Take Care Of Your Mental Health Too
While stress is never pleasant, it can be especially hard on your heart. Anger management is also an important aspect of heart health.
Talking with a therapist or joining a support group can help with keeping your stress levels down and giving you accountability for the lifestyle changes youre making.
When To Get Medical Advice
See a GP if you experience persistent or gradually worsening symptoms of heart failure.
Call 999 for an ambulance or go to your nearest A& E department as soon as possible if you have sudden or very severe symptoms.
A number of tests can be used to help check how well your heart is working, including blood tests, an ECG and an echocardiogram.
How Is Congestive Heart Failure Diagnosed
Patients will typically have an intake visit with a heart specialist and nurse or physicians assistant. During this visit, a review of the patients prior records and his or her current health status is incorporated to establish a picture of where the patient is along the spectrum, and then a plan is established for prognosis and treatment.
The process often takes more than one meeting and involves both the patients local cardiologist or referring physician.
Recommended Reading: How To Improve Your Resting Heart Rate
Why Is This Treatment Done/used
A heart transplant is a last-resort treatment when you have end-stage heart failure. That means your heart has permanent damage or weakness that keeps it from pumping enough blood to your body.
This kind of heart failure can happen for a wide variety of reasons, ranging from infections that damage your heart muscle to abnormal heart rhythms that may cause a reversible weakening of the heart.
Diagnoses most likely to result in heart transplant
The following conditions make up the majority of reasons for heart transplant:
- Cardiomyopathy. This refers to any disease that damages your heart muscle . Diseases that cause this kind of damage include infections, genetic diseases and damage from medical treatments .
- Coronary artery disease. This is a condition that affects the arteries that supply your heart. Its a common cause of heart attack.
- Congenital heart disease. This is any heart disease you have when youre born.
- Valvular heart disease. These are conditions that involve damage to your heart valves.
- Retransplants. These are instances where a person needs a second transplant to replace the first. This can happen because the donor’s body rejects the first transplanted heart or for other reasons.
What Medications Should I Avoid If I Have Heart Failure
There are several different types of medications that are best avoided in those with heart failure including:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications such as Motrin or Aleve. For relief of aches, pains, or fever take Tylenol instead.
- Most calcium channel blockers
- Some nutritional supplements, such as salt substitutes, and growth hormone therapies
- Antacids that contain sodium
If youâre taking any of these drugs, discuss them with your doctor.
Itâs important to know the names of your medications, what theyâre used for, and how often and at what times you take them. Keep a list of your medications and bring them with you to each of your doctor visits. Never stop taking your medications without discussing it with your doctor. Even if you have no symptoms, your medications decrease the work of your heart so that it can pump more effectively.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Normal Heart Rate For An Infant
What Happens Before This Procedure
Because there are far more people who need hearts than donors, there’s a strict selection process that you have to undergo to receive a heart transplant. The goal of this process is to select recipients who have the best chance of long-term survival based on their overall health.
After a healthcare provider refers you to a transplant program, youll undergo the following.
Medical evaluation
To ensure that donor hearts go to people with the best chance of survival, healthcare providers will evaluate your overall health by running several different tests. Some, but not all, of the possible tests are listed below.
Lab tests will include tests on your blood, urine and other screenings. These tests will look for the following:
- Blood composition. This analyzes your bloods levels of red blood cells, platelets, and more. These tests will also analyze your blood chemistry, looking for signs of other conditions that might affect your ability to undergo a heart transplant.
- Immune system analysis. These tests help providers anticipate how well your immune system can tolerate a donor organ.
- Kidney function. These tests analyze your urine to see how well your kidneys are working.
- Tests for alcohol, tobacco and drugs. These are often important tests if you have a history of using recreational drugs or drinking too much alcohol. Most transplant centers require that youre sober and avoid using tobacco products and recreational drugs for an extended time before your transplant.
Treatments For Heart Failure
Treatment for heart failure usually aims to control the symptoms for as long as possible and slow down the progression of the condition.
How you’re treated will depend on what is causing your heart failure.
Common treatments include:
- lifestyle changes including eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly and stopping smoking
- medicine a range of medicines can help many people need to take 2 or 3 different types
- devices implanted in your chest these can help control your heart rhythm
- surgery such as a or a heart transplant
Treatment will usually be needed for life.
A cure may be possible when heart failure has a treatable cause. For example, if your heart valves are damaged, replacing or repairing them may cure the condition.
Read Also: What Is A Normal Heart Rate While Walking
Monitoring Congestive Heart Failure
If you are living with congestive heart failure, your doctor will help you determine the best way to monitor your condition and reduce your chance of future hospitalizations.
Self-Management SkillsDoctors recommend that people with congestive heart failure develop good self-management skills to help manage their conditions. These self-management skills include:
- Weighing yourself and recording your weight daily, reporting any gains of more than 2-3 pounds over two days or 4-5 pounds over one week to your doctor
- Following a low-sodium diet
- Taking all the medications your doctor prescribes
Your doctor can also provide recommendations for limiting your fluid intake, getting regular exercise, and quitting smoking, all of which can help manage your heart failure.
CardioMEMS HF SystemSelect patients may be eligible for the CardioMEMS HF System. Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2014, the system uses a small sensor implanted in your pulmonary artery and an external electronic system to transmit information directly to your doctor’s office.
With the CardioMEMS HF System, you take daily readings of our pulmonary artery pressure from home. The readings are delivered securely to your doctor’s office through an external electronic system, and can help your doctor determine if your condition is getting worse before you have symptoms. Your doctor can then adjust your medication or treatment plan and help you avoid hospitalization.
How Are Pediatric Congenital Heart Defects Treated
Many children who are born with heart defects do not need treatment. In these cases, the defects are mild or they simply correct on their own .
For children who have a heart defect that must be treated, there are 2 main options: treatment with a catheter, or open heart surgery.
Catheter treatment
Treatment with a catheter is much easier for the child to go through than surgery. Instead of opening the body with an incision as in surgery, the doctor makes a small cut in the skin and inserts a catheter into the body through an artery or vein.
Catheters are used to treat simple heart defects, such as an atrial septal defect. In this procedure, the catheter is moved through a vein until it reaches the septum . There, the catheter places a small device into the septal defect to close it up. The catheter is then removed.
To treat pulmonary valve stenosis, the catheter is equipped with a small balloon that is inflated at the pulmonary valve in order to separate the fused leaflets.
Open heart surgery
In cases where the heart defect cannot be treated with a catheter, the child may need open heart surgery. In these situations, the pediatric heart surgeon opens the chest and operates directly on the heart to repair the defect. This type of treatment is usually done for more serious heart defects.
You May Like: What Should My Heart Rate Be While Running
Is Chf Due Mainly To Heart Valve Disease
CHF is most commonly caused by valvular insufficiency. It is estimated that 80% of the canine CHF cases are caused by MVI. However, there are many other causes. Disease of the heart muscle , irregularities of rhythm, and narrowing of some of the major blood vessels can also cause CHF. Initially, MVI results in left-sided congestive heart failure. If left untreated, the heart failure may progress to involve both sides of the heart.
Stage B Treatment Options
While stage A CHF is managed with lifestyle changes, the treatment plan for stage B typically includes taking medications regularly. People at this stage should still make the same lifestyle changes as those appropriate for stage A. However, your doctor may also prescribe additional treatments such as:
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers, if you arent taking any as part of your stage A treatment plan
- Beta blockers if youve had a heart attack and your EF is 40% or lower, if you arent taking any as part of your stage A treatment plan
- Possible surgery or intervention as a treatment for coronary artery blockage, heart attack, valve disease, or congenital heart disease
Don’t Miss: Is Congestive Heart Failure Treatable
Stage C Treatment Options
Treatment at this stage focuses on managing your symptoms, optimizing your heart function, and preventing worsening of your condition.
Medications to treat stage C heart failure include:
- Diuretics to reduce fluid retention
- Beta blockers to help make your heart work less hard
- SGLT2 inhibitors to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers
- Entresto , which reduces the risk of death and hospitalization among patients with chronic heart failure
- Aldosterone antagonists
- Digoxin to help the heart beat stronger and more regularly
- Possible cardiac resynchronization therapy
- Possible implantable cardiac defibrillator therapy
In addition to the lifestyle changes for stages A and B, you may need to make the following changes:
- Reduce your sodium intake
- Restrict fluid intake
- Keep track of your weight daily
Remember that even if the treatment causes your symptoms to get better or stop, you still need to continue treatment to slow the progression of your condition to stage D.
Prognosis By Ejection Fraction
Ejection fraction is a measure of how much blood is pumped out of your heart each time it contracts. A healthy heart has an EF of between about 55 percent to 75 percent.
Some people with CHF have a reduced EF. This means their heart is pumping less blood out to the rest of their body than a healthy heart. Studies have shown that people who have CHF and a reduced EF have a more challenging outlook than people with CHF who do not have a reduced EF.
The exact survival rates varied among studies, but have shown that EF has an impact on prognosis. Your doctor will have the best information about how your ejection fraction can affect your prognosis.
You May Like: Can Gas Bubbles Feel Like Heart Palpitations
What Is The Recovery Time
Heart transplant surgery is a complicated, extensive surgery procedure and recovery times are typically longer than most heart surgeries. The expected hospital stay is at least seven to 10 days, and usually up to three weeks. The time you spend in the hospital depends on your specific situation, health and how the surgery went. Overall, recovery from this procedure usually takes several months.
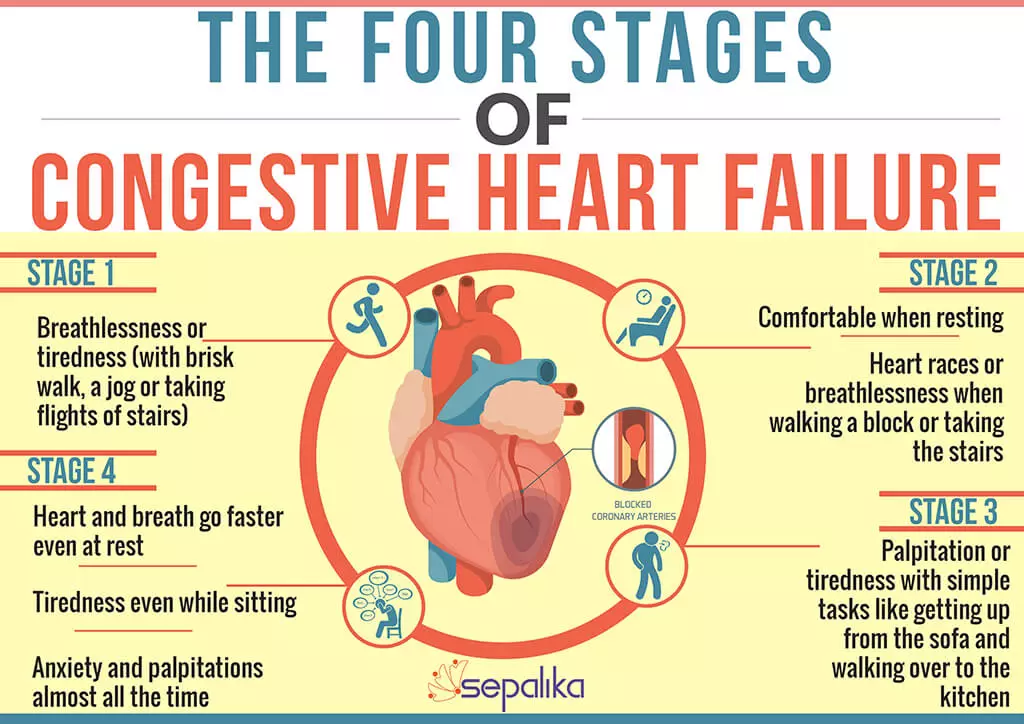
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Congestive Heart Failure
Shortness of breath
The hallmark and most common symptom of left heart failure is shortness of breath and may occur:
Chest Pain
Right heart failure, left heart failure, or both
Also Check: How Accurate Is Fitbit Charge 2 Heart Rate
What Are The Symptoms Of Heart Failure
You may not have any symptoms of heart failure, or the symptoms may be mild to severe. Symptoms can be constant or can come and go. The symptoms can include:
- Congested lungs. Fluid backup in the lungs can cause shortness of breath with exercise or difficulty breathing at rest or when lying flat in bed. Lung congestion can also cause a dry, hacking cough or wheezing.
- Fluid and water retention. Less blood to your kidneys causes fluid and water retention, resulting in swollen ankles, legs, abdomen , and weight gain. Symptoms may cause an increased need to urinate during the night. Bloating in your stomach may cause a loss of appetite or nausea.
- Dizziness, fatigue, and weakness. Less blood to your major organs and muscles makes you feel tired and weak. Less blood to the brain can cause dizziness or confusion.
- Rapid or irregular heartbeats. The heart beats faster to pump enough blood to the body. This can cause a rapid or irregular heartbeat.
If you have heart failure, you may have one or all of these symptoms or you may have none of them. They may or may not indicate a weakened heart.
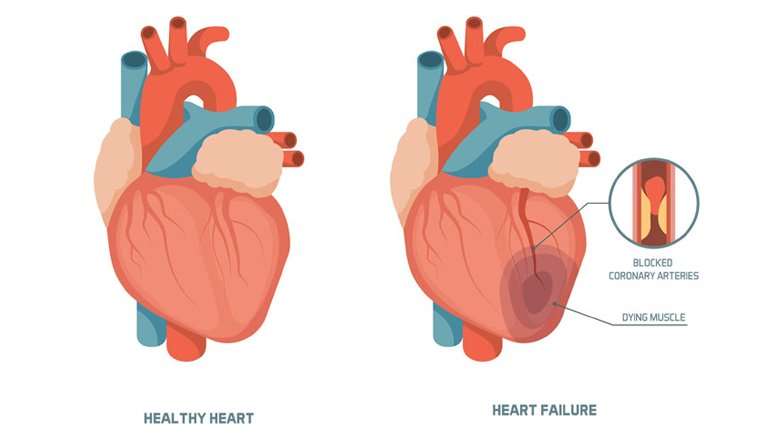
How Does A Healthy Heart Work
The heart is part of the circulatory system, which carries blood throughout the body. The heart is made of muscle and works like a pump to keep the blood moving through the blood vessels .
The heart has 4 chambers the right atrium and the left atrium on top and the right and left ventricles on the bottom. The heart is divided by a solid wall called the septum into 2 sides: the right side sends blood to the lungs to get oxygen, while the left side of the heart moves oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body through the aorta .
Blood enters the heart through the right atrium and moves to the right ventricle, where it then moves through the pulmonary artery to the lungs to pick up oxygen. The newly oxygenated blood then enters the heart through the left atrium and moves to the left ventricle, where it is sent through the aorta to the rest of the body.
There are also 4 valves in the heart, which open and close to allow blood to move through the chambers:
- The aortic valve, located on the left side of the heart, between the aorta and the left ventricle.
- The mitral valve, located between the left ventricle and the left atrium.
- The pulmonary valve, located on the right side of the heart between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery .
- The tricuspid valve, located on the right side of the heart between the right ventricle and the right atrium.
The exterior of the heart.
Blood vesselsarteries, veins, and capillaries–are also involved in helping blood flow:
Don’t Miss: Congestive Heart Failure End Of Life
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider
Your healthcare provider will set up a schedule of visits after your procedure, especially within the first three months. Those visits are critical to making sure you are recovering and arent experiencing any complications or problems related to your new heart.
Your provider will also tell you what signs and symptoms to watch for that mean you need emergency medical attention. Most commonly, the signs and symptoms involve the rejection of your new heart or infections. These symptoms include:
- Fever.
- Drainage or oozing from the incision in your chest.
- Redness or warmth around the incision.
- If your breastbone moves, shifts or causes any kind of cracking or popping sound/feeling when you move.
Your healthcare provider will also recommend and help you do the following:
- Make sure you get preventive dental care .
- Stay current on all your vaccinations .
- Get routine health screenings as needed .
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Facts About Heart Failure In The United States
- About 6.2 million adults in the United States have heart failure.1
- In 2018, heart failure was mentioned on 379,800 death certificates .1
- Heart failure costs the nation an estimated $30.7 billion in 2012.2 This total includes the cost of health care services, medicines to treat heart failure, and missed days of work.
Don’t Miss: What Does A Normal Heart Rate Look Like
