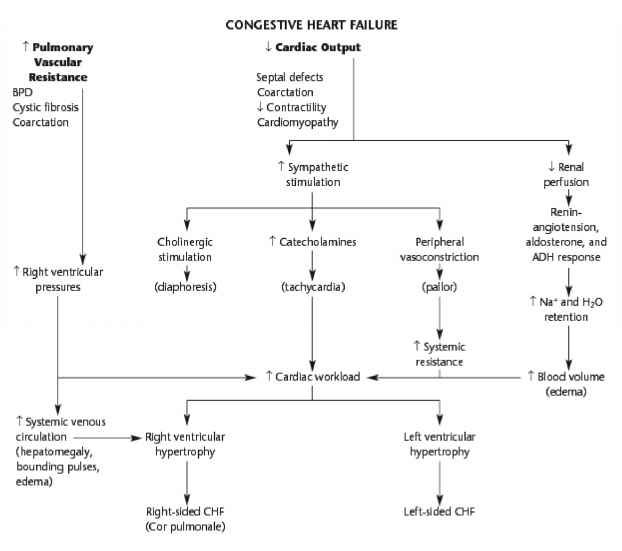
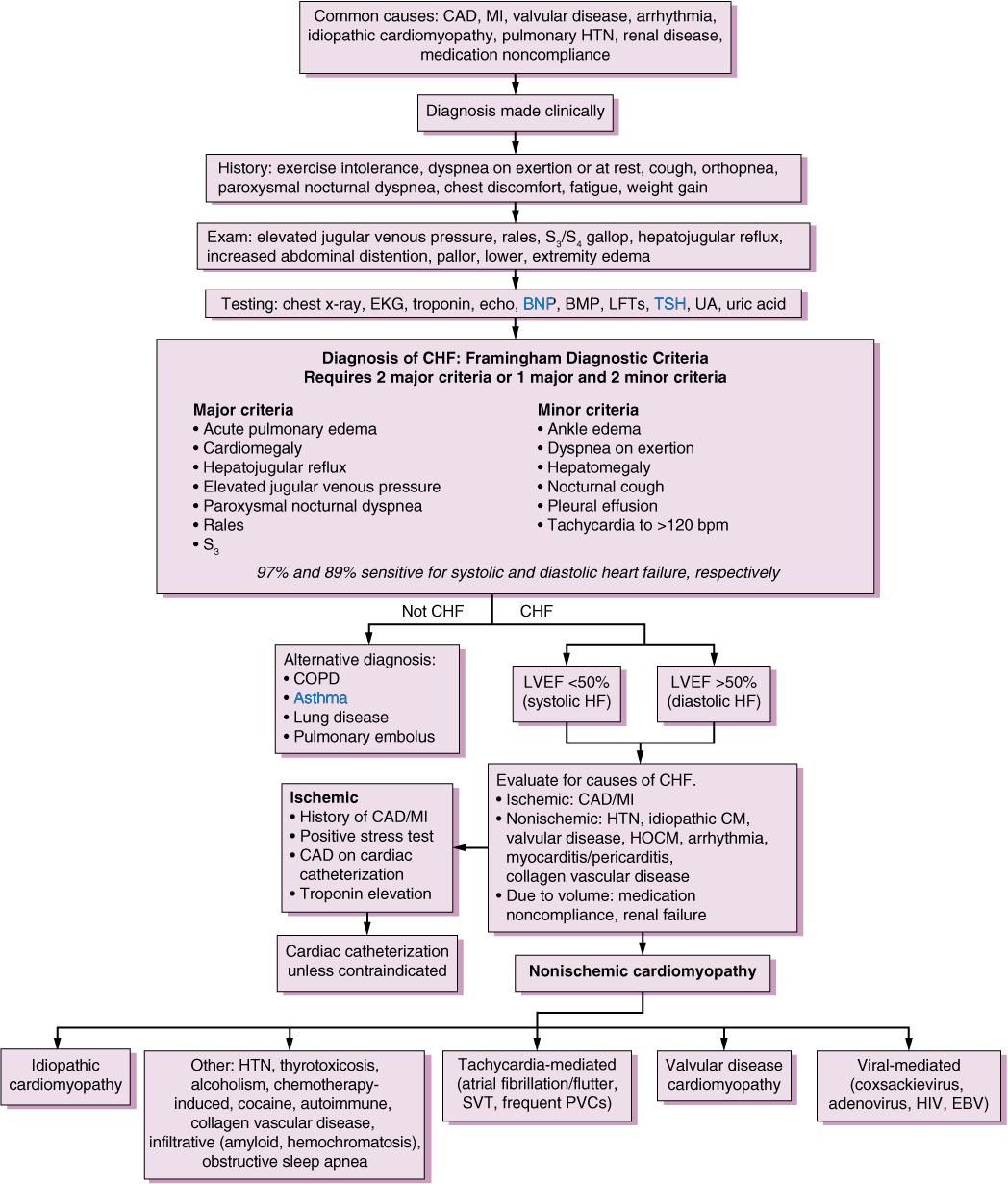
What Is Congestive Heart Failure
Heart failure is a chronic, progressive condition. It occurs when the heart is unable to pump effectively and produce enough cardiac output to successfully perfuse the rest of the bodys tissues and organs. An individual can have right-sided or left-sided heart failure as well as systolic or diastolic heart failure.
Left-sided heart failure is also known as Congestive Heart Failure . In CHF, the heart is either unable to contract completely or fill completely during relaxation. It can lead to an inadequate amount of blood pumping out of the heart. Thereby, backing up into the right side and then ultimately to the lungs and throughout the body causing congestion.
Systolic heart failure means the heart is not able to contract completely and affects its ability to pump blood out of the heart.
Diastolic heart failure means the heart is unable to relax fully between heartbeats and allows the appropriate amount of blood into the ventricle.
In this post, well formulate a sample nursing care plan for a patient with Congestive Heart Failure based on a hypothetical case scenario.
Nursing Diagnosis For Cardiovascular Diseases
by Daisy Jane Antipuesto RN MN·August 4, 2009
Cardiovascular diseases are a group of disorders of the heart and blood vessels and include:
- Coronary heart disease disease of the blood vessels supplying the heart muscle
- Cerebrovascular disease disease of the blood vessels supplying the brain
- Peripheral arterial disease disease of blood vessels supplying the arms and legs
- Rheumatic heart disease damage to the heart muscle and heart valves from rheumatic fever, caused by streptococcal bacteria
- Congenital heart disease malformations of heart structure existing at birth.
- Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism blood clots in the leg veins, which can dislodge and move to the heart and lungs.
Heart attacks and strokes are usually acute events and are mainly caused by a blockage that prevents blood from flowing to the heart or brain. The most common reason for this is a build-up of fatty deposits on the inner walls of the blood vessels that supply the heart or brain. Strokes can also be caused by bleeding from a blood vessel in the brain or from blood clots.
FACTS ABOUT CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES
COMMON SYMPTOMS OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES
POTENTIAL NURSING DIAGNOSIS FOR SEVERE HYPERTENSION:
Read Also: Congestive Heart Failure Exercise
Read Also: Classes Of Heart Failure
Nursing Assessment Of Heart Failure
- Take the complete history of symptoms, onset and duration of symptoms, the response of the symptom to rest. Assess the neurological status of the patient.
- Auscultate the heart sound, rhythm and measure the blood pressure. Assess for any peripheral edema.
- Assess for any defect in respiratory systems like, respiratory effort, presence of wheezes, crackles. Do percussion to find out any pleural effusion.
- Inspect neck for jugular vein distension and take hemodynamic measurements.
- Check abdomen for ascites and determine any weight change.
- Do laboratory tests to check serum electrolyte levels.
- Identify sleep patterns.
Nursing Care Plan And Diagnosis For Fluid Volume Excess Fluid Overload Congestive Heart Failure Pulmonary Edema Ascites Edema And Fluid And Electrolyte Imbalance
This online nursing care plan below includes the following conditions: Fluid Volume Excess, Fluid Overload, Congestive Heart Failure, Pulmonary Edema, Ascites, Edema, and Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalance. What are nursing care plans? How do you develop a nursing care plan? What nursing care plan book do you recommend helping you develop a nursing care plan? This care plan
Also Check: How To Determine Maximum Heart Rate
Don’t Miss: Tests For Heart Attack
Encountering A New Situation
This sub-concept means that once the patients with HF understood how HF was related to their lifestyle, they noticed how the hospital environment was different from their own life at home in terms of activity, reducing salt intake, and management of blood pressure. They began confronting the reality that simple acts, like putting on their socks or cutting their nails, would become more difficult after hospitalization.
Causes Of Heart Failure:
Mainly due to the heart muscle becoming damaged or too stiff.
Remember the mnemonic: Failure
Faulty heart valves: AV and SL valve problems that causes blood to back flow or stenosis . This causes the heart to work harder and become weak over time.
Arrhythmias: atrial fibrillation or tachycardia
Infarction coronary artery disease: part of the heart muscle dies due to a blockage in the coronary arteriesmuscle become ischemic and can die
Lineage family history
Uncontrolled Hypertension: overtime this can lead to stiffening of the heart walls because with untreated HTN the heart has to work harder and this causes the ventricles to become stiff.
Recreational Drug Use or alcohol abuse
Envaders : viruses or infections that attack the heart muscle
Don’t Miss: Which Is A Potassium-sparing Diuretic Used In The Treatment Of Heart Failure
Nursing Care Plan Diagnosis Interventions For Anxiety Nervousness Inability To Cope And Ineffective Individual Coping
This free nursing care plan is for the following conditions: Anxiety, Nervousness, Inability to Cope, and Ineffective Individual Coping What are nursing care plans? How do you develop a nursing care plan? What nursing care plan book do you recommend helping you develop a nursing care plan? This care plan is listed to give an
Perform These Interventions For Congestive Heart Failure
Perform these interventions for congestive heart failure
Nurses should use standing orders
Congestive heart failure patients often wait too long to seek medical treatment and arrive in the ED in an acutely exacerbated state, says Eileen Swailes, RN, nurse manager of the ED overflow unit at Good Samaritan Hospital Medical Center in West Islip, NY.
“Delayed recognition of acute events results in a more complicated length of stay and increases the chances of mortality,” says Swailes. Here are three ways to speed care of CHF patients:
Recognize signs and symptoms.
“To avoid a delay in treatment for this population, it is imperative the ED nurse recognizes the signs and symptoms of CHF,” says Swailes. In addition to shortness of breath, CHF patients may present with lower extremity edema, chest pain, cough, exhaustion, irregular heartbeats, or palpitations, she says.
Have the same index of suspicion for CHF whether the patient arrives via triage or ambulance, says Jennifer Zanotti, MS, RN, CEN, CCRN, ED clinical nurse specialist at Ronald Reagan University of California Los Angeles Medical Center. Zanotti says to look for dyspnea, orthopnea, fatigue, abdominal discomfort secondary to ascites or hepatomegaly, edema that is dependent, jugular venous distention, bilateral crackles, and S3 heart sound. “Recognize the patient populations at risk, then work to discover the primary precipitating event for heart failure,” she says.
Use standing orders.
Don’t Miss: Signs Of Dog Heart Failure
Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Ventilation/perfusion Imbalance As Evidenced By Breath Sounds Crackling Sounds Coughing Up Mucus And/or Blood Use Of Accessory Muscles Dyspnea
Breathing problems may be a sign of heart failure. As the heart gets weaker, it cant pump blood well enough to support your lungs and other organs. The amount and quality of blood flowing through your lungs may be reduced or cut off entirely because the heart has lost its ability to pump blood effectively.
- Crackling sound : This happens when fluid builds up in the lungs and gets pushed out with each breath you take. The fluid in your lungs produces raspy sounds as it passes through them when you breathe out.
- Coughing up mucus: Mucus buildup in the throat causes coughing as it tries to clear itself out when you swallow or move around too much during sleep this is known as dyspnea .
Acta Paul Enferm 2007 : 357
ISSUE Cover
DOI: 10.1590/S0103-21002007000300019
OBJECTIVE: To evaluate expected outcomes of nursing interventions to address the nursing diagnosis of fatigue. METHODS: A cross-sectional quasi-experimental design was used. The sample consisted of 30 coronary care unit in-patient with congestive heart failure and fatigue. A specific tool designed for this study was used to collect specific data on outcomes of nursing interventions to manage the nursing diagnosis of fatigue. RESULTS: Nursing interventions to manage patients fatigue had positive outcomes. The use of the nursing process to identify the nursing diagnosis of fatigue, design and implement specific nursing interventions, and evaluate patient outcomes leads to quality nursing care.
How to cite this article
AssisCC, BarrosALBL, GanzarolliMZ. Evaluation of expected outcomes of nursing interventions to address the nursing diagnosis of fatigue among patients with congestive heart failure. Acta Paul Enferm. 2007 20:357-61.
Assis,Cinthia Calsinski de Barros,Alba Lúcia Bottura Leite de Ganzarolli,Marcela Zanatta. Evaluation of expected outcomes of nursing interventions to address the nursing diagnosis of fatigue among patients with congestive heart failure. Acta Paul Enferm., v. 20, n. 3, p. 357-361, Mar. 2007.
Don’t Miss: What Should Your Resting Heart Rate Be
Types Of Heart Failures:
Left & Right Side Heart Failure
Left-Sided Heart failure: the left side of the heart cannot pump blood out of the heart efficiently so blood starts to back-up in the lungs.
- Most common type of heart failure.
- Left-sided heart failure is likely to lead to right-sided heart failure.
The left ventricle becomes too weak and doesnt squeeze blood out properly.the heart failure can be either SYSTOLIC OR DIASTOLIC.
- Systolic: Left ventricular systolic dysfunction remember systolic is the contraction or squeezing phase of the heart. In systolic dysfunction, there is an issue with the left ventricle being able to eject blood properly out of the ventricle and the organs cant get all that rich-oxygenated blood it just received from the lungs. Patients will have a low ejection fraction.
- What is ejection fraction? Ejection fraction is a calculation used to determine the severity of heart failure on the left side. A normal EF is 50% or greater meaning that more than half of the blood that fills inside the ventricles is being pumped out. An EF can be measured with an echocardiogram, heart cath, nuclear stress test. An EF of 40% or less is a diagnosis for heart failure.
- Diastolic: left ventricular diastolic dysfunction remember diastole is the filling or resting phase of the heart. In diastolic dysfunction, the ventricle is too stiff to allow for normal filling of blood. Since there isnt an issue with contraction but filling the ejection fraction is usually normal.
Chronic Heart Failure Part : Treatment And Management
Rebecca Brake Advanced nurse practitioner in cardiology, Mid Cheshire NHS Foundation Trust, Cheshire, England
Ian David Jones Professor of cardiovascular nursing, School of Nursing and Allied Health, Liverpool John Moores University, Liverpool, England
Chronic heart failure is a common and complex clinical syndrome that results from impaired cardiac relaxation or contraction. There have been considerable advances in the management of chronic heart failure however, the mortality rate remains high. Patients with chronic heart failure may experience multiple debilitating symptoms, such as fatigue, pain, and peripheral oedema. However, breathlessness may be considered the most debilitating symptom. The management of chronic heart failure aims to improve the patients quality of life by reducing symptoms and supporting the patient to manage their condition. Treatment of patients with chronic heart failure may involve a combination of pharmacological therapy, device implantation and cardiac rehabilitation. This is the second of two articles on chronic heart failure. Part 1 discussed the pathophysiology of chronic heart failure, its causes, assessment, signs and symptoms. Part 2 outlines the treatment and management of patients with the condition, including pharmacological strategies, device implantation, lifestyle modification, cardiac rehabilitation and palliative care.
Nursing Standard.31, 20, 53-63. doi: 10.7748/ns.2017.e10762
CorrespondencePeer reviewConflict of interest
Don’t Miss: Why Do Anti Inflammatories Cause Heart Attacks
