Diastolic Chf Icd 10 Code
The diastolic CHF ICD 10 code is I50.30. The subcategory for diastolic heart failure is I50.3 should only use this category for a further selection of codes whenever a condition is mentioned as Diastolic. If a medical note states that the condition is diastolic but does not mention its severity as chronic or acute, use the first code unspecified diastolic heart failure I50.30 for reimbursement purposes.
Dont Miss: Can Ecg Tell Heart Attack
Combined Systolic And Diastolic Heart Failure
- 20162017201820192020202120222023Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code
- end stage heart failure, if applicable
- Chronic combined systolic and diastolic heart failure
- Combined systolic and diastolic heart failure, chronic
- 222 Cardiac defibrillator implant with cardiac catheterization with ami, hf or shock with mcc
- 223 Cardiac defibrillator implant with cardiac catheterization with ami, hf or shock without mcc
- 291 Heart failure and shock with mcc
- 292 Heart failure and shock with cc
- 293 Heart failure and shock without cc/mcc
- 791 Prematurity with major problems
- 793 Full term neonate with major problems
- Cardiac, heart or myocardial failure NOS
- Congestive heart disease
Heart Failure Nyha Class 1 Icd 10
2 days ago Powershell class methods Sa life academy Electrical training course Powershell class private method Powershell class static Dod data classification levels Heart failurenyhaclass 1 icd 10 Pre licensing insurance onlinecourse St joseph academy titusville pa Qatar a380 first class Life center academy
Read Also: How Can You Get A Heart Attack
Icd 10 Chronic Diastolic Heart Failure
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- I50.20 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I50.20 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I50.20 other international versions of ICD-10 I50.20 may differ.
- Applicable To annotations, or
Unspecified Combined Systolic And Diastolic Heart Failure
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- Edema of lung with heart disease NOS
- Edema of lung with heart failure
- Left heart failure
- Pulmonary edema with heart disease NOS
- Pulmonary edema with heart failure
- edema of lung without heart disease or heart failure
- pulmonary edema without heart disease or failure
Read Also: Women Heart Attack Symptom
Validity Of Heart Failure Diagnoses
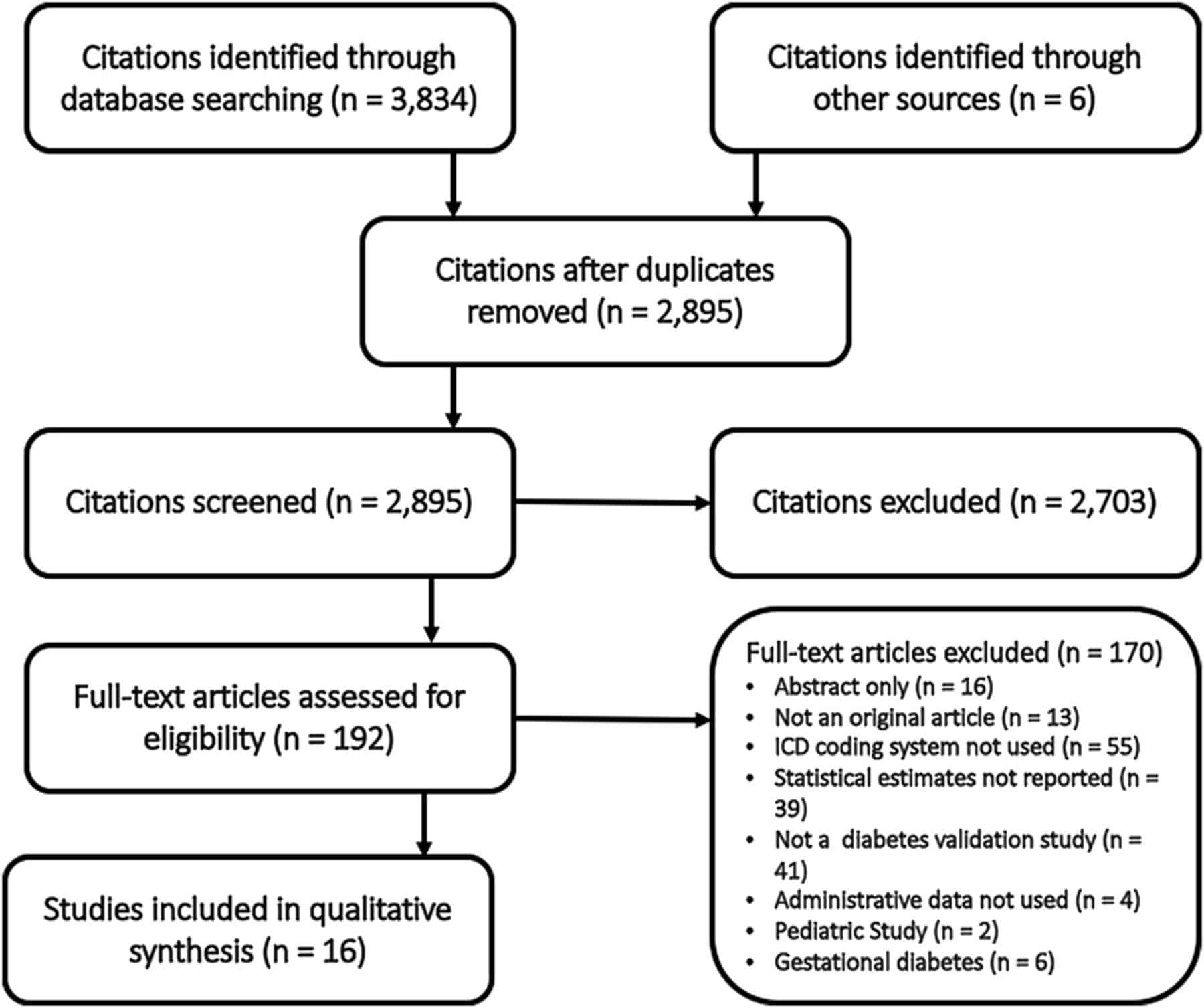
The validation statistics reported by each of the included studies are provided in Table 2. Sensitivity was reported by 14 studies, and was â¥69% in half of them . PPV was undefined in one of the studies , but was at least 87% in nine of the 17 remaining studies . Specificity was â¥95% in all 13 studies reporting this statistic, and NPV was â¥88% in all but two of the 14 studies where this data was available. Kappa was only reported in six studies , , , , , . The values in three of the studies indicated there was moderate agreement between the diagnostic codes and reference standard, while those in the other three indicated there was substantial to almost perfect agreement.
Causes Of Acute Heart Failure
Many conditions can weaken or damage the heart over time. This can lead to heart failure.
With chronic heart failure, your heart tries to adapt to the additional strain over time until it just cant adapt anymore. Thats when acute heart failure happens.
Its also possible for acute heart failure to happen even in people who otherwise seem healthy. There are a number of conditions that can put a sudden strain on your heart.
Causes of acute heart failure include:
- coronary artery disease, which can cause a narrowing of the arteries
- heart attack, which causes damage to the heart muscle and is often caused by coronary artery disease
- use of certain illegal drugs, such as cocaine
- chemotherapy and radiation treatments
In the United States, Black and Hispanic people receive heart failure diagnoses more often than people from other racial or ethnic groups. And Black people in the United States are also at the highest risk of dying from heart failure.
These trends are related to racism and inequities in healthcare, according to the American College of Cardiology.
To diagnose acute heart failure, your doctor will run certain tests. Your doctor can then identify your stage of heart failure, to help find the right treatment for you.
You May Like: How Does Fitbit Measure Heart Rate
Acute On Chronic Chf Icd 10
The Acute On Chronic CHF ICD 10 code is I50.89. In the ICD 10 coding system, acute on chronic CHF have a separate list of codes but only if systolic, diastolic, or literality is mentioned like if the condition exists on the right side or left side. If the severity of literality is not mentioned, the Code of choice should be I50.9 or more appropriately I50.89 as other specified heart failures.
Acute on chronic does fall not elsewhere classified category as the condition is specified more accurately by the doctor but there is no existence of specific code in that case.
Acute Diastolic Chf Icd 10
When improper relaxation becomes an emergency condition, a doctor calls it an acute diastolic condition. The first code under the main subcategory, I50.31 is the most appropriate code for this condition.
If the provider has described the condition as an acute one, a coder cannot self-analyze the condition even if the treatment is described as an emergency one in medical notes. The ICD 10 code for acute CHF diastolic is I50.31.
You May Like: Chest Pain But Doctor Says Heart Is Fine
Read Also: How To Determine Resting Heart Rate
Palliative And Hospice Care
Someone living with a serious condition like heart failure can access palliative care at any stage of their condition. Palliative care is intended to support overall wellness and quality of life and can happen alongside other treatments.
With very severe heart failure, people may choose to access hospice care to receive supportive care at the end of life.
Applied Behavior Analysis Medical Necessity Guide
The Applied Behavior Analysis Medical Necessity Guide helps determine appropriate levels and types of care for patients in need of evaluation and treatment for behavioral health conditions. The ABA Medical Necessity Guide does not constitute medical advice. Treating providers are solely responsible for medical advice and treatment of members. Members should discuss any matters related to their coverage or condition with their treating provider.
Each benefit plan defines which services are covered, which are excluded, and which are subject to dollar caps or other limits. Members and their providers will need to consult the members benefit plan to determine if there are any exclusions or other benefit limitations applicable to this service or supply.
The conclusion that a particular service or supply is medically necessary does not constitute a representation or warranty that this service or supply is covered for a particular member. The members benefit plan determines coverage. Some plans exclude coverage for services or supplies that Aetna considers medically necessary.
Please note also that the ABA Medical Necessity Guide may be updated and are, therefore, subject to change.
Also Check: How Does Blood Flow Through The Heart Step By Step
Read Also: How Does Alcohol Affect The Heart Rate
Search Page 1/: Heart Failure Nyha Class Iii
3 days ago500 results found. Showing 1-25: ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code M26.213 Malocclusion, Angles class III. Malocclusion, angle class iii Malocclusion, angles class iii Mesio-occlusion. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code T86.32 Heart -lung transplant failure. Failure of heart-lung transplant.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Signs Of Heart Attack In Women
Heart Failure Device Therapy Icd And Crt
2 days agoICD in Class ll/lll Heart Failure I IIa IIb III ICD therapy is recommended for primary prevention of SCD in patients with nonischemic or ischemic heart disease with EF 35%, and NYHA class II or III on GDMT, who have anticipated survival for more than 1 year Death All arrhythmic
Dont Miss: How To Find My Heart Rate
Read Also: Does Dopamine Increase Heart Rate
Index To Diseases And Injuries
The Index to Diseases and Injuries is an alphabetical listing of medical terms, with each term mapped to one or more ICD-10 code. The following references for the code I50.9 are found in the index:
- cardiacSee Also: Failure, heart I50.9
- cardiovascularSee Also: Failure, heart I50.9
- heartSee Also: Failure, heart I50.9
- myocardialSee Also: Failure, heart I50.9
- cardiacSee Also: Failure, heart I50.9
- SyndromeSee Also: Disease
Dont Miss: How To Calculate Target Heart Rate Zone
Chronic Diastolic Heart Failure
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- I50.32 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I50.32 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I50.32 â other international versions of ICD-10 I50.32 may differ.
- Applicable To annotations, or
Don’t Miss: Heart Rate Numbers
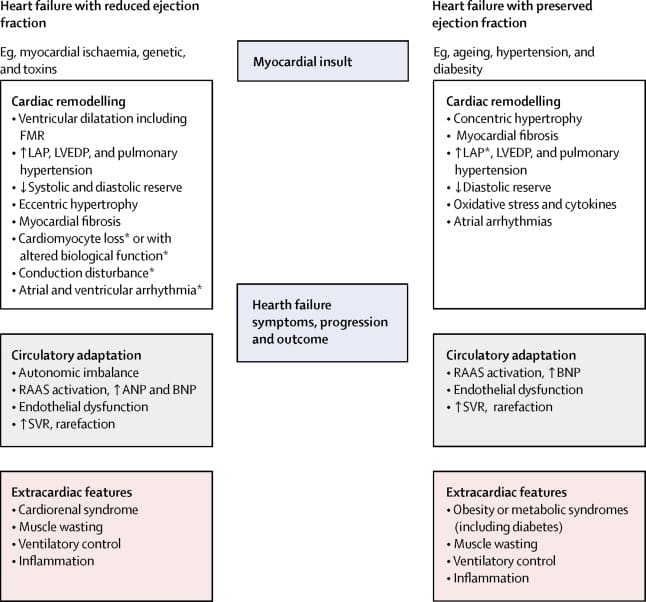
Is Diastolic Dysfunction Considered Heart Failure
Chagasic heart disease may represent an optimal academic model of diastolic heart failure that spares systolic function. A patient is said to have diastolic dysfunction if he has signs and symptoms of heart failure but the left ventricular ejection fraction is normal.
Also question is, is diastolic dysfunction congestive heart failure?
Congestive heart failure occurs when the cardiac output is not adequate enough to meet the demands of the body. Heart failure can be due to the following: Systolic dysfunction Diastolic dysfunction
What are the signs and symptoms of diastolic heart failure?
Heart failure signs and symptoms may include:
- Shortness of breath when you exert yourself or when you lie down.
- Fatigue and weakness.
- Persistent cough or wheezing with white or pink blood-tinged phlegm.
How do you diagnose diastolic heart failure?
It is characterized by a stiff left ventricle with decreased compliance and impaired relaxation, which leads to increased end diastolic pressure. Signs and symptoms are similar to those of heart failure with systolic dysfunction. The diagnosis of diastolic heart failure is best made with Doppler echocardiography.
You May Like: What Causes Elevated Heart Rate
What Is Htn With Chf
Hypertension can be defined as chronic high blood pressure, causes can be environmental or genetics but it mostly leads to heart failure in most patients. The most important effect of hypertension is on the left ventricle making it weak and causing hypertrophy of the ventricle. Whenever HTN becomes the developmental factor of CHF, its called hypertensive heart disease.
Also Check: Diarrhea Due To Congestive Heart Failure
Acute On Chronic Diastolic Chf Icd 10
The Acute On Chronic Diastolic CHF ICD 10 code is I50.33.
When looking at diastolic under failure/heart in the alphabetic index, the ICD 10 system provides subcategory I50.3 for diastolic heart failure. Under this category, several codes according to different specified descriptions are provided I50.33 at the bottom of this subcategory is the code of choice to fully describe the condition acute on chronic diastolic heart failure.
Tabular List Of Diseases And Injuries
The Tabular List of Diseases and Injuries is a list of ICD-10 codes, organized head to toe into chapters and sections with coding notes and guidance for inclusions, exclusions, descriptions and more. The following references are applicable to the code I50.9:
Inclusion Terms
Donât Miss: How To Prevent Congestive Heart Failure
You May Like: Is Blood Pressure The Same As Heart Rate
Acute On Chronic Systolic Heart Failure
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- I50.23 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I50.23 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I50.23 other international versions of ICD-10 I50.23 may differ.
- Applicable To annotations, or
Q& A: Congestive Heart Failure Coding

Q: In the past few weeks, we noticed physicians are documenting acute congestive heart failure with preserved ejection fraction , instead of diastolic or systolic. In speaking with the physicians, they say the heart failure is not diastolic or systolic. What is the best way to approach this issue?
A: You are experiencing a very common frustration for both coders and CDI specialists. The term preserved EF in general equates to a diastolic heart failure. But, as you clearly understand, we cannot apply the code for the diastolic heart failure with the use of that verbiage.
The descriptions of diastolic and systolic in categorizing heart failure are older terms, and the code set has not yet caught up to the new wording. I encouraged my providers to state diastolic heart failure with preserved EF. This documentation gives coders what they need, and allows physicians to use clinically-accepted language.
AHAs Coding Clinic for ICD-10-CM, First Quarter, 2014 speaks to this. It provides two examples. First, can heart failure with preserved EF or heart failure with preserved systolic function be coded as diastolic heart failure? Second, can heart failure with reduced EF, heart failure with low EF, or heart failure with reduced systolic function be coded as systolic heart failure?
Also Check: Dogs In Heart Failure
Acute Systolic Chf Icd 10
If the patients condition is acute, the second code under this subcategory should be used for reimbursement purposes. If the medical note states that the patients condition has been worsening or there is an emergency condition of chronic failure but does not document it as acute, do not presume it as an acute condition.
A query to the medical doctor would work here best asking about the exact condition. The ICD 10 code for acute systolic CHF is I50.21.
Nyha Class Ii Or Iii Heart Failure: Who Will Need An
4 days agoin the prevention of SCD in NYHA class II HF. One of the trials which found a sig-nificant role of ICD in type III heartfailure was underpowered. Thus, further trials are needed to validate the use of ICD in the prevention of SCD in type III HF. Keywords Heart Failure, Sudden Cardiac Death, Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator, ICD, NYHA, ESC 1.
Don’t Miss: Dehydration And Heart Failure
Chronic Diastolic Chf Icd 10
Chronic CHF has the same subcategory to find the right code for this description. I50.33 is the second last code of this subcategory that states Chronic diastolic heart failure is most appropriately describing this condition.
According to CMS guidelines, verifying each code in the tabular index of CPT code and/or using a coding tool, there must be a complete description against each code with matching keywords and synonyms. The ICD 10 code for chronic CHF diastolic is I50.33.
Fransoo Et Al And Fransoo Et Al
- In The 2013 RHA Indicators Atlas by Fransoo et al. and The 2019 RHA Indicators Atlas by Fransoo et al. residents were considered to have CHF if they met one of the following conditions:
- one or more inpatient hospitalizations in one year with a diagnosis for CHF: ICD-9-CM code 428 or ICD-10-CA code I50 OR
- two or more physician visits in one year with a diagnosis for CHF .
Only Manitoba residents aged 40 and older were included.For more information, please see:
Also Check: Why Heart Attack Happens In The Morning
Q& a: Documentation For Coding Heart Failure
Sharme Brodie,RN, CCDS
Q: If the documentation states, diastolic heart failure euvolemic or diastolic HF hypervolemic, can we code chronic diastolic HF and acute diastolic HF, respectively?
A: Unfortunately, you may not like my answer, which is no, this documentation would not be acceptable to pick up either diagnoses of chronic or acute diastolic heart failure.
Code assignment is based on the physician documentation of the type and acuity of the HF. Euvolemic is a medical term that implies the patient appears to have normal circulatory or blood fluid volume. Hypervolemia or fluid overload is the medical condition where there is too much fluid in the blood, because not every patient is in fluid overload or hypervolemia at the time of admission, many physicians are now use HF versus congestive heart failure in their documentation.
There are many types of HF, and CHF is just one type. There is a code in ICD-10-CM for fluid overload: E87.70, Fluid over, unspecified. This is also where hypervolemia would be coded.
Now, in AHA Coding Clinic, First Quarter 2016, it did state that HFpEF could be referred to as diastolic heart failure and that HFrEF could be referred to as systolic heart failure. This advice supersedes information previously given in Coding Clinic, First Quarter 2014. This is why its very important to keep up with the advice given by Coding Clinic.
The Icd Code I50 Is Used To Code Acute Decompensated Heart Failure
Acute decompensated heart failure is a sudden worsening of the signs and symptoms of heart failure, which typically includes difficulty breathing , leg or feet swelling, and fatigue. ADHF is a common and potentially serious cause of acute respiratory distress. The condition is caused by severe congestion of multiple organs by fluid that is inadequately circulated by the failing heart. An attack of decompensation can be caused by underlying medical illness, such as myocardial infarction, infection, or thyroid disease.
| Specialty: |
You May Like: What Is The Normal Resting Heart Rate For A Woman
Q& A: Documentation For Coding Heart Failure
Sharme Brodie,RN, CCDS
Q: If the documentation states, diastolic heart failure euvolemic or diastolic HF hypervolemic, can we code chronic diastolic HF and acute diastolic HF, respectively?
A: Unfortunately, you may not like my answer, which is no, this documentation would not be acceptable to pick up either diagnoses of chronic or acute diastolic heart failure.
Code assignment is based on the physician documentation of the type and acuity of the HF. Euvolemic is a medical term that implies the patient appears to have normal circulatory or blood fluid volume. Hypervolemia or fluid overload is the medical condition where there is too much fluid in the blood, because not every patient is in fluid overload or hypervolemia at the time of admission, many physicians are now use HF versus congestive heart failure in their documentation.
There are many types of HF, and CHF is just one type. There is a code in ICD-10-CM for fluid overload: E87.70, Fluid over, unspecified. This is also where hypervolemia would be coded.
Now, in AHA Coding Clinic, First Quarter 2016, it did state that HFpEF could be referred to as diastolic heart failure and that HFrEF could be referred to as systolic heart failure. This advice supersedes information previously given in Coding Clinic, First Quarter 2014. This is why its very important to keep up with the advice given by Coding Clinic.
You May Like: Heart Attacks And Headaches
