How Is It Diagnosed
A diagnosis of thrombosis usually happens in a hospital. However, healthcare providers may start suspecting it in a healthcare setting like a doctors office or an urgent care-type clinic. If it happens outside a hospital, medical professionals will likely treat your case as a medical emergency because of the risk of heart attack, stroke or pulmonary embolism, all of which are life-threatening.
A healthcare provider diagnoses thrombosis based on a combination of your medical history, questions they ask you, a physical examination, laboratory tests, imaging tests and other diagnostic methods. The tests they use may vary greatly depending on the conditions they suspect or are possible.
How Does This Condition Affect My Body
Thrombosis falls into two categories, depending on the type of blood vessel where it starts.
Arterial thrombosis
This is thrombosis that happens in arteries, which are blood vessels that carry blood from your heart to the rest of your body. Arterial thrombosis is the most common cause of heart attacks and strokes.
Venous thrombosis
This is thrombosis that happens in veins, which are blood vessels that carry blood back to your heart from your body. Venous thrombosis is the most common cause of pulmonary embolism .
Why clot location matters
Thrombosis is dangerous because it creates clots that could block blood flow somewhere in your body. That happens in one of two ways:
- Blockage where the clot forms. A clot that forms because of thrombosis can stay in place and grow until its big enough to block blood flow. The severity of that blockage depends on where that clot forms and how big it grows.
- Clots that cause blockages in other places. A major risk with thrombosis is that a clot will break free from where it forms and becomes an embolus . Once it breaks free, it can travel in your blood and end up in blood vessels that are too small for it to pass, which creates a blockage . This is usually what causes conditions like stroke and pulmonary embolism .
Who Is Most At Risk For Blood Clots
Some risk factors put certain people at higher risk for developing a blood clot.
Blood clots become more common as people get older, especially when they are over age 65. Long hospital stays, surgeries and trauma may significantly increase your risk of blood clots.
Other factors can increase your risk to a lesser degree. You might be more at risk if you:
- Take birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy.
- Have cancer, or have been treated for cancer.
- Have a family history of blood clots, or a specific condition, such as Factor V Leiden disease, antiphospholipid syndrome or polycythemia vera, that makes clots more likely.
- Have coronavirus disease 2019 .
Some factors are based on lifestyle choices. Risks might be higher if you:
- Have overweight/obesity.
- Live a sedentary lifestyle.
- Smoke cigarettes.
You May Like: Life Expectancy Congestive Heart Failure
Causes Of Arterial Thrombosis
Arterial thrombosis usually affects people whose arteries are clogged with fatty deposits. This is known as atherosclerosis.
These deposits cause the arteries to harden and narrow over time and increase the risk of blood clots.
The following can increase your risk of developing atherosclerosis:
If you’re at a high risk of getting a blood clot, your doctor may also recommend taking medicines such as:
- statins to manage high cholesterol
- medicines to reduce the risk of your blood clotting. For example, an anticoagulant such as warfarin and an antiplatelet such as low-dose aspirin or clopidogrel
What Tests Will Be Done To Diagnose This Condition

The following test types are most likely when a healthcare provider suspects thrombosis:
Physical exam
A physical exam is where a doctor looks at different areas on your body for visible signs of a problem. Theyll also feel areas of concern , and listen to your heart, breathing and digestive system.
In cases where they suspect thrombosis in your arms or legs, they might listen to the sound of your pulses in your affected limb. That can help them figure out the approximate location of a clot.
Imaging tests
Healthcare providers will use a wide range of imaging tests to let them see inside your body, too. These tests help with diagnosing and locating blood clots, as well as guide treatment.
Some of the possible tests include the following methods:
Laboratory tests
Because clotting is something your blood does naturally, lab tests on your blood can help analyze and determine if your blood clots too easily. These tests can also help discover why your blood is clotting and can help decide on possible treatments.
These tests usually look for the following:
Read Also: Hypertensive Heart Disease Without Heart Failure Icd 10
What Should You Do If You Have A Stroke
Ischemic strokes make up 87 percent of all strokes. They are caused by a blockageoften from a blood clotin the artery that supplies blood to the brain. These strokes can be treated with a tPA, or tissue plasminogen activator. tPA can break down the clot causing the blockage, but the drug needs to be administered within the first three hours after the stroke.
tPA should not be given for a hemorrhagic stroke, or a bleeding stroke. A hemorrhagic stroke happens when an artery in the brain leaks blood and puts too much pressure on the brain, Tong said. Because the issue with a hemorrhagic stroke is too much blood, tPA would increase the blood flow and be severely detrimental to the recovery of the stroke victim.
What Is A Pulmonary Embolism
A pulmonary embolism is a blood clot that develops in a blood vessel in the body . It then travels to a lung artery where it suddenly blocks blood flow.
A blood clot that forms in a blood vessel in one area of the body, breaks off, and travels to another area of the body in the blood is called an embolus. An embolus can lodge itself in a blood vessel. This can block the blood supply to a particular organ. This blockage of a blood vessel by an embolus is called an embolism.
The heart, arteries, capillaries, and veins make up the bodys circulatory system. Blood is pumped with great force from the heart into the arteries. From there blood flows into the capillaries . Blood returns to the heart through the veins. As it moves through the veins back to the heart, blood flow slows. Sometimes this slower blood flow may lead to clot formation.
Read Also: Why Do Nsaids Increase Risk Of Heart Attack
What Should You Know About Living With A Higher Risk Of Blood Clots Or If You Have Already Had A Blood Clot
If you are concerned about your blood clot risk in certain situations, such as when you are traveling or after a surgery, your doctor can give you more information on other habits that can help.
If you are able to walk around while you are traveling, you should make sure you do so at least once every couple of hours. If you are traveling by air, your provider might suggest you wear compression stockings. You can do exercises that move your feet and legs while you are sitting.
If you have a blood clot, your provider might suggest that you take anticoagulants for a certain period of time. Some people may need to take them for life. Make sure you understand how you should take this medication and what types of interactions you should avoid. It is important to have regular follow with a provider who is specifically discussing blood thinner medication with you.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
A blood clot can be serious, even fatal. If you know you are at risk for blood clots, you can help yourself by moving around, by eating well and maintaining a healthy weight and following your healthcare providers suggestions on medication and lifestyle changes.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 09/24/2020.
References
Symptoms And Risks Of Arterial Thrombosis
A blood clot does not usually have any symptoms until it blocks the flow of blood to part of the body.
This can cause several serious problems, including:
- a heart attack, when blood flow to the heart muscle is suddenly blocked, causing chest pain, shortness of breath and dizziness
- a stroke, when blood flow to the brain is cut off the main symptoms are one side of the face dropping, weakness in one side of the body and slurred speech
- a transient ischaemic attack or “mini-stroke”, when blood flow to the brain is temporarily blocked, causing short-lived stroke symptoms
- critical limb ischaemia , when the blood supply to a limb is blocked, causing it to become painful, discoloured and cold
These conditions are all medical emergencies. Get medical help straight away by calling 999 if you or someone in your care is experiencing these symptoms.
You May Like: What Is Optimal Heart Rate
What Is Coronary Artery Disease
Most heart attacks are caused by coronary artery disease . This is when a gradual build-up of fatty streaks form in the coronary arteries. These are the arteries that deliver oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. The build-up of fatty streaks makes the coronary arteries narrow and stiffen over time.
As the coronary arteries narrow, it becomes more difficult for oxygenated blood to reach the heart muscle, sometimes causing pain and discomfort known as angina.
If a piece of plaque cracks, it may cause a blood clot to form and block a coronary artery, cutting off the blood supply to a part of the heart muscle. This causes a heart attack.
The heart attack symptoms you feel during a heart attack are caused by your heart muscle being starved of oxygen. This prevents your heart from beating as normal.
What Should I Expect If I Have Coronary Artery Disease Can It Be Cured
Technically coronary artery disease cant be cured. If youve been diagnosed with coronary artery disease, follow your healthcare providers treatment plan to help prevent your condition from getting worse. Your treatment plan may include procedures and surgery to increase the blood supply to your heart, lifestyle changes to target your risk factors and medications.
If your coronary artery disease has led to a heart attack, your healthcare provider can recommend a cardiac rehabilitation program to reduce your risk of future heart problems, regain strength and improve the quality of your life.
It is important to keep all follow-up appointments and have all tests ordered by your healthcare provider. These are needed to keep track of your condition, monitor how well your treatment plan is working and make adjustments if needed.
Also Check: Does Acid Reflux Cause Heart Palpitations
Read Also: Chest Muscle Pain After Open Heart Surgery
Blood Clots In The Brain
A blood clot in the brain can block the supply of oxygen-carrying blood to the brain, causing a stroke. Brain tissue starts dying without a constant supply of oxygen, so it is critical to treat the stroke as soon as possible. The longer a stroke remains untreated, the greater the chance that brain cells will die, leaving behind permanent stroke-related brain damage. These debilitating effects can include weakness on one side of the body, difficulty controlling movements, personality or behaviour changes, or problems speaking and understanding.
Symptoms Of A Blood Clot In The Brain
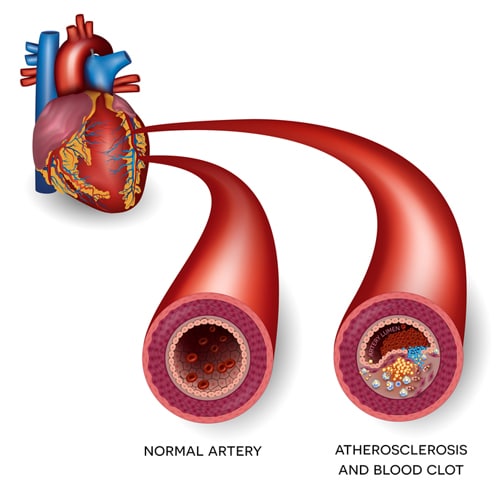
A blood clot in the brain is also known as a stroke.
These blood clots can develop anywhere in the body, or directly in the brain. When this happens, blood can not bring oxygen to your brain, resulting in hypoxia. Brain tissue cant survive without a constant supply of oxygen, and hypoxia can cause severe symptoms and even death.
A blood clot in your brain will cause all the symptoms of a stroke, like:
- severe, sudden headache with an unknown cause
- nausea or vomiting
If these symptoms appear and disappear suddenly, you should still seek emergency care. Stroke symptoms that come and go can be a sign of a transient ischemic attack, or ministroke. These are also usually caused by blood clots, but the clots resolve or dont entirely block the flow of blood to your brain.
A blood clot that travels to your lungs is called a pulmonary embolism . Symptoms that could be a sign of a PE are:
- sudden shortness of breath that isnt caused by exercise
CDC , almost 50 percent of people with DVT have no symptoms.
You should call your doctor immediately if you think you might have a blood clot. A healthcare professional will look at your symptoms and medical history and let you know what steps to take from there.
Your doctor or other healthcare professional will be able to tell whether theres a reason for concern and can send you for more tests to determine the exact cause.
Recommended Reading: What Can Cause Heart Attack
What Problems Can Dvt Cause
Pulmonary embolism is the most serious problem that can happen when you have DVT. About half of people with DVT will develop PE symptoms within 3 months.
When you have PE, part of the clot in your vein breaks off and travels upstream, first through your limbs and then through your heart toward your lungs. If this clot gets trapped and blocks blood from reaching your lungs, the blood canât be refueled with the oxygen that the heart and the rest of your body need to work properly.
PE is serious and can be fatal. One in 4 people who have it die suddenly. But it can be treated if you catch it in time.
The key to quick treatment is spotting the warning signs of PE. They include:
- Shortness of breath or rapid breathing
- Dizziness or fainting
- Chest pain or discomfort, especially when you breathe deeply or cough
- Coughing up blood
If you have DVT, you can get complications in the veins and skin of your legs and arms. This condition is called postthrombotic syndrome or postphlebitic syndrome. Itâs not life-threatening, but the lack of blood flow in your limbs can result in swelling, pain, skin discoloration, and skin sores. These symptoms wonât affect your heart.
What Are Some Of The Conditions That Happen When Blood Clots Get Stuck In Critical Organs Or Areas
Blood clots that get stuck in certain organs typically cause certain symptoms. The symptoms depend heavily on the affected organ.
Brain
A clot that gets stuck in your brain causes a stroke. Blockage of blood flow in your brain causes those areas to stop working. If blood flow isnt restored quickly, permanent damage to those cells is possible. Thats why a stroke is a medical emergency, and getting immediate medical care is critical.
Symptoms of a stroke include:
- Weakness or trouble controlling muscles on one side of your body.
- Slurred or garbled speech.
- Noticeable droop and lack of muscle control on one side of your face.
- Confusion, agitation or otherwise unusual behavior changes.
Lungs
Blood clots can easily get stuck in your lungs because the blood vessels inside of them are very small. Clots that get stuck there cause pulmonary embolism, a life-threatening condition that needs immediate medical care.
Symptoms of a pulmonary embolism include:
Pulmonary embolisms are most likely to happen because of deep-vein thrombosis, which is when a blood clot forms in a major artery in your leg.
Heart
A heart attack happens when a clot forms or gets stuck in your coronary arteries, which supply your heart muscle with blood. There are many symptoms possible with a heart attack, and a few common ones include:
- Bloating or feeling of pressure in your stomach and gut.
Don’t Miss: What Is A Good Average Resting Heart Rate
Were Sorry The Page Youre Looking For Cant Be Found
It is possible that you used an outdated or expired MedicineNet link or you may have typed the address incorrectly.
Please try searching using the search field above. If youre not sure of the spelling, type the first few letters, followed by an asterisk.
To help you find what you are looking for, these links may help.
Browse our A-Z Lists:
Also Check: List The Steps Of How To Calculate Your Target Heart Rate Zone
Does Blood Pressure Always Increase During A Heart Attack
Bloodpressure may increase, decrease, or do not change at all duringa heartattack. Bloodpressure is the force of your blood as it is pushed from your heart and circulated throughout your body. When blood flow is restricted or blocked completely, the heart muscle is starved of oxygen leading to a heartattack .
Also Check: End Stage Heart Failure Symptoms Death
Blood Clot Testing & Diagnosis
If you have blood clot symptoms or risk factors related to a clotting disorder, your doctor will ask you about your personal and family medical histories. They may also order some tests, such as:
- Blood work: We may recommend lab tests or refer you to a hematologist, a doctor who specializes in blood disorders.
- CT scan, MRI or other imaging tests: In some cases, we may need images of your veins, abdomen, chest, brain or other location a clot may have formed.
- Echocardiogram: This imaging method uses sound waves to create pictures of your bodys organs and blood vessels.
Find out more about our heart and vascular testing and diagnosis.
What Are The Different Types Of Thrombosis
There are three typesvenous thromboembolism, pulmonary embolism, and coronary thrombosis. Venous thromboembolism occurs in veins or arteries, most commonly in the legs. When a blood clot travels to the lungs and causes a blockage of an artery, its called a pulmonary embolism. Coronary thrombosis is a blockage of an artery in the heart, which can lead to a heart attack.
You May Like: Congestive Heart Failure Belching
How Serious Is A Heart Attack
This often depends on the amount of heart muscle that is damaged. In many cases, only a small part of the heart muscle is damaged and then heals as a small patch of scar tissue. The heart can usually function normally with a small patch of scar tissue. A larger heart attack is more likely to be life-threatening or cause complications.
Even before treatments became available to restore blood flow, many people made a full recovery. With the help of modern treatment, particularly if you are given treatment within a few hours to restore blood flow, a higher percentage of people now make a full recovery.
Some possible complications include the following:
- Abnormal heart rhythms.
- A further heart attack which may occur sometime in the future.
The most crucial time is during the first day or so. If no complications arise and you are well after a couple of weeks then you have a good chance of making a full recovery. A main objective then is to get back into normal life and to minimise the risk of a further heart attack.
