What Are The Symptoms Of Heart Failure
You may not have any symptoms of heart failure, or the symptoms may be mild to severe. Symptoms can be constant or can come and go. The symptoms can include:
- Congested lungs. Fluid backup in the lungs can cause shortness of breath with exercise or difficulty breathing at rest or when lying flat in bed. Lung congestion can also cause a dry, hacking cough or wheezing.
- Fluid and water retention. Less blood to your kidneys causes fluid and water retention, resulting in swollen ankles, legs, abdomen , and weight gain. Symptoms may cause an increased need to urinate during the night. Bloating in your stomach may cause a loss of appetite or nausea.
- Dizziness, fatigue, and weakness. Less blood to your major organs and muscles makes you feel tired and weak. Less blood to the brain can cause dizziness or confusion.
- Rapid or irregular heartbeats. The heart beats faster to pump enough blood to the body. This can cause a rapid or irregular heartbeat.
If you have heart failure, you may have one or all of these symptoms or you may have none of them. They may or may not indicate a weakened heart.
How Is Heart Failure Diagnosed
Your doctor will ask you many questions about your symptoms and medical history. Youâll be asked about any conditions you have that may cause heart failure . Youâll be asked if you smoke, take drugs, drink alcohol , and about what drugs you take.
Youâll also get a complete physical exam. Your doctor will listen to your heart and look for signs of heart failure as well as other illnesses that may have caused your heart muscle to weaken or stiffen.
Your doctor may also order other tests to determine the cause and severity of your heart failure. These include:
Other tests may be ordered, depending on your condition.
Articles On Heart Failure Types & Stages
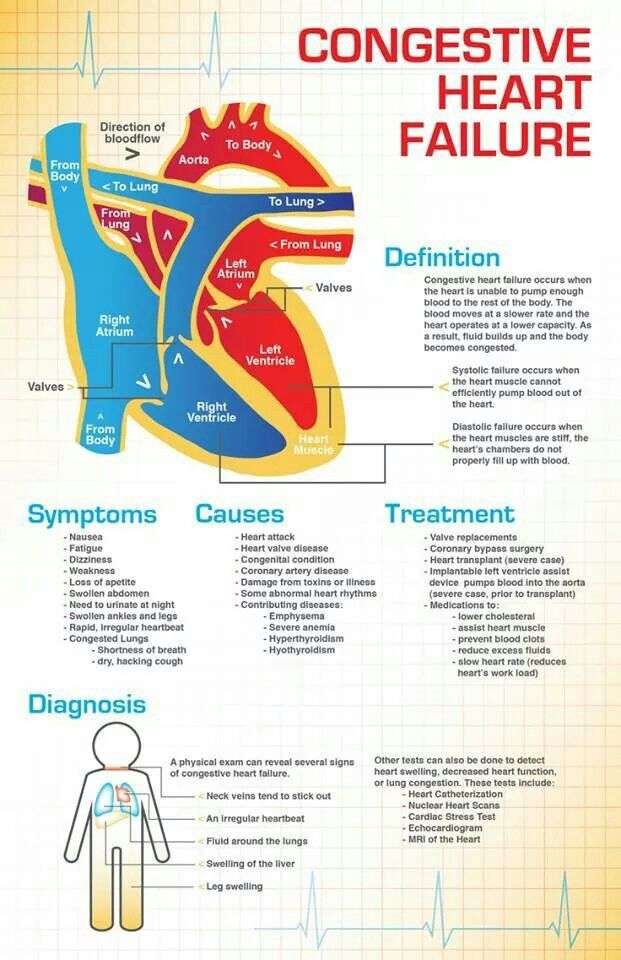
Congestive heart failure doesn’t mean your heart has stopped. It means it’s not pumping blood the way it should. When that happens, blood and fluid can back up in your body and make it harder for your kidneys to flush out sodium and water. That can make you hold on to too much fluid, which causes swelling.
There’s no cure. But your doctor may give you medication to do things like lower your blood pressure, relax your blood vessels, make your heart beat stronger, or ease swelling. And diet and lifestyle changes — like not smoking — can help, too.
Recommended Reading: Prognosis Of Congestive Heart Failure
About Congestive Heart Failure
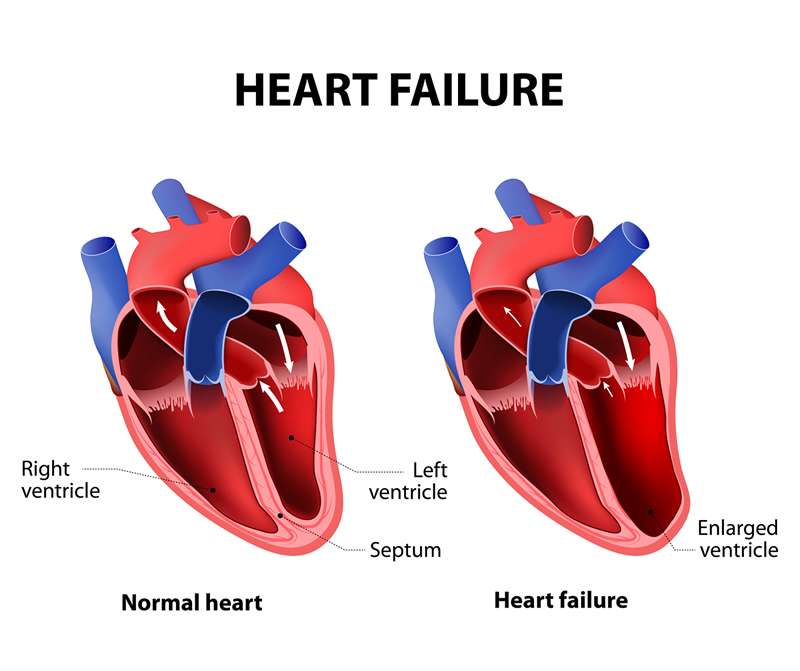
Heart failure, sometimes called congestive cardiac failure , is a condition in which the heart muscle is weakened and cant pump as well as it usually does. The main pumping chambers of the heart can change size and thickness, and either cant contract or cant relax as well as they should. This triggers fluid retention, particularly in the lungs, legs and abdomen.
The major causes of heart failure include coronary heart disease and heart attack, high blood pressure, damage to the heart muscle , heart valve problems and abnormal heart rhythms. Of these, coronary heart disease and heart attack are the most common causes.
The major factors that contribute to coronary heart disease include:
- reduced emotional and social wellbeing
- physical inactivity.
Heart failure is more common in elderly people. The survival rate for people with this disorder depends on the severity of their condition.
Most common treatments for heart failure are medications and self-managed lifestyle changes. Some less-common treatments may require insertion of implantable cardiac devices or valve replacement.
Treatments For Heart Failure
Treatment for heart failure usually aims to control the symptoms for as long as possible and slow down the progression of the condition.
How you’re treated will depend on what is causing your heart failure.
Common treatments include:
- lifestyle changes including eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly and stopping smoking
- medicine a range of medicines can help many people need to take 2 or 3 different types
- devices implanted in your chest these can help control your heart rhythm
- surgery such as a or a heart transplant
Treatment will usually be needed for life.
A cure may be possible when heart failure has a treatable cause. For example, if your heart valves are damaged, replacing or repairing them may cure the condition.
You May Like: Dialysis And Heart Failure
Management Of Iron Deficiency In Chronic Heart Failure
The following information is taken from a research review education series.
- “Anaemia is a frequent finding in patients with chronic heart failure , being present in approximately one-third of patients with CHF.
- Anaemia in CHF increases the risk of hospitalisation and death, and also leads to substantial reductions in exercise tolerance and quality of life .
- The pathophysiology of anaemia in CHF is multifactorial. Iron deficiency is the most common cause of anaemia in patients with CHF, and it is increasingly being recognised that CHF is an iron-deficient state.
- Measurement of serum ferritin alone cannot exclude iron deficiency in patients with CHF. Ferritin is an acute phase reactant and levels increase in response to inflammation, which complicates the diagnosis of iron deficiency.
- Due to the inflammation associated with CHF, diagnosis of iron deficiency in patients with CHF should be based on both serum ferritin levels and transferrin saturation as follows: ‘Ferritin < 100 g/L or Ferritin 100300 g/L with TSAT < 20% ‘
- Australia and New Zealand 2018 guidelines practice advise that oral iron supplementation is ineffective at normalising iron status or improving QOL in patients with CHF. IV iron should be considered in patients with CHF associated with iron deficiency, with or without anaemia.”
Read more about Management of iron deficiency in chronic heart failure Research Review, NZ, 2019
Heart Failure Treatment Is A Team Effort
Heart failure management is a team effort, and you are the key player on the team. Your heart doctor will prescribe your medications and manage other medical problems. Other team members — including nurses, dietitians, pharmacists, exercise specialists, and social workers — will help you achieve success. But it is up to YOU to take your medications, make dietary changes, live a healthy lifestyle, keep your follow-up appointments, and be an active member of the team.
If you notice anything unusual, don’t wait until your next appointment to discuss it with your doctor. Call them right away if you have:
- Unexplained weight gain
- Swelling in your ankles, feet, legs, or belly that gets worse
- Shortness of breath that gets worse or happens more often, especially if you wake up feeling that way
- Bloating with a loss of appetite or nausea
- Extreme fatigue or more trouble finishing your daily activities
- A lung infection or a cough that gets worse
- Fast heart rate
- New irregular heartbeat
Also Check: What Are The First Signs Of A Heart Attack
Symptoms Of Heart Failure
The main symptoms of heart failure are:
- breathlessness after activity or at rest
- feeling tired most of the time and finding exercise exhausting
- feeling lightheaded or fainting
- swollen ankles and legs
Some people also experience other symptoms, such as a persistent cough, a fast heart rate and dizziness.
Symptoms can develop quickly or gradually over weeks or months .
When Should I Call An Ambulance
If you have any of the symptoms below, call triple zero immediately and ask for an ambulance. If calling triple zero does not work on your mobile phone, try calling 112.
- chest pain thats severe or worsening, or has lasted longer than 10 minutes
- chest pain that feels heavy, crushing or tight
- other symptoms, such as breathlessness, nausea, dizziness or a cold sweat
- pain in your jaw or down your left arm
Also Check: Does Tylenol Increase Heart Rate
Stage C Treatment Options
Treatment at this stage focuses on managing your symptoms, optimizing your heart function, and preventing worsening of your condition.
Medications to treat stage C heart failure include:
- Diuretics to reduce fluid retention
- Beta blockers to help make your heart work less hard
- SGLT2 inhibitors to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers
- Entresto , which reduces the risk of death and hospitalization among patients with chronic heart failure
- Aldosterone antagonists
- Digoxin to help the heart beat stronger and more regularly
- Possible cardiac resynchronization therapy
- Possible implantable cardiac defibrillator therapy
In addition to the lifestyle changes for stages A and B, you may need to make the following changes:
- Reduce your sodium intake
- Restrict fluid intake
- Keep track of your weight daily
Remember that even if the treatment causes your symptoms to get better or stop, you still need to continue treatment to slow the progression of your condition to stage D.
What Are The Causes Of Heart Failure
There are many conditions that can cause heart failure, most of them conditions that affect your heart, including:
Coronary heart disease is the most common cause of heart failure. Coronary heart disease describes the blockage of the blood vessels that supply your heart. Coronary heart disease includes heart attack or angina . Coronary heart disease can cause scarring of your heart muscles and weaken your hearts pumping action.
High blood pressure can put extra strain on your heart, as your heart needs to pump harder. Over time, your heart muscles can be damaged and your hearts pumping action can get weaker.
Cardiomyopathy is a disease of the heart muscle itself. It commonly refers to an abnormally large, baggy heart that cannot pump well enough. It can be caused by some viral infections or drinking too much alcohol.
Myocarditis is the inflammation or infection of the heart muscle. This is commonly caused by a virus and may lead to heart failure, especially of the left side of your heart.
Non-heart conditions include:
|
You May Like: Does Your Heart Rate Increase When Pregnant
Prevention Of Congestive Heart Failure
The best way to prevent heart failure is to control your risk factors. The good news is that you can reduce or eliminate many of the risk factors that lead to heart disease, such as high blood pressure. Lifestyle changes and adhering to any medication your doctor prescribes can go a long way in preventing heart failure.
What Are The Treatments For Heart Failure
Your treatment will depend on the type of heart failure you have and how serious it is. There’s no cure for heart failure. But treatment can help you live longer with fewer symptoms.
Even with treatment, heart failure usually gets worse over time, so you’ll likely need treatment for the rest of your life.
Most treatment plans include:
You may need heart surgery if:
- You have a congenital heart defect or damage to your heart that can be fixed.
- The left side of your heart is getting weaker and putting a device in your chest could help. Devices include:
- A biventricular pacemaker .
- A mechanical heart pump or a total artificial heart).
As part of your treatment, you’ll need to pay close attention to your symptoms, because heart failure can worsen suddenly. Your provider may suggest a cardiac rehabilitation program to help you learn how to manage your condition.
Read Also: Acute Exacerbation Of Heart Failure
Complications Of Congestive Heart Failure
- Rapid Weight Loss Severe heart failure can lead to a rapid loss of weight that can be life-threatening. Heart failure can cause blood to back up into the liver and intestines, causing these organs to swell. This swelling can lead to nausea and loss of appetite, and can prevent the body from absorbing nutrients from food.
- Impaired Kidney Function Congestive heart failure weakens the hearts ability to pump blood, reducing blood flow to the kidneys. This can lead to kidney damage or kidney failure, if left untreated.
- Liver Damage Heart failure can cause fluid to build up in the liver, which can lead to scarring. This makes it more difficult for the liver to carry out its day-to-day functions.
- Arrhythmias Heart failure results in damaged heart muscles, which can lead to the development of an arrhythmia, or abnormal heart beat. Arrhythmias can include the heart beating too quickly, beating too slowly, or beating irregularly.
- Heart Valve Problems If the heart is enlarged due to heart failure, the valves of the heart, which ensure appropriate direction of blood flow through the organ, may not function properly.
- Angina and Heart Attack Heart disease is a major contributing factor in many heart failure cases, and people with congestive heart failure are at continued risk of angina and heart attack.
What Support Is Available With Advanced Heart Failure
The Heart Foundation NZ provides resources and support for those living with a heart condition. You can also find a local support group in your area here. Contact them using their online form or visit their website here.
Extra support is also available if you need it. Talk to your healthcare team to find out how you can access this. It includes:
- equipment to help with your daily chores, such as chair raisers and shower stools
- mobility parking and taxi vouchers to help you get around your community
- carer support to help support your carer who is looking after you
- counselling or mental health support
- needs assessment if you want to move into a rest home or other residential care.
Also Check: What Side Of The Heart Has Oxygenated Blood
Prognosis By Ejection Fraction
Ejection fraction is a measure of how much blood is pumped out of your heart each time it contracts. A healthy heart has an EF of between about 55 percent to 75 percent.
Some people with CHF have a reduced EF. This means their heart is pumping less blood out to the rest of their body than a healthy heart. Studies have shown that people who have CHF and a reduced EF have a more challenging outlook than people with CHF who do not have a reduced EF.
The exact survival rates varied among studies, but have shown that EF has an impact on prognosis. Your doctor will have the best information about how your ejection fraction can affect your prognosis.
Stages Of Heart Failure
In 2001, the American Heart Association and American College of Cardiology described the “Stages of Heart Failure.” These stages, which were updated in 2005, will help you understand that heart failure is often a progressive condition and can worsen over time. They will also help you understand why a new medication was added to your treatment plan and may help you understand why lifestyle changes and other treatments are needed.
The stages classified by the AHA and ACC are different than the New York Heart Association clinical classifications of heart failure that rank patients as class I-II-III-IV, according to the degree of symptoms or functional limits. Ask your doctor what stage of heart failure you are in.
Check the table below to see if your therapy matches what the AHA and ACC recommend. Note that you cannot go backward in stage, only forward.
The table below outlines a basic plan of care that may or may not apply to you, based on the cause of your heart failure and your special needs. Ask your doctor to explain therapies that are listed if you do not understand why you are or are not receiving them.
The New York Heart Association clinical classifications of heart failure rank people as class I-II-III-IV, according to the degree of symptoms or functional limits. You can ask your doctor if you want to know what stage of heart failure youâre in.
You May Like: How To Calculate Your Resting Heart Rate
Stage A Treatment Options
Treatment options in stage A mainly focus on promoting your overall health and disease prevention. If you meet the stage A criteria, your doctor will recommend lifestyle changes to slow or stop disease progression.
Heart Failure Doctor Discussion Guide
Edema And Heart Failure
Edema is swelling that is caused by excess fluid trapped in the bodys tissue.
The condition often occurs as the result of congestive heart failure. It can also be the result of medication, pregnancy, or another underlying condition, such as kidney disease or cirrhosis of the liver.
Signs that you have edema include:
- Swelling or puffiness of the tissue directly under the skin, especially in the legs or arms
- Arms or legs start to feel full or heavy
- Shiny or stretched skin
- Skin that retains pits, or dimples, after being pressed for several seconds
- Clothing or jewelry starts to feel tight and uncomfortable
- Skin near the swelling feels tight or warm
- It becomes more difficult to move the joints that are affected
- Increased abdominal size
Don’t Miss: Survival Rate Of Open Heart Surgery
Is Chf Due Mainly To Heart Valve Disease
CHF is most commonly caused by valvular insufficiency. It is estimated that 80% of the canine CHF cases are caused by MVI. However, there are many other causes. Disease of the heart muscle , irregularities of rhythm, and narrowing of some of the major blood vessels can also cause CHF. Initially, MVI results in left-sided congestive heart failure. If left untreated, the heart failure may progress to involve both sides of the heart.
How Is A Flare
In hospital, your doctor will try to find out the cause of your flare-up by doing blood tests, an electrocardiogram , a chest x-ray or an echocardiogram .
Treatment of a flare-up depends on the cause. It may include:
- a higher dose of your diuretics by mouth or you may be given the medicine through a vein instead
- oxygen if your oxygen level is low
- nebulised bronchodilators to help open your airways
- antibiotics if you have an infection
- pain relief medicines if you have any pain
- treatment of heart attack such as aspirin if you have a heart attack.
Your healthcare team will let you know what is causing your flare-up and talk to you about the best treatment option for you.
Also Check: Heart Attacks In Morning
