Considering Complexity Of Heart Disease
The researchers looked at results based on the patients underlying coronary disease. They found that patients with less complex coronary artery disease did better with stents, as physicians could limit the number of the mesh tubes they had to place.
I think the study results will guide both physicians and patients on the best strategy for their circumstances, Fearon said. If patients have very complex disease that would require numerous stents, then bypass might be a better option. If they have less complex disease, they can feel reassured that by receiving the latest generation of drug-eluting stents guided by FFR, their outcomes would be just as good as they would be with surgery.
He said stents also have an advantage in that they entail shorter hospital stays and faster recoveries. Patients who receive stents generally go home the same day and recover quickly. Bypass patients, on the other hand, may remain in the hospital for as many as five days or longer, with a recovery time of six to eight weeks. In the study, bypass patients also had a higher incidence of major bleeding, arrythmia, acute kidney injury and rehospitalization within 30 days.
The FAME 3 trial was initiated by Fearon and two of the other investigators and was sponsored by Stanford Medicine. Medtronic Inc. and Abbott Vascular Inc. provided research grants for the study but were not involved in its design or implementation.
- Ruthann Richter Ruthann Richter is a freelance writer.
What Are The Risks Associated With Heart Stents
There are two kinds of stents. One type is a bare stent which is made up of 316 L type stainless steel. Heart stents being foreign objects for the body, they have certain associated side effects. They trigger an immune response from the body causing platelet accumulation at the stent site. This is taken care of, by lifelong intake of aspirin and intake of drugs likeClopidogrel for 6 months after the procedure. Still the scarring left by the stents does cause problems and in time, there may be renarrowing of the arteries at the operated site.
To prevent this, drug-coated or drug-eluting stents were developed that prevent the accumulation of arterial tissue over the stent and suppress immune response against it. Heart stent surgery using these drug-eluting stents is preferred now. However, this type has been known to cause blood clots in some case studies. About 1% to 2% people undergoing a drug-eluted stent surgery suffer from the growth of blood clots at the stent site. Hence the patient has to use blood thinning, anti-blood clotting drugs like Plavix for a prolonged period of time, which causes additional side effects. These effects include gastrointestinal bleeding and strokes in some cases. So stents are lifesavers but they also come with their share of risks.
Cardiology Services On The West Bank
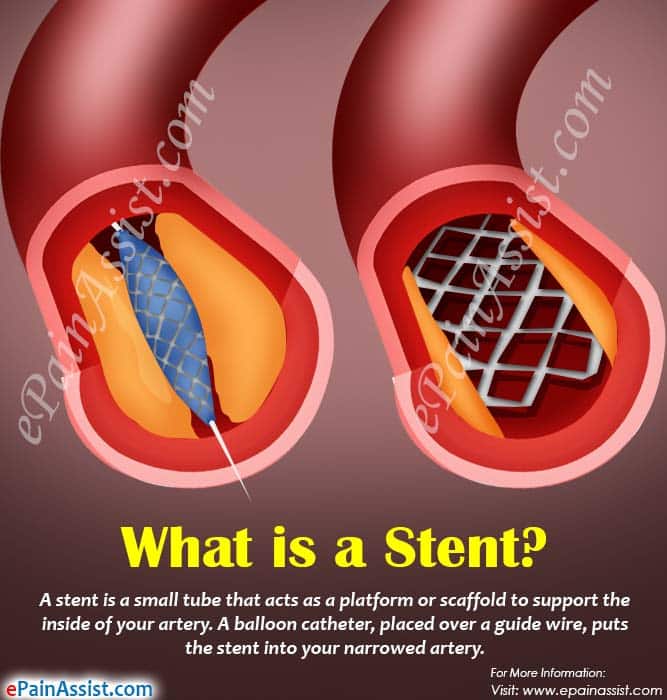
A stent is a small mesh tube made of stainless steel that is placed into blood vessels to prevent blood clots. Stenting is usually recommended for patients with severe cases of atherosclerosis- a common condition that describes plaque buildup in the arteries. When plaque builds in the arteries, it makes it difficult for blood to flow and increases the likelihood of a blot clot. Blood clots are very serious and could result in life threatening conditions like a heart attack or stroke. The good news is that they are preventable.
You May Like: How Does A Heart Attack Affect The Body
Diagnostic Tests And Procedures
To diagnose narrowed arteries or an aortic aneurysm, your doctor may have you undergo some of the following tests and procedures:
- Chest magnetic resonance imaging to look for aneurysms in the aorta. This test works well for detecting aneurysms and pinpointing their size and exact location.
- Computer tomography angiography and magnetic resonance angiography to take pictures of your blood vessels. These tests may give your doctor more information about the flow of blood and whether arteries are narrowed or have aneurysms.
- Coronary angiography to see how blood flows through your coronary arteries. This type of test involves injecting dye into your blood so that your blood vessels can be seen by X-ray.
- Fractional flow reserve can help determine how narrow the artery is. This is an added test done during CTA or coronary angiography to check the blood pressure in a specific artery.
- Ultrasound to see whether plaque has narrowed or blocked your carotid or peripheral arteries or to see if you have an aneurysm and where it may be located. This painless test uses high-energy sound waves to create pictures of the insides of your blood vessels.
- Echocardiography to evaluate the structure and function of your heart. Echocardiography uses sound waves to create moving pictures of your heart.
- Nuclear imaging to see whether the blood is flowing normally to the heart. Your doctor will inject a tracer substance that will show whether the heart is receiving enough blood flow.
What Are The Risks Of Coronary Angioplasty
Coronary angioplasty is a common medical procedure. Although angioplasty is normally safe, there is a small risk of serious complications, such as:
- Bleeding from the blood vessel where the catheter was placed.
- Damage to blood vessels from the catheter.
- An allergic reaction to the dye given during the angioplasty.
- An arrhythmia .
- The need for emergency coronary artery bypass grafting during the procedure . This may occur when an artery closes down instead of opening up.
- Damage to the kidneys caused by the dye used.
As with any procedure involving the heart, complications can sometimes, though rarely, cause death. Less than two percent of people die during angioplasty.
Sometimes chest pain can occur during angioplasty because the balloon briefly blocks off the blood supply to the heart.
The risk of complications is higher in:
- People age 75 years and older
- People who have kidney disease or diabetes
- People who have poor pumping function in their hearts
- People who have extensive heart disease and blockages
Research on angioplasty is ongoing to make it safer and more effective, to prevent treated arteries from closing again and to make the procedure an option for more people.
Don’t Miss: Do Heart Attack Symptoms Come And Go Over Weeks
Why The Procedure Is Performed
Arteries can become narrowed or blocked by deposits called plaque. Plaque is made up of fat and cholesterol that builds up on the inside of artery walls. This condition is called hardening of the arteries .
Angioplasty may be used to treat:
- Blockage in a coronary artery during or after a heart attack
- Blockage or narrowing of one or more coronary arteries that may lead to poor heart function
- Narrowings that reduce blood flow and cause persistent chest pain that medicines do not control
Not every blockage can be treated with angioplasty. Some people who have several blockages or blockages in certain locations may need coronary bypass surgery.
Heart Surgery Using Stents: The Procedure In A Nutshell
Lets try and understand how this advanced surgical procedure is carried out in detail. When a cardiologist suspects blockage in blood circulation network or narrowing of arteries, he carries out an angiography procedure. This procedure is an X-ray imaging technique which provides a clear image of all the arteries. By observing the angiogram, the doctor can exactly ascertain and locate the presence of any heart blockage or narrowing of arteries. Intravascular ultrasound may also be used to assess the size and exact position of the blockage.
The angiography procedure is carried out by first inserting a very narrow guidance line through the femoral artery in the thigh, from where it is progressively inserted to the desired location. By desired location, we mean the part of the network that has to be imaged. Consequently, a catheter is inserted along the guidance line to that point and an x-ray opaque dye is inserted. The dye spreads with the blood flow in that local region. Then a detailed x-ray image is created and blockage if any, is spotted and marked. The catheter is removed, but the guidance line stays in the location. Then the catheter is reinserted inside, with a balloon attached to its tip to predilate the blockage site and restore the normal size of the artery.
Read Also: Can Congestive Heart Failure Be Cured
Meeting With Your Doctor
If your angioplasty isnt done as emergency treatment, youll meet with your doctor before the procedure. Your doctor will go over your medical history , do a physical exam and talk about the procedure with you. Your doctor also will order some routine tests, including:
When the procedure is scheduled, you will be advised:
- When to begin fasting before the procedure. Often you have to stop eating or drinking by midnight the night before the procedure.
- What medicines you should and shouldnt take on the day of the angioplasty.
- When to arrive at the hospital and where to go.
Even though angioplasty takes one to two hours, you will likely need to stay in the hospital overnight. In some cases, you will need to stay in the hospital longer. Your doctor may advise you not to drive for a certain amount of time after the procedure, so you may have to arrange for a ride home.
Also Check: 10 Second Trick To Prevent Heart Attack
Possible Risks Of The Stenting Procedure
There are risks from placing a stent in an artery, including:
- Allergic reactions to the contrast dye used to show the blood vessels by X-ray
- Arrhythmia, or an irregular heartbeat
- Bleeding or discomfort where the catheter was inserted
- Damage to blood vessels from the catheter
- Rarely, damage to kidneys from contrast dye
Its also rare for more serious or life-threatening problems to occur during a stenting procedure. People who have had other procedures to treat blocked arteries or who have congestive heart failure, chronic kidney disease, or diabetes are usually at higher risk for complications, which may include:
- Blood flow being cut off from the gut or the lower part of the body during an aortic aneurysm repair
Risks from an airway stenting procedure include:
You May Like: What Does It Mean When Your Heart Rate Is High
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider
Contact your provider when:
- You have bleeding, swelling, discharge or numbness where the catheter went into your skin.
- You have a fever or chills.
- You faint or get dizzy.
- Your pulse isnt normal.
- You have chest pain.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Although your angioplasty and stent will help your blood circulate better, youll still need to do your part and live a healthy lifestyle. That means eating healthy foods, exercising and avoiding tobacco products. Youll also feel your best when you keep taking the medicines your provider prescribed and keep going to your follow-up appointments.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 02/13/2022.
References
When A Coronary Angioplasty Is Used
Like all organs in the body, the heart needs a constant supply of blood. This is supplied by the coronary arteries.
In older people, these arteries can become narrowed and hardened , which can cause coronary heart disease.
If the flow of blood to the heart becomes restricted, it can lead to chest pain known as angina, which is usually triggered by physical activity or stress.
While angina can often be treated with medication, a coronary angioplasty may be required to restore the blood supply to the heart in severe cases where medication is ineffective.
Coronary angioplasties are also often used as an emergency treatment after a heart attack.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Best Heart Rate To Burn Fat
Your Cardiac Catheterization At The University Of Michigan
If you have reduced blood flow to the heart due to a narrowed coronary artery, you may be a good candidate for angioplasty and stenting, minimally invasive procedures that can restore blood flow and let you get back to your daily life. At Michigan Medicine, our Advanced Interventional Cardiology Program offers comprehensive and individualized care, using the latest technologies currently available for angioplasty and stenting, performed by our skilled team of interventional cardiologists.
Surgery For Blocked Arteries Is Often Unwarranted Researchers Find
Drug therapy alone may save lives as effectively as bypass or stenting procedures, a large federal study showed.
By Gina Kolata
The findings of a large federal study on bypass surgeries and stents call into question the medical care provided to tens of thousands of heart disease patients with blocked coronary arteries, scientists reported at the annual meeting of the American Heart Association on Saturday.
The new study found that patients who received drug therapy alone did not experience more heart attacks or die more often than those who also received bypass surgery or stents, tiny wire cages used to open narrowed arteries.
That finding held true for patients with several severely blocked coronary arteries. Stenting and bypass procedures, however, did help some patients with intractable chest pain, called angina.
You would think that if you fix the blockage the patient will feel better or do better, said Dr. Alice Jacobs, director of Cath Lab and Interventional Cardiology at Boston University. The study, she added, certainly will challenge our clinical thinking.
This is far from the first study to suggest that stents and bypass are overused. But previous results have not deterred doctors, who have called earlier research on the subject inconclusive and the design of the trials flawed.
With its size and rigorous design, the new study, called Ischemia, was intended to settle questions about the benefits of stents and bypass.
Recommended Reading: Dialysis And Heart Failure
What Happens During Angioplasty
Angioplasty may be done as part of your stay in a hospital. Procedures may vary depending on your condition and your doctor’s practices. Most people who have angioplasty and stent placement are monitored overnight in the hospital.
Generally, angioplasty follows this process:
You will be asked to remove any jewelry or other objects that may interfere with the procedure. You may wear your dentures or hearing aid if you use either of these.
You will be asked to remove your clothing and will be given a gown to wear.
You will be asked to empty your bladder before the procedure.
If there is a lot of hair at the area of the catheter insertion , the hair may be shaved off.
An IV line will be started in your hand or arm before the procedure. It will be used for injection of medicine and to give IV fluids, if needed.
You will be placed on your back on the procedure table.
You will be connected to an electrocardiogram monitor that records the electrical activity of your heart and monitors your heart rate using electrodes that stick to your skin. Your vital signs will be monitored during the procedure.
There will be several monitor screens in the room, showing your vital signs, the images of the catheter being moved through your body into your heart, and the structures of your heart as the dye is injected.
You will get a sedative in your IV to help you relax. However, you will likely stay awake during the procedure.
One Of The Central Questions
This has been one of the central questions of cardiovascular medicine for a long time: Is medical therapy alone or medical therapy combined with routine invasive procedures the best treatment for this group of stable heart patients? said study co-investigator Robert Harrington, MD, professor and chair of medicine at Stanford and the Arthur L. Bloomfield Professor of Medicine. I do see this as reducing the number of invasive procedures.
Robert Harrington
The study was designed to reflect current clinical practice, in which patients with severe blockages in their arteries often undergo an angiogram and revascularization with a stent implant or bypass surgery. Until now, there has been little scientific evidence to support whether these procedures are more effective in preventing adverse heart events than simply treating patients with medications such as aspirin and statins.
If you think about it, theres an intuitiveness that if there is blockage in an artery and evidence that that blockage is causing a problem, opening that blockage is going to make people feel better and live longer, said Harrington, who regularly sees patients with cardiovascular disease at Stanford Health Care. But there has been no evidence that this is necessarily true. Thats why we did this study.
Ischemia, which is reduced blood flow, often causes symptoms of chest pain known as angina. About two-thirds of those heart patients enrolled in the study suffered symptoms of chest pain.
Also Check: What Are Signs Of A Heart Attack
Who Needs A Stent
Stents are used to reduce symptoms in patients with obstructive artery disease who suffer chest pain/tightness or shortness of breath that might be experienced with exercise or during periods of strong emotions. Stents may be used instead of bypass surgery in some selected patients. Diabetic patients with multiple coronary blockages may do better with bypass surgery.
Peripheral And Iliac Arteries
2016 research review suggested that peripheral stents in your legs are more likely to fail than other types of stents. Many people who have peripheral stents placed end up needing new stents or other artery-opening procedures within 1 or 2 years of stent placement.
This need might be because these stents are under added pressure in this anatomy. The chances of your arteries re-narrowing are increased because of the movement of your vessels when you:
Research is being done to determine how to best address the concern. One 2019 study showed that iliac stents can have similar concerns but, so far, they dont seem to have concerns at the same rate as stents in your legs.
There are two main types of stents in use today:
- bare metal stent : traditional metal mesh stents
- drug-eluting stent : mesh tubes that release medication into your artery to reduce scar tissue formation and prevent narrowing
Both DESs and BMSs are meant to be permanent. However, a 2016 research review showed that DESs are less likely to re-narrow. So, while the stents themselves will last the same amount of time, you may have fewer complications with a DES.
The medication in a DES prevents scar tissue buildup. It will not treat the underlying condition that caused your artery to narrow.
That means its important to treat the underlying condition with medications and lifestyle changes, as noted above, no matter what type of stent you have.
The two primary ways that a stent can narrow, include:
Recommended Reading: How To Prevent Future Heart Attacks
