How Is It Diagnosed
To diagnose a sinus arrhythmia, your doctor will conduct an electrocardiogram . This test measures your hearts electrical signals. It can detect every aspect of your heartbeat and help your doctor see any potential irregularities, like a sinus arrhythmia.
Keep in mind that for the majority of people, a sinus arrhythmia is neither dangerous nor problematic. Even if your doctor suspects you have this irregular heartbeat, he may not order the test to check for it. Thats because an EKG can be costly, and a sinus arrhythmia is considered a benign condition. Your doctor might order an EKG only if they suspect another condition or youre experiencing other symptoms.
Medical Conditions That Can Increase Breathing Rate
There are several lung conditions that can cause shortness of breath. This can make exercise harder than it is because you need as much oxygen as you can get when you exercise. Some of these conditions include asthma, COPD or lung fibrosis. These conditions can make exercises difficult and when the proper precautionary measures are not put in place, exercising in any of these conditions can become life threatening.
If you have any problem with your lungs but you still want to work out, you can still do it. However you must seek a doctors advice on the measures to take to prevent getting injured.
Calculating The Optimal Hr Function
In all the calculations that are shown here, qin is defined as :
Typical calculations of optimal heart rate and partial pressures in Models 1a and 1b
The inspired ventilation, qin, is the same for both models . The shaded areas show the inspiration period. The averaged arterial partial pressure of O2 was constrained to 104 mmHg, the averaged arterial partial pressure of CO2 was constrained to 41 mmHg, and VT= 0.5 l. All other parameters are the same as in . Heart rate calculated for Model 1a continuous line, HR calculated for Model 1b dashed line. TI and TE are the inspiration and expiration periods, respectively. Note that O2 and CO2 are uncoupled.
where VT is the tidal volume and T is the period of respiration. This choice gives . We chose the inspiration/expiration ratio to be 1:1 as in and . The effect of other inspiration/expiration ratios is explored in .
Increased TI/TE ratio leads to a weaker RSA and a growing phase-shift between the maximum heart rate and the end of inspiration
The calculation was performed using Model 1b. The shaded areas show the inspiration period for each case. The respiratory cycle is 5 s and VT= 0.5 l in all cases. All other parameters are as in . In blue TI/TE= 1:1, in red TI/TE= 1:2, and in black TI/TE= 2:1. The inspired ventilation, qin, is shown in the top panel.
The RSA-like shape of the R-R interval is preserved by all three modelsStronger RSA as a result of increased average arterial partial pressure of CO2
You May Like: Benadryl Arrhythmia
Evidence For Hrvs Influence On Cardiac Issues & General Health Outcomes
Like smoking, diabetes and elevated lipids, low HRV is a risk factor for mortality in all patients. For several decades it has been known that low heart rate variability predicts sudden cardiac death from arrhythmias after a heart attack and that it also predicts post-heart attack survival .
Low HRV is also associated with depression, anxiety disorders, and post-traumatic stress disorder . Low HRV is an index of compromised health overall, but especially important in coronary artery disease. Thus, for patients with a history of cardiac issues or risks, increasing heart rate variability is highly recommended.
As far back as 1996, it was known that reduced heart rate variability predicted increased risk for subsequent cardiac events such as coronary heart disease, congestive heart failure, and myocardial infarction in both men and women who had no clinical symptoms of heart disease . Previous research has already shown that lowered Heart Rate Variability predicted increased risk for all-cause mortality.
In 2013, a European study showed that low HRV is associated with an increased risk of a first cardiovascular event in populations without known cardiovascular disease . On the positive side, increasing HRV may result in a lower risk of fatal or non-fatal cardiovascular disease.
Synchronizing Breathing With The Heart Rate Yields Maximal Coherence
Coherence, a measure of the consistency of wave phenomena, is often used in the context of the heart beat. Here, it can pertain to the beat itself, i.e. the physical consistency of consecutive beats where each beat is a wave, or it can pertain to the longer term cycle of variation in the heart beat. Note that the latter is not itself a wave but a mathematical abstraction of the heart beat rate. Yet, when breathing slowly, deeply, and rhythmically, the abstraction certainly resembles a wave why?
Many years ago, the breathing induced change in heart rate was given the name Respiratory Sinus Arrhythmia or RSA, referring to the sine wave-like variation in heart rate as a consequence of breathing.
While the groundwork for this understanding goes back thousands of years, in the first half of the 1900s researchers made a series of measurements with the newly invented catheter, which was inserted into the thoracic cavity, major arteries, and chambers of the heart in an effort to understand the subtle relationships between breathing, blood flow, and the heart rate.
Figure 1 – The Heart Rate Variability Cycle Resembles A Wave
At first this seems counter-intuitive. Most of us accept that the heart is the primary determinant of blood flow. Secondly, wed expect that as heart rate increases blood volume should increase, and as heart rate decreases blood volume should decrease .
Figure 2 – View of Valsalva Wave And Heart Rate And Their Correlation
You May Like: Can Lexapro Cause Heart Palpitations
Why Does Ithlete Use Paced Breathing
As HR speeds up when you inhale and slows when you exhale the time gap between beats and breathing are intimately connected.
We often tell our users consistency is key to getting a good ithlete heart rate variability measurement, and the paced breathing element of the reading is a huge part of this. We are aiming to get a snapshot of the autonomic nervous system under the same conditions every day and compare that to both the previous day, and to the baseline. The paced breathing stimulating your nervous in a consistent way also enables ithlete to use the short 1 minute measurement.
The following quote from Dr Liz Miller, a former neurosurgeon, psychologist & author explains this further
The emphasis is getting people to breathe right, which maximises HRV because breathing profoundly affects HRV Heart Rate Variation is largely due to the changes that occur during breathing breathe in Heart Rate goes up breathe out Heart Rate goes down. These changes are healthy, normal and partly relate to the mechanics and partly to the autonomic nervous system. The greater the changes between breathing in and breathing out, the healthier and fitter your heart, lungs and autonomic system.
Benefits Of Exercise On The Respiratory System
Exercise does the body good in a number of ways, but one of which is the benefit to the respiratory system. The more oxygen you take in the more you exercise your lungs, and the stronger they get. The stronger your lungs get, the better they are at taking in oxygen and storing it in your bloodstream. As mentioned previously, you dont need to breathe as hard at the beginning of your workout because theres already a reserve of oxygen to be utilized. In the same way, your lungs will become more efficient over time so that the body will be able to store more oxygen in your blood so that you wont be so out of breath when you exercise over time.
This is something you can tell your clients: The more they exercise, the less likely theyll be to get winded during simple activities like going up the stairs or walking across a large parking lot.
Its worth noting that certain types of activity have a greater impact on the bodys energy expenditure to repay the oxygen debt created from exercise: the more intense the exercise, such as in HIIT, the more oxygen is used, and the more effort the body must make to rebuild its oxygen store. This phenomenon known as excess post-exercise consumption or EPOC is highest right after concluding exercise and can burn up to 50 to 120 more calories.
References:
Also Check: How Do You Say Heart Attack In Spanish
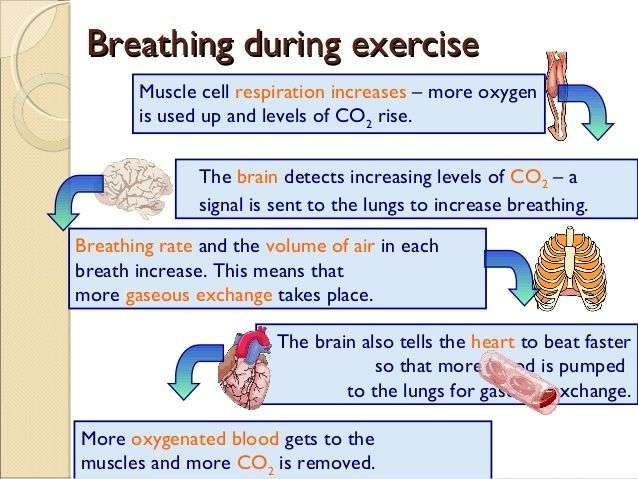
Effects Of Exercise On Breathing
During exercise there is an increase in physical activity and muscle cells respire more than they do when the body is at rest.
The heart rate increases during exercise. The rate and depth of breathing increases – this makes sure that more oxygen is absorbed into the blood, and more carbon dioxide is removed from it.
The rate of breathing can be measured by counting the number of breaths in one minute. The depth of breathing can be measured using a spirometer .
To investigate the effects of exercise on breathing, record the rate of breathing for a few minutes when the person is at rest. After they do some exercise, record their rate of breathing every minute until it returns to the normal resting value.
Effect Of Exercise On Breathing Rate
Just as exercise raises your heart rate, it also raises your breathing rate. The direct relationship between exercise and respiratory rate is that you will begin to take in more oxygen about three to four times as much, to be exact. That doesnt necessarily mean that youll be taking more breaths. You can take in one long, slow, deep breath and get more Oxygen than you would if you were taking a series of shallow, quick breaths. Yet, the latter is what people tend to do when they exercise.
In many schools of exercise, the focus is on heart rate and form, which are both important for physical health, weight loss, and stress relief. However, the way you breathe during exercise is also important. When doing slow and controlled movements , youll want your breathing to mirror your movements meaning that it should be slow and controlled too. If your body is moving quickly, then your breath will also be quick. Its important to note that quick and shallow are not necessarily the same thing. Youll want to direct your clients to breathe in deep enough to puff up the diaphragm, as shallow breathing can lead to dizziness, hyperventilation, and even fainting.
Also Check: Benadryl Heart Arrhythmia
What Causes Sinus Arrhythmia
Its not clear what causes people to develop a sinus arrhythmia. Researchers suspect that a connection between the heart, lungs, and vascular system may play a role.
In older individuals, a sinus arrhythmia can occur as a result of heart disease or another heart condition. Damage to the sinus node can prevent the electrical signals from leaving the node and producing a steady, normal heartbeat. In these cases, the sinus arrhythmia is the result of damage to the heart, and its likely to show up after the heart condition develops.
Some Limitations And Caveats
Respiratory parameters can profoundly alter heart rate and RR interval variability independent of changes in cardiac autonomic regulation . It is now well established that increases in respiratory frequency reduce the amplitude of heart rate oscillations while either increases in tidal or static lung volume provoke increases in the RR interval variability. Conversely, reductions in respiratory frequency increase HRV while decreases in tidal volume lead to reductions in the RR interval variability . Thus, it is critical to control breathing in order to interpret HRV data accurately. For obvious reasons, it is much more difficult to control respiratory parameters in conscious animal than in human studies. However, these respiratory parameters frequently are not controlled even in human studies . Brown et al. , reviewed the human literature and found that only about 51% controlled respiratory rate, and even fewer studies controlled for tidal volume . They further reported that respiratory parameters not only altered HF power but also strongly influenced the LF components of the RR interval power spectrum, a component that previously was viewed to vary independently of changes in respiration .
Read Also: Ibs And Palpitations
Practical Applications For Utilizing Hrv
Firstbeat has developed ways of utilizing HRV in real-life conditions. The HRV data is turned into valuable and understandable feedback that helps to perform better, make correct training and coaching decisions, and improve wellbeing and health. Firstbeat Lifestyle Assessment is a professional-grade stress and recovery monitoring tool for wellness coaching. Firstbeat Sports is a complete solution to optimize training load and recovery for sports teams. Firstbeat is also trusted by top brands in wearable markets to help you make the best possible health, fitness and performance decisions.
Want to know more about the science behind Firstbeats technology across all our specialist areas?
Heart Rate During Exhaling
A typical healthy adult’s heart beats an average of 70 times per minute, but this is not a constant rate. Your heart beats faster when you inhale and slower when you exhale. Understanding this cycle will help you regulate your breathing to optimize your blood pressure and heart beat during exercise as well as when performing calming or relaxation techniques.
Recommended Reading: What Heart Chamber Pushes Blood Through The Aortic Semilunar Valve
Treatment For Low Heart Rate Variability
A patient can increase/improve their heart rate variability through biofeedback training, a process referred to as HRV Biofeedback Treatment/Training, which helps synchronize respiratory and heart rate to a measured individualized breathing frequency pattern, maximizing heart rate variability.
But HRV Biofeedback therapy is far more involved than simply learning to slow your breathing and relax. In fact, heart rate variability biofeedback training/treatments are a clinical process requiring sensitive and sophisticated testing instrumentation, including a heart rate variability monitor to display your HRV and provide instantaneous feedback to the patient.
Your Maximum Heart Rate
While we’re talking about why does heart rate increase during exercise, I’d like to point out a few more things about your heart rate.
First, we need to discuss your maximum heart rate. Bear with me for a minute here because we need to do a little math.
In order to find your maximum heart rate, you subtract your age from 220. So for example, if you’re 40 years old, you subtract 40 from 220 to get a max heart rate of 180. That means that the fastest your heart should ever beat during exercise is 180 beats per minute.
Now that doesn’t mean that you should try to get your heart rate up to 180 the whole time you’re working out. It doesn’t mean that at all. No, that’s your maximum. You don’t want to work at the max. Instead, you want to work in your target zone.
You May Like: Does Benadryl Lower Heart Rate
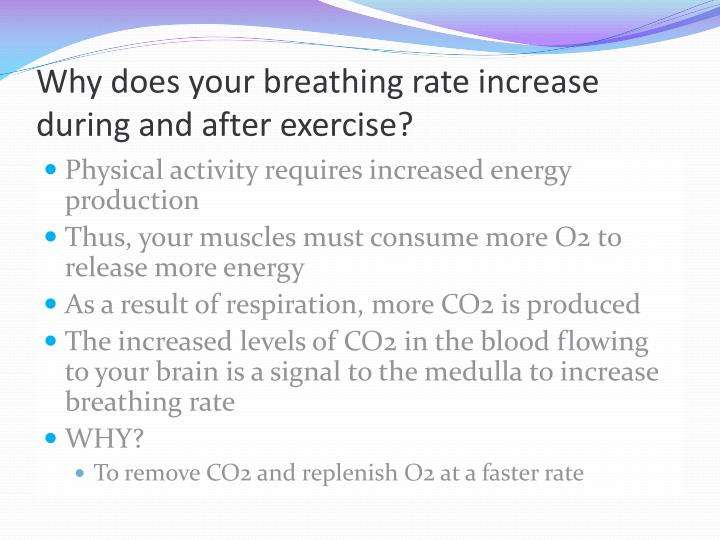
Why Does Heart Rate Increase During Physical Activity
The main organs to have an impact during physical activity are the heart and lungs. The latter ones are responsible for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide . It gets O2 to increase muscle function and eliminates CO2 as organic waste from the organism.
The heart is in charge of pumping oxygen-charged blood to the muscles in order to provide them with the necessary energy. It then allows the CO2-laden blood to go to the lungs and come out.
The muscles need to work harder when we exercise. Thus, the body needs to consume O2 and expel CO2 in greater quantities. This is because theres an increase in energy demands.
Check out these Six Cardio Exercises You Can Do at Home
How Do I Find My Target Heart Rate During Exercise
Now that you know how to find your max heart rate you can calculate your target heart rate zone. That’s where you want to be working throughout your training. The target zone is generally between 60 and 85 percent of your max heart rate. If your goal is to burn body fat, then your target zone is between 60 and 70 percent of your maximum rate.
According to the American Heart Association, for moderate-intensity exercise, you should be working at 50 to 70 percent of your max heart rate. As I just said, this is where you will burn the most fat. For vigorous-intensity exercise, you will work at 70 to 85 percent of your max heart rate.
As you can see, there’s a lot more to understanding your heart than just answering the question, “Why does heart rate increase during exercise?”
Image via Pexels
Here’s how you calculate your target heart rate:
We already established that you get your max heart rate by subtracting your age from 220.
So for a 40-year-old, the maximum heart rate would be 180. From there you need to find your resting heart rate. You can find it by taking your pulse first thing in the morning when you wake up or when you are at rest. Once you know your resting heart rate, you can find your heart rate reserves. To calculate that you subtract your resting heart rate from your max heart rate.
That means that throughout your workout you want to keep your heart rate between 136 and 147 optimally.
Let’s review:
Image via Pexels
Read Also: How Much Can Marijuana Increase A Person’s Heart Rate
Heart Rate Variability And The Autonomic Nervous System
HRV is regulated by the autonomic nervous system , and its sympathetic and parasympathetic branches, and it is commonly accepted as a non-invasive marker of autonomic nervous system activity. The sympathetic branch of the ANS is the stress or fight or flight system, getting us ready to act, react, and perform to meet the different demands that life throws at us.
The parasympathetic side is characterized as the rest and digest system that allows the body to power down and recover once the fight is over. The sympathetic branch activates stress hormone production and increases the hearts contraction rate and force and decreases HRV, which is needed during exercise and mentally or physically stressful situations. Conversely, the parasympathetic branch slows the heart rate and increases HRV to restore homeostasis after the stress passes. This natural interplay between the two systems allows the heart to quickly respond to different situations and needs.
Would you like to read more content like this?
