Heart Failure Survival Rates
The survival rates from heart failure have been improving over the years. The improvement is slow, but gradual. Clinicians measure overall patient survival from a disease by comparing large groups of people with the disease to large groups of the same age range without it. For example, a 1-year survival rate of 90% is good. It means people with the disease are 90% as likely as people without the disease to be alive for at least one year after diagnosis. For heart failure, the 1-year survival rate rose from 74% in 2000 to about 81% in 2016. The 5-year survival rate increased from 41% to 48%, and the 10-year survival rate rose from about 20% to 26%.
Keep in mind prognosis and life expectancy information is based on data registries from several years ago . Someone diagnosed with heart failure today may have a better prognosis because heart failure treatment, including heart transplant, improves with time.
If you or a loved one has heart failure and you would like to know more about your case, ask your doctor how your age, overall health, and treatment affect your prognosis and life expectancy. Knowing what to expect can help you make plans for the time you have.
Mortality Of Heart Failure
As discussed previously, the data available suggest that the prevalence of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction increased over time. As its survival remained unchanged, its prevalence can be assumed to be increasing, thereby underscoring the growing importance of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction as a public health problem.
Aref Albakri, Thomas Klingenheben, in, 2020
Heart Failure Life Expectancy Calculator
Prognostic Utility and Clinical Significance of Cardiac Mechanics in Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection FractionPredicting survival in heart failure: a risk score based on 39 372 patients from 30 studiesACC/AHA Guidelines for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Heart Failure in the Adult: Executive Summary A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines
The heart failure life expectancy calculator is a simple, yet effective, tool for predicting the 1-year and 3-year survival odds of someone with congestive heart failure.
In the article below, we will focus on congestive heart failure/CHF prognosis, the estimates on how long can you live with congestive heart failure, and the average CHF life expectancy for a given stage of the disease.
Don’t Miss: What Is Another Word For Heart Attack
Congestive Heart Failure: Symptoms Treatment And Prognosis
Sharing is caring!
Congestive heart failure is a condition that may develop when the heart cant pump enough blood through to the body.
Heart failure does not imply that the heart has ceased beating Rather, it signifies that coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, or infections have weakened or harmed the heart.
Heart failure can gradually develop and worsen over time, or come about very quickly, depending on the cause.
Most of those living with CHF control their condition, with a healthy heart patient diet and regular exercise.
Stages Of Heart Failure
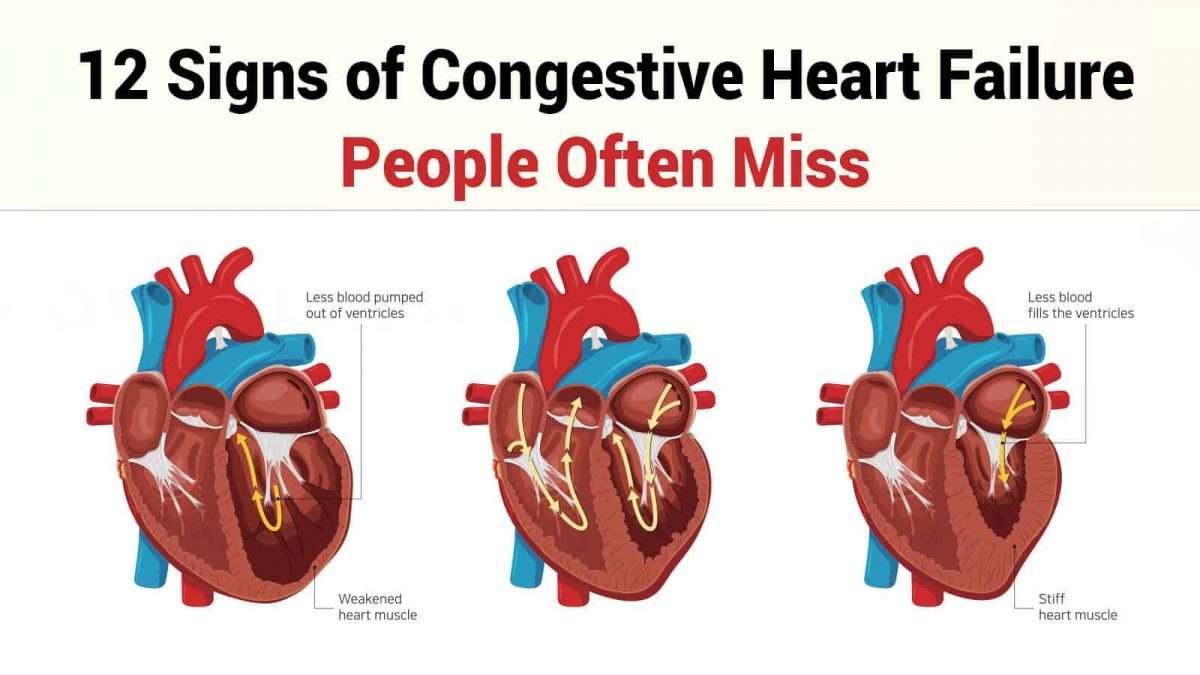
According to statistics, every year about 550,000 people in the United States are diagnosed with heart failure. Some cardiologists describe heart failure by stages. They indicate the risk and/or severity of the condition:
-
A: No signs of structural damage to the heart or symptoms or heart failure, but you are at high risk of developing heart failure.
-
B: No signs or symptoms of heart failure, but tissue damage can be seen with imaging tests, such as MRI .
-
C: Symptoms of heart failure and damage to the heart.
-
D: Serious signs and symptoms of heart failure.
Other doctors use a classification system called the New York Heart Association classification, or functional classification:
-
1: You have heart disease but dont have any symptoms and you dont have to limit everyday physical activity.
-
2: You have mild symptoms of heart disease that may slightly limit your regular physical activities.
-
3: You experience enough symptoms to significantly limit your ability to be active. You only feel comfortable when you are resting.
-
4: You have severe symptoms and limitations. You even have symptoms while resting.
Also Check: Does Amlodipine Lower Heart Rate
Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction
In diastolic heart failure , the same pathophysiologic processes occur that lead to decreased cardiac output in systolic heart failure, but they do so in response to a different set of hemodynamic and circulatory environmental factors that depress cardiac output.
In HFpEF, altered relaxation and increased stiffness of the ventricle occur in response to an increase in ventricular afterload . The impaired relaxation of the ventricle then leads to impaired diastolic filling of the left ventricle .
Morris et al found that right venticular subendocardial systolic dysfunction and diastolic dysfunction, as detected by echocardiographic strain rate imaging, are common in patients with HFpEF. This dysfunction is potentially associated with the same fibrotic processes that affect the subendocardial layer of the LV and, to a lesser extent, with RV pressure overload. It may play a role in the symptomatology of patients with HFpEF.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Congestive Heart Failure
Shortness of breath
The hallmark and most common symptom of left heart failure is shortness of breath and may occur:
Chest Pain
Right heart failure, left heart failure, or both
Don’t Miss: What Should My Max Heart Rate Be
What’s The Systolic Heart Failure Life Expectancy
Systolic heart failure is an insufficiency of a heart caused by the malfunction of its left ventricle. This kind of HF is characterized by a low ejection fraction , also taken into account in this heart failure life expectancy calculator.
EF is given in percent, and should be equal to around 50-70%. Mortality increases as the ejection fraction value . The smaller the EF, the shorter the estimated survival.
Unfortunately, plenty of studies proved that the mortality in patients with systolic heart failure and low EF is higher than in those with preserved EF.
For example: 1 year mortality rate for low EF = 26%, and for the high EF = 22%.
What Is The Prognosis Of Congestive Heart Failure
Your ability to survive congestive heart failure depends on the stage at which you are diagnosed. If you can get it diagnosed early, your chances of survival will be higher. According to a 2017 review, the five-year survival rate is about 97% when diagnosed in stage A but reduces to only 20% when diagnosed in Class 4..
With the advancement of medical science, your chances of surviving this disease are also high. You can improve it with proper medication, surgery, or lifestyle changes. However, the treatment and survival largely depend on your health conditions. For instance, people with acute diabetes and blood pressure have lower survival chances.
Therefore, as you can see, congestive heart failure is a severe health concern. When fluids build up in your system, blocking the activities of the heart, you develop this disease. Doctors suggest patients get it diagnosed in the initial stages so that the treatment begins early. The survival rates are usually high when diagnosed in the early stages.
You May Like: What Happens If Your Heart Rate Is Too High During Exercise
Causes Of Heart Failure
Heart failure is often the result of a number of problems affecting the heart at the same time.
Conditions that can lead to heart failure include:
- coronary heart disease where the arteries that supply blood to the heart become clogged up with fatty substances , which may cause angina or a heart attack
- high blood pressure this can put extra strain on the heart, which over time can lead to heart failure
- conditions affecting the heart muscle
- heart rhythm problems , such as atrial fibrillation
- damage or other problems with the heart valves
- congenital heart disease birth defects that affect the normal workings of the heart
Sometimes obesity, anaemia, drinking too much alcohol, an overactive thyroid or high pressure in the lungs can also lead to heart failure.
Treatments For Heart Failure
Treatment for heart failure usually aims to control the symptoms for as long as possible and slow down the progression of the condition.
How you’re treated will depend on what is causing your heart failure.
Common treatments include:
- lifestyle changes including eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly and stopping smoking
- medicine a range of medicines can help many people need to take 2 or 3 different types
- devices implanted in your chest these can help control your heart rhythm
- surgery such as a or a heart transplant
Treatment will usually be needed for life.
A cure may be possible when heart failure has a treatable cause. For example, if your heart valves are damaged, replacing or repairing them may cure the condition.
Recommended Reading: Does Drinking Raise Your Heart Rate
Diagnosing Heart Failure Before It Shows
If you have no symptoms or signs of heart failure, how can you be diagnosed with heart failure? Some people are at a much higher risk of developing heart failure than others. By diagnosing you with stage A heart failure, your doctor will monitor your heart health closely, and suggest treatments that may ward off heart failure signs for as long as possible. A few examples of people who are at risk of developing heart failure include those who have:
-
A family history of heart failure
-
Chronic medical conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, or coronary heart disease
-
A history of alcohol abuse
-
Taken medications, like chemotherapy, that could damage heart tissue
What Is The Outlook With Heart Failure
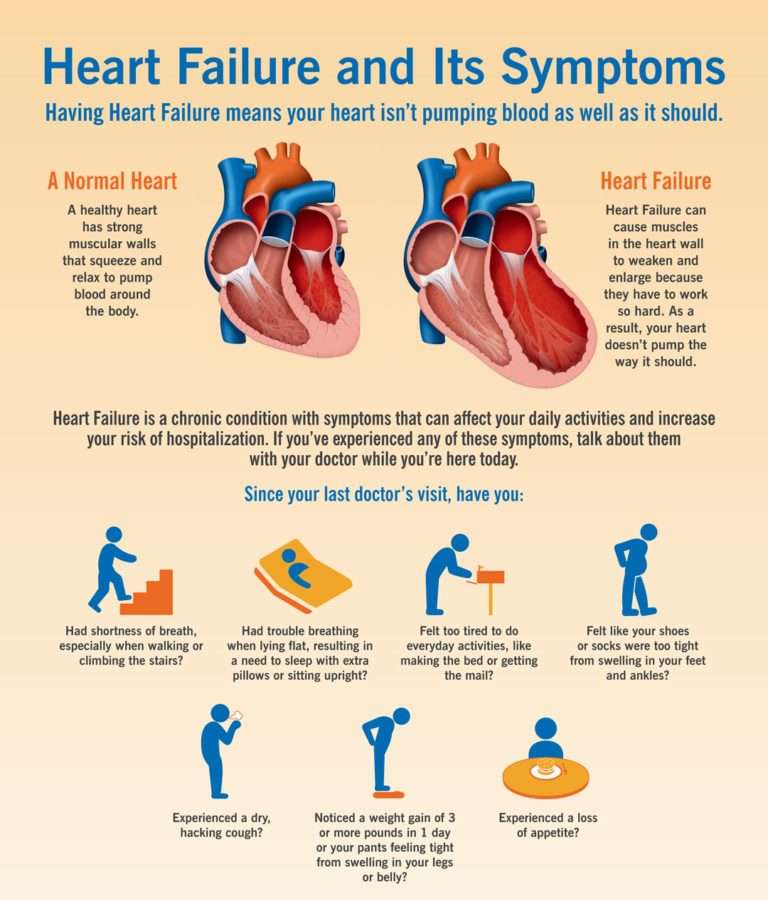
With the right care, congestive heart failure wont stop you from doing the things you enjoy. Your prognosis, or outlook for the future, will depend on:
- How well your heart muscle is working.
- Your symptoms.
- How well you respond to your treatment plan.
- How well you follow your treatment plan.
One study says that people with heart failure have a life span 10 years shorter than those who dont have heart failure. Another study showed that the survival rates of people with chronic heart failure were 80% to 90% for one year, but that dropped to 50% to 60% for year five and down to 30% for 10 years.
A different study found that people who had heart failure and were discharged from the hospital had expected life spans ranging from three to 20 years, depending on various factors like age and gender. Its important to look at your specific situation when considering your prognosis.
Also Check: What Should Your Heart Rate Be At Rest
What Are The Symptoms Of End
Heart Failure: Quick Facts
1. More than 6 million U.S. adults have heart failure.
2. About half of people who develop heart failure die within 5 years of diagnosis.
3. Most people with end-stage heart failure have a life expectancy of less than 1 year.
4. The leading causes of heart failure are diseases that damage the heart, such as heart disease, high blood pressure, and diabetes.
Heart failure worsens over time, so symptoms are most severe during the final stages. It causes fluid to build up in the body, which produces many of these symptoms:
- Shortness of breath . In the final stages of heart failure, people feel breathless both during activity and at rest.
- Persistent coughing or wheezing. This may produce white or pink mucus. The cough may be worse at night or when lying down.
- Weight gain or swelling of the feet, ankles, legs, abdomen, or neck veins.
- Tiredness, weakness.
In addition, people in the final stages of heart failure may suffer from:
- depression, fear, insomnia, and isolation
- anxiety about their future
- trouble navigating the health care system
Causes Of Congestive Heart Failure
Almost any disease or condition that damages the heart can lead to congestive heart failure. Whether you have an acute or chronic cardiovascular issue, the strain puts pressure on your heart and reduces its ability to pump blood efficiently. The following conditions are common causes:
- Coronary heart disease
Read Also: Is Blood Pressure The Same As Heart Rate
Factors That Can Worsen Symptoms Of Heart Failure
The symptoms of heart failure can be worsened by a number of factors, including:
- anaemia
- too much salt, fluid, or alcohol in the diet
- pregnancy
- some viral and bacterial infections
- kidney diseases
Treatment for heart failure may include:
- medicines, such as
- diuretics to remove excess fluid and improve symptoms of heart failure
- mineralcortiocoid receptor antagonists are also recommended and used in most patients with heart failure to reduce mortality and hospitalisation
- ACE inhibitors to open up blood vessels, reduce blood pressure and reduce sodium retention and water retention
- certain beta-blockers to slow the heart rate and reduce its work
- aldosterone blockers to reduce blood pressure and reduce the effects of damage to the heart muscle
- ACE inhibitors, beta blockers and aldosterone blockers can increase survival and reduce the likelihood of hospitalisation.
How Palliative And Hospice Care Can Help With End
Both palliative and hospice care focus on the whole person, including their physical, emotional, social, and spiritual needs. The main difference is that palliative care can be given at any time during a serious illness, and hospice care is given near the end of life typically when a persons prognosis is six months or less.
Palliative and hospice care can also provide help with making difficult treatment decisions, such as whether to be resuscitated if the persons heart stops, or whether to have a tube placed in their throat to help them breathe.
Similarly, people with end-stage heart failure may need to decide when to disable certain medical devices implanted in their body:
- Implantable cardioverter defibrillator . Patients can have the shock function turned off, or not replace the battery when the current one runs out. Electrical shocks from ICDs can cause unnecessary distress for patients and loved ones at the end of life.
- Left ventricular assist device . Typically, the patient decides when this heart pump will be shut off before it is implanted. The decision can be discussed again as the end of life nears.
Don’t Miss: How Blood Pumps Through The Heart
Systolic And Diastolic Failure
Systolic and diastolic heart failure each result in a decrease in stroke volume. This leads to activation of peripheral and central baroreflexes and chemoreflexes that are capable of eliciting marked increases in sympathetic nerve traffic.
Although there are commonalities in the neurohormonal responses to decreased stroke volume, the neurohormone-mediated events that follow have been most clearly elucidated for individuals with systolic heart failure. The ensuing elevation in plasma norepinephrine directly correlates with the degree of cardiac dysfunction and has significant prognostic implications. Norepinephrine, while directly toxic to cardiac myocytes, is also responsible for a variety of signal-transduction abnormalities, such as downregulation of beta1-adrenergic receptors, uncoupling of beta2-adrenergic receptors, and increased activity of inhibitory G-protein. Changes in beta1-adrenergic receptors result in overexpression and promote myocardial hypertrophy.
How Is Congestive Heart Failure Treated
Doctors will assess the current health status of the patient to establish a baseline, and develop a long-term health plan with the goal of improving the patients health. This may involve the optimization of medicines and therapies, adding new medication, or possibly enrollment in a clinical trial.
Stabilizing and/or reversing a patients condition often involves long-term, collaborative follow-up with a referring cardiologist or physician.
In serious situations, advanced therapies, which include mechanical solutions, a heart transplant, or hospice, may be offered.
Don’t Miss: Does Arousal Increase Heart Rate
In All Heart Failure Patients
The 2016 ESC guidelines recognize the importance of ECG in the diagnosis and prognosis of HF patients. The guidelines recommend ECG to all HF patients at presentation to assess potential etiology, inform appropriate therapy, and predict cardiac events . The guidelines also indicate that normal ECG findings are unlikely in HF patients . In support of these recommendations, current data on some ECG parameters including QRS duration, T wave, ST-segment elevation, and/or depression at presentation strongly support their ability in predicting cardiac events and clinical outcomes in HF patients .
Other significant ECG parameters on admission that can predict cardiac events in HF patients include QTc duration, changes in ST segment, low voltage, and Q waves. Admission ECG done on 246 consecutive HF patients demonstrate that QTc peak duration is a significant multivariate predictor of a composite endpoint of cardiac events, rehospitalization, or death . The prognostic value of the presence of atrial fibrillation in HF patients has been known for decades in a cohort of patients admitted with acute HF and were followed for 30 days with regard to cardiac events, those patients with an event had a significantly higher incidence of atrial fibrillation on admission ECG as compared to those without .
Kyung U. Hong, Roberto Bolli, in, 2016
K. Ono, in, 2017
